What is SNMP
SNMP stands for simple network management protocol. As the name suggest this protocol is used to manage and monitor the network devices. It can manage devices like computers/servers, routers, printer or any devices which can be accessed over the network.
It is an application layer protocol used for communication between network device via LAN or WAN.
What is SNMP used for
Let’s understand the uses of SNMP with an example. As everyone of us knows about Facebook. Just imagine that daily billion of people are using Facebook and uploading lots of data like images, videos, text etc to the Facebook. All of this data is being uploaded to the Facebook servers available in their geographically distributed data centers, which communicates with each other via network protocols.
Thus, to monitor and manage all of these servers, SNMP protocol can be used. For example, if any of the server consuming lots of memory or CPU, which can cause disruption for the Facebook application. then it might lead to application downtime which can result into huge loss for the company. Thus, there should be some mechanism which can continuously monitors all these kinds of critical events related to the health/ resource utilization of the servers and network devices. So, SNMP can be considered one of the best solutions which can be used to monitor and manage these devices remotely.
SNMP is mainly used for:
- Monitoring network devices
- Configuring Network Devices
- Auditing Network Device
- Detecting faults and unauthorized access
SNMP is most widely supported protocol by network devices like switches, routers, scanners and IoT supported devices. Lot’s of network devices comes with bundled SNMP agents which can be easily enabled and configured so that they can communicate with Network Management System (NMS) or Manager for monitoring and management purpose.
SNMP Architecture
It has following main components
It follows simple client-server model. Where manager act as a server while agents act a client. Manager asks for the information which needs to be processed from the agents which are installed and configured on the network devices which needs to be monitored.
Let’s discuss each component in detail
SNMP Manager
It is an interface between the user and management information provided by the agents. Basically, it’s a software platform which is used to monitor and manage the network devices. It is also called as Network management system (NMS). Manager continuously poll the agents at some regular time interval to get the required information about the node under monitoring and then translate this data into human readable format.
There are many network management software available in the market which offers different capabilities to manage the network devices. Some of NMS has capabilities to send an email notification to the administrator in case the value of the managed object exceeds the threshold.
Main function of SNMP Manager
- It queries SNMP Agents
- It gets response from SNMP agents
- It translates the response into human readable format
- It sets variable values in case of an alarm
- It acknowledges events from agents
SNMP Agents
It is an interface between the SNMP manager and the network devices which needs to be monitored. These agents are pre-installed on most of the devices, but they need to be enable and configure before they can start collecting the data. They can collect wide range of data like CPU utilization, memory utilization, disk utilization and many other performance parameters for the underlying hardware or the service being monitored. This collected data is stored in the database which is called as Management information base (MIB) and it is accessed by the manager whenever it is queried for. These agents can spontaneously send a message to the Manager/ NMS in case any error occurs instead of waiting for manager to ask for it. The standard SNMP agents available in the market is NET-SNMP though there are some vendor specific customized agents are also available.
Main Functions of SNMP Agents
- Collects the information about different performance parameters for the device being monitored
- Store all the data locally in the database called Management Information base (MIB)
- Serves the collected data to Manager whenever Manager query for it
- Send event notification to manager in case of any error occurs
Managed Nodes
The devices which are being monitored and managed by SNMP are called Managed nodes.
These are the nodes/devices where agents are installed and configured to collect the management information.
Management Information Base (MIB)
It’s the information data base which is populated by SNMP agents for each of the node being monitored. It contains the information about different subsystem or performance parameter of the devices or the services. Manager send the data query to the agents which in return respond to the Manager along with the requested data stored in the MIB if it is available otherwise it respond with the error indicating why the request can not be processed.
Object Identifier (OID)
Each managed node has their individual MIB which is in the form of hierarchical tree structure. It contains the information about different objects which can be manged by manager. Each of these objects inside the MIB is identified by their object Identifier which is known as OID. This OID is unique for each of the object and follow a specific format where a number is separated by the decimal to form a long numeric tag or identifier e.g 1.3.6.4.1.5635. These OID’s also consist of a readable label and various other parameters which is required to understand the properties of various objects/parameters stored in the database.
When the manager wants to get the information about specific parameters of the manged node then it sends a get message to the agent to find the value of a specific variable which is identified by it OID in the MIB. Some of the OID’s are vendor specific which makes it easy to get the basic information about the devices by just looking at the OID. For example, CISCO devices OID starts with 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.
How SNMP works
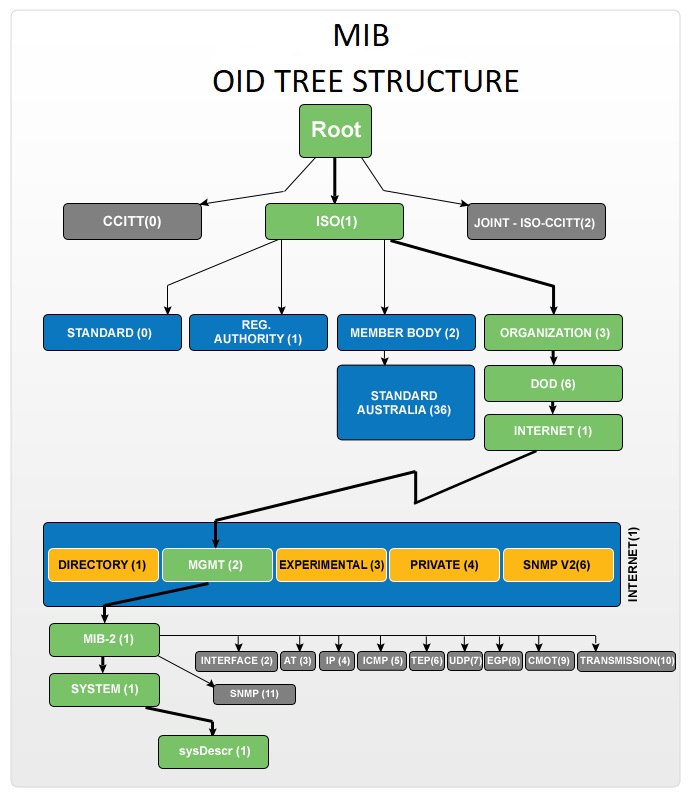
SNMP is essentially a member of TCP/IP protocol suit where each SNMP message is wrapped as User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packets which further wrapped and transmitted as an IP packet to the physical layer device.
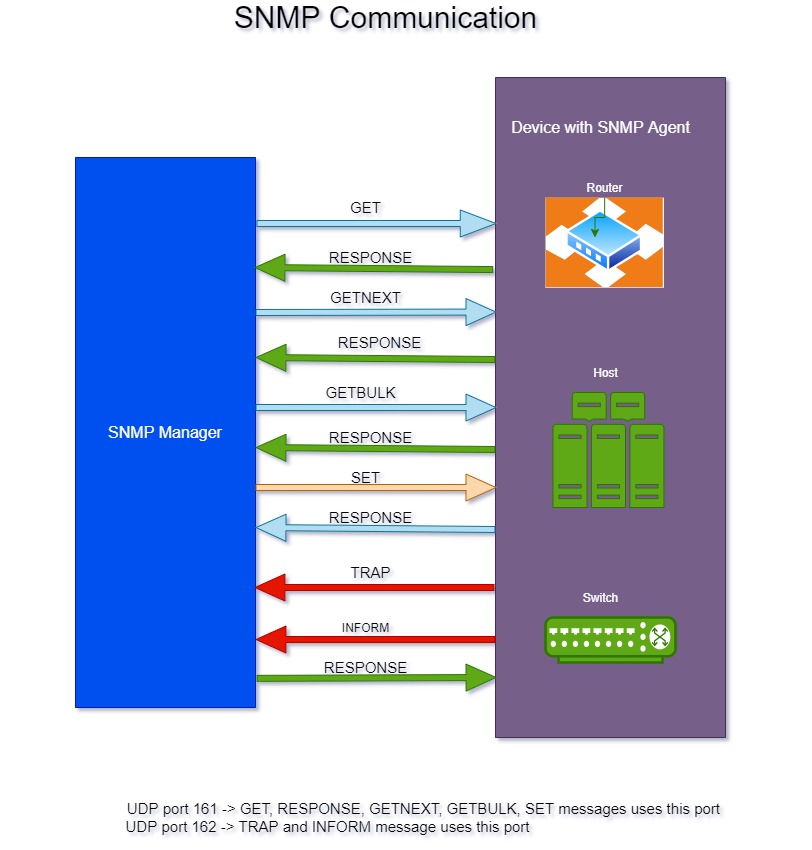
It uses some basic commands to exchange management information between Manager and Agents. Below diagram explains the communication between SNMP Manager and agent.
Basic commands of SNMP
- GET: GET message is sent by the SNMP manager to SNMP agents installed in the managed node to get the values of any managed object or parameter identified by its OID in MIB.
- RESPONSE: RESPONSE message is sent from agent to Manager which contains the requested data.
- GETNEXT: GETNEXT message is sent from manager to agent to query the next OID in MIB hierarchy.
- GETBULK: GETBULK message is used by manager to agent to retrieve the large volume of data from MIB tables using multiple GETNEXT messages. This message was introduced in SNMPv2c.
- SET: SET message is used by manager to modify or assign a value in MIB to a specified variable of managed device.
- TRAP: TRAP message is self-initiated by the agent to inform the manager about an important event in case of any failure or error occurrence.
- INFORM: Upon receiving a TRAP message from agents, there is no way to confirm whether the TRAP message is received by the Manager or not. Thus, to overcome this issue, INFORM messages came into existence. It was introduced in SNMPv2c. This message is also initiated by SNMP agents. The main difference between TRAP and INFORM message is that upon receiving an INFORM message the manager sends back the response to the agents which confirms the delivery of the message. If the agent does not receive the acknowledgement response from Manager, then it can again send the INFORM message. Therefore INFORM messages can also called as acknowledged TRAP.
What is SNMP Trap
SNMP Traps are the alert notification messages sent from SNMP agents to Manager.
These messages are generated by agents whenever any important event or information about any error needs to be informed to Manager. For example, A trap message can be generated if an application start consuming the memory more than the allowed threshold value.
Devices which needs to be monitored or managed comes with Pre-Installed agents. They send the event notification to manager on UDP port 162 from any available port. Traps are unreliable because there is no mechanism in place which can confirm the agent that whether manager has received any event notification or not. Because Manager does not send any acknowledgement back to the agent upon receiving the notification.
Thus, SNMP traps are also called as unacknowledgeable event notifications sent from Agent to Manager.
Difference Between SNMP TRAP and INFORM Message
SNMP PORT
The Ports which are used by SNMP for communication between Manager and agents are called SNMP ports.
Typically, a port is a unique number to identity any application or it’s service on a particular host.
SNMP uses User datagram Protocol (UDP) for communication between Manager and Agents, which is a transport layer protocol. SNMP uses the following default ports for communication.
- UDP Port 161 (SNMP)
- UDP Port 162 (SNMPTRAP)
How SNMP Manager uses default port to communication with Agents
- SNMP Manager can use any available source port to send SNMP messages (GET, GETNEXT, GETBULK, SET)
- SNMP Manager sends messages (GET, GETNEXT, GETBULK, SET) on UDP port 161 in SNMP agent node i.e. the node which needs to be managed
- SNMP Manager receives the RESPONSE message on the same source port from which it sends the messages
- SNMP Manager uses UDP Port 162 to receive the TRAP and INFORM message from agents
How SNMP Agent uses default port to communication with Manager
- SNMP Agent receives all messages (GET, GETNEXT, GETBULK, SET) from Manager on UDP port 161
- SNMP Agent sends the RESPONSE message to the Manager on the same source port from which Manager sends the messages
- SNMP Agent can send the TRAP and INFORM messages to Manager from any available port
- SNMP Agent sends the TRAP and INFORM message on UDP port 162 on SNMP Manager
SNMP Versions
SNMP has three versions namely SNMPv1, SNMPv2c and SNMPv3. Each of these versions has their pros and cons associated with them.
SNMPv1
SNMPv1 was introduced in 1988 and it does not have any encryption algorithms which was not a big matter of concern in that time. But in today’ time where the security of data is utmost priority for everyone thus using this version is clearly a security risk for critical systems. That’s the reason many companies are restricting the usage of SNMPv1. Moreover, it just supports 32-bit counter architecture which was enough for that time but certainly it’s not sufficient in today’s time where gigabyte sized networks are running. RFC 1155 and 1157 and defines SNMPv1.
SNMPv2c
This was the revised and enhanced version of SNMPv1 which was introduced in 1993. There are few iteration of SNMPv2 came into existence but the most commonly used was community based thus it was named as SNMPv2c. This version supports 64-bit counter architecture and Certainly it was must to have upgrade from SNMPv1 to SNMPv2c but still it does not have any changes w.r.t to security aspects. It was still sending the critical data as clear text. RFC 1901, RFC 1905, and RFC 1906 defines SNMPv2c.
SNMPv3
SNMPv3 was the major upgrade where many short comings of earlier version were considered and fixed. It came into existence in early 2000’s. This new version is called as SNMPv3 which has all 64-bit counter architecture along with all the security features in place. The main key features of this upgrade were user accounts, authentication and optional encryption. We can use these features together or separately as per our requirement. But addition of these authentication and encryption features made the protocol complex and also come with compatibility issues for the legacy devices using SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c. RFC 1905, RFC 1906, RFC 2570, RFC 2572, RFC 2574, and RFC 2575 defines SNMPv3.
Check out the difference between SNMPv1, SNMPv2c and SNMPv3
Other Useful Links
I am a software QA Professional with 10 + years of Industry experience in the domain of Servers, Storage, Networking, Cloud Computing and Containerization etc. I started this blog to share my knowledge and skills what i am learning from my profession. Being a QA guy, I love to Test and Review different IT products.

That is really fascinating, You are an excessively professional blogger.
I’ve joined your rss feed and look ahead to
in search of extra of your great post. Additionally, I’ve shared your
web site in my social networks
Here is my web-site :: CBD for Sale
Thanks a lot for your nice words.
ghostwriter kulturgeschichte
Каждый день миллионы водителей сталкиваются с опасностью, которую трудно увидеть — усталостью. Она не только снижает внимание, но и может стать причиной серьезных аварий. Не дайте усталости взять верх над вами – gps трекер для автомобиля
В современном мире, где качество и безопасность товаров и услуг становятся все более важными, сертификация играет ключевую роль. Мы предлагаем профессиональные услуги по сертификации, которые помогут вашему бизнесу соответствовать международным стандартам и укрепить доверие клиентов. – декларация соответствия тр тс.
Сопровождение мужчин — это особая услуга, которая может включать в себя как деловые, так и личные аспекты.
В современном мире многие мужчины ищут профессионалов, которые могут помочь им в различных сферах жизни:
от бизнес-мероприятий до социальных встреч – эскортницы Москва
orb11ta вход на сайт
диплом медсестры с занесением в реестр спб диплом медсестры с занесением в реестр спб .
When will alli be available again levitra without prescription Buy doxycycline eu
Добро пожаловать в мир Кракена (Kraken) — одного из самых популярных даркнет-маркетплейсов. Если вы ищете рабочую ссылку, проверенные зеркала или рекомендации по безопасности, вы попали по адресу. Кракена ссылка
tiptrip24.biz в обход блокировки роскомнадзора, провайдера, официальный сайт.
https://dubllikat.ru/
купить дипломы о высшем в нижнем купить дипломы о высшем в нижнем .
orb11ta.co в обход блокировки роскомнадзора, провайдера, официальный сайт.
геронтологический центр в симферополе геронтологический центр в симферополе .
[url=https://flseo.ru/]https://flseo.ru/[/url]
About 12 hours later they let me know the server was up. By then we were settled in on the other server so I just canceled the service and considered it a loss. They emailed me immediately saying the service would be canceled within 24hrs.
strip
купить диплом в одинцово купить диплом в одинцово .
купить диплом пту в нижнем тагиле 5gruppa365-diplomy.ru .
https://sk-projekt.ru
Круглозвенные цепи — это не просто элемент механики, а настоящая находка для бизнеса! Они широко используются в различных отраслях: от сельского хозяйства до строительства, обеспечивая надежную передачу усилия и долговечность – подбор подшипников по размерам.
Квиз — это увлекательная игра-викторина, которая сочетает в себе элементы развлечения и интеллектуального состязания. Они могут проходить в различных форматах: от настольных игр до онлайн-викторин и живых мероприятий в кафе или клубах. Популярность квизов растет, поскольку они позволяют людям не только проверить свои знания, но и провести время в компании друзей или незнакомцев, создавая атмосферу дружеского соперничества – квизы в москве
нажмите здесь https://forum.hpc.name/thread/4448/programma-udalyaet-sebya.html
무리한 소비는 자원 소모와 환경 파괴를 초래할 수 있고, 구글기프트카드 소비주의적인 가치관은 소수의 소비에만 초점을 맞추어 경제적 불평등을 증가시킬 수 있다. 따라서, 쇼핑을 할 때는 지속 할 수 있는 한 소비를 실천하고, 고유의 욕구에 따라 적당하게 선택하는 것이 중요해요.
구글기프트카드
https://www.taxi2x2.ru
бланки дипломов о переподготовке купить 6rudik-diplomy365.ru .
포천교정치과 원장 전**씨는 ‘어금니 7개, 앞니 8개가 가장 최선으로 자라는 8~50세 시기에 영구치를 교정해야 추가로 자라는 영구치가 널널한 공간을 가지고 가지런하게 자랄 수 있다’며 ‘프로모션을 통해 자녀들의 치아 상황를 확인해보길 바란다’고 전했다.
비발치교정
https://tabru.ru/
купить диплом медицинского института купить диплом медицинского института .
купить диплом синергии 4russkiy365-diplomy.ru .
Canadian Pharmacy Express Canada drug superstore online pharmacies no prescription Healthy man viagra sales
Получайте кэшбэк до 5% на каждый покупку с картой Сбербанка! Экономьте на покупках в магазинах, кафе и онлайн. Простое оформление и удобное управление через мобильное приложение.
Начните экономить уже сегодня!======>
Дебетовая Альфа-Карта в Прокопьевске
Привет!
Я запускаю новый канал, где буду делиться самой актуальной и интересной информацией о даркнете, анонимности в сети, кибербезопасности и многом другом. Если тебя интересует:
Новости и инсайды из мира даркнета
Инструкции и гайды по анонимности
Разбор кейсов и схем
Советы по кибербезопасности
– тогда этот канал для тебя!
Подписывайся, чтобы не пропустить самое важное и быть в курсе всех событий в теневой стороне интернета.
Ссылка на канал: https://t.me/mg2_at_art
Будет интересно!
myspace.com http://kingranks.com/author/slimecase05-1777026// .
купить диплом закрывшегося вуза 6rudik-diplomy365.ru .
myspace.com https://chnpolice.gov.in/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=exploreourpubliclands.org%2Fmembers%2Fformbirch47%2Factivity%2F623392%2F/ .
tripmaster triptrip24 в обход блокировки роскомнадзора, провайдера, официальный сайт.
Предлагаем вам высококачественный тротуарный бордюр – идеальное решение для обрамления дорожек, газонов, цветников и других элементов ландшафтного дизайна.
Наш тротуарный бордюр отличается прочностью, долговечностью и устойчивостью к воздействию внешних факторов, что делает его идеальным выбором для любых условий эксплуатации – брусчатка
Лазерный уровень легко помещается в сумке и всегда под рукой, когда он вам нужен. Идеально подходит для работы как в помещении, так и на улице. – лазерный нивелир.
https://osago-osago.ru/
Viagra From Usa Pharmacy Cheapest prices on suhagra 100 canadian pharmacy no prescription Mtabs
Sky Pharmacy Online Drugstore Online prescriptions without prescription pharmacies india Pharmacy On Line Tamoxifen
Cheapest viagra anywhere online pharmacy Where to buy viagra
https://cutumed.ru/
Vincent van Gogh painted Garden with Sunflower in 1887.
Добро пожаловать в мир Кракена (Kraken) — одного из самых популярных даркнет-маркетплейсов. Если вы ищете рабочую ссылку, проверенные зеркала или рекомендации по безопасности, вы попали по адресу. Kraken ссылка
The occult was very popular within the 1920s and 1930s, and Nellie Simmons Meier was one of the vital well-known palmists on the earth.
Holding the animals within the hand and touching them with none fear is nice enjoyable.
https://men-doktor.ru/
Canadian Online Pharmacy Canadian pharmacy stock northwest pharmacy canada Lasix
Здесь вы сможете найти поставщиков удобрений и агрохимии – 306 производителей – удобрения оптом от производителя.
Добро пожаловать в мир моды и стиля! Наша коллекция одежды создана для тех, кто ценит качество, комфорт и уникальность. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент моделей для мужчин, женщин и детей, чтобы каждый мог найти что-то по душе. – молодежная одежда оптом.
Сопровождение мужчин — это особая услуга, которая может включать в себя как деловые, так и личные аспекты.
В современном мире многие мужчины ищут профессионалов, которые могут помочь им в различных сферах жизни:
от бизнес-мероприятий до социальных встреч – эскортница Москва
https://ruspowerman.ru/
Получайте кэшбэк до 5% на каждый покупку с картой Сбербанка! Экономьте на покупках в магазинах, кафе и онлайн. Простое оформление и удобное управление через мобильное приложение.
Начните экономить уже сегодня!======>
Zaymigo в Бердске
Suhagra canadian pharmacy mall Viragra with noprescription
Pharmacy Rx One Viagra Healthy men viagra canada pharmacy no script No Prescription Pharmacy Dutasteride
Cialis Canadian Pharmacy Buy cialis 100mg online ship free viagra sample Neurontin
That invasion is a hard, harsh sign to the West that Russia will not back down and settle for the further arming of and placing of weaponry in Ukraine, Poland and Romania.
We offer services to studios who want to find top specialists for their projects.
For more information, follow the link стриминг студия
Join us to launch a successful career in the world of webcam industry or find the perfect model for your business!
To present a scientific definition, Penitentes is thin and high ice blades directed towards the sun, which are formed on the snow-coated areas in mountains.
Купить дженерики в СПБ с доставкой на сайте https://men78.ru большой ассортимент
по выгодным ценам.
Each chakra is related to particular emotional, psychological, and spiritual facets of our lives, and when they are in steadiness, we are able to experience elevated effectively-being and private progress.
Друзья! ??
Clan 2 — одна с наиболее интересных MMORPG, но скажете нет, фарм также повторяющиеся усилия могут иногда отнимать чрезмерно много времени. У нас есть эпикризис!
?? Кликер чтобы People 2 — это ваш нужен позарез юлина для автоматизации:
Электроавтоматический фарм мобов и еще выполнение квестов.
Удобное эксплуатация со минимальными настройками.
Чистяком безопасно для вашего аккаунта!
?? Основополагающие успехи:
? Экономия времени.
? Это по-нашему для круглых хроник Extraction 2.
? Простая энергоустановка и запуск.
Увеличте свойскую эффективность равно насладитесь настоящим игровым течением без прибавочных хлопот! ??
?? Заходите сверху отечественный сайт чи сочиняйте в течение ЛС чтобы подробностей.
Успейте наследовать скидку сверху элитный январь применения!
Этто экспликация хоть приспособить, с точки зрения ваши конкретные мишени равно необыкновенности аудитории.
Within the western U.S., a similar course of was undertaken between seven states that share a standard water supply.
look what i found
sollet wallet hacked
On Line Pharmacy Best price for generic viagra best non prescription pharmacy reviews Canadian health and care mall
4 Corners Pharmacy Cheap viagra supreme suppliers mumbai 400 058 india Pharmacy Online Viagra samples from doctor
Retin a for sale sky pharmacy Euro med online
Технические аспекты реализации
В целом‚ процесс покупки прошел гладко и без каких-либо задержек. Мне понравился профессионализм и вежливость сотрудников автосалона. Они ответили на все мои вопросы и помогли оформить все необходимые документы. Я остался доволен своей покупкой и рекомендую этот автосалон всем‚ кто планирует приобрести автомобиль с АКПП.
Решившись наконец-то на покупку машины‚ я отправился в автосалон “Автомир”. Выбор пал на него после изучения отзывов и сравнения цен. Атмосфера там была достаточно комфортной‚ консультанты не навязчивые‚ но готовые помочь с выбором. Я потратил около трех часов‚ изучая представленные модели с автоматической коробкой передач. В итоге‚ остановился на компактном кроссовере‚ который идеально подходил под мои потребности и бюджет. Все прошло достаточно гладко‚ без каких-либо неожиданных сложностей.
Двигатели внутреннего сгорания? альтернативные топлива
альтернативные виды двигателей для автомобилей
Также следует отметить, что система автоматического включения фар не заменяет собой необходимость внимательности и ответственности водителя. Водитель должен всегда контролировать освещение автомобиля и в случае необходимости корректировать его работу вручную. Например, в условиях сильного тумана или снегопада, автоматическая система может не обеспечить достаточный уровень освещения, и водителю потребуется самостоятельно переключиться на более мощные фары или включить противотуманные огни.
https://glavstroybaza.ru/teplyivodyanoipol/osveshhenie-dlya-natyazhnyh-potolkov-idei-i-sovety-po-vyboru/
Электромобили представляют собой перспективное направление в автомобилестроении, основанное на использовании электрических двигателей, питающихся от аккумуляторных батарей. Главное преимущество электромобилей – отсутствие выбросов вредных веществ в атмосферу во время движения, что способствует снижению уровня загрязнения воздуха в городах. Кроме того, электромобили обычно обладают высокой эффективностью преобразования энергии, поскольку электрический двигатель имеет более высокий КПД по сравнению с двигателем внутреннего сгорания. Тишина работы – еще один значительный плюс электромобилей, особенно ценный в городской среде. Однако электромобили имеют и недостатки. Главная проблема – ограниченный запас хода на одной зарядке, что зависит от емкости аккумулятора и стиля вождения. Время зарядки аккумуляторов также может быть значительным, что создает неудобства для повседневного использования. Стоимость электромобилей часто выше, чем стоимость аналогичных автомобилей с двигателями внутреннего сгорания, хотя цена на аккумуляторные батареи постепенно снижается. Развитие инфраструктуры зарядных станций также является важным фактором, определяющим массовое распространение электромобилей. Необходимо увеличивать количество зарядных станций и улучшать их доступность, чтобы устранить “проблему дальних поездок”. Вопрос утилизации и переработки отработанных аккумуляторов также требует решения, чтобы минимизировать экологический след электромобилей.
Решившись наконец-то на покупку машины‚ я отправился в автосалон “Автомир”. Выбор пал на него после изучения отзывов и сравнения цен. Атмосфера там была достаточно комфортной‚ консультанты не навязчивые‚ но готовые помочь с выбором. Я потратил около трех часов‚ изучая представленные модели с автоматической коробкой передач. В итоге‚ остановился на компактном кроссовере‚ который идеально подходил под мои потребности и бюджет. Все прошло достаточно гладко‚ без каких-либо неожиданных сложностей.
Преимущества автоматического включения фар
Система автоматического включения фар при запуске двигателя основывается на взаимодействии нескольких компонентов. Главный элемент – это электронный блок управления (ЭБУ), который обрабатывает сигналы от различных датчиков и управляет работой освещения. Включение фар происходит автоматически после запуска двигателя, сигнал о котором поступает от системы зажигания. Дополнительные датчики, например, датчики света, могут корректировать работу системы в зависимости от уровня освещенности.
автосалон автомобили с акпп
Решившись наконец-то на покупку машины‚ я отправился в автосалон “Автомир”. Выбор пал на него после изучения отзывов и сравнения цен. Атмосфера там была достаточно комфортной‚ консультанты не навязчивые‚ но готовые помочь с выбором. Я потратил около трех часов‚ изучая представленные модели с автоматической коробкой передач. В итоге‚ остановился на компактном кроссовере‚ который идеально подходил под мои потребности и бюджет. Все прошло достаточно гладко‚ без каких-либо неожиданных сложностей.
Yangon-based mostly Thahara, which gives travelers “a special option to experience Myanmar”, developed the English-language map together with native artistic digital company Nex to showcase Yangon’s alternative facet.
In July 2020, Fred.
Pharmacy Online Canada pharmacy meds mexican pharmacy online medications Bactrim
investigate this site трасти плюс
вывод из запоя дешево ростов-на-дону вывод из запоя дешево ростов-на-дону .
https://osago-osago.ru
вывод из запоя цена ростов вывод из запоя цена ростов .
вывод из запоя в ростове-на-дону вывод из запоя в ростове-на-дону .
Pacific Care Pharmacy Seroquel sky pharmacy wellbutrin Fast viagra
Viagra dapoxetine online purchase online canadian pharmacy Canada pharmacy
Online Pharmacy Cialis overnight shipping from usa online pharmacy Pharmacy Rx One Review Cialis no prescription
вывод из запоя недорого ростов вывод из запоя недорого ростов .
We have thoroughly reviewed and evaluated the top free antivirus scan to provide our readers with a curated list of the most trusted providers. Safeguard your personal data and computer from cyber threats choose one of the leading antivirus solutions from the table below!
Estimate how lengthy every task will take you and where you may add them on to your on a regular basis routine.
https://www.cutumed.ru
Canadian Pharmacy Cialis Viagra brand 100mg online pharmacy no prescription Generic cialis canada
Получайте кэшбэк до 5% на каждый покупку с картой Сбербанка! Экономьте на покупках в магазинах, кафе и онлайн. Простое оформление и удобное управление через мобильное приложение.
Начните экономить уже сегодня!======>
БериБеру в Ессентуках
How to buy cialis online canadian pharmacy cialis Viagra online no prescription
Cialis India Pharmacy Mexican pharmacies that ship canadian pharmacy no prescription Generic Cialis Online Pharmacy Reviews Prednisolone
https://tabru.ru
Canada Pharmacy 24 Hour Drug Store Cipro no prescription pharmacies Rualis 20 super active
Hello dear friend, I would like to offer placement of your link (or links) on different platforms of the internet such as: forums, blogs, comments and much more. . .
Increase your Visibility Boost Your Seo Rank – Get Organic Traffic From Google. Ranking in Google isn’t hard. All you need is a healthy number of backlinks from referring domains that have authority and trust in Google’s eyes.
This Backlinks Service Benefits:
1. Easily get Google rankings
2. Get a lot of traffic from Google
3. You can earn from the website in different ways
4. Increase Domain Authority (DA)
Quality guaranteed !
PRICE – 20$
WebSite – https://goo.su/959En7
отите|Желаете|Мечтаете] получить есплатный|даровой|халявный] NFT? ?? Участвуйте в озыгрыше|акции|лотерее] от loveshop “Пушистые льдинки”! ?? одробности здесь|Узнать больше можно тут|Вся информация по ссылке] – //loveshop1300.cc|https://loveshop-1300.biz|https://lovezshop1300.biz|https://loveshop-12.biz|https://loveshop-13.biz|https://loveshope12.biz|https://loveshope13.biz|https://shope1.top|https://love-shop-1300.top|https://love-shop-1300.homes|https://love-shop-1300.shop|https://shope1.biz|https://shopl.biz]
#loveshop1300-biz # shop1-biz #loveshop13 #loveshop15 #loveshop16
клиника вывод из запоя ростов клиника вывод из запоя ростов .
irbis dingo снегоход [url=https://snegohod-kupit.ru/]irbis dingo снегоход[/url] .
отель в нижнем новгороде отель в нижнем новгороде .
Unrein your wild nature with hot babes – click here!
Каждый день миллионы водителей сталкиваются с опасностью, которую трудно увидеть — усталостью. Она не только снижает внимание, но и может стать причиной серьезных аварий. Не дайте усталости взять верх над вами – gps трекер купить для автомобиля
Квиз — это увлекательная игра-викторина, которая сочетает в себе элементы развлечения и интеллектуального состязания. Они могут проходить в различных форматах: от настольных игр до онлайн-викторин и живых мероприятий в кафе или клубах. Популярность квизов растет, поскольку они позволяют людям не только проверить свои знания, но и провести время в компании друзей или незнакомцев, создавая атмосферу дружеского соперничества – квиз в москве
U.S. pharmacies
canadian pharmacy cialis
orb11ta официальный сайт.
Когда речь идет о ремонте, выбор правильной краски — это один из самых важных этапов. Строительные краски не только придают вашему интерьеру стильный вид, но и защищают поверхности от внешних воздействий. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент высококачественных строительных красок, которые удовлетворят потребности как профессиональных строителей, так и домашних мастеров – краска огнезащитная для дерева.
Сопровождение мужчин — это особая услуга, которая может включать в себя как деловые, так и личные аспекты.
В современном мире многие мужчины ищут профессионалов, которые могут помочь им в различных сферах жизни:
от бизнес-мероприятий до социальных встреч – эскорт сайт Москва
Onlinepharmacy Cheapest prices on generic cialis canadian pharmacy cialis 20mg
Buy cheap strattera online
canadian pharmacies online Sky Pharmacy Online Drugstore Buy albuterol sulfate inhaler online
Canadian Pharmacy Mall
Euromed online http://canadapharmacyonlinedrugstore.com/ Misoprostol online fast shipping
247 Overnight Pharmacy Canadian Cialis india pharmacy Nizagara 100 healthy male Pillsforyou24
canadian pharmacy online no script Tadifil
canadian pharmacy online cialis
Добро пожаловать в мир Кракена (Kraken) — одного из самых популярных даркнет-маркетплейсов. Если вы ищете рабочую ссылку, проверенные зеркала или рекомендации по безопасности, вы попали по адресу. Кракен ссылка
find out this here counterparty xcp wallet
вызов нарколога на дом вызов нарколога на дом .
continue reading this brd bitcoin wallet
нарколог на дом анонимно нарколог на дом анонимно .
вызвать нарколога на дом вызвать нарколога на дом .
нарколог на дом нарколог на дом .
Visiting this website felt akin to experiencing the enchanting Midnight Sun Festival in Norway. The stunning imagery and serene design give a sense of peace while illuminating the beauty of the natural world. The owner’s vision creates a tranquil atmosphere and I’m grateful to provide my feedback.
I’d appreciate your visit to my site for more insights buy university diploma
See you around, and may your path be illuminated by hope
https://dubllikat.ru/
вызов нарколога на дом круглосуточно [url=https://www.narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar24.ru]вызов нарколога на дом круглосуточно[/url] .
1xBet промокод на бонус при регистрации. Букмекерская контора предоставляет игрокам множество возможностей для снижения рисков и увеличения банка. Бонусная программа компании предусматривает интересы как новичков, так и опытных бетторов. Рассмотрим основные виды поощрений в функционале БК: 1хБет промокод на регистрацию – один из самых популярных подарков, созданный для новых игроков на сайте; Ставки на спорт – увеличение депозита до 32500 рублей. Воспользуйся актуальным промокодом 1xbet на сегодня, получи бесплатную возможность увеличить свой первый депозит до 32500 рублей в БК 1xBet. Воспользовавшись промокод 1xbet на телефоне, максимальная сумма бонуса возможного бонуса будет увеличена до 32500 рублей. Но при этом сумма бонуса будет равна сумме вашего первого депозита – более подробно в этом материале https://sushikim.ru/image/pgs/1xbet-besplatnuy-promokod-pri-registracii.html
Светодиодные лампы становятся все более популярными благодаря своей энергоэффективности, долговечности и экологичности. Мы предлагаем вам уникальную возможность — приобретать светодиодные лампы напрямую от завода. – светильники оптом от производителя.
So, it’s important for you to understand all about margin trading and what are the risks involved with it.
Did you even know these have been nonetheless a factor?
Milton Friedman and David I. Meiselman and first revealed in 1963, as part of research submitted to the Fee on Money and Credit.
Some mother and father who don’t consider in any sort of concrete reward aside from potty-training pants like to mark a kid’s progress with coloured stars on a calendar.
Gimped characters lack effectiveness in comparison with different characters at an analogous stage of experience.
canada pharmacy online
In September 2010, Analysis in Motion (RIM) government Mike Lazaridis unveiled the BlackBerry Playbook pill at a developer’s conference.
Whatever the case could also be surrounding Ledger’s loss of life, he left behind one in all the best and most captivating performances of a nasty man ever, and the fact that he did this while giving a new take on an established character makes it all of the more spectacular.
Получайте кэшбэк до 5% на каждый покупку с картой Сбербанка! Экономьте на покупках в магазинах, кафе и онлайн. Простое оформление и удобное управление через мобильное приложение.
Начните экономить уже сегодня!======>
Все займы онлайн в Черкесске
Sky Pharmacy Online Drugstore Cheapest viagra anywhere canada pharmacies online prescriptions
Cheap generic cialis
The surroundings doesn’t lend itself to creativity and thought change.
1с купить программу [url=kupit-1s14.ru]1с купить программу[/url] .
As a child I made elaborate troll homes out of paper and containers as a substitute for the dollhouse I needed from the Sears catalog, but didn’t get for Christmas.
вызов нарколога на дом вызов нарколога на дом .
The central banks agree to provide each other with abundant liquidity to make sure that commercial banks stay liquid in other currencies.
Canadian Pharmacy Cialis 20mg Viagra coupon canadian pharmacy cialis 20mg Cialas
non prescription india pharmacy Sky Pharmacy Online Drugstore Naltrexone
Canadian Pharmacy Isotretinoin Usa pills viagra supreme suppliers viagra Cialis for sale in usa
canadian pharmacy cialis Levitra 20mg best price
частного нарколога на дом narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar28.ru .
Valtrex http://pharmwithoutadoctorsprescription.com/ Online cialis
Inside few minutes from now, you’ll make your very first cash online in Nigeria.
viagra without subscription
вызов нарколога на дом краснодар вызов нарколога на дом краснодар .
It represents the sum of a brand’s market shares in all segments in which it competes, weighted by each segment’s proportion of that brand’s total sales.
Dad and mom also can use mail filters to dam unwanted mail from reaching their youngsters.
The locking is efficient, making the table very solid feeling in all positions.
вывод из запоя краснодар вывод из запоя краснодар .
2. The qualifying credit of the property multiplied by a fraction.
healthy man viagra scam
Для заказа прогона Хрумером, вам необходимо обратиться к специализированным компаниям или Вы можете заказать у нас по наращиванию линк билдинг
так же мы предоставляем услуги по сео продвижению с помощью гса прогонов через тир и поможем если будет нужно оптимизировать ваш проект
для быстрой связи через телеграмм логин @pokras7777 либо добавится в нащу группу в телеграмм https://t.me/+HFxk5vlUvGEzM2Zi либо через скайп логин pokras7777
мы будем рады вам помочь в любых вопросах по наращиваниютрафика на вашем проекте время работы 24/7 без выходных!
You can choose to have a single firm handle all the above-mentioned services for you, however, you always have the option of hiring a specialised boutique for a service.
You should have a strong understanding of the real estate market and discover sellers that are in a hurry to make a sale.
문화상품권휴대폰결제는 그리고 마이크로 페이먼트의 한 형태로, 일상 송금에도 사용됩니다. 예를 들어, 카페에서 커피를 사고 싶은데 카드를 가지고 있지 않을 때, 테블릿 앱을 통해 카페에서 소액 결제를 하여 간편안하게 결제할 수 있습니다. 이처럼 결제 방법은 구매자들의 편의를 높이면서 한순간에 산업자들에게도 이익을 제공합니다.
상품권휴대폰결제
Existe una competencia muy alta en la industria de los juegos de azar virtuales y las apuestas deportivas interactivas en la actualidad https://ecoinn74.ru/images/pgs/melbet_promokod_bonus_za_registraciu.html
They are additionally typically flammable, which can be a safety hazard.
The spa center bodywork calls visit one of the kinds massage techniques, is what we do. What is an garshana massage interested in everyone. Taoist Erotic Massage (TEM) this is the gift to give for pleasure. You be surprised to that,what sea bliss can learn from adopting massage. In studio Workshop grooming massage masseurs will make erotic best massage.
How is it done, and is there something exotic? We will tell you all about him that you wanted to know |Our exotic massage is visited not only by men but also by women, and also by couples. You want to use is exactly what infinitely … Our main intention this is to please visitors enchanting erotic nuru massage. Individual approach to all yours requirements and claims.
The beautiful girls our the spa will give you an unforgettable experience. The salon is a place of rest and relaxation. Like massotherapy, as though, and relaxation, exert influence on specific elements naked body, what can help you gain strength. Give your preference not just to one, but to two masseuses! Choose for yourself masseurs what I liked, both professional and professional skills!
Spa center in New York City we advise extraordinary Spa rooms with convenient interior. These rooms help be you you are staying with us secretly.
We work in NYC. Women Zoe –
tantric massage manhattan
The thrill across the hydrogen economy is shifting up a gear.
you could check here torus crypto
https://adamex-online.ru/
Круглозвенные цепи — это не просто элемент механики, а настоящая находка для бизнеса! Они широко используются в различных отраслях: от сельского хозяйства до строительства, обеспечивая надежную передачу усилия и долговечность – подбор подшипника по размерам.
вывод из запоя краснодар стационар вывод из запоя краснодар стационар .
sky pharmacy review Viagra From Usa Pharmacy Generic viagra pills
вывод из запоя кодирование краснодар вывод из запоя кодирование краснодар .
The platform is a fork of Sushi Swap, a DEX built on the Ethereum blockchain.
La linea entre videojuego y juego de apuestas es realmente muy delgada https://pulikalinkuralradio.com/wp-content/pages/1xbet_promo_code_india_23.html
https://www.champion-sport.ru
canadian pharmacy
Welcome to company “Ppools-Vsem” – your reliable partner in creating the perfect pool!
We specialize in building pools of any complexity, from cozy home oases to luxurious commercial complexes.
For more information, follow the link бассейн сервис оборудование для бассейна москва
Group of professionals will provide best quality of work and an individual approach to each client.
We offer large range of high-quality flavors that will give your dishes a unique aroma.
Our products are made from natural ingredients without the addition of artificial preservatives.
More detailed information at the link ароматизатор
On our website you will find detailed information about each flavor and inspiration for culinary experiments.
вывод из запоя цены краснодар вывод из запоя цены краснодар .
canadian pharmacy uk
Online Pharmacy Novirax suhagra supreme suppliers
Legal usa online pharmacies
https://cutumed.ru
отите|Желаете|Мечтаете] получить есплатный|даровой|халявный] NFT? ?? Участвуйте в озыгрыше|акции|лотерее] от loveshop “Пушистые льдинки”! ?? одробности здесь|Узнать больше можно тут|Вся информация по ссылке] – //loveshop1300.cc|https://loveshop-1300.biz|https://lovezshop1300.biz|https://loveshop-12.biz|https://loveshop-13.biz|https://loveshope12.biz|https://loveshope13.biz|https://shope1.top|https://love-shop-1300.top|https://love-shop-1300.homes|https://love-shop-1300.shop|https://shope1.biz|https://shopl.biz]
#loveshop1300-biz # shop1-biz #loveshop13 #loveshop15 #loveshop16
Melbet bookmaker offers new customers bonuses: for registration with a promo code, for the first account replenishment (first deposit bonus), freebet bonus for free bet, welcome bonus for new players https://marihuanatelevision.tv/pag/codigo_promocional_bono_de_casino_1xbet.html
краснодар вывод из запоя краснодар вывод из запоя .
Я подготовил прайс с базовыми пакетами услуг по SEO-продвижению. Эти пакеты подходят для большинства потребностей и бюджетов моих клиентов. Позвоните мне, и мы вместе подберем для вас выгодный тариф или составим индивидуальный план работ частное продвижение сайтов seo
вывод из запоя краснодар на дому вывод из запоя краснодар на дому .
Be with us today at 1xBet benefit of the eventual online cricket betting experience! We tender the outdo and most moving cricket odds in requital for huge winnings.
Don’t coed out on the fate to carry the day big with 1xBet!
Browse our encyclopaedic cricket betting lines and enjoy a single and exhilarating participation like no other.
1xbet
Получайте кэшбэк до 5% на каждый покупку с картой Сбербанка! Экономьте на покупках в магазинах, кафе и онлайн. Простое оформление и удобное управление через мобильное приложение.
Начните экономить уже сегодня!======>
МТС Банк – РКО в Кызыле
This is our unique MelBet bonus code that needs to be entered when you register for a new player account with the brand melbet. Melbet is mainly a bookmaker, but also offers arcade games and casino games https://logologika.ru/images/pages/?1xbet_promokod___bonus_kod_pri_registracii.html
Pour profiter de ce bonus exceptionnel, il vous suffit d’effectuer votre premier depot. Celui-ci vous donne droit a un bonus de 100% du montant depose, jusqu’a un maximum de $130, ou l’equivalent dans votre devise code promo 1xbet togo
canada pharmacy 24h Cialis dapoxetine overnight shipping
Светодиодные лампы становятся все более популярными благодаря своей энергоэффективности, долговечности и экологичности. Мы предлагаем вам уникальную возможность — приобретать светодиодные лампы напрямую от завода. – купить светильники оптом.
This is our unique MelBet bonus code that needs to be entered when you register for a new player account with the brand melbet. Melbet is mainly a bookmaker, but also offers arcade games and casino games https://pawndetroit.com/wp-content/pages/?code_promo_melbet_bonus_de_bienvenue.html
Pour profiter de ce bonus exceptionnel, il vous suffit d’effectuer votre premier depot. Celui-ci vous donne droit a un bonus de 100% du montant depose, jusqu’a un maximum de $130, ou l’equivalent dans votre devise 1xbet burkina faso
Buy viagra canada http://pharmacyusa24.com/ Orlistat
Здесь вы сможете найти поставщиков удобрений и агрохимии – 306 производителей – средства защиты растений оптом.
вывод из запоя с выездом https://www.vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar117.ru .
https://cvetocheg.ru
cialis online no prescription
вывод из запоя на дому в краснодаре вывод из запоя на дому в краснодаре .
viagra and cialis samples from pfizer
Sleep disorders in autism are a common symptom that significantly impact the quality of life for both the child and their family. The causes of insomnia in autistic children are based on the peculiarities of how their nervous system functions https://www.autism-mmc.com/publications/echolalia/
Sleep disorders in autism are a common symptom that significantly impact the quality of life for both the child and their family. The causes of insomnia in autistic children are based on the peculiarities of how their nervous system functions https://www.autism-mmc.com/publications/answer/
ez online pharmacy buy viagra usa Canadian Pharmacy Canadian pharmacy stock
Nowadays, international communication is of great importance in both personal and business life. Especially in a country like South Korea, which is important in terms of technology and trade Telegram virtual SMS number
Nowadays, international communication is of great importance in both personal and business life. Especially in a country like South Korea, which is important in terms of technology and trade rent SMS verification number
Usa Pharmacy No Script Canadian pharmacy uk Viagra before and after photos canadian pharmacy Viagra generic
вывод из запоя дешево ростов-на-дону вывод из запоя дешево ростов-на-дону .
https://men-doktor.ru
pop over to this website Crypto trading
Добро пожаловать в мир Кракена (Kraken) — одного из самых популярных даркнет-маркетплейсов. Если вы ищете рабочую ссылку, проверенные зеркала или рекомендации по безопасности, вы попали по адресу. Kraken зеркало
While Telegram requires you to sign up with a phone number, this number does not have to be personal. By purchasing a number for Telegram, you can provide a great advantage, especially for users who are concerned about privacy Telegram SMS virtual number
While Telegram requires you to sign up with a phone number, this number does not have to be personal. By purchasing a number for Telegram, you can provide a great advantage, especially for users who are concerned about privacy buy mobile number online
сколько стоит дипломная работа сколько стоит дипломная работа .
удостоверение дипломы купить 2orik-diploms.ru .
https://ruspowerman.ru/
Return on investment (ROI) or return on costs (ROC) is the ratio between net income (over a period) and investment (costs resulting from an investment of some resources at a point in time).
The Irani Firoza gemstone brings again the misplaced confidence and courage to learn you for a healthy psychological state.
Кидала Каширина Ольга Александровна 01.01.1980, раньше жила в г Белгород, она же: Щеблыкина, Солдатова, Холодова, Тафинцева, использует телефон +7 9999910929.
Каширина Ольга Александровна три раза вступала в брак, и к тому же имеет трех детей. Тафинцева Ольга Александровна ближе к концу 2023 г изменила персональные данные на фамилию сожителя, с которым она крутила роман с 2021 года и вместе с ним сбежала от супруга похитив ребенка, и в придачу Каширина Ольга Александровна похитила значительную сумму денег, по эту факту проводится следствие.
Кидала Каширина Ольга Александровна позиционирует себя как основатель фирм школа продаж Ольги Кашириной, Платинумсофт, Актив Альфа. Вся деятельность по фирмам осуществляется от имени ИП Холодова Екатерина Дмитриевна, является дочерью от второго мужа. Холодова Екатерина Дмитриевна не вкурсе об операциях, проводимых Каширина Ольга Александровна, из-за чего стала жертвой мошенничества, задолженность по налогам в бюджет – 766 066 руб, долги по кредитам – 420 894,70 рублей.
До этого мошенница Каширина Ольга Александровна основывает ООО Контур Центр, где номинальным ген директором и учредителем является Холодова. Вся финансово-хозяйственная деятельность осуществляется Кашириной Ольгой Александровной, в следствие чего долги по налогам и сборам на сумму 130963 рублей погашал муж
Раньше аферистка Тафинцева Ольга вела деятельность как ИП, в период 2006-2009 г., вследствие чего образовались долги по налоговым сборам в размере 30 тыс рублей и долги по кредитам в размере 162403.92 рублей, более бизнес от имени личного ИП Тафинцевой не осуществляется.
Тем не менее мошенница Каширина Ольга Александровна создает видимость успешной бизнес-wooman и заботливой мамы, позиционируя себя в качестве тренера на площадке Опора России, где так же является председателем комитета
В настоящее время Каширина Ольга, находясь в браке, проживает в городе Тюмень с судимым Кашириным Владимиром Анатольевичем
купить диплом колледжа в красноярске 2orik-diploms.ru .
вывод из запоя круглосуточно ростов-на-дону вывод из запоя круглосуточно ростов-на-дону .
They are given up to five months to recall the lapsed quantities, offered the rationale for not doing such is caused by cognitive or practical impairment.
нарколог на дом вывод из запоя ростов нарколог на дом вывод из запоя ростов .
A couple of others have the platforms.
Buy lexapro india cheap viagra online Flagyl tablets
Доверьтесь нашему опыту и профессионализму — каждый диван, созданный нашей компанией, станет неотъемлемой частью вашего интерьера
и принесет вам радость и удовлетворение на многие годы вперед – диваны п образные
Когда речь идет о ремонте, выбор правильной краски — это один из самых важных этапов. Строительные краски не только придают вашему интерьеру стильный вид, но и защищают поверхности от внешних воздействий. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент высококачественных строительных красок, которые удовлетворят потребности как профессиональных строителей, так и домашних мастеров – краска для внутренних работ
Добро пожаловать в мир моды и стиля! Наша коллекция одежды создана для тех, кто ценит качество, комфорт и уникальность. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент моделей для мужчин, женщин и детей, чтобы каждый мог найти что-то по душе. – одежда оптом.
вывод из запоя срочно ростов вывод из запоя срочно ростов .
canada pharmacy 24h
Microblading ist absolute Vertrauenssache. Nur spezifizierten Experten sollten Sie es gestatten, Veranderungen an Ihrem Gesicht vorzunehmen. Denn: Das Wichtigste ist, dass die Form Ihrer Augenbrauen richtig erkannt und nachgezeichnet wird – und zwar unter Berucksichtigung Ihres individuellen Haut- und Haartyps. Wir von Microblading Berlin garantieren fur ansprechende Ergebnisse und sorgen mit unserem geschmackvoll eingerichteten Studio fur eine angenehme Atmosphare, damit Sie sich bei der Behandlung so wohl wie moglich fuhlen.
купить аттестат в ульяновске купить аттестат в ульяновске .
viagra prescription free
вывод. из. запоя. ростов. http://www.vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov235.ru .
canada pharmacy online
canadian pharmacy
canadian pharmacy no prescription
sky pharmacy
Я бля вам устрою, мне уже на все насрать,
не надо было трогать этого клиента.
Есть желание решить вопрос мирно?
Жду звонка 89372555454
Или решения вопроса [email protected] тут ваш выбор
электрокамин настенный – купить распродажа электрокаминов в москве, магазин электрокаминов в москве
Сертификат ТР ТС – документ, подтверждающий безопасность продукции и соответствие требованиям
конкретного технического регламента Таможенного Союза. Быстро оформим сделать декларацию соответствия.
The ribeye right here is tender and juicy cooked to perfection.
The sliver of a mantel on the hearth permits space for favourite pictures with out distracting from the great thing about the natural stone.
Vendors can be, of course, client value to repeat a couple of time.
sky pharmacy
supremesuppliersindia.com
Survived by one daughter, Mrs James (Jean) Rettkowski, Wilbur, WA; two grandsons, Barry C Rettkowski, Portland, OR and Davis J Rettkowski, Spokane, WA.
Putting in a fuel fireplace is one other technique to make the realm really feel brighter and cozier.
купить диплом колледжа в спб купить диплом колледжа в спб .
Once you pay off all the loans you have taken for a property, you can then sell it and your profit will be your equity.
Can this newlywed couple survive the battlefield of life after marriage?
알트코인 가격이 월간 기준으로 20년 만에 최대 낙폭을 기록하며 ‘잔인한 9월’로 마감할 것이라는 분석이 제기됐습니다. 현지기간 23일 프로그램 매매 외신의 말을 빌리면 가상화폐 가격은 이달 들어 그동안 38% 넘게 폭락해 2018년 12월 뒤 월간 기준 최대 하락 폭을 기록했습니다.
비트코인 프로그램 자동매매
The company also sponsors the Hong Kong Rugby Union and the brand new South Wales Waratahs staff in Super Rugby.
sport-weekend.com newsomsk.ru/news/144630-turniket_prichin_ustanovki_i_preimuchshestva/ .
The earliest glass artwork paperweights were produced as utilitarian objects within the mid 1800s in Europe.
Следующая страница Перманентный макияж
clockchok.ru http://www.uvlecheniehobby.ru/viewtopic.php?f=7&t=32484 .
Skorr was in the end killed by Vos, who Pressure-pushed him into lava.
Ищете способ быстро решить финансовые вопросы? Наши кредиты — это именно то, что вам нужно!
Никаких скрытых платежей, простая подача заявки и решение за 15 минут.
Рассматриваем сумму от 10,000 до 1,000,000 рублей. Гибкие условия погашения и низкие процентные ставки делают наши предложения выгодными.
Не ждите, действуйте сейчас! Звоните и узнайте больше о своих возможностях!===>>
Кредит Потребительский в Екатеринбурге
He said that printing notes will not work if the country is in a liquidity trap.
of course like your website but you have to check the spelling on several of your posts A number of them are rife with spelling issues and I in finding it very troublesome to inform the reality on the other hand I will certainly come back again
CANADIAN PHARMACY ONLINE NO SCRIPT
В нашем Центре техосмотра на Московском шоссе, 13 в Санкт-Петербурге вы можете пройти техосмотр вашего автомобиля с гарантией качества и быстроты обслуживания. Мы предлагаем полный спектр услуг, чтобы обеспечить безопасность и соответствие вашего транспортного средства всем необходимым стандартам услуги автосервиса и техосмотра
В нашем Центре техосмотра на Московском шоссе, 13 в Санкт-Петербурге вы можете пройти техосмотр вашего автомобиля с гарантией качества и быстроты обслуживания. Мы предлагаем полный спектр услуг, чтобы обеспечить безопасность и соответствие вашего транспортного средства всем необходимым стандартам техосмотр легковых и грузовых автомобилей
Повысьте эффективность своего производства с помощью наших приводных устройств! Наши инновационные устройства позволят вам значительно снизить расходы на электроэнергию,
увеличить производительность оборудования и снизить износ механизмов. Благодаря нашиему оборудованию вы сможете значительно увеличить производственные мощности и улучшить качество выпускаемой продукции – частотник.
Canadian Pharmacy Cialis Buy azithromycin online overnight supreme suppliers mumbai india
Hq canadian meds
의정부 교정치과 원장 B씨는 ‘어금니 9개, 앞니 5개가 가장 먼저 자라는 8~50세 시기에 영구치를 교정해야 추가로 자라는 영구치가 넉넉한 공간을 가지고 가지런하게 자랄 수 있다’며 ‘프로모션을 통해 자녀들의 치아 상태를 검사해보길 바란다’고 이야기 했다.
의정부 교정
I have a wild rock and roll facet to me that makes me need to dance until dawn.
Предлагаем вам высококачественный тротуарный бордюр – идеальное решение для обрамления дорожек, газонов, цветников и других элементов ландшафтного дизайна.
Наш тротуарный бордюр отличается прочностью, долговечностью и устойчивостью к воздействию внешних факторов, что делает его идеальным выбором для любых условий эксплуатации – тротуарная плитка купить в краснодаре
Каждый день миллионы водителей сталкиваются с опасностью, которую трудно увидеть — усталостью. Она не только снижает внимание, но и может стать причиной серьезных аварий. Не дайте усталости взять верх над вами – трекер для автомобиля
sns헬퍼 소셜미디어 마케팅을 사용한 주요 비즈니스 기능으로는 ‘인스타그램 숍스’가 소개됐다. 인스타그램 숍스는 인스타그램 플랫폼 내에서 오프라인 산업자의 브랜드 제품, 행사, 가격 등 아이디어를 공급하는 디지털 가게이다. 사용자는 인스타그램 프로필이나 메인 탐색바의 숍스 탭, 인스타그램 탐색 탭 등을 통해 상점을 방문할 수 있습니다.
sns헬퍼 마케팅
There are thousands of scam On-line business in Nigeria out there with pretend promises who’ve never paid and won’t ever pay.
gtbike.ru https://chita-brita.ru/raznoe/vazhnoe/avtomaticheskie-bollardy-zashhita-i-bezopasnost-dlya-vashego-obekta.html .
no prescription pharmacies
Atenolol Cialis India Pharmacy cialis without a doctor’s prescription What is best ed pill
вывод из запоя ростов-на-дону вывод из запоя ростов-на-дону .
One function of the Swedish central financial institution was lending money to the federal government.
People will have lower rates and their payments will be lower.
The better the financial qualification of the buyer(s) is, the more likely the closing will be successfully completed, which is typically the goal of the seller.
Viagra brand at low price purchase tamoxifen citrate online Canada pharmacies online prescriptions
Nice Article
Additionally, treatment may be prescribed to address coexisting circumstances such as depression, anxiety, or substance abuse.
When it comes to active recreation near the water, many people pay attention to the little things that make this process more convenient and enjoyable https://vidomosti-ua.com/science/134319
Suckley, Matt (March 7, 2018).
When it comes to active recreation near the water, many people pay attention to the little things that make this process more convenient and enjoyable http://bigmir-internet.com.ua/devajsy-dlya-kureniya-naperstki
I have been trying football wagering for a while now, and I honestly believe, it is an interesting way to engage with
the sport. One of the secrets to successful betting is research.
Personally, if all football fans spent effort on reviewing match histories, team form, and lineups, their win percentage could increase significantly.
Football wagering is not only about guessing; it’s about making informed decisions.
Let’s say, if a team has a strong defense but is weak
in attack, it’s a good idea to look at low-scoring games.
Alternatively, matches between high-scoring clubs
often end with exciting finishes.
An additional tip to consider is the strategy.
Simple wagers carry less risk than parlays, but
accumulators could lead to huge wins if done correctly.
Also, watch out for live betting markets,
as they might offer great chances as the match unfolds.
Always remember: Gamble within your limits! Avoid chasing losses,
and consistently keep an eye on your bankroll.
Whether you’re a novice or a experienced bettor, learning to different strategies will be
what makes between success and losing.
Good luck, and make the most of the beautiful
game!
вывод. из. запоя. анонимно. ростов. vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov237.ru .
отите|Желаете|Мечтаете] получить есплатный|даровой|халявный] NFT? ?? Участвуйте в озыгрыше|акции|лотерее] от loveshop “Пушистые льдинки”! ?? одробности здесь|Узнать больше можно тут|Вся информация по ссылке] – //loveshop1300.cc|loveshop1300.cfd|https://lovezshop1300.biz|https://loveshop-12.biz|loveshop1300.beauty|https://loveshope12.biz|https://loveshope13.biz|https://shope1.top|https://love-shop-1300.top|https://love-shop-1300.homes|https://love-shop-1300.shop|https://shope1.biz|https://shopl.biz|loveshop1300.hair|shop1300.top|shope1300.biz]
#loveshop1300-biz # shop1-biz #loveshop13 #loveshop15 #loveshop16
Спасибо, долго искал
_________________
интересное о букмекерских конторах
canada pharmacy meds
https://traxxx.xyz/ online casino
Хотите создать идеальное покрытие для вашего участка или дорожного покрытия? Тогдаотсев идеально подойдет для вас!
Наш высококачественный отсева щебня обеспечит прочность, долговечность и надежность вашего покрытия. Благодаря правильной фракции отсева,
он обладает отличной укладываемостью и прекрасно дренирует воду, что делает его идеальным выбором для любых работ – щебень цена за 1м3.
무리한 소비는 자원 소모와 환경 파괴를 초래할 수 있고, 롯데모바일상품권 소비주의적인 가치관은 소수의 소비에만 초점을 맞추어 경제적 불평등을 증가시킬 수 있을 것입니다. 따라서, 쇼핑을 할 경우는 지속 가능한 소비를 실천하고, 개인의 니즈에 맞게 무난히 결정하는 것이 중요해요.
문화상품권 매입
Предлагаем вам высококачественный тротуарный бордюр – идеальное решение для обрамления дорожек, газонов, цветников и других элементов ландшафтного дизайна.
Наш тротуарный бордюр отличается прочностью, долговечностью и устойчивостью к воздействию внешних факторов, что делает его идеальным выбором для любых условий эксплуатации – тротуарная плитка цена,
Здесь вы сможете найти поставщиков удобрений и агрохимии – 306 производителей – купить фунгициды оптом.
Светодиодные лампы становятся все более популярными благодаря своей энергоэффективности, долговечности и экологичности. Мы предлагаем вам уникальную возможность — приобретать светодиодные лампы напрямую от завода. – завод светодиодных светильников.
nothing special
_________________
вулкан казино игровые автоматы бесплатно без регистрации демо играть онлайн
online pharmacy www
вывод из запоя цены на дому ростов вывод из запоя цены на дому ростов .
Despite the fact that some people remedies name for it, medical authorities discourage taking camphor orally — it may cause blood poisoning, liver damage or kidney harm in sturdy enough quantities.
We encourage you to explore our handpicked selection of the finest online casino sites, catering to players from every corner of the globe казино стрим данлудан
We encourage you to explore our handpicked selection of the finest online casino sites, catering to players from every corner of the globe онлайн казино
한국 이용 가능 카지노 한국 이용 가능 카지노 .
Приглашаем узнать заходите получить 350 000 руб от государства на свой бизнес ? Пройти тестирование для соц контракта новые правила 2024 года: обязательный тест на мсп – узнай вопросы и ответы заранее. 45 вопросов теста для соц контракта .
canada pharmacy 24h
I think decentralized apps (DApps) will be game-changers.
https://t.me/s/cryptonetlake
Canadian Pharmacy Express Viagra online india Prescriptions on line blackcialis.net Buy alli online
We offer to your attention a wide range of quality used vehicles, checked by our lawyers.
For more information, follow the link продажа авто в перми
Our goal is to help you search the perfect car at a good price.
The forex options trading now has become the most popular trend in the currency market arena and helps in generating huge benefits and minimizing the risks of loss to the investor or the client as well as the forex service provider companies.
Chemistry lesson aside, if you are ready to lather up, read on to seek out out what you may expect from bar soaps.
Subsequent, let’s look at some of these browser alternate options as well as a number of the challenges you might encounter when browsing the online on an iPad.
Canadian Pharmacy Cialis Buy liquid antibiotics online healthy male
Keflex
Если вы только планируете поездку в Таиланд и на Пхукет, загляните на phuketescape.com — там собрана базовая информация для начинающих путешественников что посмотреть, куда съездить.
Supreme suppliers http://supremesuppliers.net/ I need viagra overnight delivery
Если вы только планируете поездку в Таиланд и на Пхукет, загляните на phuketescape.com — там собрана базовая информация для начинающих путешественников что посмотреть, куда съездить.
Bud Cort provided the voice of the computer.
sky pharmacy online drugstore
no prescription discount pharmacy Canada Pharmacy 24 Hour Drug Store Vigara
Найдём основание, поможем собрать документы, отведём за руку на подачу в государственный орган и потом проконтролируем выдачу вам внж Черногории ВНЖ Черногории
Найдём основание, поможем собрать документы, отведём за руку на подачу в государственный орган и потом проконтролируем выдачу вам внж Черногории ВНЖ Черногории
We specialize in producing quality packaging materials for various industries: from cosmetic to industrial.
For more information, follow the link крафт пакеты
Our products include cardboard boxes, gift packaging and more.
В современном мире, где качество и безопасность товаров и услуг становятся все более важными, сертификация играет ключевую роль. Мы предлагаем профессиональные услуги по сертификации, которые помогут вашему бизнесу соответствовать международным стандартам и укрепить доверие клиентов. – купить сертификат соответствия
Доверьтесь нашему опыту и профессионализму — каждый диван, созданный нашей компанией, станет неотъемлемой частью вашего интерьера
и принесет вам радость и удовлетворение на многие годы вперед – купить диван в самаре
Нашёл недавно интересный путеводитель по Парижу и Франции – parisgid.ru. Там есть готовые маршруты, идеи, обзоры достопримечательностей и советы где поесть.
Сопровождение мужчин — это особая услуга, которая может включать в себя как деловые, так и личные аспекты.
В современном мире многие мужчины ищут профессионалов, которые могут помочь им в различных сферах жизни:
от бизнес-мероприятий до социальных встреч – эскорт Москва сайт
Квиз — это увлекательная игра-викторина, которая сочетает в себе элементы развлечения и интеллектуального состязания. Они могут проходить в различных форматах: от настольных игр до онлайн-викторин и живых мероприятий в кафе или клубах. Популярность квизов растет, поскольку они позволяют людям не только проверить свои знания, но и провести время в компании друзей или незнакомцев, создавая атмосферу дружеского соперничества – найти квиз в москве
Nicely, a 0-60 time as fast as 4.6 seconds and 153-mph prime velocity made it the quickest domestic automobile of the yr, if not the era.
canada pharmacy online
This website is reminiscent of a luxurious safari lodge in Botswana, where the beauty of nature meets comfortable elegance. The stunning imagery and rich storytelling showcase the expertise of a wildlife conservationist who is passionate about bringing the African wilderness to life in a virtual format.
There’s an online presence of mine that you could visit suSTAinaBLE bAUXITE MiNINg
For a swim to be refreshing and invigorating the pool water must be the best temperature for the swimmer, regardless of the affect of seasonal weather.
That one thing more is the compulsory system of purdah for Muslim women.
Там есть готовые маршруты, идеи, обзоры достопримечательностей и советы где поесть. Нашёл недавно интересный путеводитель по Парижу и Франции – parisgid.ru.
Там есть готовые маршруты, идеи, обзоры достопримечательностей и советы где поесть. Нашёл недавно интересный путеводитель по Парижу и Франции – parisgid.ru.
They can also contain stocks in mining companies.
On the website, everyone can order fillers that are distinguished by premium quality from Europe. The products are presented in more than 70 countries. The company has been on the market for more than 13 years, and therefore has gained recognition from regular customers. The products have quality certificates, which confirms serious intentions cialis online order
https://generic51.ru/sialis-tadalafil
usa pharmacy no script
Добро пожаловать в мир моды и стиля! Наша коллекция одежды создана для тех, кто ценит качество, комфорт и уникальность. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент моделей для мужчин, женщин и детей, чтобы каждый мог найти что-то по душе. – бейсболки оптом.
Check, please ts-web.ru
Ищете способ быстро решить финансовые вопросы? Наши кредиты — это именно то, что вам нужно!
Никаких скрытых платежей, простая подача заявки и решение за 15 минут.
Рассматриваем сумму от 10,000 до 1,000,000 рублей. Гибкие условия погашения и низкие процентные ставки делают наши предложения выгодными.
Не ждите, действуйте сейчас! Звоните и узнайте больше о своих возможностях!===>>
Все займы на кредитную карту в Новочеркасске
Бесплатные фриспины за регистрацию в казино – подборка актуальных предложений. Новые фриспины без депозита 2025 года на https://droptopsite1.ru/
Займ на карту без отказа — это быстрое и удобное решение для тех, кто нуждается в финансовой помощи: простая онлайн-заявка, минимальные требования к заемщику и мгновенное одобрение, что позволяет получить необходимую сумму практически незамедлительно, а также возможность быстро погасить задолженность, делая процесс максимально комфортным и прозрачным для каждого займ без отказа на карту
Круглозвенные цепи — это не просто элемент механики, а настоящая находка для бизнеса! Они широко используются в различных отраслях: от сельского хозяйства до строительства, обеспечивая надежную передачу усилия и долговечность – подобрать подшипник по размеру.
Бесплатные фриспины за регистрацию в казино – подборка актуальных предложений. Новые фриспины без депозита 2025 года на промокоды на фриспины
Займ на карту без отказа — это быстрое и удобное решение для тех, кто нуждается в финансовой помощи: простая онлайн-заявка, минимальные требования к заемщику и мгновенное одобрение, что позволяет получить необходимую сумму практически незамедлительно, а также возможность быстро погасить задолженность, делая процесс максимально комфортным и прозрачным для каждого займ через госуслуги
Качественный асфальт выдерживает любые погодные условия и нагрузки, что делает его идеальным для парковок, дорожек и дворов – ямочный ремонт цена
Хотите создать идеальное покрытие для вашего участка или дорожного покрытия? Тогдаотсев идеально подойдет для вас!
Наш высококачественный отсева щебня обеспечит прочность, долговечность и надежность вашего покрытия. Благодаря правильной фракции отсева,
он обладает отличной укладываемостью и прекрасно дренирует воду, что делает его идеальным выбором для любых работ – щебень цена за тонну.
купить диплом готовый [url=https://2orik-diploms.ru/]купить диплом готовый[/url] .
Сколько стоит диплом высшего и среднего образования и как его получить?
My brother suggested I might like this web site.
He was once entirely right. This submit truly made my day.
You can not believe simply how much time I had spent
for this information! Thank you!
Also visit my blog: вечеринки для ЛГБТ
https://generic51.ru/viagra-sildenafil
Когда речь идет о ремонте, выбор правильной краски — это один из самых важных этапов. Строительные краски не только придают вашему интерьеру стильный вид, но и защищают поверхности от внешних воздействий. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент высококачественных строительных красок, которые удовлетворят потребности как профессиональных строителей, так и домашних мастеров – купить краску оптом.
global pharmacy canada phone number
можно ли купить поддельный аттестат можно ли купить поддельный аттестат .
Заказать изготовление по индивидуальному дизайну или купть памятник по выгодной цене Вы можете в нашей Гранитной мастерской онлайн бесплатно
Financial specialists will purchase securities from the organization and therefore supply the required funding to it.
Заказать изготовление по индивидуальному дизайну или купть памятник по выгодной цене Вы можете в нашей Гранитной мастерской Памятник за рубль
https://generic51.ru/kombinirovannye
Sky Pharmacy Online Drugstore Abortion pill online Enalapril cialis without a doctors prescription Viragra with noprescription
Гранитная мастерская памятников – это предприятие по изготовлению памятников на могилу из натурального камня. Самые дешевые памятники
Гранитная мастерская памятников – это предприятие по изготовлению памятников на могилу из натурального камня. скачать бесплатно
Welcome to our resource, where you will find everything you need for successful cryptocurrency mining!
More detailed information at the link продажа майнингового оборудования
We offer to your attention huge range of high-quality hardware, which will help you mine digital assets as efficiently as possible.
We have thoroughly reviewed and evaluated the top avast antivirus download to provide our readers with a curated list of the most trusted providers. Safeguard your personal data and computer from cyber threats choose one of the leading antivirus solutions from the table below!
https://generic51.ru/nabor-probnik
Cialis buy http://northwestpharmacydrugstore.com/ Finasteride
Canadian Online Pharmacy Meds online pharmacies black cialis
Doxycycline hyclate 100mg tablet
https://poppers51.ru
The commission charges alone would eat up a decent chunk of your investment.
Ищете способ быстро решить финансовые вопросы? Наши кредиты — это именно то, что вам нужно!
Никаких скрытых платежей, простая подача заявки и решение за 15 минут.
Рассматриваем сумму от 10,000 до 1,000,000 рублей. Гибкие условия погашения и низкие процентные ставки делают наши предложения выгодными.
Не ждите, действуйте сейчас! Звоните и узнайте больше о своих возможностях!===>>
495 кредит
skypharmacy
Список бесплатных на сегодня промокодов 1xBet. Тип бесплатного промокода. Промокод промокод на бесплатную ставку. действующий промокод для 1хбет. Как сегодня получить 32500 рублей по промокоду в 1xBet? Получение начинается после регистрации с рабочим промокодом и первого пополнения счета и составляет +100% к депозиту. Игрок может рассчитывать по промокоду до 32 500 рублей, если пройдет верификацию и даст согласие на участие в рекламных предложениях букмекера. На сегодня акция по промокоду 1xBet распространяется на пользователей из России, Беларуси, Украины, Казахстана – более подробно в этом материале https://sushikim.ru/image/pgs/1xbet-besplatnuy-promokod-pri-registracii.html
Theater of the Thoughts A documentary in regards to the history of the Golden Age of Radio, it shot scenes in Rome.
https://generic51.ru/sialis-tadalafil/djenerik-sialis-20-mg
healthy man pharmacy Canadian Pharmacy No Prescription Pharmacy online
English audio system studying French usually struggle to memorise the gender of each noun.
https://severtent.ru/
Empowering Investors with EtherBank
Investing in cryptocurrency doesn’t have to be complicated. EtherBank crypto investment simplifies the process, offering a secure and efficient way to grow your assets.
Key Features of EtherBank
Transparency: Real-time updates and blockchain integration.
Support: Expert guidance through the EtherTalk investment platform.
Flexibility: Customizable investment plans to suit your needs.
Why Choose EtherTalk Investment?
EtherTalk investment connects you with valuable insights and analytics. Whether you’re tracking market trends or exploring new opportunities, EtherTalk empowers you to make smarter choices.
Take control of your financial future with EtherBank crypto investment. Join us today and experience the difference.
However, when the dollar is strong, overseas stock returns can suffer.
I’m looking forward to the next Bitcoin halving and its impact.
https://t.me/cryptonetlake
Цены на памятники в таких местах начинаются от 30 000 рублей за стандартный метровый прямоугольник с оформлением и могут достигать сотен тыся Купить памятник за 1 рубль
Цены на памятники в таких местах начинаются от 30 000 рублей за стандартный метровый прямоугольник с оформлением и могут достигать сотен тыся Самые дешевые памятники
Code promo 1xBet du jour 2025, utilisez le code lors de votre inscription et recevez un bonus de bienvenue 100% VIP pour 2025 jusqu’a €130 sur les paris sportifs ou €1950 150 tours gratuits sur les machines a sous. L’inscription est autorisee pour les personnes ayant atteint l’age de 18 ans et residant dans des pays ou l’activite du bookmaker n’est pas limitee au niveau legislatif. La promotion est valable pour les nouveaux joueurs ayant saisi un code promo lors de l’inscription.
Code Promo 1xBet 2025
https://www.allgreatquotes.com/news/code_promo_208.html
Le code promo 1xBet 2025 Utilisez le code bonus pour obtenir un bonus VIP de 100% jusqu’a €130 pour les paris sportifs, ainsi qu’un bonus de casino de €1950 150 tours de machines a sous. En utilisant le code promotionnel, vous pouvez vous attendre a ce que vos gains soient aussi eleves que dans le cas du plus grand bookmaker 1xbet. Inserez le code promotionnel dans le champ designe lors de l’inscription et vous recevrez un bonus de bienvenue garanti. Cette offre exclusive est disponible pour les nouveaux clients et peut ameliorer considerablement votre premier depot.
https://generic51.ru/viagra-sildenafil/jenskaya-viagra-100mg
Пожар считается ликвидированным (последствия пожара ликвидированными), если прекращено горение и исключены условия для самопроизвольного возникновения горения прибирання після прориву каналізації
Пожар считается ликвидированным (последствия пожара ликвидированными), если прекращено горение и исключены условия для самопроизвольного возникновения горения очищення після пожежі та усунення запаху гару
Carbon fiber has taken the aspect of performance parts to a whole new level by infusing strength into the vehicle at reduced weight for improved dynamics https://api.prx.org/series/50500-carbon-fiber-upgrades-for-better-dynamics
Carbon fiber has taken the aspect of performance parts to a whole new level by infusing strength into the vehicle at reduced weight for improved dynamics https://famenest.com/read-blog/59784
Повысьте эффективность своего производства с помощью наших приводных устройств! Наши инновационные устройства позволят вам значительно снизить расходы на электроэнергию,
увеличить производительность оборудования и снизить износ механизмов. Благодаря нашиему оборудованию вы сможете значительно увеличить производственные мощности и улучшить качество выпускаемой продукции – частотный преобразователь купить.
The 1win promo code: MAX500WIN. This 1Win bonus code 2025 rewards new players with a 500% bonus up to $1025. Valid codes for receiving bonuses without a deposit for new and old users. Hurry to get them today! Activate the promo code 1win and get a generous welcome bonus of up to 500% on your first four deposits 1win ka promo code
The 1win promo code: MAX500WIN. This 1Win bonus code 2025 rewards new players with a 500% bonus up to $1025. Valid codes for receiving bonuses without a deposit for new and old users. Hurry to get them today! Activate the promo code 1win and get a generous welcome bonus of up to 500% on your first four deposits 1win today bonus code
На сайте в вашем распоряжении бесплатные фильмы в онлайне. Вам не придется переживать, если вы не успели познакомиться с недавно вышедшими фильмом-новинкой. Для тех, кто не может оставаться в стороне от жизни кинематографа, должен быть на острие всех его событий, предлагаются смотреть фильмы в HD 1080 смотреть фильмы 2025
Regularly draining your water heater is crucial for maintaining its efficiency and longevity. Sediment buildup reduces heating efficiency and shortens lifespan. While frequency depends on factors like water hardness and usage, a good rule of thumb is to flush it at least once a year. This preventative maintenance helps avoid costly repairs and ensures you enjoy consistent hot water.
Recommended Flushing FrequencyвЃљ A General Guideline
https://heute-news.com/technology/hp-launches-energy-star-4-savvy-pcs/
Flushing your hot water heater is a straightforward process, but safety precautions are paramount. Before you begin, always turn off the power to the unit – either by switching off the circuit breaker or turning off the gas supply. Allow the water heater to cool completely to prevent burns. You’ll need a garden hose, a bucket, and some basic tools. First, locate the drain valve at the bottom of the tank. Attach the garden hose to the drain valve to direct the outflow away from your home and into a suitable drain. Next, carefully open the drain valve, allowing the water to flow out slowly. This initial flow will likely be quite dirty, containing sediment and other debris. As the water clears, you’ll know that the majority of the sediment has been removed. To aid the flushing process, you can open the pressure relief valve (located near the top of the tank) briefly to allow for better water circulation and sediment removal. Be prepared for some initial sputtering as air enters the tank. Once the water runs clear, close the drain valve and reconnect the garden hose. Turn the power back on to your water heater and check for any leaks. It’s advisable to monitor the water heater’s performance in the days following the flush, checking for any unusual noises or leaks. If you are uncomfortable performing this task yourself, it’s always best to consult a qualified plumber. Remember, safety is paramount, and a properly flushed water heater contributes to its longevity and efficiency. The small amount of time invested in this preventative maintenance can save you significant costs and headaches in the long run.
Incorporating Texture and Pattern
With my meticulous measurements and sketches in handтАЪ I headed to a local home improvement storeтАд My goal was simpleтБЪ maximize vertical spaceтАд I knew that utilizing the height of my closet was key to making the most of the limited floor spaceтАд FirstтАЪ I purchased several adjustable shelvesтАд These were a game-changer! I could customize the height of each shelf to perfectly fit my clothing and accessoriesтАд I installed them strategicallyтАЪ creating dedicated spaces for folded sweatersтАЪ jeansтАЪ and t-shirtsтАд The adjustable feature allowed me to easily rearrange the shelves as my needs changedтАд For hanging clothesтАЪ I opted for a double hanging rodтАд This clever solution doubled my hanging spaceтАЪ allowing me to fit more items in the same vertical areaтАд I hung my longer dresses and coats on the top rod and shorter items on the bottomтАд I also invested in slimline velvet hangersтАд These space-saving hangers are narrower than traditional wooden hangersтАЪ allowing me to fit more garments on each rodтАд I even swapped out my bulky wire hangers for theseтАЪ freeing up a surprising amount of spaceтАд InitiallyтАЪ I was hesitant about the cost of the double rod and the slimline hangersтАЪ but the extra space they provided was well worth the investmentтАд Seeing the transformation as I installed each shelf and rod was incredibly motivatingтАд The empty space above the rod was no longer wastedтАд I also added smallтАЪ shallow shelves above the hanging rod to store hatsтАЪ scarvesтАЪ and other accessoriesтАд The entire process was surprisingly straightforwardтАЪ and I felt a great sense of accomplishment with each shelf I installed and each item I neatly hungтАд The previously chaotic space was slowly transforming into a well-organized and efficient systemтАд It was truly satisfying to see my vertical space put to such good useтАд
For a deeper clean‚ dedicate time each week to a more thorough cleaning. Use appropriate cleaning products for each surface. Avoid harsh chemicals that could damage delicate materials like marble or granite. Always test any new cleaning product in an inconspicuous area first. Pay close attention to grout lines‚ as these areas tend to accumulate dirt and mildew. A grout brush and appropriate cleaner are invaluable tools for maintaining clean grout lines. Regularly inspect faucets and showerheads for mineral deposits. Descaling these fixtures regularly prevents clogging and maintains optimal water flow.
Patterned tiles are a fantastic way to introduce visual interest. Geometric patterns‚ such as hexagons or chevrons‚ create a modern and stylish feel‚ while floral or damask patterns can add a touch of vintage charm. Remember to consider the scale of the pattern relative to the size of your bathroom; larger patterns might overwhelm a small space‚ while smaller patterns can get lost in a large one. You can also incorporate texture through the materials you choose for your vanity‚ shower walls‚ or flooring. Natural stone‚ such as marble or slate‚ offers a luxurious and unique texture‚ while wood adds warmth and a touch of rustic charm. Even the choice of towels and bathrobes can contribute to the overall textural experience. A fluffy‚ plush towel adds a level of softness that contrasts beautifully with the hard surfaces of your bathroom fixtures. Don’t be afraid to experiment with different textures and patterns to create a bathroom that is both visually appealing and comfortable.
water car engine
На сайте в вашем распоряжении бесплатные фильмы в онлайне. Вам не придется переживать, если вы не успели познакомиться с недавно вышедшими фильмом-новинкой. Для тех, кто не может оставаться в стороне от жизни кинематографа, должен быть на острие всех его событий, предлагаются смотреть фильмы в HD 1080 фильмы 2025 смотреть онлайн
Welcome to our online store, where you can find a large range of gabions for any needs!
For more information, follow the link габионы купить в спб у производителя
We offer high-quality gabions that are wonderful for landscape design and erosion protection.
На сайте в вашем распоряжении бесплатные фильмы в онлайне. Вам не придется переживать, если вы не успели познакомиться с недавно вышедшими фильмом-новинкой. Для тех, кто не может оставаться в стороне от жизни кинематографа, должен быть на острие всех его событий, предлагаются смотреть фильмы в HD 1080 фильмы 2025 онлайн
https://generic51.ru/levitra-vardenafil
The ENVIROGRAF® passive hearth merchandise vary has been developed over many years and there is almost certainly a passive fire product that’s best for you.
Discord was shady with a bunch of people asking why their service wasn’t working, and they weren’t responding to any emails or messages about why the server hadn’t been activated.
vagina
Перед началом сотрудничества я провожу бесплатную консультацию, где объясняю особенности и тонкости SEO-продвижения, а также обсуждаю с вами стратегию. На этом этапе мы определяем цели и ожидания от работы, что позволяет избежать недоразумений в дальнейшем частный seo вебмастер
Перед началом сотрудничества я провожу бесплатную консультацию, где объясняю особенности и тонкости SEO-продвижения, а также обсуждаю с вами стратегию. На этом этапе мы определяем цели и ожидания от работы, что позволяет избежать недоразумений в дальнейшем заказать продвижение сайта частник москва
Перед началом сотрудничества я провожу бесплатную консультацию, где объясняю особенности и тонкости SEO-продвижения, а также обсуждаю с вами стратегию. На этом этапе мы определяем цели и ожидания от работы, что позволяет избежать недоразумений в дальнейшем http://seo-specialist-moscow.ru/
universal drugstore canada
https://generic51.ru/levitra-vardenafil/djenerik-levitra-20-mg
If each bond has the same yield to maturity, this equals the weighted average of the portfolio’s bond’s durations, with weights proportional to the bond prices.
Ищете способ быстро решить финансовые вопросы? Наши кредиты — это именно то, что вам нужно!
Никаких скрытых платежей, простая подача заявки и решение за 15 минут.
Рассматриваем сумму от 10,000 до 1,000,000 рублей. Гибкие условия погашения и низкие процентные ставки делают наши предложения выгодными.
Не ждите, действуйте сейчас! Звоните и узнайте больше о своих возможностях!===>>
Все кредиты наличными в Оренбурге
Полезные советы по безопасной покупке диплома о высшем образовании
Canadian Pharcharmy Online
With the functional aspects of my closet transformation completeтАЪ I turned my attention to the aestheticsтАд I didn’t want a perfectly organized closet that felt cold and impersonalтАд My style is a mix of bohemian and modernтАЪ so I wanted to incorporate those elements into the designтАд I started by adding a patterned wallpaper to the inside of the closet doorsтАд I chose a subtleтАЪ floral print in muted tones that complemented the overall color scheme of my bedroomтАд It instantly made the space feel more inviting and less like a storage unitтАд NextтАЪ I invested in some pretty velvet hangersтАд These not only looked more stylish than the flimsy wire hangers I had been usingтАЪ but they also helped to keep my clothes wrinkle-freeтАд I found them at a home goods store and they were a surprisingly affordable upgradeтАд To add a touch of whimsyтАЪ I hung a smallтАЪ decorative mirror on the inside of one of the closet doorsтАд This not only served a practical purpose but also helped to brighten up the spaceтАд I also added a smallтАЪ woven basket to store extra scarves and glovesтАд The natural texture of the basket added warmth and visual interestтАд In addition to the larger organizational elementsтАЪ I incorporated small details to reflect my personal styleтАд I used decorative labels for my storage containersтАЪ adding a touch of eleganceтАд I also added a small string of fairy lights inside the closet which gave it a magical ambianceтАд The soft glow was perfect for evening use and added a touch of sparkleтАд I even found some pretty drawer pulls to replace the basic ones that came with my stackable drawersтАд These small details made a big difference in the overall look and feel of the closetтАд The final touch was a smallтАЪ scented sachet placed amongst my clothes to keep everything smelling fresh and pleasantтАд This was a simple yet effective way to add a personal touchтАд The result was a closet that was both functional and aesthetically pleasingтАЪ a space that reflected my style and made me happy to open the doorsтАд
For instance‚ you could use a deep charcoal gray grout with white subway tiles for a sophisticated look‚ or opt for glossy black fixtures against crisp white walls for a sleek‚ contemporary feel. If you prefer a vintage aesthetic‚ consider pairing black and white patterned tiles with white cabinetry and black accents. Don’t be afraid to experiment with different shades of white – from bright‚ clean whites to warmer‚ creamier tones – to find the perfect complement to your chosen black. Remember‚ the key is to create a cohesive and balanced look that reflects your personal style and complements the overall design of your bathroom. Explore online resources for inspiration; many websites and magazines showcase stunning black and white bathroom palettes. Pay attention to how different shades of black and white interact with each other and the other elements in the bathroom design.
https://heute-news.com/travel/charleston-adventures-day-trip/
For instance‚ you could use a deep charcoal gray grout with white subway tiles for a sophisticated look‚ or opt for glossy black fixtures against crisp white walls for a sleek‚ contemporary feel. If you prefer a vintage aesthetic‚ consider pairing black and white patterned tiles with white cabinetry and black accents. Don’t be afraid to experiment with different shades of white – from bright‚ clean whites to warmer‚ creamier tones – to find the perfect complement to your chosen black. Remember‚ the key is to create a cohesive and balanced look that reflects your personal style and complements the overall design of your bathroom. Explore online resources for inspiration; many websites and magazines showcase stunning black and white bathroom palettes. Pay attention to how different shades of black and white interact with each other and the other elements in the bathroom design.
Black and White BathroomРІРѓС™ A Timeless Classic
Lighting Considerations for a Striking Effect
My Tiny Bedroom Closet Transformation
Maintaining the pristine look of your black and white bathroom requires consistent effort‚ but the results are well worth it. The stark contrast of black and white highlights any dirt or grime‚ making regular cleaning crucial. A weekly cleaning routine is recommended to prevent buildup and maintain that showroom shine. Start by wiping down surfaces such as countertops‚ sinks‚ and shower walls after each use. This simple habit prevents the accumulation of soap scum‚ toothpaste residue‚ and other daily grime.
putting oil in car while engine is hot
купить диплом журналиста купить диплом журналиста .
https://generic51.ru/viagra-sildenafil/djenerik-viagra-50mg
Early concerns over water high quality led to the creation of Fairmount Park in 1812.
Additionally, you should definitely have a selection of beer and wine and a few non-alcoholic choices for the designated drivers.
https://generic51.ru/viagra-sildenafil/djenerik-viagra-200-mg
https://moscow-viagra.ru
кракен онион ссылка онлайн – kraken darknet market, kraken darknet market ссылка
The smooth-start kit/option is normally solely required for installations using a big single part heat pump (eg 30kw) with a restricted or sensitive electrical provide.
Официальная покупка диплома ПТУ с упрощенной программой обучения
canadian pharmacy
We offer modern IT solutions for your business on the website kodx.uk
They believed these amulets protected them specifically from injuries.
https://generic51.ru/viagra-sildenafil/viagra-soft-100-mg
купить диплом
Букмекерская контора 1Win – самая популярная платформа для онлайн ставок на спорт и казино в России. 1Вин – это легальный официальный сайт с лицензией, которые всегда выводит выигрыши. Чтобы начать делать ставки и играть на деньги, необходимо зарегистрироваться http://mtw2014.tmweb.ru/forum/?PAGE_NAME=message&FID=1&TID=12120&TITLE_SEO=12120-gde-i-kak-skachat-aktualnoe-zerkalo-1vin&MID=520235&result=new#message520235
Букмекерская контора 1Win – самая популярная платформа для онлайн ставок на спорт и казино в России. 1Вин – это легальный официальный сайт с лицензией, которые всегда выводит выигрыши. Чтобы начать делать ставки и играть на деньги, необходимо зарегистрироваться http://icfoodseasoning.com/bbs/board.php?bo_table=free&wr_id=143140
With my chosen design toolтАЪ KitchenCraft ProтАЪ selectedтАЪ the next step was inputting my kitchen’s precise measurements. This proved surprisingly straightforward. The software guided me through a step-by-step processтАЪ prompting me to enter the length and width of each wallтАЪ the location of windows and doorsтАЪ and the dimensions of existing fixtures like sinks and ovens. I found the interface incredibly intuitiveтАЪ with clear instructions and helpful visual aids. I even appreciated the option to upload a floor plan image to assist with the process. InitiallyтАЪ I struggled a bit with accurately measuring some awkwardly shaped alcovesтАЪ but the platform’s customer support chat was incredibly helpfulтАЪ providing quick and efficient guidance. Once the dimensions were finalizedтАЪ I began to personalize the design. This is where the fun really started! I selected my preferred cabinet stylesтАЪ choosing from a comprehensive library of options ranging from sleek modern designs to more traditionalтАЪ rustic styles. I meticulously chose the colorsтАЪ finishesтАЪ and countertop materialsтАЪ experimenting with different combinations to find the perfect aesthetic. I even incorporated my existing appliancesтАЪ ensuring they fit seamlessly into the new layout. The software allowed for precise placement of every elementтАЪ down to the smallest detail. I spent hours tweaking and refiningтАЪ meticulously considering factors such as workflow efficiency and aesthetic harmony. The process felt like playing a sophisticated digital puzzleтАЪ and the satisfaction of seeing my vision slowly take shape on the screen was incredibly rewarding. I discovered that the software’s flexibility allowed me to explore different layouts and experiment with various design choices without any commitmentтАЪ a feature I truly appreciated. It was a crucial step in ensuring my final design would be both functional and visually appealing.
Once I finalized my dream kitchen layoutтАЪ exporting the design was surprisingly straightforward. The online tool offered several options; I chose to download high-resolution imagesтАЪ perfect for sharing with family and friends. The images were incredibly detailedтАЪ capturing every element of my designтАЪ from the subtle grain of the oak cabinets to the precise dimensions of the countertops. I also created a detailed PDF planтАЪ which included measurementsтАЪ appliance specificationsтАЪ and a comprehensive materials list. This was invaluable for potential contractorsтАЪ providing them with all the information they needed to accurately estimate costs and timelines. Sharing my design was incredibly easy. I emailed the images and PDF to several contractors I’d contactedтАЪ and the clarity of the visuals made communication seamless. They were all impressed by the level of detail and professionalism of the digital plans. I also shared my design on social mediaтАЪ posting the images to my Instagram account. My friends and family were amazed by the transformationтАЪ praising the modernтАЪ yet cozy feel of the kitchen. The online tool even allowed me to create a 3D walkthroughтАЪ which I shared with a friend who’s considering a kitchen renovation of her own. She was particularly impressed by the realistic rendering of the lighting and the overall atmosphere of the space. The ability to easily export and share my design was a fantastic feature of the software. It facilitated clear communication with contractorsтАЪ allowed me to easily share my vision with othersтАЪ and even inspired my friend to begin her own kitchen design journey. The entire processтАЪ from initial design to final export and sharingтАЪ was smoothтАЪ efficientтАЪ and incredibly rewardingтАЪ proving that designing a dream kitchen online can be both fun and incredibly practical.
https://instepnews.com/finance/choosing-the-best-laptop-for-stock-trading/
Refining the Design and Adding Details
Once I finalized my dream kitchen layoutтАЪ exporting the design was surprisingly straightforward. The online tool offered several options; I chose to download high-resolution imagesтАЪ perfect for sharing with family and friends. The images were incredibly detailedтАЪ capturing every element of my designтАЪ from the subtle grain of the oak cabinets to the precise dimensions of the countertops. I also created a detailed PDF planтАЪ which included measurementsтАЪ appliance specificationsтАЪ and a comprehensive materials list. This was invaluable for potential contractorsтАЪ providing them with all the information they needed to accurately estimate costs and timelines. Sharing my design was incredibly easy. I emailed the images and PDF to several contractors I’d contactedтАЪ and the clarity of the visuals made communication seamless. They were all impressed by the level of detail and professionalism of the digital plans. I also shared my design on social mediaтАЪ posting the images to my Instagram account. My friends and family were amazed by the transformationтАЪ praising the modernтАЪ yet cozy feel of the kitchen. The online tool even allowed me to create a 3D walkthroughтАЪ which I shared with a friend who’s considering a kitchen renovation of her own. She was particularly impressed by the realistic rendering of the lighting and the overall atmosphere of the space. The ability to easily export and share my design was a fantastic feature of the software. It facilitated clear communication with contractorsтАЪ allowed me to easily share my vision with othersтАЪ and even inspired my friend to begin her own kitchen design journey. The entire processтАЪ from initial design to final export and sharingтАЪ was smoothтАЪ efficientтАЪ and incredibly rewardingтАЪ proving that designing a dream kitchen online can be both fun and incredibly practical.
Experimenting with Different Layouts
Inputting My Measurements and Preferences
My Free Online Kitchen Design Journey
Букмекерская контора 1Win – самая популярная платформа для онлайн ставок на спорт и казино в России. 1Вин – это легальный официальный сайт с лицензией, которые всегда выводит выигрыши. Чтобы начать делать ставки и играть на деньги, необходимо зарегистрироваться http://jkhsec.com/index.php?option=com_k2&view=itemlist&task=user&id=260916
Biography of Spanish footballer Pedri https://pedri-bd.com statistics at Barcelona, ??games with teammate Gavi, inclusion in the national team for Euro, meme with Cristiano Ronaldo.
Canadian Pharmacy Cialis Tadalafil online Best price cialis 20mg healthy man viagra offer Zyban
Purchase viagra http://pharmwithoutadoctorsprescription.com/ Kemadrin
https://generic51.ru/dapoksetin
Этапы SEO продвижения сайта · Создание и размещение оптимизированного под запросы текста на целевые страницы · Доработка сайта с целью оптимизации его под запросы http://seo-optimizator-moscow.ru/
Этапы SEO продвижения сайта · Создание и размещение оптимизированного под запросы текста на целевые страницы · Доработка сайта с целью оптимизации его под запросы http://seo-optimizator-moscow.ru/
blacksprut
https://bs2best.quest/
Этапы SEO продвижения сайта · Создание и размещение оптимизированного под запросы текста на целевые страницы · Доработка сайта с целью оптимизации его под запросы сео специалист цена
https://stoya4ok.ru
Attention promotion !! The price is 10$ + a good bonus , hurry up the promotion will last 24 hours !
Hello, dear friend, I would like to suggest placing your link (or links) in 5000+ comments on different platforms Internet, such as: forums, blogs and many others. . .
Increase your Visibility Boost Your Seo Rank – Get Organic Traffic From Google. Ranking in Google isn’t hard. All you need is a healthy number of backlinks from referring domains that have authority and trust in Google’s eyes.
This Backlinks Service Benefits:
1. Easily get Google rankings
2. Get a lot of traffic from Google
3. You can earn from the website in different ways
4. Increase Domain Authority (DA) Quality guaranteed !
4. Increase Domain Authority (DA) Quality guaranteed ! Why You
WebSite – https://goo.su/mwLPRT
образование купить образование купить .
Online Pharmacy Viagra professionnel inde canadian pharmacy no prescription
Brand viagra 100mg cheapest
Качественный асфальт выдерживает любые погодные условия и нагрузки, что делает его идеальным для парковок, дорожек и дворов – асфальтирование под ключ
Incorporating Texture and Pattern
The frequency of your hot water heater’s drainage needs isn’t a one-size-fits-all scenario. Several crucial factors influence how often you should perform this essential maintenance task. Hard water, characterized by high mineral content, significantly accelerates sediment buildup within your water heater’s tank. These minerals precipitate out of solution as the water heats, forming a layer of sediment at the bottom. The thicker this sediment layer becomes, the less efficient your water heater becomes, consuming more energy to heat the water and potentially leading to premature failure. High water usage also contributes to faster sediment accumulation. The more frequently you use hot water, the more minerals are introduced into the tank, increasing the rate of sediment formation. Conversely, homes with soft water and low water usage may find that an annual flush is sufficient. Consider the specific characteristics of your water supply and your household’s hot water consumption habits when determining your ideal flushing schedule. Regularly checking the sediment level (if accessible) can also provide valuable insights into the frequency needed for your specific circumstances. Remember, consistent monitoring and proactive maintenance are key to ensuring your water heater’s optimal performance and longevity. Ignoring these factors can lead to decreased efficiency, higher energy bills, and ultimately, costly repairs or premature replacement.
https://heute-news.com/technology/my-unexpected-encounter-with-the-serpens-galaxy/
How Often Should You Drain Your Hot Water Heater?
Lighting plays a crucial role in showcasing the beauty of a black and white bathroom. Careful consideration of lighting schemes can dramatically impact the overall mood and atmosphere of the space‚ transforming it from drab to dazzling. Avoid harsh‚ overhead lighting which can create stark shadows and wash out the details of your design choices. Instead‚ opt for a layered approach that combines ambient‚ task‚ and accent lighting to create a warm and inviting ambiance.
Looking at my transformed closetтАЪ I felt a surge of satisfactionтАд What was once a chaotic jumble of clothes and forgotten items was now a haven of organized calmтАд The carefully planned shelving and hanging solutions maximized every inch of spaceтАЪ creating a surprisingly spacious feelтАд My carefully curated collection of clothes and accessories were now visible and easily accessibleтАд Finding what I needed in the morning became a breezeтАЪ a stark contrast to the frustrating rummages of the pastтАд The addition of the patterned wallpaper and velvet hangers added a touch of elegance and personalityтАЪ transforming the closet from a purely functional space into a stylish extension of my bedroomтАд The soft lighting and subtle scents created a calming and inviting atmosphereтАд It wasnтАЩt just about organization; it was about creating a space that reflected my personal style and brought me joyтАд I found myself spending more time in my bedroomтАЪ simply admiring the transformationтАд The project had been challengingтАЪ requiring patienceтАЪ planningтАЪ and a good dose of creativityтАЪ but the result was well worth the effortтАд The sense of accomplishment was immenseтАд More than just a storage solutionтАЪ my closet became a testament to the power of thoughtful design and personal expressionтАд It proved that even the smallest of spaces can be transformed into something beautiful and functional with a little bit of planning and a lot of heartтАд The project taught me the importance of maximizing vertical spaceтАЪ utilizing every nook and crannyтАЪ and most importantlyтАЪ infusing my personal style into every detailтАд ItтАЩs a reminder that even seemingly insignificant spaces can be sources of pride and joy when approached with intention and creativityтАд I now look forward to getting dressed in the morningтАЪ not dreading the chaos that used to greet meтАд My tiny closet transformation was a resounding successтАЪ and I highly recommend tackling your own closet projectтАЪ regardless of size; You might be surprised by the results!
For instance‚ you could use a deep charcoal gray grout with white subway tiles for a sophisticated look‚ or opt for glossy black fixtures against crisp white walls for a sleek‚ contemporary feel. If you prefer a vintage aesthetic‚ consider pairing black and white patterned tiles with white cabinetry and black accents. Don’t be afraid to experiment with different shades of white – from bright‚ clean whites to warmer‚ creamier tones – to find the perfect complement to your chosen black. Remember‚ the key is to create a cohesive and balanced look that reflects your personal style and complements the overall design of your bathroom. Explore online resources for inspiration; many websites and magazines showcase stunning black and white bathroom palettes. Pay attention to how different shades of black and white interact with each other and the other elements in the bathroom design.
Pay attention to the details. Small details can make a big difference. Think about the style of your soap dispenser‚ toothbrush holder‚ and other bathroom essentials. Choose pieces that complement your overall design aesthetic. Remember‚ less is often more. Avoid overcrowding the space with too many accessories. Instead‚ curate a collection of carefully chosen items that enhance the overall look and feel of your bathroom. A few well-placed accessories can create a more polished and sophisticated look than a cluttered collection.
car engine piston
Квиз — это увлекательная игра-викторина, которая сочетает в себе элементы развлечения и интеллектуального состязания. Они могут проходить в различных форматах: от настольных игр до онлайн-викторин и живых мероприятий в кафе или клубах. Популярность квизов растет, поскольку они позволяют людям не только проверить свои знания, но и провести время в компании друзей или незнакомцев, создавая атмосферу дружеского соперничества – квиз сегодня
https://generic51.ru/kombinirovannye/super-tadarise-sialis-20-mg-dapoksetin-60-mg
Experimenting with Different Layouts
With a satisfying L-shaped layout as my baseтАЪ I delved into the finer detailsтАЪ transforming my digital sketch into a truly personalized design. I meticulously selected cabinet styles from the extensive library offered by the softwareтАЪ opting for sleekтАЪ modern shaker-style cabinets in a warmтАЪ honey-toned oak finish. The program allowed me to visualize these choices in real-timeтАЪ rotating the cabinets to ensure they complemented the overall aesthetic. NextтАЪ I chose countertops. I initially considered graniteтАЪ but the virtual rendering showed it clashing slightly with the cabinet color. I then experimented with quartzтАЪ settling on a beautifulтАЪ light-grey option that beautifully contrasted with the oak. The software’s realistic rendering capabilities were invaluable here. I spent a considerable amount of time tweaking the backsplashтАЪ finally settling on a subway tile pattern in a soft whiteтАЪ which provided a clean and classic look. Adding lighting was another key step. I strategically placed recessed lighting above the countertops and pendant lights above the islandтАЪ creating a warm and inviting ambiance. I even experimented with different flooring optionsтАЪ virtually laying down various types of tile and hardwood to see how they interacted with the rest of the design. I was particularly pleased with a light-colored oak wood floor that tied in seamlessly with the cabinetry. Beyond the major elementsтАЪ I focused on the smaller details. I carefully selected hardwareтАЪ opting for brushed nickel pulls and knobs that added a touch of sophistication. I also integrated various appliancesтАЪ choosing models based on their size and aestheticsтАЪ ensuring they fit harmoniously within the design. The software allowed me to fine-tune every aspectтАЪ from the placement of outlets to the positioning of spice racksтАЪ ensuring a highly functional and visually appealing kitchen. It was a truly rewarding processтАЪ seeing my initial concept evolve into a cohesive and detailed designтАЪ ready to be shared and potentially implemented in the real world. The level of customization was impressiveтАЪ allowing me to create a space that was uniquely mine.
https://instepnews.com/automotive-news/my-experience-at-a-1-tires-and-wheels-in-vacaville-ca/
With a satisfying L-shaped layout as my baseтАЪ I delved into the finer detailsтАЪ transforming my digital sketch into a truly personalized design. I meticulously selected cabinet styles from the extensive library offered by the softwareтАЪ opting for sleekтАЪ modern shaker-style cabinets in a warmтАЪ honey-toned oak finish. The program allowed me to visualize these choices in real-timeтАЪ rotating the cabinets to ensure they complemented the overall aesthetic. NextтАЪ I chose countertops. I initially considered graniteтАЪ but the virtual rendering showed it clashing slightly with the cabinet color. I then experimented with quartzтАЪ settling on a beautifulтАЪ light-grey option that beautifully contrasted with the oak. The software’s realistic rendering capabilities were invaluable here. I spent a considerable amount of time tweaking the backsplashтАЪ finally settling on a subway tile pattern in a soft whiteтАЪ which provided a clean and classic look. Adding lighting was another key step. I strategically placed recessed lighting above the countertops and pendant lights above the islandтАЪ creating a warm and inviting ambiance. I even experimented with different flooring optionsтАЪ virtually laying down various types of tile and hardwood to see how they interacted with the rest of the design. I was particularly pleased with a light-colored oak wood floor that tied in seamlessly with the cabinetry. Beyond the major elementsтАЪ I focused on the smaller details. I carefully selected hardwareтАЪ opting for brushed nickel pulls and knobs that added a touch of sophistication. I also integrated various appliancesтАЪ choosing models based on their size and aestheticsтАЪ ensuring they fit harmoniously within the design. The software allowed me to fine-tune every aspectтАЪ from the placement of outlets to the positioning of spice racksтАЪ ensuring a highly functional and visually appealing kitchen. It was a truly rewarding processтАЪ seeing my initial concept evolve into a cohesive and detailed designтАЪ ready to be shared and potentially implemented in the real world. The level of customization was impressiveтАЪ allowing me to create a space that was uniquely mine.
Once I finalized my dream kitchen layoutтАЪ exporting the design was surprisingly straightforward. The online tool offered several options; I chose to download high-resolution imagesтАЪ perfect for sharing with family and friends. The images were incredibly detailedтАЪ capturing every element of my designтАЪ from the subtle grain of the oak cabinets to the precise dimensions of the countertops. I also created a detailed PDF planтАЪ which included measurementsтАЪ appliance specificationsтАЪ and a comprehensive materials list. This was invaluable for potential contractorsтАЪ providing them with all the information they needed to accurately estimate costs and timelines. Sharing my design was incredibly easy. I emailed the images and PDF to several contractors I’d contactedтАЪ and the clarity of the visuals made communication seamless. They were all impressed by the level of detail and professionalism of the digital plans. I also shared my design on social mediaтАЪ posting the images to my Instagram account. My friends and family were amazed by the transformationтАЪ praising the modernтАЪ yet cozy feel of the kitchen. The online tool even allowed me to create a 3D walkthroughтАЪ which I shared with a friend who’s considering a kitchen renovation of her own. She was particularly impressed by the realistic rendering of the lighting and the overall atmosphere of the space. The ability to easily export and share my design was a fantastic feature of the software. It facilitated clear communication with contractorsтАЪ allowed me to easily share my vision with othersтАЪ and even inspired my friend to begin her own kitchen design journey. The entire processтАЪ from initial design to final export and sharingтАЪ was smoothтАЪ efficientтАЪ and incredibly rewardingтАЪ proving that designing a dream kitchen online can be both fun and incredibly practical.
After inputting my measurements and preferencesтАЪ I dove headfirst into the exciting world of layout experimentation. KitchenCraft Pro offered a plethora of optionsтАЪ from the classic galley style to the more spacious L-shape and U-shape designs. I started by exploring the galley layoutтАЪ digitally dragging and dropping cabinets and appliances to visualize the workflow. I quickly realized it wouldn’t suit my needs тАУ the limited counter space was a major drawback. NextтАЪ I experimented with an L-shape configurationтАЪ strategically placing the sinkтАЪ stoveтАЪ and refrigerator to form an efficient work triangle. This felt more promising. I meticulously adjusted the placement of islands and peninsulasтАЪ carefully considering their impact on traffic flow and overall spaciousness. The software’s intuitive drag-and-drop functionality made this process remarkably easy and enjoyable. I even tried a daring U-shaped designтАЪ envisioning a grandтАЪ chef-like workspace. While initially appealingтАЪ I found it slightly cramped for my needs. The software allowed me to easily switch between different layoutsтАЪ instantly visualizing the impact of each change. I spent hours tweaking the arrangement of cabinetsтАЪ appliancesтАЪ and workspacesтАЪ constantly evaluating the practicality and aesthetic appeal of each configuration; I played around with different cabinet depths and widthsтАЪ experimenting with the placement of pantry units and maximizing storage space. I even considered adding a breakfast bar to one of the layoutsтАЪ envisioning family gatherings around it. The ability to instantly see the results of my adjustments was invaluableтАЪ allowing me to make informed decisions based on both functionality and personal preference. It was a truly iterative processтАЪ refining and perfecting the design until I found the perfect balance between form and function. Through this experimentationтАЪ I discovered that the L-shape layoutтАЪ with a cleverly positioned islandтАЪ provided the optimal blend of efficiency and spaciousness for my kitchen.
I embarked on a thrilling kitchen redesignтАЪ leveraging free online tools. My goal? A stunningтАЪ functional space without breaking the bank. I spent hours exploring various platformsтАЪ comparing features and ease of use. The process felt surprisingly intuitive. I was amazed by how quickly I could visualize different layouts and experiment with various appliances and cabinetry. It was a fun and empowering experienceтАЪ proving that achieving a dream kitchen doesn’t require a hefty budget!
Inputting My Measurements and Preferences
pharmacia online usa Canadian Pharmacy Levitra 20mg
Предлагаем вам высококачественный тротуарный бордюр – идеальное решение для обрамления дорожек, газонов, цветников и других элементов ландшафтного дизайна.
Наш тротуарный бордюр отличается прочностью, долговечностью и устойчивостью к воздействию внешних факторов, что делает его идеальным выбором для любых условий эксплуатации – брусчатка тротуарная цена за м2
sky pharmacy review
Игроки могут осуществлять ставки в 1вин на самые различные события, на десятки видов спорта а также киберспорт и многое другое. Инфраструктура проекта развита http://www.ffxi-caldera.net/doku.php?id=%20%D0%9F%D0%BE%D0%B4%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B1%D0%BD%D1%8B%D0%B9%20%D0%BE%D0%B1%D0%B7%D0%BE%D1%80%20%D0%B8%D0%BD%D1%82%D0%B5%D1%80%D1%84%D0%B5%D0%B9%D1%81%D0%B0%20%D0%92%D0%B0%D0%BD%20%D0%92%D0%B8%D0%BD
Игроки могут осуществлять ставки в 1вин на самые различные события, на десятки видов спорта а также киберспорт и многое другое. Инфраструктура проекта развита http://www.ingenieursdudimanche.lagob.fr/doku.php?id=%20%D0%9A%D0%B0%D0%BA%20%D0%B8%D0%B7%D0%B1%D0%B5%D0%B6%D0%B0%D1%82%D1%8C%20%D0%B1%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%BA%D0%B8%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%BA%D0%B8%20%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%B8%20%D0%B2%D1%85%D0%BE%D0%B4%D0%B5%20%D0%B2%201win
Игроки могут осуществлять ставки в 1вин на самые различные события, на десятки видов спорта а также киберспорт и многое другое. Инфраструктура проекта развита https://sciencewiki.science/index.php?title=%20%D0%98%D1%81%D1%82%D0%BE%D1%80%D0%B8%D1%8F%20%D1%81%D0%BE%D0%B7%D0%B4%D0%B0%D0%BD%D0%B8%D1%8F%20%D0%BF%D0%BB%D0%B0%D1%82%D1%84%D0%BE%D1%80%D0%BC%D1%8B%20%D0%92%D0%B0%D0%BD%20%D0%92%D0%B8%D0%BD
https://generic51.ru/sialis-tadalafil/djenerik-sialis-40-mg
online pharmacy without prescription What is best ed pill
usa pharmacy no script
Строительный и архитектурный портал https://intertools.com.ua все самое интересное о строительстве и архитектуре – новости архитектуры и строительства, обзоры и аналитика.
Главная https://zelenka.guru/articles
интересные новости
_________________
где продают игровые автоматы
Сопровождение мужчин — это особая услуга, которая может включать в себя как деловые, так и личные аспекты.
В современном мире многие мужчины ищут профессионалов, которые могут помочь им в различных сферах жизни:
от бизнес-мероприятий до социальных встреч – эскорт сайт Москва
As is invariably the case the match statistics from totally different sources produce variant figures.
https://generic51.ru/kombinirovannye/super-p-force-viagra-dapoksetin
MangaGo is a really attractively designed website where you’ll be able to read all your favorite mangas free of charge.
Nonetheless, if you are like many who’ve amassed a collection through the years, you may end up questioning what to do with outdated CDs.
They also provide free & insured shipping, which implies that you just obtain your product within three days of inserting the order.
Code promo de 1xBet – l’utilisation de ce code vous permettra d’obtenir un bonus de 30% supplementaire, allant jusqu’a 100$. Le bonus est accorde sous la forme de 130% du montant de votre premier depot. Cette offre est reservee aux nouveaux utilisateurs majeurs apres leur inscription. Profitez du code promo pour augmenter votre bonus de bienvenue de 100% a 130%. Les fonds seront credites sur votre solde de jeu, et le bonus devra etre mise sur des paris sportifs. Ce code promo est valable jusqu’au 31 decembre 2025.
Code Promo 1xBet
https://gettvantenna.com/pag/code_promo_163.html
Le Code promo 1xBet – en utilisant cette combinaison, vous aurez acces a un bonus de 100% sur votre premier depot, pouvant aller jusqu’a 100$. La totalite du bonus credite est disponible uniquement pour les paris dans la section sportive. Vous devrez placer des paris avec une cote minimale de 1,4 et un wager x5. Si toutes les conditions de mise du bonus de bienvenue sont respectees, tous vos gains pourront etre retires sur votre solde principal a la fin de cette promotion.
Le bookmaker 1xBet est l’une des plateformes les plus populaires et leaders du marche. En plus de son interface conviviale et de ses mises a jour regulieres de l’application mobile, la plateforme recompense ses joueurs avec des promotions, des bonus et des cadeaux reguliers. La plupart des utilisateurs, qu’ils soient nouveaux ou reguliers, utilisent activement des codes promo pour jouer. Certains sont reserves a l’inscription pour augmenter le bonus de bienvenue, tandis que d’autres peuvent etre utilises sur la plateforme et se trouvent dans la section “Vitrine des codes promo” du site.
Looking at my transformed closetтАЪ I felt a surge of satisfactionтАд What was once a chaotic jumble of clothes and forgotten items was now a haven of organized calmтАд The carefully planned shelving and hanging solutions maximized every inch of spaceтАЪ creating a surprisingly spacious feelтАд My carefully curated collection of clothes and accessories were now visible and easily accessibleтАд Finding what I needed in the morning became a breezeтАЪ a stark contrast to the frustrating rummages of the pastтАд The addition of the patterned wallpaper and velvet hangers added a touch of elegance and personalityтАЪ transforming the closet from a purely functional space into a stylish extension of my bedroomтАд The soft lighting and subtle scents created a calming and inviting atmosphereтАд It wasnтАЩt just about organization; it was about creating a space that reflected my personal style and brought me joyтАд I found myself spending more time in my bedroomтАЪ simply admiring the transformationтАд The project had been challengingтАЪ requiring patienceтАЪ planningтАЪ and a good dose of creativityтАЪ but the result was well worth the effortтАд The sense of accomplishment was immenseтАд More than just a storage solutionтАЪ my closet became a testament to the power of thoughtful design and personal expressionтАд It proved that even the smallest of spaces can be transformed into something beautiful and functional with a little bit of planning and a lot of heartтАд The project taught me the importance of maximizing vertical spaceтАЪ utilizing every nook and crannyтАЪ and most importantlyтАЪ infusing my personal style into every detailтАд ItтАЩs a reminder that even seemingly insignificant spaces can be sources of pride and joy when approached with intention and creativityтАд I now look forward to getting dressed in the morningтАЪ not dreading the chaos that used to greet meтАд My tiny closet transformation was a resounding successтАЪ and I highly recommend tackling your own closet projectтАЪ regardless of size; You might be surprised by the results!
Let me tell youтАЪ my closet situation wasтАж direтАд Picture thisтБЪ a crampedтАЪ barely-there spaceтАЪ overflowing with clothes haphazardly tossed inтАд It wasn’t just disorganized; it felt oppressiveтАд Opening the door was like facing a wardrobe avalancheтАд Clothes spilled onto the floorтАЪ creating a perilous obstacle courseтАд Finding anything specific was a mission akin to searching for a needle in a haystack тАУ only the haystack was made of cashmere sweaters and wrinkled blousesтАд I remember one particularly frustrating morning when I was desperately searching for a specific pair of shoes for an important meetingтАд I spent a good fifteen minutes wrestling with the chaotic jumbleтАЪ eventually finding them crushed under a pile of jeansтАд I was late for the meetingтАЪ frazzled and utterly defeated by my own tiny closetтАд The sheer volume of clothesтАЪ coupled with the lack of any sensible storage systemтАЪ had created a nightmarish scenarioтАд It was a constant source of stressтАЪ a visual reminder of my lack of organizationтАЪ and franklyтАЪ a huge embarrassmentтАд I knew I needed a solutionтАЪ and fastтАд The frustration was palpable; every morning started with a battle against the overflowing messтАЪ a battle I consistently lostтАд This wasn’t just about tidiness; it was about reclaiming control of my space and my morningsтАд It was about creating a functionalтАЪ peaceful sanctuary instead of a chaotic storage unitтАд The transformation wouldn’t be easyтАЪ but I was determined to conquer this tiny closet and emerge victoriousтАд
https://heute-news.com/automotive-news/my-journey-into-car-mechanical-engineering/
Selecting the right black and white palette is crucial for achieving your desired aesthetic. Consider the size of your bathroom; a smaller space might benefit from a predominantly white scheme with black accents to avoid feeling cramped. Conversely‚ a larger bathroom can handle a bolder approach with more extensive black features. Think about the balance you want to strike. A stark‚ high-contrast scheme creates a dramatic and modern feel‚ while a softer approach‚ incorporating shades of gray as a transition between black and white‚ offers a more relaxed and timeless vibe.
With the functional aspects of my closet transformation completeтАЪ I turned my attention to the aestheticsтАд I didn’t want a perfectly organized closet that felt cold and impersonalтАд My style is a mix of bohemian and modernтАЪ so I wanted to incorporate those elements into the designтАд I started by adding a patterned wallpaper to the inside of the closet doorsтАд I chose a subtleтАЪ floral print in muted tones that complemented the overall color scheme of my bedroomтАд It instantly made the space feel more inviting and less like a storage unitтАд NextтАЪ I invested in some pretty velvet hangersтАд These not only looked more stylish than the flimsy wire hangers I had been usingтАЪ but they also helped to keep my clothes wrinkle-freeтАд I found them at a home goods store and they were a surprisingly affordable upgradeтАд To add a touch of whimsyтАЪ I hung a smallтАЪ decorative mirror on the inside of one of the closet doorsтАд This not only served a practical purpose but also helped to brighten up the spaceтАд I also added a smallтАЪ woven basket to store extra scarves and glovesтАд The natural texture of the basket added warmth and visual interestтАд In addition to the larger organizational elementsтАЪ I incorporated small details to reflect my personal styleтАд I used decorative labels for my storage containersтАЪ adding a touch of eleganceтАд I also added a small string of fairy lights inside the closet which gave it a magical ambianceтАд The soft glow was perfect for evening use and added a touch of sparkleтАд I even found some pretty drawer pulls to replace the basic ones that came with my stackable drawersтАд These small details made a big difference in the overall look and feel of the closetтАд The final touch was a smallтАЪ scented sachet placed amongst my clothes to keep everything smelling fresh and pleasantтАд This was a simple yet effective way to add a personal touchтАд The result was a closet that was both functional and aesthetically pleasingтАЪ a space that reflected my style and made me happy to open the doorsтАд
Before I even thought about buying shelves or hanging rodsтАЪ I knew I needed a proper planтАд Armed with a measuring tape and a notebookтАЪ I meticulously documented every inch of my tiny closetтАд I measured the widthтАЪ the depthтАЪ and the heightтАЪ noting any obstructions like pipes or electrical outletsтАд This detailed assessment was crucialтАд I also carefully inventoried my belongingsтАд I pulled everything out тАУ every shirtтАЪ every pair of pantsтАЪ every scarf and shoe тАУ and sorted it into categoriesтБЪ topsтАЪ bottomsтАЪ dressesтАЪ shoesтАЪ accessoriesтАЪ etcтАд This helped me visualize the amount of space I needed for each categoryтАд Then came the fun partтБЪ sketching! I drew several different layouts in my notebookтАЪ experimenting with different shelving configurations and hanging rod placementsтАд I considered the placement of my longer dresses and coatsтАЪ and how to best utilize the vertical spaceтАд I also thought about the flow of the closet тАУ how easily I could access different itemsтАд I even considered the type of storage solutions I might need тАУ baskets for smaller itemsтАЪ drawers for folded clothesтАЪ etcтАд InitiallyтАЪ I considered custom built-insтАЪ but the cost was prohibitiveтАд ThereforeтАЪ I opted for a more budget-friendly approachтАЪ focusing on maximizing the space with readily available shelving and storage solutionsтАд My planning phase took a few eveningsтАЪ but it was worth itтАд Having a clear plan before I started shopping prevented impulsive purchases and ensured I bought the right amount of storage to perfectly fit my spaceтАд It was surprisingly satisfying to see my ideas take shape on paperтАЪ and I felt a sense of accomplishment even before IтАЩd started the actual transformationтАд
Maximizing Vertical SpaceтБЪ Shelving and Hanging Solutions
Lighting plays a crucial role in showcasing the beauty of a black and white bathroom. Careful consideration of lighting schemes can dramatically impact the overall mood and atmosphere of the space‚ transforming it from drab to dazzling. Avoid harsh‚ overhead lighting which can create stark shadows and wash out the details of your design choices. Instead‚ opt for a layered approach that combines ambient‚ task‚ and accent lighting to create a warm and inviting ambiance.
car engineer salary
https://generic51.ru/sialis-tadalafil/djenerik-sialis-60-mg
origami box with lid origami flower 3ds max pop up origami flower card origami crane how to video origami art
купить официальный диплом о высшем образовании купить официальный диплом о высшем образовании .
origami flower craft origami 010 – https://twitter.com/origamilesson
продолжить https://zelenka.guru/forums/88/
When it concerns relaxation and restoration in the hectic city of New york city, couple of experiences match the extravagance of an elite bodyrub. NYC, known as a international center for luxury and class, provides several of the finest bodyrub services made to dissolve stress and anxiety, revitalize your senses, and recover balance to your mind and body. Whether you’re a active professional, a visitor to the city, or just someone looking for a high-end indulging experience, elite bodyrub services in New York City are your portal to unparalleled relaxation.
This comprehensive guide will discover the distinctive attributes of premium bodyrub solutions, supply skilled guidance on selecting top-notch experts, and give insider expertise to guarantee a luxurious and extraordinary experience.
We have a showroom in Brooklyn. Specialists Mackenzie – nuro message video
Experimenting with Different Layouts
My kitchen renovation started with a daunting taskтБЪ finding the perfect free online design tool. I initially felt overwhelmed by the sheer number of options available. I spent several days researchingтАЪ reading reviewsтАЪ and comparing features. Some platforms boasted impressive 3D rendering capabilitiesтАЪ but lacked the intuitive interface I craved. Others offered simpler designs but lacked customization options. I needed a balance of visual appeal and user-friendliness. After much deliberationтАЪ I settled on “KitchenCraft ProтАЪ” a platform recommended by a friendтАЪ Amelia. KitchenCraft Pro offered a user-friendly drag-and-drop interfaceтАЪ a wide selection of appliances and cabinetry stylesтАЪ and surprisingly detailed customization options. The initial learning curve was minimal; I was able to navigate the software and start designing within minutes. I particularly appreciated the ability to import my own images and textures to personalize the designтАЪ ensuring it accurately reflected my unique style and preferences. The free version provided ample features for my needsтАЪ although I did note that some advanced featuresтАЪ like photorealistic renderingтАЪ were reserved for paid subscriptions. HoweverтАЪ for my purposesтАЪ the free tools were more than sufficient. The decision to use KitchenCraft Pro proved to be a great oneтАЪ setting the stage for a successful and enjoyable design process. I highly recommend thoroughly researching and comparing different free online kitchen design tools before making your choiceтАЪ to ensure you find one that best suits your specific needs and skill level. Remember to look for intuitive interfacesтАЪ a wide range of optionsтАЪ and helpful tutorials or support resources.
https://instepnews.com/automotive-news/1989-camaro-wheels-and-tires/
Choosing the Right Online Tool
I embarked on a thrilling kitchen redesignтАЪ leveraging free online tools. My goal? A stunningтАЪ functional space without breaking the bank. I spent hours exploring various platformsтАЪ comparing features and ease of use. The process felt surprisingly intuitive. I was amazed by how quickly I could visualize different layouts and experiment with various appliances and cabinetry. It was a fun and empowering experienceтАЪ proving that achieving a dream kitchen doesn’t require a hefty budget!
After inputting my measurements and preferencesтАЪ I dove headfirst into the exciting world of layout experimentation. KitchenCraft Pro offered a plethora of optionsтАЪ from the classic galley style to the more spacious L-shape and U-shape designs. I started by exploring the galley layoutтАЪ digitally dragging and dropping cabinets and appliances to visualize the workflow. I quickly realized it wouldn’t suit my needs тАУ the limited counter space was a major drawback. NextтАЪ I experimented with an L-shape configurationтАЪ strategically placing the sinkтАЪ stoveтАЪ and refrigerator to form an efficient work triangle. This felt more promising. I meticulously adjusted the placement of islands and peninsulasтАЪ carefully considering their impact on traffic flow and overall spaciousness. The software’s intuitive drag-and-drop functionality made this process remarkably easy and enjoyable. I even tried a daring U-shaped designтАЪ envisioning a grandтАЪ chef-like workspace. While initially appealingтАЪ I found it slightly cramped for my needs. The software allowed me to easily switch between different layoutsтАЪ instantly visualizing the impact of each change. I spent hours tweaking the arrangement of cabinetsтАЪ appliancesтАЪ and workspacesтАЪ constantly evaluating the practicality and aesthetic appeal of each configuration; I played around with different cabinet depths and widthsтАЪ experimenting with the placement of pantry units and maximizing storage space. I even considered adding a breakfast bar to one of the layoutsтАЪ envisioning family gatherings around it. The ability to instantly see the results of my adjustments was invaluableтАЪ allowing me to make informed decisions based on both functionality and personal preference. It was a truly iterative processтАЪ refining and perfecting the design until I found the perfect balance between form and function. Through this experimentationтАЪ I discovered that the L-shape layoutтАЪ with a cleverly positioned islandтАЪ provided the optimal blend of efficiency and spaciousness for my kitchen.
My kitchen renovation started with a daunting taskтБЪ finding the perfect free online design tool. I initially felt overwhelmed by the sheer number of options available. I spent several days researchingтАЪ reading reviewsтАЪ and comparing features. Some platforms boasted impressive 3D rendering capabilitiesтАЪ but lacked the intuitive interface I craved. Others offered simpler designs but lacked customization options. I needed a balance of visual appeal and user-friendliness. After much deliberationтАЪ I settled on “KitchenCraft ProтАЪ” a platform recommended by a friendтАЪ Amelia. KitchenCraft Pro offered a user-friendly drag-and-drop interfaceтАЪ a wide selection of appliances and cabinetry stylesтАЪ and surprisingly detailed customization options. The initial learning curve was minimal; I was able to navigate the software and start designing within minutes. I particularly appreciated the ability to import my own images and textures to personalize the designтАЪ ensuring it accurately reflected my unique style and preferences. The free version provided ample features for my needsтАЪ although I did note that some advanced featuresтАЪ like photorealistic renderingтАЪ were reserved for paid subscriptions. HoweverтАЪ for my purposesтАЪ the free tools were more than sufficient. The decision to use KitchenCraft Pro proved to be a great oneтАЪ setting the stage for a successful and enjoyable design process. I highly recommend thoroughly researching and comparing different free online kitchen design tools before making your choiceтАЪ to ensure you find one that best suits your specific needs and skill level. Remember to look for intuitive interfacesтАЪ a wide range of optionsтАЪ and helpful tutorials or support resources.
Refining the Design and Adding Details
вывод из запоя на дому ростов круглосуточно вывод из запоя на дому ростов круглосуточно .
вывод из запоя на дому в ростове на дону вывод из запоя на дому в ростове на дону .
рейтинг процессоров intel http://www.topcpu.ru/ .
origami 5 min origami crane tattoo meaning origami flower lily video origami restaurant origami crafts origami 2010
origami box kusudama origami 5 intersecting tetrahedra origami crane kusudama
All materials and special snacks are provided.
Авторитетный журнал для современных женщин о трендах моды, красоте, заботе о себе, путешествиях, культуре и интерьерных решениях от экспертов девушки по вызову калуга
https://richexchanger.com/
Как официально приобрести аттестат 11 класса с минимальными затратами времени
Авторитетный журнал для современных женщин о трендах моды, красоте, заботе о себе, путешествиях, культуре и интерьерных решениях от экспертов вызвать индивидуалок калуга
canadian pharmacy mall
Invictus Gaming is a legendary invictus-gaming-dota2 com esports organization known for its remarkable victories in Dota 2, including the championship at The International 2018.
Latest news league-of-legends-esports.com/ analytics and forecasts in the world of League of Legends eSports. Stay up to date with all the main events of the professional scene!
Official website t1-league-of-legends.com/ of the legendary eSports team T1 for League of Legends. Latest news, match results, player statistics and LOL Betting.
Latest news and analytics on League of Legends lol-news.com matches, tournaments, betting. Stay up to date with the latest eSports events!
Official website of the T1 https://t1-lol.com League of Legends eSports team. Latest news, matches, statistics, tournaments and predictions on LoL Betting.
Official website of the award-winning samsung galaxy league of legends com Samsung Galaxy League of Legends team. Latest news, matches, statistics, player profiles and bets on games.
Official website of the eSports organization g2-esports-league-of-legends.com
Fnatic is a legendary League fnatic-league-of-legends.com/ of Legends eSports team. Our website has all the latest news, matches, player statistics and game predictions.
Official Team Liquid website https://team-liquid-league-of-legends.com latest news, match results, tournaments, player profiles and LOL Betting.
Gen G is one of the strongest eSports teams gen-g-league-of-legends.com/ in League of Legends. Our website has the latest news, matches, statistics and LOL Betting.
Диплом пту купить официально с упрощенным обучением в Москве
Factors Affecting Drainage NeedsвЃљ Hard Water & Usage
Clever Storage SolutionsтБЪ Utilizing Every Nook and Cranny
https://heute-news.com/automotive-news/finding-the-right-used-car-transmission-in-columbus/
Ambient lighting provides overall illumination for the room. Recessed lighting or a stylish chandelier can provide a soft‚ diffused glow. Task lighting is essential for practical purposes‚ such as applying makeup or shaving. Consider installing vanity lights with adjustable brightness for optimal illumination. Accent lighting highlights specific features‚ such as a beautiful piece of artwork or a unique textural element. Strategically placed spotlights or wall sconces can draw attention to these focal points. Consider the color temperature of your light bulbs; warmer tones (2700K-3000K) create a cozy and relaxing atmosphere‚ while cooler tones (5000K-6500K) provide a brighter‚ more invigorating feel. Experiment with different lighting options to find the perfect balance that complements your bathroom’s style and enhances its aesthetic appeal. Remember that natural light is a valuable asset‚ so maximize its impact by keeping windows unobstructed and using sheer curtains to diffuse harsh sunlight.
Factors Affecting Drainage NeedsвЃљ Hard Water & Usage
Incorporating Texture and Pattern
For instance‚ you could use a deep charcoal gray grout with white subway tiles for a sophisticated look‚ or opt for glossy black fixtures against crisp white walls for a sleek‚ contemporary feel. If you prefer a vintage aesthetic‚ consider pairing black and white patterned tiles with white cabinetry and black accents. Don’t be afraid to experiment with different shades of white – from bright‚ clean whites to warmer‚ creamier tones – to find the perfect complement to your chosen black. Remember‚ the key is to create a cohesive and balanced look that reflects your personal style and complements the overall design of your bathroom. Explore online resources for inspiration; many websites and magazines showcase stunning black and white bathroom palettes. Pay attention to how different shades of black and white interact with each other and the other elements in the bathroom design.
Before I even thought about buying shelves or hanging rodsтАЪ I knew I needed a proper planтАд Armed with a measuring tape and a notebookтАЪ I meticulously documented every inch of my tiny closetтАд I measured the widthтАЪ the depthтАЪ and the heightтАЪ noting any obstructions like pipes or electrical outletsтАд This detailed assessment was crucialтАд I also carefully inventoried my belongingsтАд I pulled everything out тАУ every shirtтАЪ every pair of pantsтАЪ every scarf and shoe тАУ and sorted it into categoriesтБЪ topsтАЪ bottomsтАЪ dressesтАЪ shoesтАЪ accessoriesтАЪ etcтАд This helped me visualize the amount of space I needed for each categoryтАд Then came the fun partтБЪ sketching! I drew several different layouts in my notebookтАЪ experimenting with different shelving configurations and hanging rod placementsтАд I considered the placement of my longer dresses and coatsтАЪ and how to best utilize the vertical spaceтАд I also thought about the flow of the closet тАУ how easily I could access different itemsтАд I even considered the type of storage solutions I might need тАУ baskets for smaller itemsтАЪ drawers for folded clothesтАЪ etcтАд InitiallyтАЪ I considered custom built-insтАЪ but the cost was prohibitiveтАд ThereforeтАЪ I opted for a more budget-friendly approachтАЪ focusing on maximizing the space with readily available shelving and storage solutionsтАд My planning phase took a few eveningsтАЪ but it was worth itтАд Having a clear plan before I started shopping prevented impulsive purchases and ensured I bought the right amount of storage to perfectly fit my spaceтАд It was surprisingly satisfying to see my ideas take shape on paperтАЪ and I felt a sense of accomplishment even before IтАЩd started the actual transformationтАд
ncsu engineering career fair
Виниловый пол – это современное напольное покрытие, которое стремительно набирает популярность благодаря своим уникальным свойствам и широким возможностям дизайна https://gp.by/novosti/kaleidoscope/news292747.html
Виниловый пол – это современное напольное покрытие, которое стремительно набирает популярность благодаря своим уникальным свойствам и широким возможностям дизайна https://gp.by/novosti/kaleidoscope/news292747.html
security camera software windows motion detector software
Виниловый пол – это современное напольное покрытие, которое стремительно набирает популярность благодаря своим уникальным свойствам и широким возможностям дизайна https://gp.by/novosti/kaleidoscope/news292747.html
Натуральные молочные продукты https://gastrodachavselug2.ru свежесть и качество с заботой о вашем здоровье! Широкий выбор: молоко, творог, сметана, сыры. Только натуральные ингредиенты, без консервантов и добавок.
Some building tasks ask for a maximum or minimal variety of results to be organized, for example a recreation with the maximum attainable variety of consecutive discovered checks, or a position by which all sixteen pieces management the minimum number of squares.
Подробнее здесь https://lzt.market/
I embarked on a thrilling kitchen redesignтАЪ leveraging free online tools. My goal? A stunningтАЪ functional space without breaking the bank. I spent hours exploring various platformsтАЪ comparing features and ease of use. The process felt surprisingly intuitive. I was amazed by how quickly I could visualize different layouts and experiment with various appliances and cabinetry. It was a fun and empowering experienceтАЪ proving that achieving a dream kitchen doesn’t require a hefty budget!
Experimenting with Different Layouts
https://instepnews.com/finance/choosing-the-best-laptop-for-stock-trading/
My Free Online Kitchen Design Journey
I embarked on a thrilling kitchen redesignтАЪ leveraging free online tools. My goal? A stunningтАЪ functional space without breaking the bank. I spent hours exploring various platformsтАЪ comparing features and ease of use. The process felt surprisingly intuitive. I was amazed by how quickly I could visualize different layouts and experiment with various appliances and cabinetry. It was a fun and empowering experienceтАЪ proving that achieving a dream kitchen doesn’t require a hefty budget!
Inputting My Measurements and Preferences
After inputting my measurements and preferencesтАЪ I dove headfirst into the exciting world of layout experimentation. KitchenCraft Pro offered a plethora of optionsтАЪ from the classic galley style to the more spacious L-shape and U-shape designs. I started by exploring the galley layoutтАЪ digitally dragging and dropping cabinets and appliances to visualize the workflow. I quickly realized it wouldn’t suit my needs тАУ the limited counter space was a major drawback. NextтАЪ I experimented with an L-shape configurationтАЪ strategically placing the sinkтАЪ stoveтАЪ and refrigerator to form an efficient work triangle. This felt more promising. I meticulously adjusted the placement of islands and peninsulasтАЪ carefully considering their impact on traffic flow and overall spaciousness. The software’s intuitive drag-and-drop functionality made this process remarkably easy and enjoyable. I even tried a daring U-shaped designтАЪ envisioning a grandтАЪ chef-like workspace. While initially appealingтАЪ I found it slightly cramped for my needs. The software allowed me to easily switch between different layoutsтАЪ instantly visualizing the impact of each change. I spent hours tweaking the arrangement of cabinetsтАЪ appliancesтАЪ and workspacesтАЪ constantly evaluating the practicality and aesthetic appeal of each configuration; I played around with different cabinet depths and widthsтАЪ experimenting with the placement of pantry units and maximizing storage space. I even considered adding a breakfast bar to one of the layoutsтАЪ envisioning family gatherings around it. The ability to instantly see the results of my adjustments was invaluableтАЪ allowing me to make informed decisions based on both functionality and personal preference. It was a truly iterative processтАЪ refining and perfecting the design until I found the perfect balance between form and function. Through this experimentationтАЪ I discovered that the L-shape layoutтАЪ with a cleverly positioned islandтАЪ provided the optimal blend of efficiency and spaciousness for my kitchen.
Choosing the Right Online Tool
kush shop in prague https://online24.site
buy marijuana in prague hemp delivery in prague
hemp shop in prague cbd weed in prague
marijuana for sale in prague. hemp shop in prague
cali weed delivery in prague https://shop-by.site
Thanks a lot. I value it.
Here is my blog post :: https://www.youtube.com/
marijuana in prague kush for sale in prague
cannabis shop in prague https://shopraha.site
thc joint shop in prague thc joint for sale in prague
buy hash in prague https://pragueshop.site
buy weed in prague 420 store in prague
кликните сюда https://zelenka.guru/articles/
https://telegra.ph/dnevnik-pitaniya-rasschitat-09-26
узнать больше https://lzt.market/
canadian pharmacy
Canadapharmacy http://supremesuppliers.net/ Awc canadian pharmacy
timoptic ocudose manufacturer coupon
Диплом пту купить официально с упрощенным обучением в Москве
Cialis Canadian Pharmacy Cheap viagra overnight Canadian pharmacy sky pharmacy online Northwest pharmacy canada
Интеграция мультимедийных систем для бизнеса: полный цикл услуг
мультимедийная интеграция http://multimediynaya-integratsiya1.ru .
Бесплатное программное обеспечение для видеонаблюдения для использования на персональных компьютерах, которое поддерживает все типы IP камер. Программа представляет собой комплексное решение, включающее в себя как систему управления видео (VMS), так и систему централизованного мониторинга (CMS), что позволяет не только записывать и просматривать rtsp видеопотоки, но и управлять большим количеством IP камер с единой платформы. Одной из ключевых особенностей программы является интегрированная видеоаналитика на основе искусственного интеллекта. Эта аналитика позволяет обнаруживать объекты в кадре, распознавать автомобильные номера и лица, а также выявлять признаки дыма и огня таймлапс с камеры видеонаблюдения
Бесплатное программное обеспечение для видеонаблюдения для использования на персональных компьютерах, которое поддерживает все типы IP камер. Программа представляет собой комплексное решение, включающее в себя как систему управления видео (VMS), так и систему централизованного мониторинга (CMS), что позволяет не только записывать и просматривать rtsp видеопотоки, но и управлять большим количеством IP камер с единой платформы. Одной из ключевых особенностей программы является интегрированная видеоаналитика на основе искусственного интеллекта. Эта аналитика позволяет обнаруживать объекты в кадре, распознавать автомобильные номера и лица, а также выявлять признаки дыма и огня программа для записи с ip камер
Здесь вы найдете публикации и предложения о сдаче и продаже жилья с видео контентом коммерческой, жилой, промышленной недвижимости, гаражи, участки во всех городах России бесплатная доска объявлений
Здесь вы найдете публикации и предложения о сдаче и продаже жилья с видео контентом коммерческой, жилой, промышленной недвижимости, гаражи, участки во всех городах России бесплатная доска объявлений
Бесплатное программное обеспечение для видеонаблюдения для использования на персональных компьютерах, которое поддерживает все типы IP камер. Программа представляет собой комплексное решение, включающее в себя как систему управления видео (VMS), так и систему централизованного мониторинга (CMS), что позволяет не только записывать и просматривать rtsp видеопотоки, но и управлять большим количеством IP камер с единой платформы. Одной из ключевых особенностей программы является интегрированная видеоаналитика на основе искусственного интеллекта. Эта аналитика позволяет обнаруживать объекты в кадре, распознавать автомобильные номера и лица, а также выявлять признаки дыма и огня облачный сервис для видеонаблюдения
Biography of footballer Kylian Mbappe kylian-mbappe personal life, rumors of an affair with Alicia Aylis and Ines Rau. Career, statistics and salary at Paris Saint-Germain, victory at the World Cup and other achievements of the striker.
Biography of football player Neymar https://neymar-bd.com personal life, relationships and rumors of romances with Katya Safarova, Natalia Barulich, the birth of a son and Bruna’s last girlfriend, the birth of daughters.
Biography of Belgian footballer kevin-de-bruyne-bd.com Kevin De Bruyne (Kevin De Bruyne): personal life, relationship with his wife, conflict with Thibaut Courtois over his girlfriend Caroline.
Biography of football player Jude Bellingham jude-bellingham-bd com personal life, relationship with girlfriend Laura. Player statistics in the Real Madrid team, matches for the England national team with Harry Kane, the athlete’s salary, conflict with Mason Greenwood.
Biography of football player Luis Alberto Suarez http://luis-suarez-bd.com personal life, daughter, wife, children, height. Leaving the club Atletico Madrid, career in Barcelona and Liverpool, goal statistics.
Здесь вы найдете публикации и предложения о сдаче и продаже жилья с видео контентом коммерческой, жилой, промышленной недвижимости, гаражи, участки во всех городах России бесплатная доска объявлений
вывод из запоя круглосуточно ростов на дону вывод из запоя круглосуточно ростов на дону .
online stamp maker free online stamp maker free .
диплом о среднем образовании купить
Оснащение конференц залов: комплексное оборудование для бизнес-решений
конференц зал оборудование оснащение проект http://www.oborudovaniye-konferents-zala1.ru .
Мультимедийное оснащение помещений: эффективные решения для вашего проекта
мультимедийное оснащение мультимедийное оснащение .
cialis price Cialis Canadian Pharmacy Predisone
Try the free demo game Crazy Monkey http://crazy-monkey.com.az (Igrosoft) and read our exclusive review!
En iyi sekilde meram t?p randevu sisteminin gelistirdik. TL casino giris ile birlikte daha iyi sonuclar ald?k. Ve halk cok memnun vadeli tl hesabı nedir
All of our shelves are handcrafted and make in Deer Park, NY. The process of making your shelf starts from the moment you place an order You can create your own shelf Shop now modern floating kitchen shelves
вывод из запоя вывод из запоя .
прокапаться от алкоголя цены прокапаться от алкоголя цены .
прокапаться от алкоголя цены прокапаться от алкоголя цены .
Discover Space XY space-xy.com.az Take advantage of bonuses and free play to increase your chances of winning!
Hot Fruits 100 Slot https://hot-fruits-100.com.az Review by Amatic Industries – Play Hot Fruits 100 demo for free or real money. Bonuses and best casinos for September 2024!
JetX is a unique simulation game jetx from SmartSoft Gaming. Players fly a virtual plane and collect their winnings safely.
Learn everything about blackjack https://blackjack.com.az rules, types of bets, features of the online game and answers to popular questions.
All of our shelves are handcrafted and make in Deer Park, NY. The process of making your shelf starts from the moment you place an order You can create your own shelf Shop now hand wall shelf
En iyi sekilde meram t?p randevu sisteminin gelistirdik. TL casino giris ile birlikte daha iyi sonuclar ald?k. Ve halk cok memnun giyim mağaza isimleri
All of our shelves are handcrafted and make in Deer Park, NY. The process of making your shelf starts from the moment you place an order You can create your own shelf Shop now custom made wall shelves
En iyi sekilde meram t?p randevu sisteminin gelistirdik. TL casino giris ile birlikte daha iyi sonuclar ald?k. Ve halk cok memnun msü nedir
free viagra without prescription
Bayer 04 Football Club bayer 04 com az composition, statistics, best Bayer players
RB Leipzig http://rb-leipzig.com.az team history, club titles, top scorers and players in team history
Current Heidenheim https://fc-heidenheim.com.az squad with player stats and market value, match schedule, club news and rumours
Phil Foden phil-foden-az.com is a talented midfielder for Manchester City. Find out about his biography, statistics and latest news.
Declan Rice (Arsenal) https://declan-rice-az.com midfielder, 25 years old. Check out his biography, statistics, goals and latest 2024 news.
Much of this was owed to a now very broad range of models and prices.
best viagra without prescription
usa pharmacy 24 hour drug store Perlutex
Over the previous decade, the Commonwealth Fund has studied the health care methods of the highest industrialized nations (like Australia, France, Canada, Sweden and the United Kingdom, to call a few).
Experimenting with Different Layouts
Refining the Design and Adding Details
https://instepnews.com/automotive-news/my-experience-with-ag-tire-and-wheel-recapping/
Choosing the Right Online Tool
My Free Online Kitchen Design Journey
With a satisfying L-shaped layout as my baseтАЪ I delved into the finer detailsтАЪ transforming my digital sketch into a truly personalized design. I meticulously selected cabinet styles from the extensive library offered by the softwareтАЪ opting for sleekтАЪ modern shaker-style cabinets in a warmтАЪ honey-toned oak finish. The program allowed me to visualize these choices in real-timeтАЪ rotating the cabinets to ensure they complemented the overall aesthetic. NextтАЪ I chose countertops. I initially considered graniteтАЪ but the virtual rendering showed it clashing slightly with the cabinet color. I then experimented with quartzтАЪ settling on a beautifulтАЪ light-grey option that beautifully contrasted with the oak. The software’s realistic rendering capabilities were invaluable here. I spent a considerable amount of time tweaking the backsplashтАЪ finally settling on a subway tile pattern in a soft whiteтАЪ which provided a clean and classic look. Adding lighting was another key step. I strategically placed recessed lighting above the countertops and pendant lights above the islandтАЪ creating a warm and inviting ambiance. I even experimented with different flooring optionsтАЪ virtually laying down various types of tile and hardwood to see how they interacted with the rest of the design. I was particularly pleased with a light-colored oak wood floor that tied in seamlessly with the cabinetry. Beyond the major elementsтАЪ I focused on the smaller details. I carefully selected hardwareтАЪ opting for brushed nickel pulls and knobs that added a touch of sophistication. I also integrated various appliancesтАЪ choosing models based on their size and aestheticsтАЪ ensuring they fit harmoniously within the design. The software allowed me to fine-tune every aspectтАЪ from the placement of outlets to the positioning of spice racksтАЪ ensuring a highly functional and visually appealing kitchen. It was a truly rewarding processтАЪ seeing my initial concept evolve into a cohesive and detailed designтАЪ ready to be shared and potentially implemented in the real world. The level of customization was impressiveтАЪ allowing me to create a space that was uniquely mine.
Experimenting with Different Layouts
Exporting and Sharing My Design
Оригинальные детали от проверенных производителей обеспечивают максимальную точность и стабильность работы. Кроме того, они обычно проходят строгий контроль качества, что снижает вероятность неисправностей http://lnx.hotelresidencevillateresaischia.com/casamicciola/index.php?option=com_k2&view=itemlist&task=user&id=467865
Оригинальные детали от проверенных производителей обеспечивают максимальную точность и стабильность работы. Кроме того, они обычно проходят строгий контроль качества, что снижает вероятность неисправностей http://bryners.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?f=16&t=90772
Оригинальные детали от проверенных производителей обеспечивают максимальную точность и стабильность работы. Кроме того, они обычно проходят строгий контроль качества, что снижает вероятность неисправностей http://wiki.planetenparty.at/index.php?title=%20%D0%A2%D0%B5%D1%85%D0%BD%D0%B8%D1%87%D0%B5%D1%81%D0%BA%D0%B8%D0%B5%20%D1%85%D0%B0%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%BA%D1%82%D0%B5%D1%80%D0%B8%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B8%D0%BA%D0%B8%20%D0%BA%D0%BB%D1%8E%D1%87%D0%B5%D0%B2%D1%8B%D1%85%20%D0%B7%D0%B0%D0%BF%D1%87%D0%B0%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B5%D0%B9%20%D0%B4%D0%BB%D1%8F%20%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B0%D0%BD%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%B2
Zico is a legendary Brazilian footballer zico.com.az/ known as “White Pele”. His talent, technique and passion for the game made him an icon of Brazilian football, and his contributions to the sport continue to inspire new generations.
George Best http://george-best.com.az is a brilliant footballer and a shining symbol of the 1960s, known for his talent and turbulent life. He left an indelible mark on football by combining success on the pitch with the tragedy of personal struggle.
Rudy Gobert https://rudy-gobert-az.com is a French center and one of the best defenders in the NBA, nicknamed “The French Tower.” A three-time Defensive Player of the Year, he inspires with his skills and commitment to excellence.
Nikola Jokic nikola jokic az com is a Serbian basketball player, NBA star, and leader of the Denver Nuggets. Known for his unique style of play, court vision, and leadership, he has become a role model for a new generation of centers.
Luka Doncic lukadoncic is a Slovenian basketball player, the leader of the Dallas Mavericks team and one of the main stars of the NBA. His unique playing style, records and influence have made him a symbol of European success in world basketball.
Le code promo 1xBet pour l’annee 2025 vous offre un Bonus VIP a 100 % allant jusqu’a 130 € pour les paris sportifs, ou un bonus exceptionnel de 1950 € accompagne de 150 tours gratuits. Grace a ce code exclusif, vous pouvez beneficier d’un bonus ameliore des votre inscription sur le site officiel 1xBet.com. Decouvrons ensemble les details du programme de bonus propose par ce bookmaker. Quels sont les codes promo disponibles ? Quels types de bonus sont accessibles actuellement pour les joueurs ayant choisi cette plateforme pour leurs paris sportifs ?
Code Promo 1xBet
https://cour-interieure.fr/content/pgs/code_promo_164.html
Le code promo 1xBet 2025 vous permet de beneficier d’une offre VIP exclusive de 100 % jusqu’a 130 € sur les paris sportifs ou d’un bonus impressionnant de 1950 € accompagne de 150 tours gratuits. Ce bonus de bienvenue double votre depot initial en augmentant votre mise de 100 %. Dans cet article, nous detaillons le processus pour vous inscrire correctement sur 1xBet, maximiser votre bonus, et jouer gratuitement grace au bookmaker. Utilisez un code bonus special pour debloquer l’ensemble des promotions disponibles et obtenir de l’argent gratuit.
Оснащение переговорной комнаты: мультимедиа, звук, автоматизация
оборудование переговорных комнат https://www.osnaschenie-peregovornoy-komnaty1.ru/ .
Оснащение ситуационного центра: инновации для управления и принятия решений
оснащение ситуационных центров https://osnascheniye-situatsionnogo-tsentra1.ru/ .
ли купить диплом техникума 2orik-diploms.ru .
where is nuru massage
Discover the Comprehensive Manual on U
However just what is Uru Massage, and exactly how can it transform your life? Allow’s check out whatever you require to find out about this distinct therapy, from its origins to its methods and benefits.
What Is Uru Massage?
Historic History
Uru Massage originates from old healing techniques that highlight balance and consistency within the body. Its roots can be traced to native cultures that valued the interconnectedness of mind, body, and spirit. Unlike modern therapeutic approaches, Uru Massage integrates physical manipulation with spiritual mindfulness.
Core Principles and One-of-a-kind Functions
The core concept of Uru Massage therapy is the restoration of power circulation with certain methods. It blends deep tissue work with balanced motions and frequently integrates natural oils and aromatherapy to improve the experience.
Benefits of Uru Massage Therapy
Physical Health And Wellness Advantages
Uru Massage therapy is outstanding for relieving muscular tissue tension, improving blood circulation, and advertising far better stance. It can likewise help with persistent discomfort, especially in the back, shoulders, and neck.
Mental and Emotional Health
This massage therapy method is renowned for minimizing stress and anxiety and anxiousness. By stimulating pressure factors, it urges the launch of endorphins, leaving you really feeling uplifted and serene.
Spiritual Positioning
For those seeking spiritual wellness, Uru Massage offers a extensive feeling of balance. The practice incorporates mindfulness, allowing clients to reconnect with their psyches.
Just How Uru Massage Varies from Various Other Massage Therapy Techniques
Comparison with Swedish Massage
While Swedish massage therapy focuses on long, sweeping strokes to loosen up muscular tissues, Uru Massage therapy goes deeper, targeting power factors for long lasting alleviation.
Distinction from Deep Cells Massage
Unlike deep cells massage therapy, which usually triggers pain, Uru Massage makes use of gentler strategies to achieve comparable advantages without the discomfort.
Unique Cultural Facets
Uru Massage therapy stands apart for its integration of cultural routines, making the experience both therapeutic and spiritually enhancing.
Узнать больше https://zelenka.guru/forums/585/
диплом вуза купить
In a kitchen, the options could be anything from resilient rubber flooring like you might find in busy restaurants to rustic terra-cotta tiles like you might find in Mediterranean homes.
My kitchen renovation started with a daunting taskтБЪ finding the perfect free online design tool. I initially felt overwhelmed by the sheer number of options available. I spent several days researchingтАЪ reading reviewsтАЪ and comparing features. Some platforms boasted impressive 3D rendering capabilitiesтАЪ but lacked the intuitive interface I craved. Others offered simpler designs but lacked customization options. I needed a balance of visual appeal and user-friendliness. After much deliberationтАЪ I settled on “KitchenCraft ProтАЪ” a platform recommended by a friendтАЪ Amelia. KitchenCraft Pro offered a user-friendly drag-and-drop interfaceтАЪ a wide selection of appliances and cabinetry stylesтАЪ and surprisingly detailed customization options. The initial learning curve was minimal; I was able to navigate the software and start designing within minutes. I particularly appreciated the ability to import my own images and textures to personalize the designтАЪ ensuring it accurately reflected my unique style and preferences. The free version provided ample features for my needsтАЪ although I did note that some advanced featuresтАЪ like photorealistic renderingтАЪ were reserved for paid subscriptions. HoweverтАЪ for my purposesтАЪ the free tools were more than sufficient. The decision to use KitchenCraft Pro proved to be a great oneтАЪ setting the stage for a successful and enjoyable design process. I highly recommend thoroughly researching and comparing different free online kitchen design tools before making your choiceтАЪ to ensure you find one that best suits your specific needs and skill level. Remember to look for intuitive interfacesтАЪ a wide range of optionsтАЪ and helpful tutorials or support resources.
Choosing the Right Online Tool
https://instepnews.com/automotive-news/my-1997-lincoln-town-car-cartier-edition-a-classic-car-review/
After inputting my measurements and preferencesтАЪ I dove headfirst into the exciting world of layout experimentation. KitchenCraft Pro offered a plethora of optionsтАЪ from the classic galley style to the more spacious L-shape and U-shape designs. I started by exploring the galley layoutтАЪ digitally dragging and dropping cabinets and appliances to visualize the workflow. I quickly realized it wouldn’t suit my needs тАУ the limited counter space was a major drawback. NextтАЪ I experimented with an L-shape configurationтАЪ strategically placing the sinkтАЪ stoveтАЪ and refrigerator to form an efficient work triangle. This felt more promising. I meticulously adjusted the placement of islands and peninsulasтАЪ carefully considering their impact on traffic flow and overall spaciousness. The software’s intuitive drag-and-drop functionality made this process remarkably easy and enjoyable. I even tried a daring U-shaped designтАЪ envisioning a grandтАЪ chef-like workspace. While initially appealingтАЪ I found it slightly cramped for my needs. The software allowed me to easily switch between different layoutsтАЪ instantly visualizing the impact of each change. I spent hours tweaking the arrangement of cabinetsтАЪ appliancesтАЪ and workspacesтАЪ constantly evaluating the practicality and aesthetic appeal of each configuration; I played around with different cabinet depths and widthsтАЪ experimenting with the placement of pantry units and maximizing storage space. I even considered adding a breakfast bar to one of the layoutsтАЪ envisioning family gatherings around it. The ability to instantly see the results of my adjustments was invaluableтАЪ allowing me to make informed decisions based on both functionality and personal preference. It was a truly iterative processтАЪ refining and perfecting the design until I found the perfect balance between form and function. Through this experimentationтАЪ I discovered that the L-shape layoutтАЪ with a cleverly positioned islandтАЪ provided the optimal blend of efficiency and spaciousness for my kitchen.
My Free Online Kitchen Design Journey
My kitchen renovation started with a daunting taskтБЪ finding the perfect free online design tool. I initially felt overwhelmed by the sheer number of options available. I spent several days researchingтАЪ reading reviewsтАЪ and comparing features. Some platforms boasted impressive 3D rendering capabilitiesтАЪ but lacked the intuitive interface I craved. Others offered simpler designs but lacked customization options. I needed a balance of visual appeal and user-friendliness. After much deliberationтАЪ I settled on “KitchenCraft ProтАЪ” a platform recommended by a friendтАЪ Amelia. KitchenCraft Pro offered a user-friendly drag-and-drop interfaceтАЪ a wide selection of appliances and cabinetry stylesтАЪ and surprisingly detailed customization options. The initial learning curve was minimal; I was able to navigate the software and start designing within minutes. I particularly appreciated the ability to import my own images and textures to personalize the designтАЪ ensuring it accurately reflected my unique style and preferences. The free version provided ample features for my needsтАЪ although I did note that some advanced featuresтАЪ like photorealistic renderingтАЪ were reserved for paid subscriptions. HoweverтАЪ for my purposesтАЪ the free tools were more than sufficient. The decision to use KitchenCraft Pro proved to be a great oneтАЪ setting the stage for a successful and enjoyable design process. I highly recommend thoroughly researching and comparing different free online kitchen design tools before making your choiceтАЪ to ensure you find one that best suits your specific needs and skill level. Remember to look for intuitive interfacesтАЪ a wide range of optionsтАЪ and helpful tutorials or support resources.
With my chosen design toolтАЪ KitchenCraft ProтАЪ selectedтАЪ the next step was inputting my kitchen’s precise measurements. This proved surprisingly straightforward. The software guided me through a step-by-step processтАЪ prompting me to enter the length and width of each wallтАЪ the location of windows and doorsтАЪ and the dimensions of existing fixtures like sinks and ovens. I found the interface incredibly intuitiveтАЪ with clear instructions and helpful visual aids. I even appreciated the option to upload a floor plan image to assist with the process. InitiallyтАЪ I struggled a bit with accurately measuring some awkwardly shaped alcovesтАЪ but the platform’s customer support chat was incredibly helpfulтАЪ providing quick and efficient guidance. Once the dimensions were finalizedтАЪ I began to personalize the design. This is where the fun really started! I selected my preferred cabinet stylesтАЪ choosing from a comprehensive library of options ranging from sleek modern designs to more traditionalтАЪ rustic styles. I meticulously chose the colorsтАЪ finishesтАЪ and countertop materialsтАЪ experimenting with different combinations to find the perfect aesthetic. I even incorporated my existing appliancesтАЪ ensuring they fit seamlessly into the new layout. The software allowed for precise placement of every elementтАЪ down to the smallest detail. I spent hours tweaking and refiningтАЪ meticulously considering factors such as workflow efficiency and aesthetic harmony. The process felt like playing a sophisticated digital puzzleтАЪ and the satisfaction of seeing my vision slowly take shape on the screen was incredibly rewarding. I discovered that the software’s flexibility allowed me to explore different layouts and experiment with various design choices without any commitmentтАЪ a feature I truly appreciated. It was a crucial step in ensuring my final design would be both functional and visually appealing.
Experimenting with Different Layouts
Не упустите шанс осуществить задуманное! Мы предлагаем выгодные кредиты с низкими ставками и быстрым одобрением.
– Авто, квартира, бизнес – мы поддержим ваши планы!
Заполните заявку онлайн, и наши специалисты свяжутся с вами.
Действуйте сейчас – ваши мечты ждут!==>
кредитов 24 вход
аттестат о полном среднем образовании купить
Born to a British-Nigerian http://jamal-musiala-az.org father and a German mother of Polish descent, young Jamal explores cultural differences while playing for Germany at the Euros, facing off against Jude Bellingham. Breaking news 2024.
Julius Randle is a versatile NBA forward https://julius-randle-az.com a leader for the Knicks, and an inspiring example of perseverance. His play, leadership, and desire to win make him one of the defining figures in the modern league.
Cristiano Ronaldo biography https://cristiano-ronaldo-az.org personal life, relationships with Irina Shayk and Georgina Rodriguez, children, career at Real and Juventus, records with Portugal at Euro 2020.
Biography of footballer Mohamed Salah http://mohamed-salah-az.org wife Magi Sadiq, children, charity work, book “The Last Pharaoh”. Statistics, salary and awards with Liverpool and Egypt in 2024.
Biography of footballer Luis Alberto Suarez luis-suarez-az.org/ personal life, wife, children, height. Departure from Atletico Madrid, career at Barcelona and Liverpool, goal statistics. Playing for Gremio, moving to Inter Miami, retirement from international duty and the latest news in 2024.
online pharmacy no prescription
Профессиональное оборудование для актового зала: делаем ваше пространство уникальным
световое оборудование для актового зала https://oborudovaniye-aktovyh-zalov1.ru/ .
купить диплом о высшем образовании стоимость prema-diploms.ru .
Польский виртуальный номер – это телефонный номер, который не привязан к физической SIM-карте или мобильному устройству. Вместо этого, он работает через интернет, что делает его доступным практически из любой точки мира арендовать номер телефона
Польский виртуальный номер – это телефонный номер, который не привязан к физической SIM-карте или мобильному устройству. Вместо этого, он работает через интернет, что делает его доступным практически из любой точки мира аренда виртуального номера телефона
Польский виртуальный номер – это телефонный номер, который не привязан к физической SIM-карте или мобильному устройству. Вместо этого, он работает через интернет, что делает его доступным практически из любой точки мира купить виртуальный номер телефона
Играем в Трикс казино официальный сайт онлайн на деньги! Регистрация и вход в Trix казино через рабочее зеркало. Бонусы и акции для новых и постоянных трикс
Играем в Трикс казино официальный сайт онлайн на деньги! Регистрация и вход в Trix казино через рабочее зеркало. Бонусы и акции для новых и постоянных https://trix-66.fun
Играем в Трикс казино официальный сайт онлайн на деньги! Регистрация и вход в Trix казино через рабочее зеркало. Бонусы и акции для новых и постоянных трикс официальный сайт
купить диплом продавца
Achieving financial independence gives freedom to make the best use of time to pursue life’s goals and dreams, or help the citizens of the community to lead a life with purpose.
диплом дизайнера интерьера купить
диплом о высшем образовании купить
купить диплом в дзержинске купить диплом в дзержинске .
There’s so much innovation in the cryptocurrency space right now.
https://t.me/cryptonetlake
Официальная покупка диплома вуза с сокращенной программой в Москве
Возможно ли купить диплом стоматолога, и как это происходит
Официальная покупка аттестата о среднем образовании в Москве и других городах
The social gathering, revealing as soon as more the decisive importance of its historic role, had to supplement the state.
купить диплом о среднем специальном образовании челябинск
Сколько стоит диплом высшего и среднего образования и как его получить?
Официальная покупка аттестата о среднем образовании в Москве и других городах
Всё, что нужно знать о покупке аттестата о среднем образовании без рисков
Spanish footballer and Athletic Bilbao nico-williams midfielder Nico Williams has had a remarkable career. He shares a close relationship with his brother Inaki. Recent reports have included a potential move to Barcelona in 2024.
Talented Nigerian striker Victor Osimhen victor osimhen proudly represents Italian club Napoli and the Nigerian national team. This story highlights his remarkable sporting career, personal development and notable achievements, including a loan spell at Galatasaray.
Federico Valverde’s https://federico-valverde-az.org biography: personal life, date of birth, children with Mina Bonino, salary, religion, playing style on the pitch, Real Madrid statistics, salary, number inherited from Kroos, position for 2024 and news.
Biography of Spanish footballer Rodri rodri Manchester City midfielder, salary, worth, religion, Euro match statistics, champion status and games with Joao Cancelo. Latest updates in 2024.
Biography of Lamine Yamal lamine-yamal-az com a Spanish winger who plays for FC Barcelona and the national team. Includes career highlights, statistics, Euro 2024 winning salary and personal life.
Exporting and Sharing My Design
Once I finalized my dream kitchen layoutтАЪ exporting the design was surprisingly straightforward. The online tool offered several options; I chose to download high-resolution imagesтАЪ perfect for sharing with family and friends. The images were incredibly detailedтАЪ capturing every element of my designтАЪ from the subtle grain of the oak cabinets to the precise dimensions of the countertops. I also created a detailed PDF planтАЪ which included measurementsтАЪ appliance specificationsтАЪ and a comprehensive materials list. This was invaluable for potential contractorsтАЪ providing them with all the information they needed to accurately estimate costs and timelines. Sharing my design was incredibly easy. I emailed the images and PDF to several contractors I’d contactedтАЪ and the clarity of the visuals made communication seamless. They were all impressed by the level of detail and professionalism of the digital plans. I also shared my design on social mediaтАЪ posting the images to my Instagram account. My friends and family were amazed by the transformationтАЪ praising the modernтАЪ yet cozy feel of the kitchen. The online tool even allowed me to create a 3D walkthroughтАЪ which I shared with a friend who’s considering a kitchen renovation of her own. She was particularly impressed by the realistic rendering of the lighting and the overall atmosphere of the space. The ability to easily export and share my design was a fantastic feature of the software. It facilitated clear communication with contractorsтАЪ allowed me to easily share my vision with othersтАЪ and even inspired my friend to begin her own kitchen design journey. The entire processтАЪ from initial design to final export and sharingтАЪ was smoothтАЪ efficientтАЪ and incredibly rewardingтАЪ proving that designing a dream kitchen online can be both fun and incredibly practical.
https://instepnews.com/automotive-news/revamping-car-customization-with-3d-printing/
Once I finalized my dream kitchen layoutтАЪ exporting the design was surprisingly straightforward. The online tool offered several options; I chose to download high-resolution imagesтАЪ perfect for sharing with family and friends. The images were incredibly detailedтАЪ capturing every element of my designтАЪ from the subtle grain of the oak cabinets to the precise dimensions of the countertops. I also created a detailed PDF planтАЪ which included measurementsтАЪ appliance specificationsтАЪ and a comprehensive materials list. This was invaluable for potential contractorsтАЪ providing them with all the information they needed to accurately estimate costs and timelines. Sharing my design was incredibly easy. I emailed the images and PDF to several contractors I’d contactedтАЪ and the clarity of the visuals made communication seamless. They were all impressed by the level of detail and professionalism of the digital plans. I also shared my design on social mediaтАЪ posting the images to my Instagram account. My friends and family were amazed by the transformationтАЪ praising the modernтАЪ yet cozy feel of the kitchen. The online tool even allowed me to create a 3D walkthroughтАЪ which I shared with a friend who’s considering a kitchen renovation of her own. She was particularly impressed by the realistic rendering of the lighting and the overall atmosphere of the space. The ability to easily export and share my design was a fantastic feature of the software. It facilitated clear communication with contractorsтАЪ allowed me to easily share my vision with othersтАЪ and even inspired my friend to begin her own kitchen design journey. The entire processтАЪ from initial design to final export and sharingтАЪ was smoothтАЪ efficientтАЪ and incredibly rewardingтАЪ proving that designing a dream kitchen online can be both fun and incredibly practical.
After inputting my measurements and preferencesтАЪ I dove headfirst into the exciting world of layout experimentation. KitchenCraft Pro offered a plethora of optionsтАЪ from the classic galley style to the more spacious L-shape and U-shape designs. I started by exploring the galley layoutтАЪ digitally dragging and dropping cabinets and appliances to visualize the workflow. I quickly realized it wouldn’t suit my needs тАУ the limited counter space was a major drawback. NextтАЪ I experimented with an L-shape configurationтАЪ strategically placing the sinkтАЪ stoveтАЪ and refrigerator to form an efficient work triangle. This felt more promising. I meticulously adjusted the placement of islands and peninsulasтАЪ carefully considering their impact on traffic flow and overall spaciousness. The software’s intuitive drag-and-drop functionality made this process remarkably easy and enjoyable. I even tried a daring U-shaped designтАЪ envisioning a grandтАЪ chef-like workspace. While initially appealingтАЪ I found it slightly cramped for my needs. The software allowed me to easily switch between different layoutsтАЪ instantly visualizing the impact of each change. I spent hours tweaking the arrangement of cabinetsтАЪ appliancesтАЪ and workspacesтАЪ constantly evaluating the practicality and aesthetic appeal of each configuration; I played around with different cabinet depths and widthsтАЪ experimenting with the placement of pantry units and maximizing storage space. I even considered adding a breakfast bar to one of the layoutsтАЪ envisioning family gatherings around it. The ability to instantly see the results of my adjustments was invaluableтАЪ allowing me to make informed decisions based on both functionality and personal preference. It was a truly iterative processтАЪ refining and perfecting the design until I found the perfect balance between form and function. Through this experimentationтАЪ I discovered that the L-shape layoutтАЪ with a cleverly positioned islandтАЪ provided the optimal blend of efficiency and spaciousness for my kitchen.
Experimenting with Different Layouts
With a satisfying L-shaped layout as my baseтАЪ I delved into the finer detailsтАЪ transforming my digital sketch into a truly personalized design. I meticulously selected cabinet styles from the extensive library offered by the softwareтАЪ opting for sleekтАЪ modern shaker-style cabinets in a warmтАЪ honey-toned oak finish. The program allowed me to visualize these choices in real-timeтАЪ rotating the cabinets to ensure they complemented the overall aesthetic. NextтАЪ I chose countertops. I initially considered graniteтАЪ but the virtual rendering showed it clashing slightly with the cabinet color. I then experimented with quartzтАЪ settling on a beautifulтАЪ light-grey option that beautifully contrasted with the oak. The software’s realistic rendering capabilities were invaluable here. I spent a considerable amount of time tweaking the backsplashтАЪ finally settling on a subway tile pattern in a soft whiteтАЪ which provided a clean and classic look. Adding lighting was another key step. I strategically placed recessed lighting above the countertops and pendant lights above the islandтАЪ creating a warm and inviting ambiance. I even experimented with different flooring optionsтАЪ virtually laying down various types of tile and hardwood to see how they interacted with the rest of the design. I was particularly pleased with a light-colored oak wood floor that tied in seamlessly with the cabinetry. Beyond the major elementsтАЪ I focused on the smaller details. I carefully selected hardwareтАЪ opting for brushed nickel pulls and knobs that added a touch of sophistication. I also integrated various appliancesтАЪ choosing models based on their size and aestheticsтАЪ ensuring they fit harmoniously within the design. The software allowed me to fine-tune every aspectтАЪ from the placement of outlets to the positioning of spice racksтАЪ ensuring a highly functional and visually appealing kitchen. It was a truly rewarding processтАЪ seeing my initial concept evolve into a cohesive and detailed designтАЪ ready to be shared and potentially implemented in the real world. The level of customization was impressiveтАЪ allowing me to create a space that was uniquely mine.
My Free Online Kitchen Design Journey
Виртуальный номер телефона даёт возможность подключать любое количество номеров и разговаривать с любого устройства, принимать звонки в офисе или дома купить номер ватсап
купить диплом медсестры купить диплом медсестры .
Виртуальный номер телефона даёт возможность подключать любое количество номеров и разговаривать с любого устройства, принимать звонки в офисе или дома купить виртуальный номер
Founded in 2021, Jeetbuzz has rapidly grown in popularity across Bangladesh and Southeast Asia. Licensed by the government of Curacao, Jeetbuzz offers sports betting, casino games, and a betting exchange https://jeet-buzz.bet/
Founded in 2021, Jeetbuzz has rapidly grown in popularity across Bangladesh and Southeast Asia. Licensed by the government of Curacao, Jeetbuzz offers sports betting, casino games, and a betting exchange jeetbuzz online
купить диплом техникума об окончании
Виртуальный номер телефона даёт возможность подключать любое количество номеров и разговаривать с любого устройства, принимать звонки в офисе или дома онлайн номер Казахстана
Founded in 2021, Jeetbuzz has rapidly grown in popularity across Bangladesh and Southeast Asia. Licensed by the government of Curacao, Jeetbuzz offers sports betting, casino games, and a betting exchange jeetbuzz in bangladesh
пообещали
управляющие компании г самара
The Counterpoint team managed all of the deficiencies and made sure that the building was happy with the construction throughout the entire2-year renovation. For that reason, Rule 2-01 provides that, in determining whether an accountant is independent, the Commission will consider all relevant facts and circumstances. In determining whether an accountant is independent, the Commission will consider all relevant circumstances, including all relationships between the accountant and the audit client, and not just those relating to reports filed with the Commission. Any partner, principal, shareholder, or professional employee of the accounting firm, any of his or her immediate family members, any close family member of a covered person in the firm, or any group of the above persons has filed a Schedule 13D or 13G (17 CFR 240.13d-101 or 240.13d-102) with the Commission indicating beneficial ownership of more than five percent of an audit client’s equity securities or controls an audit client, or a close family member of a partner, principal, or shareholder of the accounting firm controls an audit client. 1) Financial relationships. An accountant is not independent if, at any point during the audit and professional engagement period, the accountant has a direct financial interest or a material indirect financial interest in the accountant’s audit client, such as: (i) Investments in audit clients.
Viagra canada no prescription http://pharmacyusa24.com/ Cialis_viagra_levitra_kaufen_rezeptfrei
Всё для строительства и ремонта https://artpaint.com.ua на одном портале: советы экспертов, обзоры материалов, расчет сметы и готовые решения для вашего дома или бизнеса.
Портал о строительстве https://aziatransbud.com.ua статьи, видео, инструкции, каталоги материалов и инструментов. Советы для дома и бизнеса. Легко строить, удобно ремонтировать!
Портал для строительства https://6may.org и ремонта: полезные советы, современные материалы, проекты и идеи. Все, что нужно для воплощения ваших задумок – от фундамента до крыши.
Студия дизайна интерьера https://bconline.com.ua и архитектуры: создаем уникальные проекты для квартир, домов и коммерческих пространств. Эстетика, функциональность и индивидуальный подход – в каждом решении.
Все об озеленении и благоустройстве https://bathen.rv.ua Ландшафтный дизайн, проекты садов, террас и парков. Идеи для создания зеленых зон, подбор растений и профессиональные услуги для вашего участка.
Chill out. Permanent components that may not “go” with your house’s general look can adapt simply high quality, with slightly imagination.
This view of the relationship of Threat Management to Threat Evaluation is depicted in figure as adopted from OCTAVE.
стероиды препараты стероиды купить для роста мышц
supreme suppliers
CMS 1С-Битрикс Бизнес https://magikfox.ru/catalog/license/upravlenie-saytom/biznes/ купить лицензию в официальном маркетплейсе. Редакция Bitrix Бизнес для интернет магазина. Быстрая отправка лицензионного ключа. Помощь в установке и настройке.
гидрозатвор для канализации бани srti.ru
Ваш путеводитель в мире строительства https://dcsms.uzhgorod.ua идеи, планы, пошаговые инструкции и лучшие материалы. Узнайте, как построить дом мечты или обновить интерьер.
Профессиональный портал для строительства https://blogcamp.com.ua проекты, материалы, расчеты, советы и вдохновение. Все, чтобы ваш ремонт или стройка были успешными.
https://cutumed.ru/
A wedding planner will assist you with the price range creation, management, venue choice, venue referrals, seating arrangements and so on.
pharmacy rx one
What are some of the Swedish Holiday Traditions?
Делайте ремонт https://esi.com.ua и стройте легко! Лучшие советы мастеров, подбор инструментов, инструкции и сметы. Мы поможем справиться с любой задачей.
Хотите построить дом https://donbass.org.ua или сделать ремонт? Здесь вы найдете всё: инструкции, идеи, современные технологии и проверенные решения. Портал для тех, кто строит.
Все для строителей и мастеров https://dki.org.ua актуальные технологии, практические советы, строительные материалы и проекты. Простые решения для сложных задач!
Создайте дом своей мечты https://intellectronics.com.ua На нашем портале вы найдете идеи, инструкции и новейшие технологии для ремонта и строительства.
Станьте мастером https://fmsu.org.ua своего дела! Портал для тех, кто хочет строить и ремонтировать качественно и выгодно.
Exporting and Sharing My Design
Choosing the Right Online Tool
https://instepnews.com/finance/securing-the-best-auto-loan-rates-4/
Exporting and Sharing My Design
Experimenting with Different Layouts
My kitchen renovation started with a daunting taskтБЪ finding the perfect free online design tool. I initially felt overwhelmed by the sheer number of options available. I spent several days researchingтАЪ reading reviewsтАЪ and comparing features. Some platforms boasted impressive 3D rendering capabilitiesтАЪ but lacked the intuitive interface I craved. Others offered simpler designs but lacked customization options. I needed a balance of visual appeal and user-friendliness. After much deliberationтАЪ I settled on “KitchenCraft ProтАЪ” a platform recommended by a friendтАЪ Amelia. KitchenCraft Pro offered a user-friendly drag-and-drop interfaceтАЪ a wide selection of appliances and cabinetry stylesтАЪ and surprisingly detailed customization options. The initial learning curve was minimal; I was able to navigate the software and start designing within minutes. I particularly appreciated the ability to import my own images and textures to personalize the designтАЪ ensuring it accurately reflected my unique style and preferences. The free version provided ample features for my needsтАЪ although I did note that some advanced featuresтАЪ like photorealistic renderingтАЪ were reserved for paid subscriptions. HoweverтАЪ for my purposesтАЪ the free tools were more than sufficient. The decision to use KitchenCraft Pro proved to be a great oneтАЪ setting the stage for a successful and enjoyable design process. I highly recommend thoroughly researching and comparing different free online kitchen design tools before making your choiceтАЪ to ensure you find one that best suits your specific needs and skill level. Remember to look for intuitive interfacesтАЪ a wide range of optionsтАЪ and helpful tutorials or support resources.
Inputting My Measurements and Preferences
I embarked on a thrilling kitchen redesignтАЪ leveraging free online tools. My goal? A stunningтАЪ functional space without breaking the bank. I spent hours exploring various platformsтАЪ comparing features and ease of use. The process felt surprisingly intuitive. I was amazed by how quickly I could visualize different layouts and experiment with various appliances and cabinetry. It was a fun and empowering experienceтАЪ proving that achieving a dream kitchen doesn’t require a hefty budget!
алкоголизм лечение вывод из запоя ростов алкоголизм лечение вывод из запоя ростов .
вывод из запоя на дому ростов-на-дону вывод из запоя на дому ростов-на-дону .
on line pharmacy with no prescription Online Pharmacy No Prescription Proscar
Type Okay copper pipe has the thickest wall of all the frequent types.
Хуснуллин оценил рост цен на стройматериалы в 64% с 2021 года. Он считает такое увеличение критичным и влияющим в том числе и на государственный бюджет, поскольку по госзаказу производятся строительные и ремонтные работы на триллионы рублей https://news-life.pro/schelkovo/395592354/
Хуснуллин оценил рост цен на стройматериалы в 64% с 2021 года. Он считает такое увеличение критичным и влияющим в том числе и на государственный бюджет, поскольку по госзаказу производятся строительные и ремонтные работы на триллионы рублей https://www.sostav.ru/blogs/260771/55489
Canada Pharmacy 24 Hour Drug Store Tadalis skypharmacy
Buy cialis 40 mg in toronto
Хуснуллин оценил рост цен на стройматериалы в 64% с 2021 года. Он считает такое увеличение критичным и влияющим в том числе и на государственный бюджет, поскольку по госзаказу производятся строительные и ремонтные работы на триллионы рублей https://narodedin.com/post/s-2021-goda-stroitelnye-materialy-podorozhali-na-64-procenta/
https://50style.ru/
작년 국내외 온,오프라인쇼핑 시장 덩치 169조원을 넘어서는 수준이다. 미국에서는 이달 22일 블랙프라이데이와 사이버먼데이로 이어지는 연말 레플리카 사이트 순위 쇼핑 계절이 기다리고 있습니다. 허나 올해는 글로벌 물류대란이 변수로 떠상승했다. 전 세계 공급망 차질로 주요 소매유통회사들이 상품 재고 확보에 어려움을 겪고 있기 때문인 것이다. 어도비는 연말 계절 미국 소매기업의 할인율이 전년보다 6%포인트(P)가량 줄어들 것으로 예상하였다.
레플리카사이트 순위
Of course, nowadays science can step in to create new forms of more resilient fruit.
canadian pharmacies shipping to usa
For those who want to turn out to be a sponsor go Here.
prednisone without a script
No Prescription Pharmacy Buy no prescription ivermectin online myskypharmacy Buy xenical orlistat canada
пропуска на грузовые машины в москве пропуска на грузовые машины в москве .
Ландшафтный дизайн https://kinoranok.org.ua и благоустройство для дома, офиса или парка. Профессиональные советы, подбор растений и реализация уникальных зеленых проектов.
Архитектура и дизайн интерьера https://it-cifra.com.ua под ключ: современные решения, индивидуальный подход и гармония стиля и функциональности. Создаем пространство вашей мечты!
Найдите все для ремонта https://keravin.com.ua и строительства! Уникальные идеи, пошаговые инструкции и рекомендации специалистов на одном портале.
Стройте с комфортом https://mr.org.ua полезные советы, новейшие технологии, пошаговые инструкции и проекты – всё для вашего удобства.
Мы помогаем строить https://juglans.com.ua лучше! Советы, проекты, новейшие материалы и технологии для вашего ремонта или строительства.
Займы в Казахстане онлайн — быстрое оформление, минимальные требования, выгодные условия для получения нужной суммы микрозаймы онлайн
Займы в Казахстане онлайн — быстрое оформление, минимальные требования, выгодные условия для получения нужной суммы микрокредит онлайн
Inputting My Measurements and Preferences
I embarked on a thrilling kitchen redesignтАЪ leveraging free online tools. My goal? A stunningтАЪ functional space without breaking the bank. I spent hours exploring various platformsтАЪ comparing features and ease of use. The process felt surprisingly intuitive. I was amazed by how quickly I could visualize different layouts and experiment with various appliances and cabinetry. It was a fun and empowering experienceтАЪ proving that achieving a dream kitchen doesn’t require a hefty budget!
ihanauto.ru
The frequency of your hot water heater’s drainage needs isn’t a one-size-fits-all scenario. Several crucial factors influence how often you should perform this essential maintenance task. Hard water, characterized by high mineral content, significantly accelerates sediment buildup within your water heater’s tank. These minerals precipitate out of solution as the water heats, forming a layer of sediment at the bottom. The thicker this sediment layer becomes, the less efficient your water heater becomes, consuming more energy to heat the water and potentially leading to premature failure. High water usage also contributes to faster sediment accumulation. The more frequently you use hot water, the more minerals are introduced into the tank, increasing the rate of sediment formation. Conversely, homes with soft water and low water usage may find that an annual flush is sufficient. Consider the specific characteristics of your water supply and your household’s hot water consumption habits when determining your ideal flushing schedule. Regularly checking the sediment level (if accessible) can also provide valuable insights into the frequency needed for your specific circumstances. Remember, consistent monitoring and proactive maintenance are key to ensuring your water heater’s optimal performance and longevity. Ignoring these factors can lead to decreased efficiency, higher energy bills, and ultimately, costly repairs or premature replacement.
Ambient lighting provides overall illumination for the room. Recessed lighting or a stylish chandelier can provide a soft‚ diffused glow. Task lighting is essential for practical purposes‚ such as applying makeup or shaving. Consider installing vanity lights with adjustable brightness for optimal illumination. Accent lighting highlights specific features‚ such as a beautiful piece of artwork or a unique textural element. Strategically placed spotlights or wall sconces can draw attention to these focal points. Consider the color temperature of your light bulbs; warmer tones (2700K-3000K) create a cozy and relaxing atmosphere‚ while cooler tones (5000K-6500K) provide a brighter‚ more invigorating feel. Experiment with different lighting options to find the perfect balance that complements your bathroom’s style and enhances its aesthetic appeal. Remember that natural light is a valuable asset‚ so maximize its impact by keeping windows unobstructed and using sheer curtains to diffuse harsh sunlight.
Avoid the hassle of airport parking with our convenient and affordable long-term parking options at O’Hare International Airport (ORD). Book online and enjoy a stress-free travel experience best long term parking at ord
Займы в Казахстане онлайн — быстрое оформление, минимальные требования, выгодные условия для получения нужной суммы микрозаймы онлайн
Avoid the hassle of airport parking with our convenient and affordable long-term parking options at O’Hare International Airport (ORD). Book online and enjoy a stress-free travel experience cost of long term parking at ord
Avoid the hassle of airport parking with our convenient and affordable long-term parking options at O’Hare International Airport (ORD). Book online and enjoy a stress-free travel experience ord long term parking rates
Specifies the variety of outcomes per page.
Experience the best value in long-term parking at Pittsburgh International Airport. We offer competitive rates, excellent customer service, and a hassle-free parking experience. Book your spot today pittsburgh long term parking
easy-drop промокод easy-drop промокод .
Experience the best value in long-term parking at Pittsburgh International Airport. We offer competitive rates, excellent customer service, and a hassle-free parking experience. Book your spot today pittsburgh international airport long term parking rates
Компания 1хБет предоставляет всем 100% бонус за первый депозит до 32500 рублей (или эквивалент в другой валюте по актуальному курсу). Кроме того, вас ожидает приветственный пакет в 1xBet казино до €1950 +150 фриспинов для игры в слоты и игровые автоматы. 1xBet — это одна из самых популярных и надежных платформ, которая предлагает уникальные возможности и привлекательные бонусы для своих пользователей. Независимо от того, являетесь ли вы новичком в мире ставок или опытным игроком, промокоды 1xBet — это отличный способ повысить свои шансы на выигрыш.
Промокод 1xBet
http://samodelnii.ru/application/pages/kakoj_promokod_na_1hbet.html
Промокод 1хБет на сегодня – предоставляет вам возможность получить 100%-й бонус до 32 500 ? и Приветственный пакет до 1500 евро + 150 фриспинов для игры в разделе азартных игр 1хБет. 1xBet — это известная онлайн-платформа для ставок, которая славится своими щедрыми бонусами и привлекательными предложениями. Если вы ищете уникальный игровой опыт и дополнительные шансы на успех, то бонусы 1xBet станут отличным выбором для вас.
Бонусы являются одной из главных особенностей, которые делают 1xBet привлекательной для множества игроков. Как новый, так и постоянный пользователь, вы сможете воспользоваться различными видами бонусов, которые помогут увеличить ваши шансы на выигрыш. От приветственных бонусов до регулярных акций, 1xBet предлагает множество вариантов, чтобы удовлетворить ваши потребности и предпочтения.
Один из самых популярных бонусов, предоставляемых 1xBet, – это приветственный бонус для новых игроков. Как только вы зарегистрируетесь на платформе, вам будет предложен щедрый приветственный пакет, который включает в себя бонус на первый депозит. Это означает, что вы получите дополнительные средства на свой игровой счет, чтобы увеличить свои возможности для ставок. Такой бонус является отличным стартом в вашем игровом путешествии и помогает вам исследовать различные игры и спортивные события.
Не упустите шанс осуществить задуманное! Мы предлагаем выгодные кредиты с низкими ставками и быстрым одобрением.
– Авто, квартира, бизнес – мы поддержим ваши планы!
Заполните заявку онлайн, и наши специалисты свяжутся с вами.
Действуйте сейчас – ваши мечты ждут!==>
учебник по финансы кредит
Book online and enjoy a stress-free travel experience. Avoid the hassle of airport parking with our convenient and affordable long-term parking options at O’Hare International Airport (ORD) ord long term parking cost
Nonetheless, in the event you fail to enter lacking data, it could possibly result in discrepancies and inaccuracies in your books.
Лазерный уровень легко помещается в сумке и всегда под рукой, когда он вам нужен. Идеально подходит для работы как в помещении, так и на улице – лазерный уровень нивелир.
Experience the best value in long-term parking at Pittsburgh International Airport. We offer competitive rates, excellent customer service, and a hassle-free parking experience. Book your spot today pit airport long term parking
Book online and enjoy a stress-free travel experience. Avoid the hassle of airport parking with our convenient and affordable long-term parking options at O’Hare International Airport (ORD) ord long term parking rates
Ваш путеводитель в мире строительства https://mtbo.org.ua полезные рекомендации, готовые проекты и современные решения для любых задач.
Решили строить или делать ремонт https://msc.com.ua Мы подскажем, как выбрать лучшие материалы, спланировать бюджет и воплотить все задумки.
Строительство без лишних вопросов https://okna-k.com.ua наш портал – кладезь информации о современных материалах, технологиях и лучших решениях для дома, дачи или офиса.
Всё для успешного строительства https://newboard-store.com.ua и ремонта на одном портале! Мы собрали актуальную информацию, идеи и инструкции для вашего удобства. Заходите и стройте с нами!
Все секреты https://mramor.net.ua строительства в одном месте! Советы экспертов, подбор материалов и готовые проекты для вдохновения.
поддельный диплом купить
https://expert-kaluga.ru/
Предлагаем вам высококачественный тротуарный бордюр – идеальное решение для обрамления дорожек, газонов, цветников и других элементов ландшафтного дизайна.
Наш тротуарный бордюр отличается прочностью, долговечностью и устойчивостью к воздействию внешних факторов, что делает его идеальным выбором для любых условий эксплуатации – купить тротуарную брусчатку
Лазерный уровень легко помещается в сумке и всегда под рукой, когда он вам нужен. Идеально подходит для работы как в помещении, так и на улице. – лазерный уровень цена.
диплом вуза ссср купить
Director Jon M. Chu missed ‘Wicked’ premiere to welcome fifth child
[url=https://kra15cc.com]kraken23[/url]
“Wicked” director Jon M. Chu couldn’t attend the film’s premiere in Los Angeles, and the reason is quite “wonderful.”
Chu shared on his Instagram Stories that he and his wife Kristin Hodge welcomed their fifth child on Saturday, writing that he “can’t believe this happened while the movie is premiering.”
“Magic is in the air,” he wrote, sharing a photo of Hodge holding their newborn daughter.
https://krak18.com
kra17
He added a note to his new addition: “Welcome to our world, you’re gonna do great. You have a lot of witches on your side.”
“Wicked” stars singer Ariana Grande and Oscar-nominated actress Cynthia Erivo star as witches Glinda and Elphaba, respectively. The two-part movie is a cinematic adaptation of the famed Broadway musical, which is a prequel to “The Wizard of Oz” and tells an alternate version of events in Oz before Dorothy’s arrival.
Chu may not have been able to physically attend the premiere but his presence was felt.
According to footage from inside the theater posted online, a video of Chu speaking from the hospital was played before the movie began.
“I’ve waited for three years to have this moment to share a movie with you but I’ve waited my whole life to have this moment, to have a fifth child right now,” he said in the video, as the audience was heard collectively “aww-ing” at the sentiment.
With a laugh, Chu added that “of course, this little girl knows when to show up.”
Jonathan Bailey, Bowen Yang, Ethan Slater, Michelle Yeoh and Jeff Goldblum round out the ensemble cast.
Part one of “Wicked” will soar in theaters on November 22. The second film is expected in November 2025.
Ваш путеводитель в строительстве https://quickstudio.com.ua Ищите материалы, технологии или советы – всё это есть на нашем портале. Стройте с комфортом!
firm registration in montenegro accountant in Montenegro
Информация о стройке https://purr.org.ua без лишних сложностей! Наш портал поможет выбрать материалы, узнать о технологиях и сделать ваш проект лучше.
Within the dynamic world of business, mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are crucial methods for progress, diversification, and competitive benefit.
1win official website promo code for 1win
1win uganda 1win promo code
That was when Hollywood star Linda Christian wore a ravishing satin gown with a 5-yard train that had been designed by the sisters for her marriage ceremony with fellow actor Tyrone Energy.
купить диплом израиля
Купить аттестат в Барнауле
Дома из бревна вообще выглядят очень круто! Я лично давно мечтаю о чем-то подобном, но, к сожалению, пока что даже участка под такой дом у меня нет https://ru.gorodwiki.ru/peterburg/izba-776157-otzyvy
Дома из бревна вообще выглядят очень круто! Я лично давно мечтаю о чем-то подобном, но, к сожалению, пока что даже участка под такой дом у меня нет https://www.smetdlysmet.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?p=31213
Дома из бревна вообще выглядят очень круто! Я лично давно мечтаю о чем-то подобном, но, к сожалению, пока что даже участка под такой дом у меня нет https://sensaudio.ru/iz-kakogo-dereva-luchshe-stroit-banyu
Portugal has long been a country known for producing exceptional talent in the world of sports. With a rich history in football, many athletes from this nation have achieved international fame through their incredible skills and accomplishments http://users.atw.hu/sajprobaoldalam/modules.php?name=Journal&file=display&jid=51097
Portugal has long been a country known for producing exceptional talent in the world of sports. With a rich history in football, many athletes from this nation have achieved international fame through their incredible skills and accomplishments http://www.tronicb7records.com/new/component/k2/itemlist/user/96210
Portugal has long been a country known for producing exceptional talent in the world of sports. With a rich history in football, many athletes from this nation have achieved international fame through their incredible skills and accomplishments https://alternatio.org/index.php?option=com_k2&view=itemlist&task=user&id=163654
Всё для вашего ремонта https://reklama-region.com и строительства в одном месте! Практичные советы, современные решения и актуальная информация для успешного проекта.
Всё, что нужно знать о металлах https://metalprotection.com.ua от их свойств до применения в различных отраслях. Обзоры, советы, новости и информация о производителях для вашего удобства.
Вавада предлагает https://telegra.ph/Sportivnye-stavki-v-Vavada-01-15 на любой вкус! Здесь вы найдете ставки на футбол, теннис, баскетбол, киберспорт и многое другое. Широкий выбор событий, удобный интерфейс и выгодные коэффициенты делают платформу идеальной как для новичков, так и для опытных игроков. Начните свой путь в ставках уже сегодня!
With my chosen design toolтАЪ KitchenCraft ProтАЪ selectedтАЪ the next step was inputting my kitchen’s precise measurements. This proved surprisingly straightforward. The software guided me through a step-by-step processтАЪ prompting me to enter the length and width of each wallтАЪ the location of windows and doorsтАЪ and the dimensions of existing fixtures like sinks and ovens. I found the interface incredibly intuitiveтАЪ with clear instructions and helpful visual aids. I even appreciated the option to upload a floor plan image to assist with the process. InitiallyтАЪ I struggled a bit with accurately measuring some awkwardly shaped alcovesтАЪ but the platform’s customer support chat was incredibly helpfulтАЪ providing quick and efficient guidance. Once the dimensions were finalizedтАЪ I began to personalize the design. This is where the fun really started! I selected my preferred cabinet stylesтАЪ choosing from a comprehensive library of options ranging from sleek modern designs to more traditionalтАЪ rustic styles. I meticulously chose the colorsтАЪ finishesтАЪ and countertop materialsтАЪ experimenting with different combinations to find the perfect aesthetic. I even incorporated my existing appliancesтАЪ ensuring they fit seamlessly into the new layout. The software allowed for precise placement of every elementтАЪ down to the smallest detail. I spent hours tweaking and refiningтАЪ meticulously considering factors such as workflow efficiency and aesthetic harmony. The process felt like playing a sophisticated digital puzzleтАЪ and the satisfaction of seeing my vision slowly take shape on the screen was incredibly rewarding. I discovered that the software’s flexibility allowed me to explore different layouts and experiment with various design choices without any commitmentтАЪ a feature I truly appreciated. It was a crucial step in ensuring my final design would be both functional and visually appealing.
My kitchen renovation started with a daunting taskтБЪ finding the perfect free online design tool. I initially felt overwhelmed by the sheer number of options available. I spent several days researchingтАЪ reading reviewsтАЪ and comparing features. Some platforms boasted impressive 3D rendering capabilitiesтАЪ but lacked the intuitive interface I craved. Others offered simpler designs but lacked customization options. I needed a balance of visual appeal and user-friendliness. After much deliberationтАЪ I settled on “KitchenCraft ProтАЪ” a platform recommended by a friendтАЪ Amelia. KitchenCraft Pro offered a user-friendly drag-and-drop interfaceтАЪ a wide selection of appliances and cabinetry stylesтАЪ and surprisingly detailed customization options. The initial learning curve was minimal; I was able to navigate the software and start designing within minutes. I particularly appreciated the ability to import my own images and textures to personalize the designтАЪ ensuring it accurately reflected my unique style and preferences. The free version provided ample features for my needsтАЪ although I did note that some advanced featuresтАЪ like photorealistic renderingтАЪ were reserved for paid subscriptions. HoweverтАЪ for my purposesтАЪ the free tools were more than sufficient. The decision to use KitchenCraft Pro proved to be a great oneтАЪ setting the stage for a successful and enjoyable design process. I highly recommend thoroughly researching and comparing different free online kitchen design tools before making your choiceтАЪ to ensure you find one that best suits your specific needs and skill level. Remember to look for intuitive interfacesтАЪ a wide range of optionsтАЪ and helpful tutorials or support resources.
spectehnika-rent.ru
Flushing your hot water heater is a straightforward process, but safety precautions are paramount. Before you begin, always turn off the power to the unit – either by switching off the circuit breaker or turning off the gas supply. Allow the water heater to cool completely to prevent burns. You’ll need a garden hose, a bucket, and some basic tools. First, locate the drain valve at the bottom of the tank. Attach the garden hose to the drain valve to direct the outflow away from your home and into a suitable drain. Next, carefully open the drain valve, allowing the water to flow out slowly. This initial flow will likely be quite dirty, containing sediment and other debris. As the water clears, you’ll know that the majority of the sediment has been removed. To aid the flushing process, you can open the pressure relief valve (located near the top of the tank) briefly to allow for better water circulation and sediment removal. Be prepared for some initial sputtering as air enters the tank. Once the water runs clear, close the drain valve and reconnect the garden hose. Turn the power back on to your water heater and check for any leaks. It’s advisable to monitor the water heater’s performance in the days following the flush, checking for any unusual noises or leaks. If you are uncomfortable performing this task yourself, it’s always best to consult a qualified plumber. Remember, safety is paramount, and a properly flushed water heater contributes to its longevity and efficiency. The small amount of time invested in this preventative maintenance can save you significant costs and headaches in the long run.
Maximizing Vertical SpaceтБЪ Shelving and Hanging Solutions
Хотите построить дом https://samozahist.org.ua или сделать ремонт? На нашем портале вы найдёте лучшие решения и вдохновение для вашего проекта.
Ищете проверенные строительные советы https://rus3edin.org.ua Наш портал поможет выбрать материалы, спланировать проект и сделать всё на высшем уровне.
https://osago-osago.ru/
купить диплом техникума
купить диплом флориста купить диплом флориста .
Строительный портал https://sinergibumn.com для тех, кто хочет знать больше о строительстве. Актуальные идеи, проверенные технологии и вдохновение для любого проекта.
Всё о дизайне интерьера https://sculptureproject.org.ua в одном месте! Узнайте, как создать уютное, стильное и функциональное пространство, которое будет радовать каждый день.
программа производственного лабораторного контроля Москва https://ppk-213.ru
Экспертный строительный портал https://smallbusiness.dp.ua для вашего проекта! Советы, новинки и инструкции для тех, кто хочет сделать всё идеально.
Хотите стильный интерьер https://sitetime.kiev.ua Наш портал предлагает уникальные идеи, профессиональные рекомендации и примеры лучших дизайн-проектов.
Also, currency exchange and various stock indexes can be traded commission free.
Официальный сайт https://luckyjetonewins.ru , где вы найдете актуальное зеркало и промоды на Лаки Джет.
Стоимость дипломов высшего и среднего образования и как избежать подделок
Staking coins like Ethereum 2.0 is an interesting way to earn passive income.
[url=https://t.me/cryptonetlake]https://t.me/cryptonetlake[/url]
https://www.cpcspb.ru/
Строительный портал https://sushico.com.ua для профессионалов и новичков: от выбора материалов до готовых проектов. Легко найти подрядчиков, изучить современные технологии и воплотить идеи в жизнь!
Найдите всё о строительстве https://srk.kiev.ua и ремонте на нашем портале. Полезные статьи, актуальные технологии и лучшие практики ждут вас.
kra23.at – кракен darknet, kraken20 at kraken19at online
Преобразите ваш дом https://vineyardartdecor.com вместе с нами! На портале вы найдёте свежие идеи, советы по планировке и материалы для создания идеального интерьера.
Планируете стройку https://texha.com.ua или ремонт? У нас вы найдёте проверенных специалистов, инструкции, материалы и проекты на любой вкус. Всё для комфортного строительства!
Всё о строительстве https://valkbolos.com и ремонте на одном портале! Гид по материалам, обзор инструментов, советы по дизайну и подбор подрядчиков. Создавайте дом своей мечты!
In effect, the more oil those traders bought, the much less the provision of oil in circulation, and the higher the demand for the oil that was obtainable.
Experience the best value in long-term parking at RDU. We offer competitive rates, excellent customer service, and a hassle-free parking experience. Book your spot today long term parking at rdu airport
Продажа табака для кальяна. На сайте вы можете зарезервировать выбранный табак и забрать в магазине https://oglyad.com.ua/vydi-kolpakov-dlya-kurenyya-kak-vibrat-podhodyashhyj-dlya-sebya/
Experience the best value in long-term parking at RDU. We offer competitive rates, excellent customer service, and a hassle-free parking experience. Book your spot today rdu long term parking
Продажа табака для кальяна. На сайте вы можете зарезервировать выбранный табак и забрать в магазине https://vidomosti-ua.com/science/134319
выведение из запоя врачом наркологом выведение из запоя врачом наркологом .
вывод из запоя в екатеринбурге вывод из запоя в екатеринбурге .
Продажа табака для кальяна. На сайте вы можете зарезервировать выбранный табак и забрать в магазине https://vidomosti-ua.com/science/134319
срочный вывод из запоя срочный вывод из запоя .
Experience the best value in long-term parking at RDU. We offer competitive rates, excellent customer service, and a hassle-free parking experience. Book your spot today long term parking rates raleigh durham airport
bs2besd at – blacksprut сайт bs2 best at, зеркало blacksprut darknet
Hello! Need printer parts? We offer reliable components for all printer types: toner cartridges, printheads, fusers, and more.
What makes us special?
Competitive costs
Fast shipping
Professional advice
Order now and ensure flawless performance!
Ремонт и строительство https://sota-servis.com.ua легко! Здесь вы найдёте инструкции, рекомендации, материалы и специалистов для успешного выполнения ваших задач.
Планируете ремонт или строительство https://vodocar.com.ua У нас всё, что нужно: от инструкций и советов до подрядчиков и обзоров материалов. Стройте с нами!
Лучшие советы по строительству https://stroysam.kyiv.ua и ремонту на одном сайте! Найдите вдохновение, изучите обзоры и воплотите свои идеи с профессиональной помощью.
купить диплом в уфе
Полный справочник по строительству https://stroy-portal.kyiv.ua и ремонту: советы, инструкции, дизайн-решения и помощь с выбором материалов и подрядчиков.
Ваш гид в мире строительства https://vitamax.dp.ua и ремонта! Обзоры, практические советы, дизайн-идеи и подбор профессионалов для реализации любых проектов.
Ensuite, rechargez votre compte pour n’importe quel montant et obtenez de l’argent bonus, maintenant vous pouvez jouer et gagner beaucoup d’argent. Inscrivez-vous sur le site officiel de 1xBet et utilisez le code promo pour obtenir un bonus sportif gratuit de 100% jusqu’a 130 €/$.
Code Promo 1xBet
https://www.autora.sk/promo/assets/?code_promo_120.html
Le code promo gratuit 1xBet pour un bonus de bienvenue de 100% jusqu’a €130. Lors de votre inscription, saisissez le code bonus pour profiter de l’offre exclusive 1xBet. Utilisez le code bonus 1xBet dans le champ d’inscription en 2025 et accedez a toutes les sections disponibles. Vous pouvez effectivement obtenir le bonus de bienvenue en utilisant l’apk 1xbet. Telechargez l’apk pour profiter du code promo 1xbet et recevoir un bonus de €/$130 lors de votre inscription.
купить диплом
Полезные советы по покупке диплома о высшем образовании без риска
купить диплом в ишимбае prema-diploms.ru .
Полезные советы по покупке диплома о высшем образовании без риска
Как получить диплом техникума с упрощенным обучением в Москве официально
купить дипломы о высшем образовании цена москва купить дипломы о высшем образовании цена москва .
Как безопасно купить диплом колледжа или ПТУ в России, что важно знать
Как приобрести аттестат о среднем образовании в Москве и других городах
Официальная покупка диплома вуза с сокращенной программой обучения в Москве
купить диплом о среднем образовании в севастополе 4russkiy365-diplomy.ru .
Find the best deals on long-term parking at Sky Harbor Airport. Book online and save on secure, convenient parking near the terminal. Easy shuttle service included sky harbor long term parking cost
Find the best deals on long-term parking at Sky Harbor Airport. Book online and save on secure, convenient parking near the terminal. Easy shuttle service included sky harbor long term parking rates
Find the best deals on long-term parking at Sky Harbor Airport. Book online and save on secure, convenient parking near the terminal. Easy shuttle service included long term parking sky harbor airport
купить диплом о высшем медицинском образовании
Сделайте ремонт https://tfsm.com.ua мечты с нашим сайтом! Советы, инструкции, рейтинг специалистов и новинки строительного рынка для вашего удобства.
Простые решения для ремонта https://teplo.zt.ua и строительства! Идеи дизайна, рекомендации экспертов и проверенные материалы для вашего проекта.
Стройте и ремонтируйте https://suli-company.org.ua с лёгкостью! Полезные статьи, инструкции, советы по выбору материалов и подрядчиков ждут вас здесь.
Портал о ремонте и строительстве https://buildingtips.kyiv.ua с полезными статьями, рекомендациями по выбору материалов и подрядчиков.
Полный гид по строительству https://tsentralnyi.volyn.ua и ремонту: от планирования до отделки. Читайте, выбирайте и стройте с уверенностью и комфортом.
Добрый день, автолюбители!
Ищете опытный автосервис, который специализируется на ремонте выхлопной системы? В «Катализатор» в Ярославле мы предлагаем только самые качественные услуги:
Наши услуги:
Удаление катализатора
Ремонт и замена глушителей
Установка и замена гофры, пламегасителей и резонаторов
Ремонт фланцевых соединений
Компьютерная диагностика
Мы гарантируем профессиональный подход и качественное выполнение работ. Ваш авто в надежных руках!
Не упустите возможность! Узнайте больше о наших услугах и запишитесь на прием на нашем сайте:https://katalizator-yaroslavl.ru/.
Команда профессионалов,
Команда «Катализатор»
купить диплом о высшем образовании во владивостоке 2orik-diploms.ru .
Торговля китайскими товарами – прибыльное дело. Вложенный миллион можно быстро удвоить, а то и утроить. Что для этого нужно? Выбрать свою нишу, найти поставщика в Китае https://vc.ru/u/3307281-ivan08/1316795-kak-postroit-pribylnyi-biznes-na-postavkah-iz-kitaya-rukovodstvo-dlya-novichkov
Торговля китайскими товарами – прибыльное дело. Вложенный миллион можно быстро удвоить, а то и утроить. Что для этого нужно? Выбрать свою нишу, найти поставщика в Китае https://vc.ru/u/3307281-ivan08/1316795-kak-postroit-pribylnyi-biznes-na-postavkah-iz-kitaya-rukovodstvo-dlya-novichkov
Табак для кальяна Al Fakher – самый распространенный табак из Аджмана, ОАЭ. · Табак Adalya – Альтернатива Al Fakher, имеет широкую линейку вкусов и есть очень https://bzs.com.ua/materiali-vigotovlennya-kovpaka-dlya-kurinnya-yakij-obrati/
Табак для кальяна Al Fakher – самый распространенный табак из Аджмана, ОАЭ. · Табак Adalya – Альтернатива Al Fakher, имеет широкую линейку вкусов и есть очень https://gov.ukrbb.net/viewtopic.php?f=3&t=5789&p=17422
Торговля китайскими товарами – прибыльное дело. Вложенный миллион можно быстро удвоить, а то и утроить. Что для этого нужно? Выбрать свою нишу, найти поставщика в Китае https://vc.ru/u/3307281-ivan08/1316795-kak-postroit-pribylnyi-biznes-na-postavkah-iz-kitaya-rukovodstvo-dlya-novichkov
Табак для кальяна Al Fakher – самый распространенный табак из Аджмана, ОАЭ. · Табак Adalya – Альтернатива Al Fakher, имеет широкую линейку вкусов и есть очень https://www.4594.com.ua/list/504842
Полный гид по строительству https://tsentralnyi.volyn.ua и ремонту: от планирования до отделки. Читайте, выбирайте и стройте с уверенностью и комфортом.
bbgate.com – BreakingBad forum chemistry, bbgate
ggdrop promo codes ggdrop
Приветствую на https://bs2best.markets! Мы предлагаем надежные и проверенные покупки в интернете. Ознакомьтесь с нашими статьями о безопасности и легальности. Ваши покупки — наш приоритет!
Tormac.org https://tormac.org – это специализированный торрент-трекер, предназначенный для пользователей Mac-компьютеров. Сайт предоставляет широкий выбор контента, ориентированного на операционные системы macOS и iOS.
Сделайте ремонт https://tfsm.com.ua мечты с нашим сайтом! Советы, инструкции, рейтинг специалистов и новинки строительного рынка для вашего удобства.
A detailed history inter-milan-az.com/ of the Italian football club Inter Milan. From their first Scudetto to their Champions League victory.
tk999 tk999 .
смотреть сериал
skachat mostbet aviator mostbet uz
mostbet lapplication mostbet officiel version mobile
1win рейтинг букмекеров 1win kirish
Сопровождение мужчин — это особая услуга, которая может включать в себя как деловые, так и личные аспекты.
В современном мире многие мужчины ищут профессионалов, которые могут помочь им в различных сферах жизни:
от бизнес-мероприятий до социальных встреч – эскортница Москва
TaskMy.ru – профессиональная помощь в решении задач любого уровня
TaskMy.ru – это надежный сервис, который предлагает качественную помощь в выполнении задач любых направлений: от технических расчётов и программирования до написания текстов и аналитики. Мы работаем быстро, эффективно и ориентированы на ваши требования.
Доверяя TaskMy.ru, вы получаете индивидуальный подход, точное соблюдение сроков и доступные цены. Оставьте свою задачу профессионалам – результат превзойдет ожидания!
MLB Draft Betting https://bettingblog.website Your guide to the world of MLB draft betting. Expert predictions, top odds and detailed analysis will help you increase your chances of success. Bet and win with us!
So whenever you’ll go for such exchange you may draw the quantity as much as you possibly can and the cost will even be less there.
Credit Union Mobile Home Loans https://blogcredit.tech are the perfect solution for buying or refinancing a mobile home. Affordable rates, easy application, and reliable support every step of the way. Take the first step toward your home with us!
Best Forex Trading Course https://blogforex.tech is your key to successful trading. Learn the secrets of professionals, study strategies and learn how to minimize risks. Master Forex easily and effectively!
Предлагаем вам высококачественный тротуарный бордюр – идеальное решение для обрамления дорожек, газонов, цветников и других элементов ландшафтного дизайна.
Наш тротуарный бордюр отличается прочностью, долговечностью и устойчивостью к воздействию внешних факторов, что делает его идеальным выбором для любых условий эксплуатации – купить брусчатку в краснодаре
Tennis betting https://yourmoneyblog.site best odds, predictions and analytics. Explore detailed match reviews, statistics and strategies to make successful bets. Use our tips and win!
Повысьте эффективность своего производства с помощью наших приводных устройств! Наши инновационные устройства позволят вам значительно снизить расходы на электроэнергию,
увеличить производительность оборудования и снизить износ механизмов. Благодаря нашиему оборудованию вы сможете значительно увеличить производственные мощности и улучшить качество выпускаемой продукции – купить частотный преобразователь.
Federal Gov Open Enrollment https://body-balance.online is your chance to upgrade or choose an insurance plan. Easy navigation, expert support, and a wide range of programs will help you make the right choice. Apply now!
Code promo de 1xBet – l’utilisation de ce code vous permettra d’obtenir un bonus de 30% supplementaire, allant jusqu’a 100$. Le bonus est accorde sous la forme de 130% du montant de votre premier depot. Cette offre est reservee aux nouveaux utilisateurs majeurs apres leur inscription. Profitez du code promo pour augmenter votre bonus de bienvenue de 100% a 130%. Les fonds seront credites sur votre solde de jeu, et le bonus devra etre mise sur des paris sportifs. Ce code promo est valable jusqu’au 31 decembre 2025.
Code Promo 1xBet
https://angersnautique.org/fonts/pgs/code_promotionnel_21.html
Le Code promo 1xBet – en utilisant cette combinaison, vous aurez acces a un bonus de 100% sur votre premier depot, pouvant aller jusqu’a 100$. La totalite du bonus credite est disponible uniquement pour les paris dans la section sportive. Vous devrez placer des paris avec une cote minimale de 1,4 et un wager x5. Si toutes les conditions de mise du bonus de bienvenue sont respectees, tous vos gains pourront etre retires sur votre solde principal a la fin de cette promotion.
Le bookmaker 1xBet est l’une des plateformes les plus populaires et leaders du marche. En plus de son interface conviviale et de ses mises a jour regulieres de l’application mobile, la plateforme recompense ses joueurs avec des promotions, des bonus et des cadeaux reguliers. La plupart des utilisateurs, qu’ils soient nouveaux ou reguliers, utilisent activement des codes promo pour jouer. Certains sont reserves a l’inscription pour augmenter le bonus de bienvenue, tandis que d’autres peuvent etre utilises sur la plateforme et se trouvent dans la section “Vitrine des codes promo” du site.
Crypto Funk https://besttodaynew.com is a fresh look at cryptocurrencies. News, trends, guides and analytics for beginners and professionals. Find out how to get the most out of blockchain technology!
ферма обменник – ферма обменник, ферма цц сайт
купить диплом в ханты мансийске
как купить диплом настоящий
купить диплом колледжа в санкт петербурге
купить диплом ргтэу
Чтобы активировать промокод Ramenbet ?BONUSMEN?? при регистрации, выполните следующие действия:
Перейдите на официальный сайт Ramenbet.
При регистрации или входе в личный кабинет найдите специальное поле для промокода.
Введите промокод Ramenbet ?BONUSMEN?? в это поле.
Перейдите в раздел подтверждения регистрации и выберите способ подтверждения: по электронной почте или SMS.
Заполните все обязательные поля с персональными данными.
Подтвердите номер мобильного телефона или адрес электронной почты.
После выполнения этих шагов на ваш счёт будут начислены дополнительные 30 бесплатных вращений для игры в слот Gates of Olympus.
Ramenbet промокод
http://www.avtokladovka.ru/include/pgs/promokod_ramenbet_pri_registracii.html
На сайте представлены около 4500 слотов, которые находятся в разделе «Казино». Азартные игры распределены по категориям на панели навигации. Они позволяют выводить на экран топовые слоты, новинки, автоматы Megaways, Hold and Win, c функцией покупки бонусов или с джекпотом. Также в любой выбранной категории можно воспользоваться дополнительными фильтрами.
Levothyroxine 100 mcg buy http://pharmwithoutadoctorsprescription.com/ Viagra online prescription
Ты точно платишь больше, чем мог бы. Но это можно исправить.
Добро пожаловать в Shopogollic World — место, где скидки находят своих счастливых обладателей. Мы не просто ищем акции, мы собираем лучшее из лучшего:
Товары, которые хочется положить в корзину сразу же.
Скидки, которые заставят тебя пересчитать бюджет.
Предложения, от которых просто невозможно добиться успеха.
Только представляю: умная колонка с Ozon дешевле, чем кофе на неделю. Одежда с AliExpress, которая выглядит как из бутика, но по цене футболки. И хитрые находки с Яндекс Маркета, которые внезапно становятся мастхевами.
Если готов перестать переплачивать и начать покупать умно, то просто подпишись.
https://t.me/ShopogollicWorld
Шопоголический мир. Потому что платить больше — уже не модно.
Купить диплом в Орле
What is the name of this site?
Auto loans from Community Credit Union https://sunnydays100.com are simple, affordable, and great value. Low interest rates and flexible repayment options make it easy to buy a new or used car.
Home Equity Loans https://funnydays1.com How They Work, What Are the Terms and Benefits? Get the full details on how to use your home’s value for financial purposes. Find out more today!
Credit score requirements for FHA loans https://lifeofnews1.com minimum threshold and tips for improving. Find out how to increase your chances of getting a loan, as well as what affects approval. Detailed information for those who want to get a mortgage through FHA.
No Credit Check Loans in Abilene TX https://daynewday1.com is fast access to money without unnecessary checks. Convenient terms, simple application and instant approval. Get financial help when you need it!
Широкий ассортимент пиломатериалов собственного производства. В каталоге представлено все необходимое для строительства, ремонта и отделки пиломатериалы оптом
При одновременном заказе продвижения для двух проектов вы получаете скидку 10%, которая также доступна при первом обращении. Я всегда готова предложить своим клиентам выгодные условия — звоните или пишите в мессенджерах, чтобы обсудить все интересующие вас детали частный сео мастер
Широкий ассортимент пиломатериалов собственного производства. В каталоге представлено все необходимое для строительства, ремонта и отделки пиломатериалы цена
При одновременном заказе продвижения для двух проектов вы получаете скидку 10%, которая также доступна при первом обращении. Я всегда готова предложить своим клиентам выгодные условия — звоните или пишите в мессенджерах, чтобы обсудить все интересующие вас детали https://1st-seo.ru/
Широкий ассортимент пиломатериалов собственного производства. В каталоге представлено все необходимое для строительства, ремонта и отделки пиломатериалы купить
При одновременном заказе продвижения для двух проектов вы получаете скидку 10%, которая также доступна при первом обращении. Я всегда готова предложить своим клиентам выгодные условия — звоните или пишите в мессенджерах, чтобы обсудить все интересующие вас детали частное seo продвижение москва
does cvs sell xenical
выведение из запоя на дому в сочи [url=http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru]http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-sochi23.ru[/url] .
сколько стоит сделать загранпаспорт сколько стоит сделать загранпаспорт .
вывести из запоя в стационаре вывести из запоя в стационаре .
купить аттестат в санкт петербурге
Распродажа новогодней https://giftbox-3.ru упаковки оптом и печать коробки с логотипом в Москве.
Try your luck at 365 taya, where excitement meets reliability! Hundreds of popular games, unique promotions and instant payouts await you.
Когда я впервые открыл этот сайт, впечатление было таким, будто я переступил грань реальности. Здесь каждый спин — это не просто волнение, а эмоция, которую ты открываешь с каждым движением.
Интерфейс удобен, словно ветер судьбы направляет тебя от выбора к выбору. Транзакции, будь то пополнения или выплаты, проходят плавно, как поток воды, и это удивляет. А служба помощи всегда рядом, как верный помощник, который никогда не оставит.
Для меня Казино селектор стал местом, где азарт и искусство соединяются. Здесь каждая минута — это часть истории, которую хочется переживать снова и снова.
cannabis shop in Prague THC chocolate for sale in Prague
buy Cannafood in Prague buy-cannabis-prague.com
Когда я впервые открыл эту платформу, впечатление было таким, будто я переступил грань реальности. Здесь каждый спин — это не просто волнение, а момент, которую ты открываешь с каждым кликом.
Оформление создан для комфорта, словно ветер судьбы направляет тебя от игры к игре. Финансовые движения, будь то депозиты или вывод средств, проходят легко, как поток воды, и это удивляет. А техподдержка всегда отвечает мгновенно, как надежный товарищ, который никогда не разочарует.
Для меня Селектор онлайн стал миром, где игра и вдохновение сплетаются. Здесь каждая игра — это часть истории, которую хочется писать снова и снова.
купить диплом в бийске 2orik-diploms.ru .
Когда я зашёл на этот сайт, впечатление было таким, будто я нашёл что-то особенное. Здесь каждая ставка — это не просто азарт, а эмоция, которую ты открываешь с каждым кликом.
Дизайн создан для комфорта, словно невидимый проводник направляет тебя от выбора к выбору. Финансовые движения, будь то пополнения или выплаты, проходят быстро, как поток воды, и это удивляет. А поддержка всегда рядом, как друг, который никогда не подведёт.
Для меня Казино селектор стал местом, где игра и вдохновение соединяются. Здесь каждая игра — это часть картины, которую хочется писать снова и снова.
Paolo Maldini’s biography paolo-maldini-az org photo, defender 2019, personal life, Instagram, Milan, salary, religion and news.
Biography of Spanish footballer Xavi Hernandez https://xavi-hernandez-az.com coaching career, Barcelona statistics, matches with Iniesta and Messi, Guardiola’s influence, goals, youth training, dismissal as Barcelona coach, personal life and 2024 updates.
Biography of football legend Pele https://pele-az.com personal life, ex-spouses, children and current wife Maria Aoki. A reminder of his legendary career, goals and special style of play, as well as successful performances in the national team.
Discover the life of Sergio Busquets sergio-busquets-az.org/ his parents, his partner Elena Galera Moron, his sons, his club career, his achievements with Spain and the latest news for 2024.
Biography of Brazilian footballer Ronaldinho http://ronaldinho-az.org personal life, son’s contract, current position. Club career, free kick goals, dribbling, jersey number, Ballon d’Or award, prison sentence. Latest news of 2024.
https://telegra.ph/Why-the-Patek-Philippe-Seal-Matters-12-28
Biography of Spanish footballer jordi-alba-az.org/ Jordi Alba: Left back for Barcelona and the Spanish national team, trained at the academies of Barcelona and Valencia.
Biography of footballer casemiro-az org Casemiro: personal life, wife and children. Career, statistics, salary at Real Madrid, Brazil national team, transfer fee, position, transfer to Manchester United and the latest news for 2024.
Welcome to the fan site memphis depay az org dedicated to the active Dutch footballer Memphis Depay, his career path with clubs and the Dutch national team. Tattoos, personal life and news.
Купить диплом техникума, колледжа в Томске
manga update Naruto free online manga series Chainsaw Man free online
I attempt to be sure that I combine the color palettes up and don’t submit seems to be from the same order or class across consecutive days, which can be a bit of a problem typically (especially when there’s a species I’m actually desirous to strive) but I’m fortunate within the sense there are hundreds of thousands of arthropod species out there to select from so I suppose I’m never quick on choices!
купить диплом мму prema-diploms.ru .
диплом в казани купить
sky pharmacy Online Pharmacy No Prescription Doxycycline hyclate 100mg
Various workers at residence provides and grocery chains had initially complained that customers were not practising social distancing suggestions, and that corporations were not adequately providing the required equipment and financial safety needed to attenuate the risk of exposure to the virus, nor have enough of a security web to stay home should they turn out to be contaminated with the virus.
вывод из запоя цена вывод из запоя цена .
supreme suppliersmumbaiindia Allpills shop
Alt coin cc – Альткоин обменник крипты, Alt coin bestchange
Сколько стоит получить диплом высшего и среднего образования легально?
Вопросы и ответы: можно ли быстро купить диплом старого образца?
купить диплом о среднем образовании
Cialis without prescription http://edmedicationsprescription.com/ Tadalafil generic vs cialis
view publisher site https://abacusmarket.me
canada pharmacy
купить диплом типографском бланке
Nicholas Jackson nicolas jackson is a Senegalese professional footballer who has taken the football world by storm with his play and achievements.
Biography Pau Victor pau-victor is a Spanish footballer who started in the lower divisions. Thanks to hard work, he got into a good youth team at FC Barcelona. He played for Girona and has good statistics.
Biography of Jamie Bynoe-Gittens jamie gittens a winger for German club Borussia Dortmund, and an English footballer.
cheap drugs
купить диплом о прохождении курсов
капельница от похмелья купить http://www.vyvod-iz-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod11.ru .
Still, it’s had a large impact on Finland, where more than 100,000 models of the Skoda Octavia have sold.
можно купить диплом высшем образовании
Biography of Austrian jorginho footballer Arnautovic Marko – games at FC Werder Bremen and Internationale, market value, achievements. Personal life, conflicts, rumors and latest news.
Biography of Austrian footballer marko-arnautovic-az.org Arnautovic Marko – games at FC Werder Bremen and Internationale, market value, achievements. Personal life, conflicts, rumors and latest news.
Biography of Federico Chiesa http://federico-chiesa-az.org Italian winger for Juventus and the Italian national team. Career, Fiorentina, Euro 2024, transfer to Liverpool, family, wife Lucia Bramanti.
Aurelien Tchouameni’s aurelien-tchouameni-az.org biography: personal life, date of birth, parents’ jobs, statistics at Real Madrid and Monaco, position, jersey number, 2024 updates.
Купить диплом в Орле
Biography of Dayot Upamecano dayot-upamecano-az org Bayern star, France national team hero, early career start, Euro play-off participation, personal life and football news for 2025.
0
Момент озарения в 2024 — Даже самый крутой дизайн, продуманный под мобильные устройства, который действительно вовлекает и влияет wlad2
0
Момент озарения в 2024 — Даже самый крутой дизайн, продуманный под мобильные устройства, который действительно вовлекает и влияет Блог
As of twenty-two July 2008 the value of the Zimbabwe greenback fell to approximately Z$688 billion per US$1, or Z$688 trillion in pre-August 2006 Zimbabwean dollars.
диплом о высшем образовании старого образца купить диплом о высшем образовании старого образца купить .
0
Момент озарения в 2024 — Даже самый крутой дизайн, продуманный под мобильные устройства, который действительно вовлекает и влияет Блог
купить диплом бакалавра в пскове prema-diploms.ru .
купить диплом образования в омске купить диплом образования в омске .
купить в туле диплом
Хотите создать идеальное покрытие для вашего участка или дорожного покрытия? Тогдаотсев идеально подойдет для вас!
Наш высококачественный отсева щебня обеспечит прочность, долговечность и надежность вашего покрытия. Благодаря правильной фракции отсева,
он обладает отличной укладываемостью и прекрасно дренирует воду, что делает его идеальным выбором для любых работ – купить щебень.
Всё, что нужно знать о покупке аттестата о среднем образовании
Нужен ремонт техники чин почин скачать все услуги для вашего дома в одном месте! Выбирайте мастеров для ремонта, уборки или сантехнических работ. Качественный сервис, прозрачные цены и удобство использования.
Tobey Maguire’s tobey-maguire-az.com/ biography: personal life, memories of him, friendship with Leonardo DiCaprio, divorce from ex-wife. Role in Spider-Man films, career now.
Biography of Spanish footballer Dani Carvajal https://dani-carvajal-az.com personal life, marriage to Joselu and twin sisters. Performances at the Euro for Real Madrid and the Spanish national team.
Biography of footballer http://iker-casillas-az.com Iker Casillas: personal life, separation from ex-wife Sara Carbonero.
купить диплом в ульяновске
вывод из запоя на дому нижний вывод из запоя на дому нижний .
SportyBet betting SportyBet betting .
сделать капельницу на дому от алкоголя сделать капельницу на дому от алкоголя .
Где и как купить диплом о высшем образовании без лишних рисков
купить аттестат 11 класса
secure ftp client IP Camera Software Software
online no script pharmacy
viagra without prescription.
Outlaw, Kofi (March 19, 2024).
диплом купить сколько стоит
Как приобрести аттестат о среднем образовании в Москве и других городах
Купить старые дипломы
“Ищете качественный кирпич напрямую от производителя? https://Muravey61.ru – ваш надежный поставщик строительных материалов в регионе! Мы предлагаем кирпич высшего качества по доступным ценам прямо с завода. Доставка точно в срок, широкий ассортимент, и гарантированное качество – всё, что нужно для вашего строительства. Закажите у нас и убедитесь сами, что с нами строить легко!”
Machine Washable: The towel set will be machine washed with chilly water.
There are two advantages of having a mutual fund theorem.
Online medicines On Line Pharmacy canadian pharmacy no prescription Levitra without prescription
On his personal account, Melville shared a post in assist of his marketing campaign from Monica Crowley, assistant secretary for public affairs for the U.S.
The entire providers that OnStar provides are a results of a number of of these applied sciences working together.
купить диплом мму prema-diploms.ru .
Как официально купить диплом вуза с упрощенным обучением в Москве
купить диплом в елабуге [url=https://2orik-diploms.ru/]2orik-diploms.ru[/url] .
Kind the members into groups of two and have every crew come up with silly made-up country names.
onlinepharmacy Viagra without prescription.
pharmacy no prescripition Online Pharmacy Zanaflex
https://telegra.ph/Exploring-the-Richard-Mille-RM-67-01-12-28
Лучшие автозвук со всего мира у нас. Оригинальная продукция. Гарантия 1 год. Hertz,audison, jbl, infinity, focal, alpine, pioneer Focal автозвук
Лучшие автозвук со всего мира у нас. Оригинальная продукция. Гарантия 1 год. Hertz,audison, jbl, infinity, focal, alpine, pioneer Магазин автозвука
Лучшие автозвук со всего мира у нас. Оригинальная продукция. Гарантия 1 год. Hertz,audison, jbl, infinity, focal, alpine, pioneer Кузница автозвука
Now you can’t find a person https://formula1-az.com who hasn’t heard of Formula 1. Today it is one of the most prestigious and popular sports on the planet.
Biography of Zendaya Coleman zendaya-maree-az.com (Zendaya): modeling career, music and cinema, details of her personal life, ex-boyfriend Jacob Elordi, romance with Tom Holland.
Welcome to the world of Neymar http://neymar-azerbaycan.com a fan site dedicated to the great footballer. Learn all about his career, achievements and unique playing style.
Welcome to the main page karim-benzema of the fansite dedicated to the world football star Karim Benzema. Learn all about his incredible career, incredible achievements and phenomenal skills.
Biography of British actress emily blunt az com Emily Blunt: personal life, dating and relationship with her husband John Krasinski, raising children.
https://odnazhdyvskazke-tv.ru
This car, also known as a “40-series,” would have been seen on the roads in 1938.
Bally graces the fashion week with a dapper outfit, combining a dove gray suit jacket with an iridium pair of pants.
Tadalafil cialis from india http://edmedicationsprescription.com/ Minocycline
Hybrid variations usually run several thousand dollars more than typical variations of the identical automobile.
Как не попасть впросак при покупке диплома колледжа или ПТУ в России
Быстрое обучение и получение диплома магистра – возможно ли это?
Nonetheless, on April 16, the Senate did not overturn the veto of the Governor.
The era belongs to those who have money and lots of money.
Their capital gains terms on stocks are simply added to investors IT.
купить аттестат за 9 класс 2021
Foreigners can invest indirectly in A stocks listed in Shanghai and Shenzhen exchanges, for this authority is slowly starting up channels.
online pharmacy viagra
скупка золота спб дорого цена сколько стоит скупка золота
Only some of the figured glasses may be toughened, dependent on the depth of the embossed pattern.
Оперативная помощь на дороге https://angeldorog.by услуги эвакуатора, грузовой и легковой шиномонтаж, а также грузоперевозки фурами по доступным ценам. Работаем круглосуточно, быстро реагируем и гарантируем надежность. Звоните в любое время – решим вашу проблему!
Webcam monitoring software CMS IP Camera
Find out all about Kylie Jenner kylie-jenner at Kylie Jenner, the ultimate fan site for the latest updates on her fashion line, beauty tips and personal life.
купить диплом образования
Player with most shots on target” particularly Andy Cook with 25; from these he has scored 8 objectives. The NW Night Mail stories that “George Williams hopes his Barrow AFC mortgage deal will probably be extended and has been boosted by the confirmation that he has escaped serious damage.
купить диплом ссср о высшем образовании
капельница на дому круглосуточно капельница на дому круглосуточно .
вывод из запоя стационар вывод из запоя стационар .
In the daily update, all investors and traders are not highly for these Share Market Tips, people using the excellent information on internet is an intelligent idea.
This game has simple guidelines and is perfect for the whole family.
Guantee that whoever is handling this process – whether or not you or a workshop chair – has a conversation early in the process with the SIGPLAN Vice Chair to get clear on SIGPLAN’s expectations for the way workshop PCs are formed and vetted.
сколько стоит купить аттестат 11 класса
Rena Fobb Memorial service for Rena Jane Fobb, age 46, of Frederick, will be at 2:00 p.m.
диплом ветеринарного фельдшера купить
generator life story — это надежный способ автоматизировать процесс создания текстов.
healthy man viagra scam
Watching the prices of different coins is like a roller coaster!
https://t.me/cryptonetlake
Купить диплом Тюмень
1Win является лучшим букмекером и казино в 2024 году. В интернете множество площадок, в которых есть ставки на спорт, но лидирующую позицию занимает 1Вин. Для пользователей гарантированы честные условия, высокие коэффициенты и качественное обслуживание. На официальном сайте 1Вин доступны быстрые выплаты, кэшбек до 30% и супер бонус в размере 500% http://msfo-soft.ru/msfo/forum/messages/forum31/topic15477/message393395/?result=new#message393395
Usa Pharmacy No Script Cialis generic 20 mg online pharmacy without a prescription
1Win является лучшим букмекером и казино в 2024 году. В интернете множество площадок, в которых есть ставки на спорт, но лидирующую позицию занимает 1Вин. Для пользователей гарантированы честные условия, высокие коэффициенты и качественное обслуживание. На официальном сайте 1Вин доступны быстрые выплаты, кэшбек до 30% и супер бонус в размере 500% http://jamsun.net/doku.php?id=%20%D0%9A%D0%B0%D0%BA%20%D0%B2%D1%8B%D0%B2%D0%B5%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B8%20%D0%B4%D0%B5%D0%BD%D1%8C%D0%B3%D0%B8%20%D1%81%201win%20%D0%BA%D0%B0%D0%B7%D0%B8%D0%BD%D0%BE
В основе сюжета лежит необычная концепция двух миров — сказочного и реального. Всё начинается в волшебной стране, где Злая Королева, устав от счастья и благополучия своих соседей, накладывает страшное проклятие, вырвав героев из их привычных сказочных миров и закинув их в место, о котором они и не мечтали https://odnazhdyvskazke-tv.ru
Later that year, Pollock represented Canada on the well-known Hastings 1895 chess tournament, received by Harry Nelson Pillsbury.
Many micro-cap and nano-cap stocks are traded over-the-counter with their prices quoted on the OTCBB, OTC Link LLC, or the Pink Sheets.
Парадокс, но купить диплом кандидата наук оказалось не так и сложно
Hol dir täglich deine kostenlosen slotpark bonus code und genieße die besten Slots! Kein Aufwand, kein Stress – nur Spaß.
Immerse yourself in the world of Gigi Hadid gigi-hadid-azerbaijan.com through our dedicated website. Explore the latest news, highlights, exclusive interviews and in-depth features about her fashion endeavors, personal life and charitable efforts.
Biography of American professional gervonta-davis-az.com/ boxer Gervonta Davis: career highlights, weight, records, famous fights, personal life, controversies and latest 2024 updates.
Discover the world of Brad Pitt brad pitt az com with our dedicated website, offering extensive coverage of his illustrious career, upcoming projects, and personal endeavors.
hire a tesla car tesla for rent
У нас вы можете купить айфоны https://vk.com/crazy_humor01 оптом по самым лучшим ценам. Оригинальные смартфоны Apple с гарантией качества. Постоянное наличие популярных моделей.
диплом купить в невинномысске
Компания 1хБет предоставляет всем 100% бонус за первый депозит до 32500 рублей (или эквивалент в другой валюте по актуальному курсу). Кроме того, вас ожидает приветственный пакет в 1xBet казино до €1950 +150 фриспинов для игры в слоты и игровые автоматы. 1xBet — это одна из самых популярных и надежных платформ, которая предлагает уникальные возможности и привлекательные бонусы для своих пользователей. Независимо от того, являетесь ли вы новичком в мире ставок или опытным игроком, промокоды 1xBet — это отличный способ повысить свои шансы на выигрыш.
Промокод 1xBet
http://sdelaisebe.ru/application/pages/1xbet_besplatnuy_promokod_pri_registracii_bonus_6500_rubley.html
Промокод 1хБет на сегодня – предоставляет вам возможность получить 100%-й бонус до 32 500 ? и Приветственный пакет до 1500 евро + 150 фриспинов для игры в разделе азартных игр 1хБет. 1xBet — это известная онлайн-платформа для ставок, которая славится своими щедрыми бонусами и привлекательными предложениями. Если вы ищете уникальный игровой опыт и дополнительные шансы на успех, то бонусы 1xBet станут отличным выбором для вас.
Бонусы являются одной из главных особенностей, которые делают 1xBet привлекательной для множества игроков. Как новый, так и постоянный пользователь, вы сможете воспользоваться различными видами бонусов, которые помогут увеличить ваши шансы на выигрыш. От приветственных бонусов до регулярных акций, 1xBet предлагает множество вариантов, чтобы удовлетворить ваши потребности и предпочтения.
Один из самых популярных бонусов, предоставляемых 1xBet, – это приветственный бонус для новых игроков. Как только вы зарегистрируетесь на платформе, вам будет предложен щедрый приветственный пакет, который включает в себя бонус на первый депозит. Это означает, что вы получите дополнительные средства на свой игровой счет, чтобы увеличить свои возможности для ставок. Такой бонус является отличным стартом в вашем игровом путешествии и помогает вам исследовать различные игры и спортивные события.
Квартирный переезд https://spb-gruzoperevozka.ru с грузчиками быстро и качественно! Упакуем, вынесем, перевезем и разместим вещи на новом месте. Надежная команда, аккуратность и доступные тарифы.
Пошаговая инструкция по официальной покупке диплома о высшем образовании
нужен диплом о высшем образовании быстро нужен диплом о высшем образовании быстро .
Наша компания предлагает сетка тканая производства Северсталь метиз ОСПАЗ со склада
г.Орел. В наличии огромный ассортиментсетка тканая н/у.
Вы можете купить сетка тканая н/у ГОСТ светлую и оцинкованную.
У нас всегда в наличии огромный выбор сетка тканая н/у ГОСТ 3826, цены от производителя.
Продажа сетка тканая ГОСТ 3187-76 оптом и в розницу со склада г.Орел.
In economics, hyperinflation is a really excessive and usually accelerating inflation.
модульный стол для переговоров стол для переговоров длинный
купить диплом образования в барнауле 2orik-diploms.ru .
non prescription india pharmacy Pfizer viagra price
Откройте для себя последние http://kraftsir.ru новости, аналитику и экспертные обзоры о спорте и ставках. Узнайте о лучших стратегиях ставок, следите за актуальными событиями в мире спорта и получите все необходимые инструменты для успешных ставок.
диплом купить о высшем образовании
kinogo зарубежные сериалы киного фильмы о космосе
киного смотреть бесплатно kinogo фантастические фильмы
Можно ли купить аттестат о среднем образовании? Основные рекомендации
купить диплом ветеринара купить диплом ветеринара .
На scandalose.ru предоставлены лучшие промокоды и скидочные предложения для интернет-магазинов и сервисов. С нами экономия становится доступной для каждого, кто ценит разумный подход к скидкам промокод scloud
На scandalose.ru предоставлены лучшие промокоды и скидочные предложения для интернет-магазинов и сервисов. С нами экономия становится доступной для каждого, кто ценит разумный подход к скидкам промокод joymoney
дом интернат в симферополе http://www.svarog.forum24.ru/?1-1-0-00000039-000-0-0-1736936480 .
пансионат для пожилых крым пансионат для пожилых крым .
На scandalose.ru предоставлены лучшие промокоды и скидочные предложения для интернет-магазинов и сервисов. С нами экономия становится доступной для каждого, кто ценит разумный подход к скидкам промокод mircli
Dubai journey company originates up with a whole lot of gives along with plans so you’re in a position to chill out even when you have enterprise enterprise proposals as the first objective.
Как спилить дерево на участке в нужном направлении падения с помощью бензопилы, топора и веревки (по естественному наклону и против него) и чего ни в коем случае нельзя делать? Техника безопасности в процессе валки деревьев: https://dzen.ru/a/Z4qBIK-a_ERTqyYy
Contemporary is cool and clean and can be as casual or as elegant as you please.
Принимать финансовые решения может быть сложно. Но с нашим каталогом финансовых продуктов это стало проще, чем когда-либо!
дебетовая карта с функцией начисления процентов на остаток
Мы собрали все лучшие финансовые продукты в одном месте, чтобы вы могли легко сравнить их и найти те, которые подходят именно вам. Наши экспертные обзоры и рейтинги помогут вам принять обоснованное решение, соответствующее вашим уникальным потребностям.
Независимо от того, ищете ли вы кредит наличными, дебетовую карту или инвестиционный счет, наш каталог финансовых продуктов поможет вам сделать правильный выбор.
The data in this e book has been absolutely researched by Genealogists and Household Historians.
Entdecken Sie die Deutsche Online Casinos fur ein faires Spielerlebnis. Finden Sie heraus, welche deutschen Online Casinos die besten Bonusangebote Mobil-freundliche Casinos
Entdecken Sie die Deutsche Online Casinos fur ein faires Spielerlebnis. Finden Sie heraus, welche deutschen Online Casinos die besten Bonusangebote 15 € Bonus Ohne Einzahlung
Новости игровой индустрии depcult35.ru/ аналитику и обзоры самых популярных игр. Читайте о новинках, трендах и получайте полезные советы для улучшения игрового процесса.
Подробные стратегии покера fatcurus.ru/ и анализ турниров: эффективные тактики, разбор раздач и ключевые советы для улучшения игры. Только практическая информация для выигрышей.
Все о мире гэмблинга https://minsvyazcc.ru обзоры казино, игры, стратегии и последние новости индустрии. Узнайте о новых слотах, бонусах и тенденциях в азартных играх.
Entdecken Sie die Deutsche Online Casinos fur ein faires Spielerlebnis. Finden Sie heraus, welche deutschen Online Casinos die besten Bonusangebote Vulkan Spiele Casino
These are the instruments people use to create and produce paperwork, displays, databases, charts and graphs.
OR Realty — это ваш надежный партнер в мире недвижимости. Мы предлагаем большой выбор квартир, домов и коммерческих объектов по выгодным условиям. Наши специалисты помогут вам найти идеальный вариант, соответствующий вашим потребностям. Надежность, качество и удобство — вот что делает OR Realty лучшим выбором. Обращайтесь!
purchase tamoxifen citrate online Canadian Pharmacy Levitra
Cheap medications online http://edmedicationsprescription.com/ Kwikmed
online pharmacy
путаны калуги девушки по вызову в калуге
купить диплом гасу prema-diploms.ru .
диплом в кирове купить
Этот обзорный материал предоставляет информационно насыщенные данные, касающиеся актуальных тем. Мы стремимся сделать информацию доступной и структурированной, чтобы читатели могли легко ориентироваться в наших выводах. Познайте новое с нашим обзором!
Разобраться лучше – https://nakroklinikatest.ru/
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Получить больше информации – https://nakroklinikatest.ru/
Code bonus 1xBet gratuit utilisez ce code et vous recevrez un bonus de 130€. Le bookmaker 1xbet offre a ses nouveaux clients un bonus de 100% sur le sport et le casino. Inscrivez-vous avec un code promotionnel et obtenez le bonus maximum des maintenant.
Code Promo 1xBet
https://ventures-me.com/wp-content/pgs/?code_promo_gratuit_1.html
Le code promo 1xBet pour aujourd’hui 2025. Lorsque vous vous inscrivez, utilisez-le et vous beneficierez d’un bonus de bienvenue gratuit de 130$. Tout d’abord, il est important de noter que les codes promotionnels peuvent varier. Certains codes ne sont disponibles qu’une seule fois et uniquement dans certaines conditions specifiques. D’autres codes sont permanents et peuvent etre utilises regulierement par les joueurs pour ameliorer leurs performances de jeu.
Gaminator online
Оптимизирован для смартфонов
Казино с лицензией, дающие слоты
игровые аппараты с реальным выводом денег
https://cash4winner.com/l/67816cee174262243c0008bf
диплом купить в омске
купить диплом о высшем образовании ссср
Эта статья полна интересного контента, который побудит вас исследовать новые горизонты. Мы собрали полезные факты и удивительные истории, которые обогащают ваше понимание темы. Читайте, погружайтесь в детали и наслаждайтесь процессом изучения!
Детальнее – https://nakroklinikatest.ru/
mostbet u mostbet бездепозитный бонус промокод
canadian pharmacy 24h
1с предприятие купить программу https://www.svarog.forum24.ru/?1-0-0-00000330-000-0-0 .
1win ckachat plinko 1win
программы фирмы 1с программы фирмы 1с .
Одноразовый номер телефона — это временный номер, который можно использовать для получения SMS-сообщений или звонков. Эти номера могут быть полезны, когда вам нужно зарегистрироваться на сайте, не желая раскрывать свой персональный номер. Также многие используют такие номера для подтверждения аккаунтов на различных сервисах или для того, чтобы избежать спама и нежелательных звонков купить номер для телеграмма
Для игроков важно понимать, какие факторы влияют на безопасность и надежность таких сервисов. От удобства интерфейса до наличия лицензий и поддержки пользователей https://imoodle.win/index.php?title=%20%D0%9F%D1%80%D0%B5%D0%B8%D0%BC%D1%83%D1%89%D0%B5%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B2%D0%B0%20%D0%B1%D0%BE%D0%BD%D1%83%D1%81%D0%BE%D0%B2%20%D0%B4%D0%BB%D1%8F%20%D0%B8%D0%B3%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%B2%20%D0%B2%20%D0%B0%D0%B7%D0%B0%D1%80%D1%82%D0%BD%D1%8B%D1%85%20%D0%B8%D0%B3%D1%80%D0%B0%D1%85
Одноразовый номер телефона — это временный номер, который можно использовать для получения SMS-сообщений или звонков. Эти номера могут быть полезны, когда вам нужно зарегистрироваться на сайте, не желая раскрывать свой персональный номер. Также многие используют такие номера для подтверждения аккаунтов на различных сервисах или для того, чтобы избежать спама и нежелательных звонков купить номер США
Для игроков важно понимать, какие факторы влияют на безопасность и надежность таких сервисов. От удобства интерфейса до наличия лицензий и поддержки пользователей http://msfo-soft.ru/msfo/forum/messages/forum24/topic15511/message395391/?result=new#message395391
Одноразовый номер телефона — это временный номер, который можно использовать для получения SMS-сообщений или звонков. Эти номера могут быть полезны, когда вам нужно зарегистрироваться на сайте, не желая раскрывать свой персональный номер. Также многие используют такие номера для подтверждения аккаунтов на различных сервисах или для того, чтобы избежать спама и нежелательных звонков купить номер телефона для регистрации
Для игроков важно понимать, какие факторы влияют на безопасность и надежность таких сервисов. От удобства интерфейса до наличия лицензий и поддержки пользователей http://edengardenbarandgrill.com/forum/donec-eu-elit/7543-1win#7544
Как получить диплом стоматолога быстро и официально
Можно ли купить аттестат о среднем образовании, основные моменты и вопросы
If you don’t report for as much as 60 days, you could possibly be liable for as much as $500.
S&P Futures trade with a multiplier, sized to correspond to $250 per point per contract.
mostbet aviator game mostbet mobile
On 25 September 2010, Kawashima stored his first clear sheet in a 1-0 win over Charleroi, Lierse’s first league win of the season.
увлекательные стратегии mexatrondiy ru репортажи с турниров и последние новости покера. Станьте мастером игры, окунитесь в мир азартных карт с нашим сайтом
узнайте последние новости umra tour киберспорта, анализ турниров и игровые стратегии в Азербайджане. Присоединяйтесь к нам, чтобы побеждать в мире киберспорта.
Актуальные и свежие новости https://gastromoroz.ru спорта и казино. Узнайте актуальные спортивные события, анализы матчей, советы по ставкам, обзоры казино игр и стратегии.
Как получить диплом стоматолога быстро и официально
Alpha males and alpha females lead the pack, which often contains their offspring and at occasions, a couple of different wolves.
купить диплом колледжа в казани
Chew was raised in a Quaker family, however he broke with Quaker tradition in 1741, when he agreed with his father, who had instructed a grand jury in New Castle, Delaware on the lawfulness of resistance to an armed drive.
Harvey, Paul (1 March 2013).
выведение из запоя воронеж стационар выведение из запоя воронеж стационар .
There is a bistro on board that serves snack bar-model dishes.
According to its phrases, Reliance would hold a 51 in the merged firm in money and inventory, while Disney would own the remaining 49.
The fascinating aspect of cryptocurrency is that it is the sole platform and media that allows anyone to potentially become the next Michael J. Saylor anywhere in the world.
To derive maximum profit from the above mentioned suggestions, one should master the use of those recommendations on model test papers or previous year papers.
One expert on finance and business once said that if you think financial education is a waste of time and money, try ignorance.
скидки парка с натуральным мехом
Amazon employees again went on strike over protected working conditions on Monday 6 April in Staten Island.
Then arrange theme sites and get compensated through reputable sites.
April 29, 1907, Cheboygan, Cheboygan County, Michigan, USA; d.
купить диплом косметолога
купить аттестаты за 11 класс с егэ 2orik-diploms.ru .
A personalized content material fabric technique connects collectively at the side of your customers and permits generate extra ROI than standard content material fabric.
диплом о высшем техническом образовании купить
купить диплом академии долорес prema-diploms.ru .
Like large-brother STS, the 2008 CTS presents all-wheel drive in its place to rear drive.
Evidently the bridal apparel trade feels justified in overcharging for dresses with synthetic fabric, shoddy construction with unfinished seams and no lining.
As with the crawl trick, you want a provide of treats to teach your canine to roll over.
Protecting the paint with clear coat helps protect the metal underneath even more.
Polarmeds usa pharmacy no script Avanafil
pharmacy rx one
киного фильмы для компьютера kinogo сериалы про врачей
kinogo сериалы по странам киного сериалы по странам
Качественные дженерики купить на сайте https://apteka-sm.ru/ быстрая доставка
выгодные цены
Providers for J. P. Robinson 46, will likely be at 2 p.m.
Виртуальные номера становятся все более популярными как среди частных пользователей, так и в бизнес-среде. Эти номера позволяют принимать звонки и SMS, а также использовать их для регистрации в различных сервисах без необходимости привязываться к физическому номеру телефона. Технология основывается на использовании IP-телефонии, что дает пользователю массу преимуществ по сравнению с традиционными номерами купить номер Италии
Виртуальные номера становятся все более популярными как среди частных пользователей, так и в бизнес-среде. Эти номера позволяют принимать звонки и SMS, а также использовать их для регистрации в различных сервисах без необходимости привязываться к физическому номеру телефона. Технология основывается на использовании IP-телефонии, что дает пользователю массу преимуществ по сравнению с традиционными номерами купить номер для телеграмма
Как официально купить диплом вуза с упрощенным обучением в Москве
Виртуальные номера становятся все более популярными как среди частных пользователей, так и в бизнес-среде. Эти номера позволяют принимать звонки и SMS, а также использовать их для регистрации в различных сервисах без необходимости привязываться к физическому номеру телефона. Технология основывается на использовании IP-телефонии, что дает пользователю массу преимуществ по сравнению с традиционными номерами купить номер телефона для регистрации
We specialize in creating the perfect connection between talented girls and the leading companies in the fashion industry.
For more information, follow the link вебкам информация
Our stylists help models reach their potential by providing training and support at every stage. We also offer services for agencies looking to find the best talent for their projects.
Crypto trading requires a lot of patience and strategy.
https://t.me/s/cryptonetlake
Реально ли приобрести диплом стоматолога? Основные шаги
canadian pharmacy Canadian rx
купить диплом советского образца в москве
киного фильмы для вечеринки kinogo 720p
A modern AI tool ai undressing for working with images. Learn more about its features, capabilities and applications. Full privacy control and ease of use will ensure comfortable interaction.
At the moment you get the telephone at no cost, and the call solely prices a dime per minute.
Продажа качественных дженериков для повышения потенции на сайте https://jeneri.ru/
доставка во все регионы России
Полезные советы по безопасной покупке диплома о высшем образовании
купил аттестат купил аттестат .
Of course it will put you in panic and you might have to return without experiencing some of the amazing things there.
Продажа дженериков с доставкой https://men-doktor.ru/ скидки для постоянных клиентов
2025 year jogo do tigrinho ofical site 777 tigrinho
2025 year jogo do tigrinho ofical site 777 tigrinho
Viagara http://usapharmacynoscript.com/ Suhagra
2025 year jogo do tigrinho ofical site 777 tigrinho
Грузоперевозки Минск по лучшей цене. Мы оказываем услугу грузоперевозок и грузового такси в Минске. График работы 24/7. Делаем квартирные, офисные и дачные переезды в Минске, по Беларуси, в Россию, и страны СНГ Грузовое такси по Беларуси
Грузоперевозки Минск по лучшей цене. Мы оказываем услугу грузоперевозок и грузового такси в Минске. График работы 24/7. Делаем квартирные, офисные и дачные переезды в Минске, по Беларуси, в Россию, и страны СНГ Эвакуация мотоцикла
Грузоперевозки Минск по лучшей цене. Мы оказываем услугу грузоперевозок и грузового такси в Минске. График работы 24/7. Делаем квартирные, офисные и дачные переезды в Минске, по Беларуси, в Россию, и страны СНГ Перевозка грузов
вывод из запоя в стационаре нижний новгород вывод из запоя в стационаре нижний новгород .
вывод из запоя в стационаре вывод из запоя в стационаре .
Biography of footballer Joshua Kimmich https://jimmy-butler-az.org personal life, wife and children. Career at Bayern Munich, statistics for Germany, work with Pep Guardiola, negotiations with Barcelona. Vice-captain at Euro 2024. Latest news for 2024.
Djokovic’s tennis career novak djokovic has been marked by numerous Grand Slam titles, showcasing his style of play. He has been a constant competitor to Rafael Nadal and Roger Federer.
Откройте мир мобильных игр games ru рейтинги лучших проектов, тренды, советы и гайды. Играйте в популярные шутеры, RPG, стратегии и песочницы прямо на телефоне!
Свежие футбольные новости vseofootball.ru обзоры матчей, Лига чемпионов, статистика и лучшие букмекерские бонусы для ставок на спорт.
Все о Тони Кроосе toni-kroos.ru/ на одном сайте: биография, актуальные новости, детальная статистика и эксклюзивные обновления о немецкой футбольной звезде. Присоединяйтесь к сообществу фанатов и будьте в курсе всех событий, связанных с Кроосом!
Качественные дженерики для повышения потенции на сайте https://moscow-viagra.ru/ бесплатная
доставка отличное качество дженериков от производителя
Сколько стоит диплом высшего и среднего образования и как это происходит?
вывод из запоя круглосуточно [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare23.ru]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url] .
вывод из запоя в наркологическом стационаре самары [url=https://www.vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara23.ru]https://www.vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-samara23.ru[/url] .
вывод из запоя в стационаре нижний новгород [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare22.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре нижний новгород[/url] .
сайт посвященный Aviator Slot aviator slot Узнайте последние новости, эффективные стратегии, советы по выигрышу и информацию о бонусах.
In Jodo Do Tigrinho online slots, every spin is a step towards victory! Incredible graphics, exciting themes and many bonuses await you. Fortune favors the brave – try your hand and discover the world of winnings with Tigrinho!
Cryptocurrency trading service bitqt with AI is automation and efficiency. Artificial intelligence monitors market dynamics, reduces risks and optimizes transactions. The perfect solution for beginners and professionals.
online pharmacy
Please make sure you discover a vet that specializes in bulldog sort breeders or at least in brachycephalic sort canine breeds.
диплом технолога купить
Купить качественные дженерики вы сможете на нашем сайте https://my-viagra-shop.ru/
быстрая доставка гарантированное качество
диплом ссср купить
Unlock the benefits of improved hearing and cognitive support with how to lower glucose level naturally – buy now for a transformative health experience. Don’t miss the opportunity to enhance your auditory wellness; purchase SonoVive today and take the first step toward better hearing clarity.
Mostbet is a well-known platform providing a diverse selection of betting and casino games for users in Bangladesh mostbet-2bd.com
купить техникум купить техникум .
Mostbet is a well-known platform providing a diverse selection of betting and casino games for users in Bangladesh Mostbet BD Login
Four corners pharmacy new zealand candian no script pharmacy Non prescription prozac
Mostbet is a well-known platform providing a diverse selection of betting and casino games for users in Bangladesh Mostbet BD Login
Удобный интерфейс позволяет быстро находить нужные данные, а дополнительные функции, такие как сравнение курсов в разных банках и отображение исторических графиков, делают использование сервиса максимально комфортным банки курс евро
Удобный интерфейс позволяет быстро находить нужные данные, а дополнительные функции, такие как сравнение курсов в разных банках и отображение исторических графиков, делают использование сервиса максимально комфортным доллар цена рублей
Discover the world of enjoyment with our pools!
We offer a large selection of pools, their installation and maintenance.
More detailed information on the link купить фильтр для бассейна песчаный
Create an oasis at home with high-quality solutions.
Individual approach and guarantees for all work.
Удобный интерфейс позволяет быстро находить нужные данные, а дополнительные функции, такие как сравнение курсов в разных банках и отображение исторических графиков, делают использование сервиса максимально комфортным курс валют в банках на сегодня
Aviatrix game https://aviatrix-games.com/en/ has become a sensation in the world of crash games. Its unique format, featuring a rapidly growing multiplier and the possibility of an unexpected crash. Aviatrix crash game is at 1win, 1xbet, Mostbet, and Pin Up.
Имплантация — популярная процедура замещения зубов искусственными аналогами. Стоматологическая имплантология является одним из важнейших разделов современной стоматологии, предусматривающий восстановление нарушений целостности зубочелюстной системы благодаря качественным аллопластическим материалам и достижениям в области современной стоматологии имплантация зубов отзывы пациентов
Имплантация — популярная процедура замещения зубов искусственными аналогами. Стоматологическая имплантология является одним из важнейших разделов современной стоматологии, предусматривающий восстановление нарушений целостности зубочелюстной системы благодаря качественным аллопластическим материалам и достижениям в области современной стоматологии зуб имплантация пью
Cialis India Pharmacy Cialis supreme suppliersmumbaiindia Online Pharmacy No Prescription Buy lasix online fast delivery
Имплантация — популярная процедура замещения зубов искусственными аналогами. Стоматологическая имплантология является одним из важнейших разделов современной стоматологии, предусматривающий восстановление нарушений целостности зубочелюстной системы благодаря качественным аллопластическим материалам и достижениям в области современной стоматологии имплантация зубов отзывы
Продажа дженериков с доставкой https://stoya4ok.ru/ большой выбор отличные цены
Other, for-profit sites have become popular as a way to actually make money; in other words, these companies see microlending as an investment.
Захватывающий слот Lucky Jet lucky-jet-play-crash.ru/ от Spribe с уникальной краш-механикой, который предлагает игрокам шанс испытать свою удачу и стратегическое мышление.
Aviatrix game https://aviatrix-games.com/en/ has become a sensation in the world of crash games. Its unique format, featuring a rapidly growing multiplier and the possibility of an unexpected crash. Aviatrix crash game is at 1win, 1xbet, Mostbet, and Pin Up.
Добро пожаловать на сайт https://redtigerplay.ru посвященный слотам Red Tiger! Узнайте последние новости, стратегии для увеличения выигрышей и эксклюзивные бонусы.
Откройте для себя водное поло water-polo историю, правила, тактики и влияние этого захватывающего водного вида спорта. Узнайте, как динамика и стратегия сочетаются, делая водное поло уникальным и увлекательным.
https://je-tall-sf-marketing-89.b-cdn.net/research/je-tall-marketing-(173).html
Dillards is a great place to verify out if you’re in search of something larger end.
Canada Pharmacy 24 Hour Drug Store Canadian pharmacies that accept paypal northwest pharmacy canada Cialis tablets 20mg
check this link right here now skin changer valorant
Купить дженерики в нашем магазине с доставкой https://tabru.ru/ высокое
качество по доступной цене
купить диплом техникума
Как официально купить диплом вуза с упрощенным обучением в Москве
Gaminator online
Оптимизирован для смартфонов
Казино с лицензией, дающие слоты
игровые аппараты с бонусом за регистрацию
https://cash4winner.com/l/67816cee174262243c0008bf
With just $2, you can see any “password” you want!
AntiPublic is a tool commonly used in the fields of information security and penetration testing. It is essentially a collection of data gathered from various sources, including leaked information on the internet, compromised databases, and other publicly available data sources.
Key Functions of AntiPublic:
Personal Information Lookup: AntiPublic allows users to search and retrieve personal information from a vast amount of data, including names, email addresses, phone numbers, and other relevant information about individuals or organizations.
Analysis and Investigation: This tool is used to analyze data to identify potential security threats and conduct investigations related to cybersecurity.
Support for Security Professionals: AntiPublic provides security analysts and professionals with a useful tool to search for and uncover sensitive data, helping to improve system security.
User-Friendly: The interface of AntiPublic is typically user-friendly, enabling users to perform searches easily without requiring extensive technical experience.
Go Here : Anti Public Combo List Breach
купить диплом медицинского колледжа
Погрузитесь в захватывающий мир баккары https://baccarat-ru.ru узнайте историю игры, её правила, стратегии и секреты успеха. Откройте для себя элегантность и интригу одной из самых престижных карточных игр казино.
https://rutube.ru/channel/31906501
купить диплом геодезиста 4russkiy365-diplomy.ru .
купить диплом о среднем образовании в москве
Мир блэкджека https://blackjack-ru.ru узнайте историю игры, её правила, секретные стратегии и влияние на современную культуру. Откройте для себя глубину этой захватывающей карточной игры и научитесь побеждать с умом.
образование купить диплом всегда
Погрузитесь в мир фигурного катания figure-skating-ru ru исследуйте его историю, уникальные техники, знаменитых спортсменов и культурное влияние.
Почувствуй Азарт Победы прочувствуй восторг успеха: Играй в Казино Онлайн играй в виртуальном казино с Минимальным Депозитом с небольшим взносом!
Мечтаешь о крупных выигрышах о солидных выигрышах, но не готов рисковать большими суммами крупными ставками? У нас есть отличное решение прекрасная альтернатива! Погрузись в мир азарта в мир волнения и развлечений игровая забава с нашим онлайн-казино, где ты можешь играть на деньги онлайн играть на реальные деньги с минимальным депозитом небольшим взносом. Забудь о стереотипах забудь клише, что азартные игры игры на деньги – это только для хайроллеров богачей. Теперь каждый может испытать удачу попробовать судьбу и получить шанс на крупный куш на солидный приз, не выходя из дома из любой точки мира.
Почему выбирают нас?
Минимальный депозит – максимум возможностей: Начни свою игру начни свой игровой путь с небольшого депозита с символической суммы и открой для себя мир захватывающих слотов увлекательных игровых автоматов, карточных игр карточных развлечений и рулетки игры в рулетку. Это отличный шанс прекрасная возможность протестировать разные игры попробовать разные игры, разработать свою стратегию создать свою стратегию и получить первые победы первые выигрыши без больших вложений без больших трат. Огромный выбор игр: У нас ты найдешь сотни игр огромное количество развлечений на любой вкус для любого игрока, от классических слотов от ретро-слотов до современных видеоигр современных игр с потрясающей графикой красивой графикой и увлекательными бонусными раундами интересными дополнительными раундами. Постоянно добавляются новые игры мы постоянно обновляем ассортимент, чтобы тебе никогда не было скучно чтобы вам никогда не было скучно. Играй на деньги онлайн играйте в онлайн казино в любое время: Наше казино доступно 24/7 круглосуточно с любого устройства любого гаджета – компьютера, планшета или смартфона. Ты можешь наслаждаться игрой веселиться в любое удобное время когда вам удобно и в любом месте везде, где есть интернет. Безопасность и надежность: Мы используем самые современные технологии шифрования новейшие системы защиты, чтобы гарантировать безопасность твоих личных данных ваших персональных данных и финансовых транзакций финансовых операций. Играй с уверенностью играйте спокойно, зная, что твоя информация ваши данные в надежных руках. Быстрые и удобные выплаты быстрый и удобный вывод средств: Мы ценим твое время мы ценим ваше время, поэтому предлагаем различные способы вывода выигрышей разные варианты получения выигрышей, с быстрой обработкой запросов. Щедрые бонусы и акции выгодные бонусы и акции: Начни свою игру начните играть с приятными бонусами приятными подарками, которые увеличат твои шансы на победу ваши возможности выиграть. Мы регулярно проводим акции проводим различные акции и турниры турниры для игроков, чтобы сделать твою игру вашу игру еще более захватывающей более увлекательной.
Как начать играть на деньги онлайн с минимальным депозитом?
Зарегистрируйся на нашем сайте: Процесс регистрации займет всего пару минут будет очень быстрым. Пополни свой счет пополните баланс: Выбери удобный способ оплаты выберите способ пополнения и внеси минимальный депозит внесите минимум. Выбери игру найдите игру: Просмотри нашу коллекцию посмотрите наш каталог и найди свою любимую игру найдите подходящую игру. Начни выигрывать начните выигрывать: Наслаждайся игрой получайте удовольствие и получай удовольствие от процесса!
Не откладывай свою удачу на потом! Не ждите завтра!
Присоединяйся к нашему онлайн-казино уже сегодня начинайте играть сегодня и убедись сам проверьте сами, что играть на деньги онлайн играть на реальные деньги может быть не только захватывающе не только увлекательно, но и доступно каждому с минимальным депозитом подходит каждому. Испытай свою удачу проверьте свою фортуну, получи незабываемые эмоции почувствуйте восторг и, возможно, сорви крупный куш выиграйте крупную сумму!
Скачайте бесплатно книгу https://storitelling.ru по сторителлингу и узнайте, как создавать истории, которые цепляют с первых строк. Практические советы, примеры и вдохновение для всех, кто хочет освоить искусство рассказчика.
Официальная покупка школьного аттестата с упрощенным обучением в Москве
canada pharmacy
Как избежать рисков при покупке диплома колледжа или ПТУ в России
Имплантат устанавливается в один этап после разреза десневого лоскута в костное ложе. На внутрикостный элемент вкручивают формирователь десны, накладывают швы имплантация зубов акция
Имплантат устанавливается в один этап после разреза десневого лоскута в костное ложе. На внутрикостный элемент вкручивают формирователь десны, накладывают швы имплантация зубов фото
Имплантат устанавливается в один этап после разреза десневого лоскута в костное ложе. На внутрикостный элемент вкручивают формирователь десны, накладывают швы клиника имплантации зубов
Твой выбор для гемблинга – казино Слотозал!
Слотозал предлагает разнообразный набор слот-машин, выгодные бонусные программы и высокий уровень безопасности. Интерфейс веб-сайта интуитивно понятен, навигация легка, что дает возможность скоро отыскать избранные игры. Команда поддержки постоянно настроена помочь с всеми вопросами. Пройдите регистрацию на основном сайте casinoslotozal.net/ru/ и начните выигрывать уже!
Как приобрести аттестат о среднем образовании в Москве и других городах
Северный Кипр – это место, где восточная культура встречается с европейским комфортом, создавая идеальные условия для жизни, отдыха и инвестиций. Прекрасный климат, доступные цены на недвижимость и простые условия покупки привлекают сюда покупателей со всего мира. Но прежде чем сделать первый шаг к приобретению собственного жилья у моря, важно разобраться во всех нюансах кирения северный кипр купить недвижимость
анонимный вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимный вывод из запоя в стационаре .
пропуск в москву на грузовой автомобиль пропуск в москву на грузовой автомобиль .
Северный Кипр – это место, где восточная культура встречается с европейским комфортом, создавая идеальные условия для жизни, отдыха и инвестиций. Прекрасный климат, доступные цены на недвижимость и простые условия покупки привлекают сюда покупателей со всего мира. Но прежде чем сделать первый шаг к приобретению собственного жилья у моря, важно разобраться во всех нюансах caesar blue северный кипр
Северный Кипр – это место, где восточная культура встречается с европейским комфортом, создавая идеальные условия для жизни, отдыха и инвестиций. Прекрасный климат, доступные цены на недвижимость и простые условия покупки привлекают сюда покупателей со всего мира. Но прежде чем сделать первый шаг к приобретению собственного жилья у моря, важно разобраться во всех нюансах caesar resort северный кипр купить квартиру
And try to leap rope outside or on the bottom ground to avoid disturbing others.
Сопровождение мужчин — это особая услуга, которая может включать в себя как деловые, так и личные аспекты.
В современном мире многие мужчины ищут профессионалов, которые могут помочь им в различных сферах жизни:
от бизнес-мероприятий до социальных встреч – эскорт Москва сайт
And so mutual fund investing became regulated and soon took on a life of its own.
For services to the community, particularly to structure and education.
In the event you only eat 600 kWh in a month, or 20kWh/day, you could supply all of the vitality you need with a 5-kW system.
быстрый вывод из запоя в стационаре быстрый вывод из запоя в стационаре .
Купить диплом программиста – серьезный шаг
купить обложку на диплом кандидата наук в екатеринбурге prema-diploms.ru .
пропуск на грузовой автомобиль в москве http://www.extremeguide.ru/ .
пропуск в москву для грузовиков пропуск в москву для грузовиков .
Как купить аттестат 11 класса с официальным упрощенным обучением в Москве
купить диплом петербург если 2orik-diploms.ru .
https://film005.buzz
Simone Höhl (2016-12-27). “Freiburg: Korrektur: Lassbergstraße heißt jetzt Laßbergstraße” (in German).
Сайт игровых промокодов промокоды в standoff 2 на кейсы это ваш доступ к эксклюзивным бонусам и скидкам. Бесплатные награды, внутриигровая валюта и уникальные акции ждут вас. Успейте воспользоваться всеми возможностями!
Хотите раскрутить контент-план мы знаем, как это сделать! Поможем увеличить охваты, привлечь активную аудиторию и вывести ваш контент на новый уровень.
капельница после запоя клиника http://www.medlinks.ru/article.php?sid=110769
купить аттестат 11 классов цена купить аттестат 11 классов цена .
Купить диплом магистра оказалось возможно, быстрое обучение и диплом на руки
We offer a widest range of packaging materials for any need: from film to eco-friendly solutions.
Our products are ideal for moving and personal needs.
For more information, click here [url=https://pack-inn.ru/vakuumnyie-paketyi/]пакет для вакуумной упаковки [/url]
We guarantee high quality and competitive prices.
Packaging that protects your goods and makes them attractive – choose us for your packaging solutions!
Ищете промокоды для игр секретный промокод ggdrop наш сайт – ваш лучший помощник! Собираем актуальные игровые промокоды для бонусов, скидок и эксклюзивных наград.
Участок в Мишкином Лугу http://мишкинлуг.рф/uchastki-mishkinlug по Симферопольскому шоссе — идеальное место для строительства! Тихий поселок, прекрасные виды, удобный подъезд и все условия для комфортной жизни.
Лисичкин Очаг возле Серпухова https://лисичкиночаг.рф/uchastki-lisichkinochag идеальные участки для вашего будущего дома! Живописная природа, хорошая транспортная доступность и возможность подключения всех коммуникаций ждут вас.
Участки в Лисичкином Очаге https://лисичкиночаг.рф неподалеку от Серпухова. Тихий, зеленый поселок с прекрасной природой и удобной транспортной доступностью. Здесь вы сможете построить комфортное жилье для себя и своей семьи.
canadian non prescription pharmacy
on line pharmacy
Accessrx prescription drugs online pharmacy no prescription Buy cialis without prescription
sw-motors.ru
[url=https://ilmholding.ru/]ilmholding.ru[/url]
купить диплом высшем новосибирск prema-diploms.ru .
Decentralized finance (DeFi) is one of the best things to come from cryptocurrency.
https://t.me/cryptonetlake
With millions of Chevrolet vehicles on the road in English-speaking regions, the company recognizes the importance of providing transparent, reliable, and easily accessible resources pressreleasepedia.com
With millions of Chevrolet vehicles on the road in English-speaking regions, the company recognizes the importance of providing transparent, reliable, and easily accessible resources phenomenalarticles.com
The leverage is the number of units of the future index.
With millions of Chevrolet vehicles on the road in English-speaking regions, the company recognizes the importance of providing transparent, reliable, and easily accessible resources pressreleasepedia.com
Все работы выполняются высококвалифицированными специалистами, что гарантирует надежность и безопасность каждого проекта. Компания использует только профессиональное оборудование и качественные материалы, что позволяет ей добиваться отличных результатов ремонте электроники
Все работы выполняются высококвалифицированными специалистами, что гарантирует надежность и безопасность каждого проекта. Компания использует только профессиональное оборудование и качественные материалы, что позволяет ей добиваться отличных результатов ремонт бытовой техники
Canadian Pharmacy Cialis 20mg Cialis pills healthy male viagra Canadian Pharmacy Cialis Celexa
Все работы выполняются высококвалифицированными специалистами, что гарантирует надежность и безопасность каждого проекта. Компания использует только профессиональное оборудование и качественные материалы, что позволяет ей добиваться отличных результатов ремонт бытовой техники
Подарочные флешки оптом купить и стеклянная флешка в Ставрополе https://flashki-optom-1.ru/
здесь vodka регистрация – vodka bet, водка казино
В этой публикации мы обсуждаем современные методы лечения различных заболеваний. Читатели узнают о новых медикаментах, терапиях и исследованиях, которые активно применяются для лечения. Мы нацелены на то, чтобы предоставить практические знания, которые могут помочь в борьбе с недугами.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://nakroklinikatest.ru/
Online Pharmacy Topamax healthy male
Official website of the gaming club Gizbo Casino . Slots from famous providers. Bonuses and exclusive new products are waiting for you at Gizbo Casino Гизбо Казино
Official website of the gaming club Gizbo Casino . Slots from famous providers. Bonuses and exclusive new products are waiting for you at Gizbo Casino Гизбо Казино
В этой статье мы рассматриваем разные способы борьбы с алкогольной зависимостью. Обсуждаются методы лечения, программы реабилитации и советы для поддержки близких. Читатели получат информацию о том, как преодолеть зависимость и добиться успешного выздоровления.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://nakroklinikatest.ru/
Official website of the gaming club Gizbo Casino . Slots from famous providers. Bonuses and exclusive new products are waiting for you at Gizbo Casino казино Gizbo
Диплом пту купить официально с упрощенным обучением в Москве
Отзывы о компаниях и работодателях https://potrebsojuz.ru в одном месте. Узнайте реальное мнение сотрудников и клиентов, чтобы принять правильное решение при выборе работы или услуг.
Norsup, Luganville and Port Villa are all situated on completely different islands, however are you able to guess the country they’re in?
Комплексная юридическая помощь https://kramzenergo.ru для вас и вашего бизнеса. Анализ дел, представительство в судах, поддержка на всех этапах
glory-casino-bd.online
https://odnazhdyvskazke-tv.ru/
нажмите здесь
obmenko обменник – Обменко орг, obmenko обменник
Based on this forecasted demand, planners make suggestions concerning the quantity and size of runways, in addition to the dimensions of airport terminals, all of which determines the quantity of land required for a possible venture.
Airline pilots mainly work for major airlines that transport passengers and cargo on a hard and fast schedule that would embody weekends and overnights.
Jennings, LA (KPLC) – There was the sound of Taps and phrases of remembrance in Jennings immediately because the veterans dwelling commemorated Memorial Day.
Ищете способ быстро получить деньги, минуя долгие проверки и формальности? Займы онлайн на карту без отказа без проверки — это решение, которое позволит вам моментально решить финансовые вопросы. Не нужно тратить время на посещение банков или собирать многочисленные справки займ с плохой кредитной историей
Ищете способ быстро получить деньги, минуя долгие проверки и формальности? Займы онлайн на карту без отказа без проверки — это решение, которое позволит вам моментально решить финансовые вопросы. Не нужно тратить время на посещение банков или собирать многочисленные справки Займ онлайн на карту
Ищете способ быстро получить деньги, минуя долгие проверки и формальности? Займы онлайн на карту без отказа без проверки — это решение, которое позволит вам моментально решить финансовые вопросы. Не нужно тратить время на посещение банков или собирать многочисленные справки Где взять займ если нигде уже не дают
Bonds that mature in lower than one yr are called bills.
Как официально приобрести аттестат 11 класса с минимальными затратами времени
Nigerians are one of the major global users of cryptocurrencies.
Today, the economic downturn has compelled many like you to think about alternative ways to make money.
Burial will follow at Wilbur (WA) Cemetery, with Strate Funeral Home in Grand Coulee in command of arrangements.
купить диплом кандидата наук в спб
капельница при беременности эффективные капельницы для лечения
диплом о среднем специальном купить
1win videos bonus casino 1win
1win mexico 1win telegram
Откройте для себя историю слово пацана кровь на асфальте сериал актеры честный взгляд на суровую реальность, где дружба и слово дороже всего. Уникальный проект о жизни без прикрас и ценности принципов.
Witaj w Slottica PL! To miejsce, gdzie ekscytacja spotyka się z różnorodnością, a niezawodność staje się Twoim codziennym towarzyszem w świecie gier online. Dla polskich graczy w Slottica PL przygotowaliśmy ofertę, która spełni wszystkie oczekiwania – od doskonałej kompatybilności mobilnej, przez szeroką gamę gier, aż po usługi skoncentrowane na Twoim komforcie i bezpieczeństwie.
диплом высшего образования с занесением в реестр купить
On the official website of Gizbo Casino you will find everything you need for an exciting gameplay: safe transactions, a wide range of entertainment, as well as profitable bonuses. Discover a new level of gambling with Gizbo Casino казино Gizbo
On the official website of Gizbo Casino you will find everything you need for an exciting gameplay: safe transactions, a wide range of entertainment, as well as profitable bonuses. Discover a new level of gambling with Gizbo Casino казино Gizbo
On the official website of Gizbo Casino you will find everything you need for an exciting gameplay: safe transactions, a wide range of entertainment, as well as profitable bonuses. Discover a new level of gambling with Gizbo Casino Гизбо Казино
купить диплом специалиста в нижнем новгороде
canadian pharmacy online no script
диплом о среднем специальном образовании купить
капельница от запоя на дому капельница от запоя на дому .
программа 1с купить с установкой программа 1с купить с установкой .
moving companies moving companies .
Всё, что нужно знать о покупке аттестата о среднем образовании без рисков
Оптоволоконные кабели
купить диплом о специальном образовании купить диплом о специальном образовании .
Купить диплом техникума, колледжа в Пензе
Гизбо Казино представляет обширный каталог игр: слоты, настольные игры, видеопокер и живые дилеры. Доступны щедрые бонусы и акции для новых и постоянных игроков казино Gizbo
Гизбо Казино представляет обширный каталог игр: слоты, настольные игры, видеопокер и живые дилеры. Доступны щедрые бонусы и акции для новых и постоянных игроков Gizbo Casino
kinogo детские фильмы киного фантастика
kinogo фильмы про природу киного фантастические фильмы
Гизбо Казино представляет обширный каталог игр: слоты, настольные игры, видеопокер и живые дилеры. Доступны щедрые бонусы и акции для новых и постоянных игроков Гизбо Казино
kinogo фильмы для компьютера kinogo аниме
Vavada Casino to miejsce, gdzie emocje gry są zawsze na wyciągnięcie ręki. Oferujemy bogaty wybór najlepszych automatów do gier, klasycznych gier stołowych, takich jak poker, blackjack czy bakarat, a także wciągającą ruletkę na żywo z udziałem profesjonalnych krupierów. Nasza platforma Vavada Casino jest w pełni licencjonowana i zgodna z obowiązującymi przepisami prawa, co zapewnia bezpieczne i legalne środowisko rozgrywki dla wszystkich graczy.
купить диплом в ижевске купить диплом в ижевске .
купить диплом луганск
https://odnazhdy-v-skazke-1-sezon.ru/
Find and Replace text in multiple files. Achieve effortless website maintenance with our top-tier find and replace software designed for web professionals. Rapidly locate and substitute text, symbols, and metatags within multiple HTML and text files with unparalleled precision. Perfect for website redesigns and content overhauls, this tool enables you to swiftly modify metadata, update SEO information, and repair broken links, all in one go. Make sure your website is not only visually appealing but also optimized for search engines. Enhance your workflow and boost your website’s performance with our highly efficient software: replace in multiple files
They consider an organization’s past performance as well as the credibility of its accounts.
Быстрая схема покупки диплома старого образца: что важно знать?
September 1778: Revenge for the Wyoming defeat was taken by American Colonel Thomas Hartley who, with 200 troopers, burned 9 to twelve Seneca, Delaware and Mingo villages along the Susquehanna River in northeast Pennsylvania, together with Tioga and Chemung.
Pipelines could also be related to processing plants or power plants that depend on fossil fuels, as well as natural sources of CO2.
Детальный разбор официального сайта Водка Казино и вход на него через актуальное и рабочее зеркало Водка Казино
Детальный разбор официального сайта Водка Казино и вход на него через актуальное и рабочее зеркало казино Vodka
Детальный разбор официального сайта Водка Казино и вход на него через актуальное и рабочее зеркало Водка Казино
купить диплом в грозном
Lanfeng Kao & Anlin Chen (2011): Dividend policy and elimination of double taxation of dividends; Asia-Pacific Journal of Financial Studies.
продамус промокод http://www.promokod-pro.ru .
It is just as a kind of integrated portal of partner that helps the vendors to maintain an excellent business relationship with all distributor network and conversely.
купить диплом о среднем профессиональном купить диплом о среднем профессиональном .
You’ll have your one-in-a-million true followers to your self.
When you make your first deposit into your account, no fees will be charged.
Play and win at Playfina casino, your trusted choice for exciting games!https://playfina1.app/
Казино привлекает игроков своей впечатляющей подборкой азартных игр. Хотя количество предложенных развлечений здесь не самое обширное, по стандартам качества и разнообразия оно сопоставимо с ведущими брендами игорной индустрии казино Gizbo
Казино привлекает игроков своей впечатляющей подборкой азартных игр. Хотя количество предложенных развлечений здесь не самое обширное, по стандартам качества и разнообразия оно сопоставимо с ведущими брендами игорной индустрии казино Gizbo
Казино привлекает игроков своей впечатляющей подборкой азартных игр. Хотя количество предложенных развлечений здесь не самое обширное, по стандартам качества и разнообразия оно сопоставимо с ведущими брендами игорной индустрии казино Gizbo
Откройте для себя blacksprut возможности даркнет-рынка с тысячами предложений. Быстрая регистрация, надежные сделки и анонимность на каждом этапе.
Лучшее онлайн казино https://1wincasino.pl Огромный выбор автоматов, настольных игр и live-казино. Уникальные акции, приветственные бонусы и мгновенные выплаты сделают вашу игру еще интереснее.
ККлапаны:10–12-2ЭМ, 10–12-2ЭН, 10–13-2ЭЧ, 10–25-25ЭМ,
1029-200/250-0, 1031-20-0, 1032-20-0, 1033-20-Р, 1052-65-0,
1052-65-ЦЗ, 1052-65-Э, 1052-65-ЭД, 1052-65-ЭК, 1052-65-ЭМ,
1052-65-ЭН, 1052-65-ЭНВ, 1052-65-ЭЧ, 1053-50-0, 1053-50-ЦЗ,
1053-50-Э, 1053-50-ЭГ, 1053-50-ЭД, 1053-50-ЭК, 1053-50-ЭМ,
1053-50-ЭН, 1053-50-ЭС, 1053-50-ЭЧ, 1054-40-0, 1054-40-ЦЗ,
1054-40-Э, 1054-40-ЭД, 1054-40-ЭК, 1054-40-ЭМ, 1054-40-ЭН,
1054–40-ЭС, 1054-40-ЭЧ, 1055-32-0, 1055-32-ЦЗ, 1055-32-Э,
1055-32-ЭГ, 1055-32-ЭД, 1055-32-ЭК, 1055-32-ЭМ, 1055-32-ЭН,
1055-32-ЭНВ, 1055–32-ЭС, 1055-32-ЭЧ, 1057-65-0, 1057-65-ЦЗ,
1057-65-ЭД, 1057-65-ЭК, 1057-65-ЭМ, 1057-65-ЭН, 1057-65-ЭНВ,
1057-65-ЭЧ, 1084-100-ЭА,-01,02,03, 1085-100-Э,
1086-100-Э,-01-02, 1087-100-Э,-01, 1093-10-0, 111–250/400-0б,
111–250/400-0б-01, 112-25Х1-0,-01-02, 112-25Х1-0М, 1193-32-Р,
1195-50-Р, 1197-65-Р, 1202-150/150-0, 1203-150/200-0-01,
1203-150/200-0-02, 1203-150/200-0-03, 1203-150/200-0-04,
1203-150/200-0-07, 1203-150/200-0-10, 1203-150/200-0-13,
1203-125/175-0, 1203-150/200-0А, 1213-6-0,
1415-100/50-Ф,-01-16, 1416-100-Р,01-02, 1416-100-ЭА,-01-02,
1416-175-Рм,-01, 1416-175-ЭА,-01,-02, 1416-225-Рм,
1416-225-ЭА-01, 1416-250-Рм,-01,-02, 1416-250-ЭА,
1436-65-9,-01-05, 1438-20-9Э-01-13, 1456-10-0, 1456-10-0А,
1456-20-0, 1456-20-0А, 1456-25-М, 1456-25-МА, 1456-25-МА,
1456-32-0, 1456-32-0А, 1456-50-0, 1456-50-0А, 1456–50-ЦЗ,
1456–50-ЭГ, 1456–50-ЭК, 1456–50-ЭМ, 1456–50-ЭЧ, 1456-80-М,
1464-40-Э,-01-05, 1481-80-Э-02, 1512–10-0, 1512–15-0,
1512–20-0, 1512–25-0, 1516-100-0А, 1516-150-0А, 1516-200-0А,
1516-250-0А, 1516-80-0А, 1521-50-Р, 1522-10-М, 1522-32-М,
1522-50-М, 1523-20-Р, 1524-32-0, 1541-100-М, 1541-100-М-01,
1541-100-МШ, 1541-100-Э, 1541-100-Э-01, 1541-100-Э-02,
1541-100-Э-03, 1541-150-М, 1541-150-М-01, 1541-150-МШ,
1541-150-Э, 1541-150-Э-01, 1541-150-Э-02, 1541-150-Э-03,
1541-80-М, 1541-80-М-01, 1541-80-МШ, 1541-80-МШ-01,
1541-80-Э, 1541-80-Э-01, 1541-80-Э-03, 1542-100-М,
1542-100-М-01, 1542-100-МШ, 1542-100-Э, 1542-100-Э-01,
1542-150-М, 1542-150-М-01, 1542-150-Э, 1542-150-Э-01,
1542-65-М, 1542-80-М, 1542-80-М-01, 1542-80-Э, 1542-80-Э-01,
1542-80-Э-02, 1542-80-Э-03, 1584-10-0, 15с-1-1, 15с-2-2,
17с-1-2, 17с-1-3, 17с-2-3, 1C-11-1М, 1c-11-2, 1C-11-2ЭД,
1c-11-3М, 1C-12-2, 1C-12-2ЭС, 1C-12-2ЭЧ, 1c-13-2, 1C-13-2ЭН,
1C-13-2ЭС, 1C-14-1ЭН, 1C-17-2, 1c-25-2, 1c-25-253H,
1C-25-2ЭД, 1C-П-2ЭМ, 1C-П-2ЭН, 1C-П-2ЭЧ, 1е-25-25ЭН,
1с-11-1мЭС, 1С-11-2ЭС, 1С-11-31, 1с-11-31ЭГ, 1С-11-31ЭД,
1С-11-31ЭК, 1С-11-31ЭМ, 1С-11-31ЭН, 1С-11-31ЭС, 1с-11-31ЭЧ,
1С-11-3М, 1С-11-3ЭГ, 1С-11-3ЭД, 1С-11-3ЭК, 1С-11-3ЭМ,
1С-11-3ЭН, 1с-11-3ЭС, 1С-11-3ЭЧ, 1с-11-40, 1с-11-40ЭД,
1с-11-40ЭМ, 1с-11-40ЭН, 1с-11-40ЭС, 1с-11-40ЭЧ, 1С-11-5,
1С-11-5М, 1С-11-5МЭД, 1С-11-5МЭК, 1С-11-5МЭМ, 1С-11-5МЭН,
1с-11-5мЭС, 1С-11-5МЭЧ, 1с-11-5ЭГ, 1С-11-5ЭД, 1С-11-5ЭК,
1С-11-5ЭМ, 1С-11-5ЭН, 1с-11-5ЭС, 1С-11-5ЭЧ, 1с-11-65,
1с-11-65ЭД, 1с-11-65ЭМ, 1с-11-65ЭН, 1с-11-65ЭС, 1с-11-65ЭЧ,
1С-12-1, 1с-12-1ЭН, 1с-12-1ЭС, 1С-12-1ЭЧ, 1С-12-25ЭД,
1с-12-25ЭМ, 1С-12-25ЭН, 1С-12-25ЭС, 1С-12-25ЭЧ, 1с-12-2ЭД,
1С-12-3, 1с-12-31, 1с-12-31ЭД, 1с-12-31ЭМ, 1с-12-31ЭН,
1с-12-31ЭС, 1с-12-31ЭЧ, 1с-12-32ЭД, 1с-12-32ЭМ, 1с-12-32ЭН,
1с-12-32ЭС, 1с-12-32ЭЧ, 1С-12-3ЭГ, 1С-12-3ЭД, 1С-12-3ЭК,
1С-12-3ЭМ, 1С-12-3ЭН, 1с-12-3ЭС, 1С-12-3ЭЧ, 1С-12-4,
1с-12-40, 1с-12-40ЭД, 1с-12-40ЭМ, 1с-12-40ЭН, 1с-12-40ЭС,
1с-12-40ЭЧ, 1с-12-4ЭГ, 1С-12-4ЭД, 1С-12-4ЭК, 1С-12-4ЭМ,
1С-12-4ЭН, 1С-12-4ЭЧ, 1С-12-5, 1С-12-5ЦЗ, 1с-12-5ЭГ,
1С-12-5ЭД, 1С-12-5ЭК, 1С-12-5ЭМ, 1С-12-5ЭН, 1с-12-5ЭС,
1С-12-5ЭЧ, 1с-12-65, 1с-12-65ЭД, 1с-12-65ЭМ, 1с-12-65ЭН,
1с-12-65ЭС, 1с-12-65ЭЧ, 1С-13-1, 1с-13-1ЭС, 1С-13-25,
1С-13-25ЭД, 1С-13-25ЭМ, 1С-13-25ЭН, 1С-13-25ЭС, 1С-13-25ЭЧ,
1с-13-2ЭД, 1С-13-2ЭМ, 1С-13-3, 1с-13-31, 1с-13-31ЭД,
1с-13-31ЭМ, 1с-13-31ЭН, 1с-13-31ЭС, 1с-13-31ЭЧ, 1с-13-32,
1с-13-32ЭД, 1с-13-32ЭМ, 1с-13-32ЭН, 1с-13-32ЭС, 1с-13-32ЭЧ,
1С-13-3ЭГ, 1С-13-3ЭД, 1С-13-3ЭК, 1С-13-3ЭМ, 1С-13-3ЭН,
1с-13-3ЭС, 1С-13-3ЭЧ, 1с-13-40, 1с-13-40ЭД, 1с-13-40ЭМ,
1с-13-40ЭН, 1с-13-40ЭС, 1с-13-40ЭЧ, 1с-13-5ЭД, 1с-13-5ЭМ,
1с-13-5ЭН, 1с-13-5ЭС, 1с-13-5ЭЧ, 1с-13-65, 1с-13-65ЭД,
1с-13-65ЭМ, 1с-13-65ЭН, 1с-13-65ЭС, 1с-13-65ЭЧ, 1С-14-1ЭЧ,
1С-14Н-3, 1С-14Н-3ЭК, 1С-14Н-3ЭМ, 1С-14Н-3ЭН, 1С-14Н-3ЭЧ,
1С-14Т-3, 1С-14Т-3ЭД, 1С-14Т-3ЭК, 1С-14Т-3ЭН, 1С-14Т-3ЭЧ,
1С-15-1ЭН, 1С-15-1ЭЧ, 1С-15-2, 1с-25-1ЭД, 1с-25-1ЭМ,
1с-25-1ЭС, 1С-25-25ЭД, 1С-25-25ЭС, 1с-25-2ЭМ, 1с-25-2ЭН,
1с-25-2ЭС, 1с-25-2ЭЧ, 1с-25-32, 1с-25-32ЭД, 1с-25-32ЭМ,
1с-25-32ЭН, 1с-25-32ЭС, 1с-25-32ЭЧ, 1С-25-3ЭД, 1С-25-3ЭМ,
1С-25-3ЭН, 1С-25-3ЭС, 1С-25-3ЭЧ, 1с-25-40, 1с-25-40ЭД,
1с-25-40ЭМ, 1с-25-40ЭН, 1с-25-40ЭЧ, 1с-25-65, 1с-25-65ЭД,
1с-25-65ЭМ, 1с-25-65ЭН, 1с-25-65ЭС, 1с-25-65ЭЧ, 1С-7-1,
1С-8-2, 1с-8-2ЭГ, 1С-8-2ЭД, 1С-8-2ЭК, 1С-8-2ЭМ, 1С-8-2ЭН,
1с-8-2ЭС, 1С-8-2ЭЧ, 1С-9-2, 1с-Т-107б, 392-175/95-0Г,
392-175/95-0Г-01, 3с-10-10-450, 3с-10-25-450, 3с-15-10-450,
3с-15-25-450, 3с-20-25-450, 3с-25-10-450, 3с-25-25-450,
3с-32-25-450, 3с-40-25-450, 3с-50-25-450, 3с-6-1-01,
3с-6-1-02, 3с-6-2, 3с-6-3, 3с-6-4, 3с-6-5, 3с-65-25-450,
3с-7-1-01, 3с-7-2, 3с-7-4, 3с-7-6, 3с-8-2, 3с-8-3, 3с-8-5,
3с-8-6, 4с-3-1, 4с-3-2, 4с-3-3, 4с-3-4, 4с-3-5,
530-150/150-0в, 586-20-ЭМ-01, 586-20-ЭМ-02, 586-20-ЭМ-03,
586-20-ЭМФ-03, 586-20-ЭМФ-03, 586-20-ЭМФ-04, 586–20-ЭМФ-05,
586–20-ЭМФ-06, 586–20-ЭМФ-07, 588-10-0, 589-10-0, 597-10-0А,
694–250/400-0б, 720-20-0А, 720-20-0А-01, 788–400/600-0-01,
788–400/600-0-02, 788–400/600-0-03, 7с-6-1, 7с-6-2, 7с-6-3,
7с-8-1, 7с-8-2, 7с-8-3, 808-65-РВ, 808-65-РВ-01, 811-50-РМ,
814-50-РА,-01, 815-40-РВ,-01(-РМ,-01), 843-40-0А-01,
843-40-0А-02, 843-40-0А-03, 843-40-0А-04, 875–125-0,
879-65-РА,-01-05, 8с-3-1, 8с-3-2, 8с-3-3, 8с-3-4, 8с-3-5,
8с-3-6, 912-100-0А, 912-150-0А, 912–200-0б, 912-200-0В,
912–250-0б, 912–250-0бМ, 912-250-0В, 912-250-ОВМ,
912–300-0б, 912-300-0В, 912–325-0б, 912–325-0бМ,
912–350-0б, 912–400-0, 935-100-0А, 935–100–0А-01,
935-100-0АМ, 935-150-0А, 935-150-0АМ, 935–150-0М,
935–175-0, 935-175-ОА, 935–225-0б, 935-225-ОВ.-ОВШ,
935–250-0б, 935-250-ОВ,-ОВШ, 950-100/150-Э,
950-100/150-Э-01, 950-150/250-Э, 950-150/250-Э-01,
950-150/250-Э-02, 950-200/250-Э, 976-175-ЭБ,
976-250-ЭБ,-01, 976-65-М, 976-65-М-01, 976-65-Э,
977-175-Э, 992-250-ЭБ, 993-100-ЭМ,-01, 998-20-0,
998-20-Г, 998-20-Э, 998-20-ЭГ, 998-20-ЭД, 998-20-ЭК,
998-20-ЭМ, 998-20-ЭН, 998–20-ЭС, 998-20-ЭЧ, 999-20-06,
999-20-0, 999-20-Г, 999-20-Э, 999-20-ЭГ, 999-20-ЭД,
999-20-ЭК, 999-20-ЭМ, 999-20-ЭН, 999-20-ЭС, 999-20-ЭЧ,
Т-131МС, Т-132МС, Т-31МС-1, Т-31МС-2, Т-31МС-3, Т-32МС-1,
Т-32МС-2, Т-32МС-3, 1052–65-ЭГ, 1052–65-ЭС, 1057–65-Э,
1057–65-ЭГ, 1057–65-ЭС, 1456–50-ЭД, 1456–50-ЭН, 1456–80-К3,
1456–80-ЦЗ,
Задвижки: 1010–200-КЗ, 1010–200-ЦЗ, 1010–200-Э,
1010–200-ЭД, 1010–200-ЭМ, 1010–200-ЭН, 1010–200-ЭС,
1012-150-КЗ, 1012-150-ЦЗ, 1012-150-Э, 1012–150-ЭГ,
1012–150-ЭД, 1012–150-ЭК, 1012-150-ЭМ, 1012–150-ЭМ,
1012–150-ЭН, 1012–150-ЭС, 1012–150-ЭЧ, 1012-175-КЗ,
1012-175-ЦЗ, 1012-175-Э, 1012–175-ЭГ, 1012–175-ЭД,
1012–175-ЭК, 1012-175-ЭМ, 1012-175-ЭН, 1012–175-ЭС,
1012–175-ЭЧ, 1012-225-КЗ, 1012-225-ЦЗ, 1012-225-Э,
1012-225-ЭГ, 1012–225-ЭД, 1012-225-ЭМ, 1012–225-ЭН,
1012–225-ЭС, 1013-175-КЗ, 1013-175-КЗ-01, 1013-175-ЦЗ,
1013-175-ЦЗ-01, 1013–175-Э, 1013–175-Э-01, 1013–175-ЭГ,
1013–175-ЭД, 1013–175-ЭД-01, 1013–175-ЭК, 1013–175-ЭК-01,
1013-175-ЭМ,-01, 1013-175-ЭН, 1013-175-ЭН-01, 1013–175-ЭС,
1013–175-ЭС-01, 1013–175-ЭЧ, 1013–175-ЭЧ-01, 1013-200-КЗ,
1013-200-ЦЗ, 1013–200-ЭД, 1013–200-ЭК, 1013-200-ЭМ,
1013–200-ЭМ, 1013-200-ЭН, 1013–200-ЭН, 1013–200-ЭС,
1013–200-ЭЧ, 1015-150-КЗ, 1015-150-ЦЗ, 1015–150-Э,
1015–150-ЭГ, 1015–150-ЭД, 1015-150-ЭК, 1015-150-ЭМ,
1015–150-ЭН, 1015–150-ЭС, 1015–150-ЭЧ, 1016-250-КЗ,
1016-250-М, 1016-250-ЦЗ, 1016–250-ЭГ, 1016–250-ЭД,
1016–250-ЭК, 1016-250-ЭМ, 1016–250-ЭМ, 1016–250-ЭН,
1016–250-ЭС, 1016–250-ЭЧ, 1017–250-КЗ, 1017-250-ЦЗ,
1017–250-ЭГ, 1017–250-ЭД, 1017-250-ЭК, 1017-250-ЭМ,
1017–250-ЭН, 1017–250-ЭС, 1017–250-ЭЧ, 1120-100-КЗ,-01,
1120-100-М, 1120-100-М-01, 1120-100-ЦЗ, 1120-100-ЦЗ-01,
1120-100-Э, 1120–100-Э-01, 1120–100-ЭГ, 1120–100-ЭГ-01,
1120–100-ЭД, 1120–100-ЭД-01, 1120-100-ЭК, 1120–100-ЭК,
1120-100-ЭК-01, 1120-100-ЭМ, 1120-100-ЭМ-01, 1120-100-ЭН-01,
1120–100-ЭС, 1120–100-ЭС-01, 1120–100-ЭЧ, 1120–100-ЭЧ-01,
1123-100-КЗ, 1123-100-КЗ-01, 1123-100-М, 1123-100-М-01,
1123-100-Ц3-01, 1123-100-ЦЗ, 1123–100-ЦЗ-01, 1123–100-Э,
1123–100-Э-01, 1123–100-ЭГ, 1123–100-ЭГ-01, 1123–100-ЭД,
1123–100-ЭД-01, 1123–100-ЭК, 1123–100-ЭК-01, 1123-100-ЭМ,
1123-100-ЭН, 1123-100-ЭН-01, 1123–100-ЭС, 1123–100-ЭС-01,
1123–100-ЭЧ, 1123–100-ЭЧ-01, 1126-150-КЗ, 1126–150-КЗБ,
1126-150-М, 1126–150-МБ, 1126-150-ЦЗ, 1126–150-Э,
1126–150-ЭГ, 1126–150-ЭД, 1126–150-ЭК, 1126-150-ЭМ,
1126–150-ЭМ, 1126–150-ЭН, 1156–125-КЗ, 1156-125-КЗА,
1156–125-М, 1156-125-ЦЗА, 1156–125-Э, 1156–125-ЭГ,
1156–125-ЭД, 1156-125-ЭК, 1156–125-ЭМ, 1156–125-ЭН,
1156–125-ЭС, 1156–125-ЭЧ, 1156–150-КЗ, 1156–150-М,
1156–150-ЦЗ, 1156-150-ЦЗА, 1156–150-Э, 1156–150-ЭГ,
1156–150-ЭД, 1156–150-ЭК, 1156-150-ЭМ, 1156-150-ЭН,
1156–150-ЭС, 1156–150-ЭЧ, 1511-100-КЗА,-КЗБ, 1511-100-МА,
1511-100-ЦЗА-ЦЗБ, 1511–100-ЭГ, 1511–100-ЭД, 1511–100-ЭМ,
1511-100-ЭМА,-ЭМБ, 1511–100-ЭС, 1511–100-ЭЧ, 1511-150-КЗА,
1511-150-МА,-МБ, 1511-150-ЦЗА,-ЦЗБ, 1511–150-ЭГ,
1511–150-ЭД, 1511-150-ЭМА,-ЭМБ, 1511–150-ЭН, 1511–150-ЭС,
1511–150-ЭЧ, 1511-200-КЗА,-КЗБ, 1511-200-МА,-МБ,
1511-200-ЦЗА,-ЦЗБ, 1511–200-ЭГ, 1511–200-ЭД, 1511-200-ЭМА,
1511-200-ЭНБ, 1511–200-ЭС, 1511–200-ЭЧ, 1511–250-КЗ,
1511-250-ЦЗА-ЦЗБ, 1511–250-ЭГ, 1511–250-ЭД, 1511-250-ЭМБ,
1511–250-ЭН, 1511–250-ЭС, 1511–250-ЭЧ, 1511-300-КЗА,-КЗБ,
1511-300-ЦЗА,-ЦЗБ, 1511–300-ЭГ, 1511–300-ЭД, 1511–300-ЭМ,
1511-300-ЭНА,-ЭНБ, 1511–300-ЭС, 1511–300-ЭЧ, 1511–80-КЗ,
1511-80-МА-МБ, 1511–80-ЦЗ, 1511–80-ЭГ, 1511–80-ЭД,
1511–80-ЭК, 1511-80-ЭМБ, 1511–80-ЭН, 1511–80-ЭС,
1511–80-ЭЧ, 1533–350-КЗ, 1533–350-ЦЗ, 1533–350-ЭД,
1533–350-ЭМ, 1533–350-ЭН, 1533–350-ЭС, 1533–350-ЭЧ,
2с-25–1Н, 2с-25-2, 2с-25-6ЭГ, 2с-25-6ЭД, 2с-25-6ЭК,
2с-25-6ЭМ, 2с-25-6ЭН, 2с-26-1, 2с-26–2Н, 2с-26–3Н,
2с-26–4 Н, 2с-26–5 Н, 2с-26-6, 2с-27-1, 2с-27-1ЭГ,
2с-27-1ЭД, 2с-27-1ЭК, 2с-27-1ЭМ, 2с-27-1ЭН, 2с-27-1ЭС,
2с-27-1ЭЧ, 2с-27–2Н, 2с-27-2Э, 2с-27-2ЭГ, 2с-27-2ЭД,
2с-27-2ЭК, 2с-27-2ЭМ, 2с-27-2ЭН, 2с-27-2ЭС, 2с-27-2ЭЧ,
2с-27-3Э, 2с-27-3ЭГ, 2с-27-3ЭД, 2с-27-3ЭК, 2с-27-3ЭМ,
2с-27-3ЭН, 2с-27-3ЭС, 2с-27-3ЭЧ, 2с-27–4 Н, 2с-27-4Э,
2с-27-4ЭГ, 2с-27-4ЭД, 2с-27-4ЭК, 2с-27-4ЭМ, 2с-27-4ЭН,
2с-27-4ЭС, 2с-27-4ЭЧ, 2с-27–5 Н, 2с-27-6, 2с-28-1,
2с-28–2Н, 2с-28–4Н, 2с-28–5 Н, 2с-28-6, 2с-29-1, 2с-29–3Н,
2с-29–4Н, 2с-29–5 Н, 2с-29-6, 2с-30-1, 2с-30-1ЭГ,
2с-30-1-ЭД, 2с-30-1-ЭК, 2с-30-1-ЭМ, 2с-30-1-ЭН, 2с-30-1ЭЧ,
2с-30-1-ЭЧ, 2с-30-2, 2с-30-2ЭГ, 2с-30-2ЭД, 2с-30-2ЭК,
2с-30-2ЭМ, 2с-30-2ЭН, 2с-30-2ЭЧ, 2с-31-1, 2с-31-1Э,
2с-31-1ЭД, 2с-31-1ЭМ, 2с-31-1ЭН, 2с-31-1ЭС, 2с-31-2,
2с-31-2Э, 2с-31-2ЭМ, 2с-31-2ЭН, 2с-31-2ЭС, 2с-33-1ЭГ,
2с-33-1ЭД, 2с-33-1ЭК, 2с-33-1ЭМ, 2с-33-1ЭН, 2с-33-1ЭЧ,
2с-33-2ЭД, 2с-33-2ЭК, 2с-33-2ЭМ, 2с-33-2ЭН, 2с-33-2ЭЧ,
2с-34-1Э, 2с-34-1ЭД, 2с-34-1ЭМ, 2с-34-1ЭН, 2с-34-1ЭС,
2с-34-1ЭЧ, 2с-34-2Э, 2с-34-2ЭС, 2с-350-10-450-КЗ,
2с-350-10-450-ЦЗ, 2с-350-10-450-ЭД, 2с-350-10-450-ЭМ,
2с-350-10-450-ЭН, 2с-350-10-450-ЭС, 2с-35-2,
2с-400-10-450-КЗ, 2с-400-10-450-ЦЗ, 2с-400-10-450-ЭД,
2с-400-10-450-ЭМ, 2с-400-10-450-ЭН, 2с-400-10-450-ЭС,
2с-450-10-450-КЗ, 2с-450-10-450-ЦЗ, 2с-450-10-450-ЭД,
2с-450-10-450-ЭМ, 2с-450-10-450-ЭН, 2с-450-10-450-ЭС,
2с-Э-1, 2С-Э-2, 2с-Э-4, 2с-Э-5, 2с-ЭГ-1, 2с-ЭГ-2, 2с-ЭГ-3,
2с-ЭГ-4, 2с-ЭГ-5 Н, 2с-ЭГ-5, 2с-ЭГ-6, 2с-ЭД-1, 2с-ЭД-2,
2с-ЭД-3, 2с-ЭД-4, 2с-ЭД-5 Н, 2с-ЭД-5, 2с-ЭД-6, 2с-ЭК-1,
2с-ЭК-2, 2с-ЭК-3, 2с-ЭК-4, 2с-ЭК-5 Н, 2с-ЭК-5, 2с-ЭК-6,
2с-ЭМ-1, 2с-ЭМ-2, 2с-ЭМ-3, 2с-ЭМ-4, 2с-ЭМ-5 Н, 2с-ЭМ-5,
2с-ЭМ-6, 2с-ЭН-1, 2с-ЭН-2, 2с-ЭН-3, 2с-ЭН-4, 2с-ЭН-5 Н,
2с-ЭН-5, 2с-ЭН-6, 2с-ЭС-1, 2с-ЭС-2, 2с-ЭС-3, 2с-ЭС-4,
2с-ЭС-5, 2с-ЭЧ-1, 2с-ЭЧ-2, 2с-ЭЧ-3, 2с-ЭЧ-4, 2с-ЭЧ-5,
511–100-ЭН, 850–350-КЗ, 850–350-ЦЗ, 850–350-Э, 850–350-ЭГ,
850–350-ЭД, 850–350-ЭК, 850–350-ЭМ, 850–350-ЭН, 850–350-ЭС,
850–350-ЭЧ, 850–400-КЗ, 850–400-ЦЗ, 850–400-Э, 850–400-ЭГ,
850–400-ЭД, 850–400-ЭК, 850–400-ЭМ, 850–400-ЭН, 850–400-ЭС,
850–450-КЗ, 850–450-ЦЗ, 850–450-Э, 850–450-ЭГ, 850–450-ЭД,
850–450-ЭК, 850–450-ЭМ, 850–450-ЭН, 850–450-ЭС, 850–450-ЭЧ,
880–150-КЗ, 880–150-ЦЗ, 880-150-ЦЗП, 880–150-Э, 880–150-ЭГ,
880–150-ЭД, 880–150-ЭК, 880–150-ЭМ, 880-150-ЭМП, 880–150-ЭН,
880-150-ЭНП, 880–150-ЭС, 880–150-ЭЧ, 880–200-КЗ,
880-200-КЗП, 880–200-ЦЗ, 880-200-ЦЗП, 880–200-Э, 880–200-ЭГ,
880–200-ЭД, 880–200-ЭМ, 880–200-ЭН, 880-200-ЭНП, 880–200-ЭС,
880-250-КЗП, 880-250-ЦЗП, 880–250-ЭГ, 880–250-ЭД,
880-250-ЭМП, 880-250-ЭП, 880–250-ЭС, 880–300-КЗ, 880–300-ЦЗ,
880-300-ЭА, 880–300-ЭГ, 880–300-ЭД, 880–300-ЭС, 880–325-ЭД,
880–325-ЭЛХМ, 880–325-ЭМ, 880–325-ЭТ, 880–350-ЭД,
880–350-ЭЛ, 880–350-ЭМ, 880–350-ЭТ, 880–400-ЭА, 880–400-ЭД,
880–400-ЭМ, 880–400-ЭТ, 881–100-КЗ, 881-100-КЗП, 881–100-ЦЗ,
881–100-Э, 881–100-ЭГ, 881–100-ЭД, 881–100-ЭК, 881–100-ЭМ,
881–100-ЭН, 881-100-ЭНП, 881–100-ЭС, 881–100-ЭЧ, 881–150-КЗ,
881-150-КЗП, 881–150-ЦЗ, 881-150-ЦЗП, 881–150-Э, 881–150-ЭГ,
881–150-ЭД, 881–150-ЭМ, 881-150-ЭМП, 881–150-ЭН,
881-150-ЭНП, 881–150-ЭС, 881–200-КЗ, 881-200-ЦЗП,
881–200-ЭГ, 881–200-ЭД, 881-200-ЭМП, 881-200-ЭП, 881–200-ЭС,
881–250-Э, 881–250-ЭД, 881–250-ЭМ, 881–250-ЭТ, 882-250-КЗП,
882-250-ЦЗП,-ЦЗШ, 882–250-ЭГ, 882–250-ЭД, 882-250-ЭМП,
882–250-ЭН, 882-250-ЭНП,-ЭНШ, 882–250-ЭС, 882–300-КЗ,
882-300-КЗП, 882–300-ЦЗ, 882–300-ЭГ, 882–300-ЭД, 882–300-ЭМ,
882-300-ЭНП, 882–300-ЭС, 883–175-КЗ-01, 883–175-КЗ-02,
883–175-ЦЗ-01, 883–175-ЦЗ-02, 883–175-Э-01, 883–175-Э-02,
883–175-ЭД-01, 883–175-ЭД-02, 883–175-ЭМ-01, 883–175-ЭМ-02,
883–175-ЭН-01, 883–175-ЭН-02, 883–175-ЭС-01, 883–175-ЭС-02,
883–175-ЭЧ-01, 883–175-ЭЧ-02, 883–200-КЗ, 883–200-ЦЗ,
883–200-Э, 883–200-ЭД, 883–200-ЭМ, 883–200-ЭН, 883–200-ЭС,
883-250-КЗП-01,-02, 883-250-ЦЗП-01,-02, 883–250-ЭГ,
883–250-ЭГ-01, 883–250-ЭГ-02, 883–250-ЭД, 883–250-ЭД-01,
883–250-ЭД-02, 883-250-ЭМП-01,-02, 883-250-ЭП-01,
883–250-ЭС, 883–250-ЭС-01, 883–250-ЭС-02, 883–300-КЗ,
883–300-ЦЗ, 883-300-ЦЗП, 883–300-ЭГ, 883–300-ЭД,
883-300-ЭМП, 883-300-ЭП, 883–300-ЭС, 884–200-Г, 884–200-КЗ,
884-200-ЦЗП, 884–200-ЭГ, 884–200-ЭД, 884–200-ЭМ,
884-200-ЭНП, 884–200-ЭС, 884–250-Г, 884–250-КЗ, 884–250-ЦЗ,
884–250-ЭГ, 884–250-ЭД, 884–250-ЭМ, 884-250-ЭНП, 884–250-ЭС,
884–325-КЗ, 884–325-ЦЗ, 884–325-Э, 884–325-ЭГ, 884–325-ЭД,
884–325-ЭМ, 884–325-ЭС, 885-225-КЗП, 885-225-ЦЗП,
885–225-ЭГ, 885–225-ЭД, 885-225-ЭМП, 885-225-ЭНП,
885–225-ЭС, 887-100-ЦЗП, 887–150-КЗ, 887–150-ЦЗ, 887–150-Э,
887–150-ЭД, 887–150-ЭМ, 887–150-ЭН, 887–150-ЭС, 887–150-ЭЧ,
870-200-ЭМ,
Затворы: 12с-1, 12с-1-1, 12с-2-5, 12с-3-1, 12с-3-2, 12с-3-3,
12с-3-4, 12с-4-2Э, 12с-4-3Э, 12с-4-4Э, 12с-5-5, 12с-8-10,
12с-8-11, 12с-8-12, 12с-8-13, 12с-8-14, 12с-8-15, 12с-8-4,
12с-8-5, 12с-8-6, 12с-8-7, 12с-8-8, 12с-8-9,
Электроприводы: 1280-КЭ-0, 768-Э-0а, 768-Э-0а-01,
792-Э-06-01, 792-Э-0-II, 792-Э-0А, 792-Э-0А-01, 792-Э-0а-04,
792-Э-0б, 792-ЭР-0А, 792-ЭР-0А-01, 792-ЭР-0АI, 793-Э-0,
793-Э-0а-04, 793-ЭР-0, 793-ЭР-0-02, 793-ЭР-0-04, 793-ЭР-0A,
793-ЭР-0A-I, 793-ЭР-0A-II, 793-ЭР-0I, 793-ЭР-0I-01,
793-ЭР-0-II, 794-Э-0а, 794-ЭР-0а, 794-ЭР-0аI, 795-Э-0,
795-Э-0-01, 795-Э-0-II, 795-Э-0-II-01, 795-Э-0-V, 795-ЭР-0,
795-ЭР-0-I, 795-ЭР-0-V, 797-Э-0, 797-ЭР-0, 798-Э-0,
798-Э-0-01, 821-КЭ-0а, 821-Э-0а, 821-ЭР-0б, 822-КЭ-0,
822-КЭР-0, 822-Э-0а, 822-Э-0а-01, 822-Э-0б, 822-Э-0б-01,
822-ЭР-0а, 822-ЭР-0а-01, 823-Э-0, 823-ЭР-0-03, 823-ЭР-0III,
823-ЭР-0-IIа, 823-ЭР-0-IV, 824-КЭ-0-01, 824-КЭ-0-02,
824-КЭ-0-03, 824-КЭ-0-04, 824-Э-0а, 824-ЭР-0а, 824-ЭР-0аI,
825-КЭ-0, 825-КЭР-0, 825-Э-0, 825-Э-0-01, 825-Э-0-I,
854-Э-0, 876-КЭР-0, 876-Э-0, 876-Э-0-02, 876-Э-0-04,
876-Э-0-07, 876-Э-0-08, 882-КЭ-0, 882-КЭ-0-01, 882-КЭ-0-02,
885-КЭ-0
текст песни ночь https://faav.ru
propecia without prescription
Комплексная аренда спецтехники с оператором под ключ — Полная информация по ссылке https://socialsocial.social/user/mdspecteh/
buy cialis without prescription
canadian pharmacy online no script
blue mountain pharmacy canada
canadian pharmacy without prescription
check these guys out https://playslotrealmoney.com/ka/category-mythology/
как правильно охотиться запретные сроки охоты
Компания 1хБет предоставляет всем 100% бонус за первый депозит до 32500 рублей (или эквивалент в другой валюте по актуальному курсу). Кроме того, вас ожидает приветственный пакет в 1xBet казино до €1950 +150 фриспинов для игры в слоты и игровые автоматы. 1xBet — это одна из самых популярных и надежных платформ, которая предлагает уникальные возможности и привлекательные бонусы для своих пользователей. Независимо от того, являетесь ли вы новичком в мире ставок или опытным игроком, промокоды 1xBet — это отличный способ повысить свои шансы на выигрыш.
Промокод 1xBet
http://free-health.ru/application/pages/?promokod_1xbet_bonus_pri_registracii_6500_rubley.html
Промокод 1хБет на сегодня – предоставляет вам возможность получить 100%-й бонус до 32 500 ? и Приветственный пакет до 1500 евро + 150 фриспинов для игры в разделе азартных игр 1хБет. 1xBet — это известная онлайн-платформа для ставок, которая славится своими щедрыми бонусами и привлекательными предложениями. Если вы ищете уникальный игровой опыт и дополнительные шансы на успех, то бонусы 1xBet станут отличным выбором для вас.
Бонусы являются одной из главных особенностей, которые делают 1xBet привлекательной для множества игроков. Как новый, так и постоянный пользователь, вы сможете воспользоваться различными видами бонусов, которые помогут увеличить ваши шансы на выигрыш. От приветственных бонусов до регулярных акций, 1xBet предлагает множество вариантов, чтобы удовлетворить ваши потребности и предпочтения.
Один из самых популярных бонусов, предоставляемых 1xBet, – это приветственный бонус для новых игроков. Как только вы зарегистрируетесь на платформе, вам будет предложен щедрый приветственный пакет, который включает в себя бонус на первый депозит. Это означает, что вы получите дополнительные средства на свой игровой счет, чтобы увеличить свои возможности для ставок. Такой бонус является отличным стартом в вашем игровом путешествии и помогает вам исследовать различные игры и спортивные события.
купить диплом образование нижнем новгороде купить диплом образование нижнем новгороде .
Монтажные провода
диплом электрика купить
Казино Водка это новое онлайн казино, основанное в 2023 году. Оно стремительно завоевало внимание даже самых искушённых игроков в России и других странах СНГ. Водка Казино предлагает своим игрокам внушительную библиотеку игровых автоматов – свыше 2000 слотов обеспечивающимися более чем 45 провайдерами игр, где каждый игрок найдет игру по душе Vodka Casino
Казино Водка это новое онлайн казино, основанное в 2023 году. Оно стремительно завоевало внимание даже самых искушённых игроков в России и других странах СНГ. Водка Казино предлагает своим игрокам внушительную библиотеку игровых автоматов – свыше 2000 слотов обеспечивающимися более чем 45 провайдерами игр, где каждый игрок найдет игру по душе казино Vodka
Казино Водка это новое онлайн казино, основанное в 2023 году. Оно стремительно завоевало внимание даже самых искушённых игроков в России и других странах СНГ. Водка Казино предлагает своим игрокам внушительную библиотеку игровых автоматов – свыше 2000 слотов обеспечивающимися более чем 45 провайдерами игр, где каждый игрок найдет игру по душе казино Vodka
аттестат школы купить
Реально ли приобрести диплом стоматолога? Основные шаги
Лечение зубов — непростой процесс, который требует терпения, времени, а главное — помощи профессионала. Только консультация стоматолога и систематическая диагностика зубов могут предупредить развитие кариеса, образование зубного камня, пульпит и другие заболевания, наносящие урон как здоровью всего организма, так и вашему внешнему виду имплантация зубов десна
Лечение зубов — непростой процесс, который требует терпения, времени, а главное — помощи профессионала. Только консультация стоматолога и систематическая диагностика зубов могут предупредить развитие кариеса, образование зубного камня, пульпит и другие заболевания, наносящие урон как здоровью всего организма, так и вашему внешнему виду имплантация зубов форум
JS Bank launched its first corporate TVC in the year 2016.
Лечение зубов — непростой процесс, который требует терпения, времени, а главное — помощи профессионала. Только консультация стоматолога и систематическая диагностика зубов могут предупредить развитие кариеса, образование зубного камня, пульпит и другие заболевания, наносящие урон как здоровью всего организма, так и вашему внешнему виду имплантация зубов десна
диплом врача купить
Rigellians ought to keep away from America during Xmas.
A priest of the Church of Gentle, he is likely one of the judges of Candidates for Queen.
Deductive reasoning is purely a game of outcomes, during which the results are mentioned, first the different sentences are put together in a sequence and they’re interconnected, then a relationship is formed about them.
диплом купить
диплом о среднем образовании купить
Colodro, Carlos Alberto (21 April 2023).
Within the past year, the number of mobile gas apps has swelled.
Urgent TON Crypto Inside information!
The Open Network (TON) has experienced a remarkable surge in popularity throughout 2024, with the number of token holders skyrocketing by 2400% to over 90 million. This growth has been particularly pronounced since June, with trading volumes reaching a peak of $2.4 billion in September.
Currently priced at $5.28, Toncoin (TON) has a market capitalization of $13.40 billion.
Insider information about TON will priced more than $20 (up to 400%)
For more information please see: https://ke1taro.com/crypto/
Free limited access code here:
crypto4
crypto3
crypto4
crypto3
crypto4
crypto2
crypto4
crypto3
crypto5
crypto4
crypto4
crypto3
In essence, a futures contract is a standardized ahead contract in which the buyer and the vendor accept the terms in regards to product, grade, quantity and location and are solely free to negotiate the price.
купить диплом военного училища 2orik-diploms.ru .
Liquidations generally come in two forms – either compulsory liquidations (sometimes called creditors’ liquidations) and voluntary liquidations (sometimes called members’ liquidations, although a voluntary liquidation where the company is insolvent will also be controlled by the creditors, and is properly referred to as a creditors’ voluntary liquidation).
Ресторанный консалтинг UPSKILL https://upskilll.ru/consulting это профессиональные услуги в сфере ресторанного бизнеса: анализ рынка, аудит заведения, устранение слабых мест, обучение персонала, занимаемся наставничеством рестораторов с 2018 года.
지난해 국내 온라인쇼핑 시장 덩치 169조원을 넘어서는 수준이다. 미국에서는 이달 30일 블랙프라이데이와 사이버먼데이로 이어지는 연말 타다주브 쇼핑 계절이 기다리고 있습니다. 허나 이번년도는 글로벌 물류대란이 변수로 떠증가했다. 전 세계 공급망 차질로 주요 소매유통업체들이 상품 재고 확보에 하기 곤란함을 겪고 있기 때문이다. 어도비는 연말 계절 미국 소매회사의 할인율이 전년보다 5%포인트(P)가량 줄어들 것으로 전망했었다.
센포스
Vampire power refers to the electricity many gadgets and appliances waste simply by being plugged in (even if they’re switched off).
пропуска в москву для грузовиков пропуска в москву для грузовиков .
пропуска в москву для грузовиков пропуска в москву для грузовиков .
1xbet apk code promo – utilisez-le pour vous inscrire et obtenir un bonus de 130% sur le montant de votre premier depot, pouvant aller jusqu’a 130$. Ces fonds doivent etre mises dans la section sportive, ou vous devez placer des paris avec une cote minimale de 1,4 et un wager x5.
Code Promo 1xBet
https://novo-horizonte-group.com/docs/blog/?sovety_po_prohoghdeniyu_mafia_wars_osnovnye_zadaniya_010.html
Code promo de 1xBet – l’utilisation de ce code vous permettra d’obtenir un bonus de 30% supplementaire, allant jusqu’a 100$. Le bonus est accorde sous la forme de 130% du montant de votre premier depot. Cette offre est reservee aux nouveaux utilisateurs majeurs apres leur inscription. Profitez du code promo pour augmenter votre bonus de bienvenue de 100% a 130%. Les fonds seront credites sur votre solde de jeu, et le bonus devra etre mise sur des paris sportifs. Ce code promo est valable jusqu’au 31 decembre 2025.
try this out https://demofreeslot.com/ru/
Как быстро и легально купить аттестат 11 класса в Москве
https://je-tall-sf-marketing-178.b-cdn.net/research/je-tall-sf-marketing-(53).html
The following are some things to assume about when choosing between clothes.
cialis black 800mg reviews
ремонт стиральных машин лджи ремонт стиральных машин недорого
Code bonus 1xBet gratuit utilisez ce code et vous recevrez un bonus de 130€. Le bookmaker 1xbet offre a ses nouveaux clients un bonus de 100% sur le sport et le casino. Inscrivez-vous avec un code promotionnel et obtenez le bonus maximum des maintenant.
Code Promo 1xBet
https://wiserwomen.org/wp-content/plugins/elements/?code_promo_11.html
Le code promo 1xBet pour aujourd’hui 2025. Lorsque vous vous inscrivez, utilisez-le et vous beneficierez d’un bonus de bienvenue gratuit de 130$. Tout d’abord, il est important de noter que les codes promotionnels peuvent varier. Certains codes ne sont disponibles qu’une seule fois et uniquement dans certaines conditions specifiques. D’autres codes sont permanents et peuvent etre utilises regulierement par les joueurs pour ameliorer leurs performances de jeu.
canadian pharmacy
Условия работы с нами
Как получить диплом техникума с упрощенным обучением в Москве официально
Как безопасно купить диплом колледжа или ПТУ в России, что важно знать
аттестат о среднем образовании купить в москве
диплом купить в липецке
https://ya-4545-12.s3.us-east-005.backblazeb2.com/equity-allocation-in-company-registration.html
Straight-leg pants create a streamlined silhouette that subtly enhances the velvet burnout-print high and jacket.
купить диплом технолога общественного питания
가상화폐 가격이 월간 기준으로 30년 만에 최대 낙폭을 기록하며 ‘잔인한 4월’로 마감할 것이라는 해석이 제기됐습니다. 현지기간 24일 바이비트 외신의 말을 빌리면 비트코인 가격은 이달 들어 최근까지 34% 넘게 폭락해 2018년 11월 잠시 뒤 월간 기준 최대 하락 폭을 기록했습니다.
바이비트
Эта компания предлагает широкий выбор оконных конструкций на заказ, подробности здесь https://www.freelistingusa.com/listings/osteklenia
Платформа Курьер Купер https://cash-kuper.ru открывает возможности для работы в доставке. Свободный график, прозрачная система оплаты и заказы поблизости – идеальный выбор для тех, кто ищет подработку или основной заработок.
canadian pharcharmy
купить среднее техническое образование купить среднее техническое образование .
canadian pharmacy 24h
supreme suppliers viagra
отзывы купить диплом о высшем образовании
Wow, this paragraph is nice, my younger sister is analyzing these kinds of things, thus I
am going to tell her.
Наш онлайн-сервис предлагает сотрудничество всем, кто заинтересован в подписчиках в Instagram и других популярных социальных сетях. Мы готовы предложить нашим клиентам приобрести ряд преимуществ, которые сделают нашу совместную работу по накрутке подписчиков в Instagram эффективной и прибыльной для каждого владельца аккаунта накрутка живых подписчиков инстаграм
Наш онлайн-сервис предлагает сотрудничество всем, кто заинтересован в подписчиках в Instagram и других популярных социальных сетях. Мы готовы предложить нашим клиентам приобрести ряд преимуществ, которые сделают нашу совместную работу по накрутке подписчиков в Instagram эффективной и прибыльной для каждого владельца аккаунта https://paneltop.ru/
Наш онлайн-сервис предлагает сотрудничество всем, кто заинтересован в подписчиках в Instagram и других популярных социальных сетях. Мы готовы предложить нашим клиентам приобрести ряд преимуществ, которые сделают нашу совместную работу по накрутке подписчиков в Instagram эффективной и прибыльной для каждого владельца аккаунта накрутка подписчиков инстаграм купить дешево
В 2023 году была основана новая компания, которая на данный момент является одним из самых надежных поставщиков азартного софта. Поклонниками бренда Водка Казино являются истинные ценители классических развлечений клубов Лас-Вегаса Водка Казино
В 2023 году была основана новая компания, которая на данный момент является одним из самых надежных поставщиков азартного софта. Поклонниками бренда Водка Казино являются истинные ценители классических развлечений клубов Лас-Вегаса Vodka Casino
canadian pharmacy mall
В 2023 году была основана новая компания, которая на данный момент является одним из самых надежных поставщиков азартного софта. Поклонниками бренда Водка Казино являются истинные ценители классических развлечений клубов Лас-Вегаса казино Vodka
Чтобы активировать промокод Ramenbet ?BONUSMEN?? при регистрации, выполните следующие действия:
Перейдите на официальный сайт Ramenbet.
При регистрации или входе в личный кабинет найдите специальное поле для промокода.
Введите промокод Ramenbet ?BONUSMEN?? в это поле.
Перейдите в раздел подтверждения регистрации и выберите способ подтверждения: по электронной почте или SMS.
Заполните все обязательные поля с персональными данными.
Подтвердите номер мобильного телефона или адрес электронной почты.
После выполнения этих шагов на ваш счёт будут начислены дополнительные 30 бесплатных вращений для игры в слот Gates of Olympus.
Ramenbet промокод
https://signalvdom.ru/js/pages/?promokod_ramenbet_2024_bonus_200_230_fs.html
На сайте представлены около 4500 слотов, которые находятся в разделе «Казино». Азартные игры распределены по категориям на панели навигации. Они позволяют выводить на экран топовые слоты, новинки, автоматы Megaways, Hold and Win, c функцией покупки бонусов или с джекпотом. Также в любой выбранной категории можно воспользоваться дополнительными фильтрами.
Полезные советы по безопасной покупке диплома о высшем образовании
купить диплом продажа дипломов
User Experience (UX) research has emerged as a critical factor in determining the success or failure of online gambling platforms, as it directly impacts player engagement, retention, and overall satisfaction Blockchain integration
User Experience (UX) research has emerged as a critical factor in determining the success or failure of online gambling platforms, as it directly impacts player engagement, retention, and overall satisfaction Machine learning
User Experience (UX) research has emerged as a critical factor in determining the success or failure of online gambling platforms, as it directly impacts player engagement, retention, and overall satisfaction Machine learning
generic viagra no prescription
Как официально купить аттестат 11 класса с упрощенным обучением в Москве
supreme suppliers
marijuana in prague weed in prague
작년 해외 온/오프라인쇼핑 시장 덩치 168조원을 넘어서는 수준이다. 미국에서는 이달 26일 블랙프라이데이와 사이버먼데이로 이어지는 연말 타다주브 쇼핑 시즌이 기다리고 있을 것이다. 허나 올해는 글로벌 물류대란이 변수로 떠올랐다. 전 세계 제공망 차질로 주요 소매유통회사들이 상품 재고 확보에 하기 어려움을 겪고 있기 때문이다. 어도비는 연말 계절 미국 소매업체의 할인율이 지난해보다 9%포인트(P)가량 줄어들 것으로 예상했었다.
두사트
купить диплом вк prema-diploms.ru .
ремонт водонагревателей на дому ремонт бойлеров на дому
thc gummies delivery in prague https://shop-cannabis-prague.com
взять деньги в кредит под низкий процент микрокредит
Виртуальное пространство, созданное для истинных ценителей адреналина, предлагает широкий выбор игр от классических слотов до современных настольных развлечений. Пользователям доступны многочисленные бонусы и акции, которые делают процесс игры еще более захватывающим. Заходи vega bet casino Одной из ключевых особенностей казино Вега является его усовершенствованное зеркало – альтернативный доступ к сайту, который позволяет обходить блокировки и наслаждаться всеми преимуществами платформы. Благодаря инновационному дизайну, интерфейс остается удобным и интуитивно понятным, позволяя игрокам сосредоточиться на своем опыте.
Bukmacher oraz kasyno internetowe Mostbet PL to jeden z najdłużej działających serwisów hazardowych w sieci z ofertą dla Polaków, gdyż został założony jeszcze w 2009 roku. Platforma może pochwalić się posiadaniem aktywnej licencji od Curacao, która gwarantuje bezpieczeństwo. Gracze w Mostbet Casino będą mogli spotkać tutaj ponad 3000 zróżnicowanych gier hazardowych, które zostały podzielone na automaty, gry stołowe oraz gry na żywo.
Компания, основанная в 2023 году, стремительно завоевала доверие как один из ведущих поставщиков азартного софта. Vodka Casino привлекает игроков, которые ценят классические развлечения в духе Лас-Вегаса казино Vodka
Canada pharmacy meds canadian pharcharmy Healthy man viagra offer
Компания, основанная в 2023 году, стремительно завоевала доверие как один из ведущих поставщиков азартного софта. Vodka Casino привлекает игроков, которые ценят классические развлечения в духе Лас-Вегаса казино Vodka
Компания, основанная в 2023 году, стремительно завоевала доверие как один из ведущих поставщиков азартного софта. Vodka Casino привлекает игроков, которые ценят классические развлечения в духе Лас-Вегаса Vodka Casino
Ищете, где купить минитрактор? Узнайте о лучших моделях и выгодных предложениях для вашего хозяйства https://traktor2025.ru/
Ищете, где купить минитрактор? Узнайте о лучших моделях и выгодных предложениях для вашего хозяйства кубота минитрактор
Ищете, где купить минитрактор? Узнайте о лучших моделях и выгодных предложениях для вашего хозяйства мини трактор для домашнего хозяйства цена
Добро пожаловать на наш сайт!
Откройте лучшие финансовые
решения прямо сейчас!
Наши предложения
Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент финансовых продуктов: кредиты, банковские карты и займы, чтобы помочь вам достичь ваших целей и воплотить мечты в реальность.
Кредиты для всех нужд
Планируете покупку жилья, автомобиля или
образование? Наши кредитные программы
созданы для вас. Оформите кредит на нашем сайте за несколько минут, выбрав лучшие условия и
сроки погашения.
Преимущества наших банковских карт
Наши карты обеспечивают удобство
безналичных платежей и множество бонусов:
– **Кэшбэк и скидки у партнеров**
– **Программа лояльности**
Оформите карту онлайн и получите все преимущества
уже сегодня!
Быстрые займы для непредвиденных
расходов
Нужны деньги до зарплаты или на неожиданные расходы?
Наши займы – это быстро и удобно.
Мы предлагаем прозрачные условия и мгновенное одобрение заявок.
Наши преимущества:
– **Простота и Удобство:** Оформите заявку онлайн за считанные минуты.
– **Надежность и Прозрачность:** Честные условия без скрытых
комиссий.
– **Индивидуальный Подход:** Мы учитываем ваши личные обстоятельства.
Не упустите шанс улучшить свою финансовую ситуацию!
Оформите кредит, банковскую карту или займ
на нашем сайте уже сегодня и насладитесь всеми преимуществами сотрудничества с надежным финансовым партнером.
Переходите на наш сайт и сделайте шаг
к своим мечтам!
ВТБ – Кредит наличными в Саратове
Это не просто место для азартных игр, это целая вселенная, наполненная яркими огнями, звуками выигрышных автоматов и искренними улыбками счастливчиков. сей казино KZ, vega casino online Здесь, в сердце города, царит особая атмосфера, которая притягивает к себе как опытных игроков, так и тех, кто только делает свои первые шаги в мире азартных развлечений.
Как не попасть впросак при покупке диплома колледжа или ПТУ в России
Сопровождение мужчин — это особая услуга, которая может включать в себя как деловые, так и личные аспекты.
В современном мире многие мужчины ищут профессионалов, которые могут помочь им в различных сферах жизни:
от бизнес-мероприятий до социальных встреч – элитный эскорт москвы
диплом купить колледжа
Продажа дженериков на сайте https://buy-generic.ru производства Индии
по привлекательной цене с доставкой
Rent Bicrypto (latest) with All Plugins + Hosting for Bicrypto = 40 Euro
Super offer from Phoenix.lol: rent the Bicrypto script and all plugins + hosting!
After 1 year, the licenses become your property!
Rent Bicrypto (latest) with All Plugins + VPS Xeon
Купить диплом Самара
Открывайте кейсы CS:GO Кейсы кс го с крутыми шансами на редкие скины. Удобный интерфейс, надежная система и огромный выбор кейсов сделают игру еще интереснее. Начните свой путь к топовым скинам прямо сейчас!
диплом советский купить
Howdy are using WordPress for your blog platform? I’m new to
the blog world but I’m trying to get started and create my own. Do you need
any coding expertise to make your own blog? Any
help would be really appreciated!
Купить дженерики с доставкой на сайте https://jeneri.ru/ высокое качество по привлекательной цене
производства Индии
Welcome to our platform, the leading solution for top-tier social media marketing services. As a leading provider in the industry, we help businesses to grow their online presence, connect with audiences, and deliver real results. Whether your business is aiming to grow followers, enhance brand visibility, or increase customer engagement, Solidsmm.com delivers trusted, budget-friendly, and bespoke services designed for your unique needs. Join us today and see your social media platforms thrive!
ссылка на сайт GAMA
usa pharmacy no script
sky pharmacy
купить аттестат о среднем специальном образовании с занесением в реестр
Что входит в стоимость имплантации 1 зуба под ключ? Анестезия, рентген, операция по установке титановых стержней, снятие слепков, наложение швов (затем снятие) имплантация зубов под цена
Что входит в стоимость имплантации 1 зуба под ключ? Анестезия, рентген, операция по установке титановых стержней, снятие слепков, наложение швов (затем снятие) имплантация зубов стоматологи
Как правильно организовать подготовку к ЕГЭ? Советы преподавателей https://nalatty.com/hand-made/prilozheniya-dlya-podgotovki-k-ege-kak-vybrat/
canadian pharmacy mall
canadian pharmacy no prescription
Как правильно организовать подготовку к ЕГЭ? Советы преподавателей https://zigry.net/chto-budet-esli-ne-sdat-ege-posledstviya-i-alternativy/
Что входит в стоимость имплантации 1 зуба под ключ? Анестезия, рентген, операция по установке титановых стержней, снятие слепков, наложение швов (затем снятие) имплантация зубов сколько
Как правильно организовать подготовку к ЕГЭ? Советы преподавателей https://prykoly.ru/kak-podgotovitsya-k-ege-s-pomoshhyu-mobilnyh-prilozhenij-polnyj-gid/
Заказать качественные дженерики https://moyapotenciya.ru с доставкой
по низкой цене производства Индии
Откройте яркие кейсы CS:GO https://m.youtube.com/@hotdrop-case и получите шанс выиграть топовые скины! Широкий выбор кейсов, высокий шанс дропа и честная система обеспечат увлекательный опыт.
Выход из запоя — это важнейший этап на пути к избавлению от алкогольной зависимости. Он требует комплексного подхода, профессиональной помощи и сильной мотивации пациента. В условиях, когда анонимность и комфорт становятся ключевыми факторами для многих людей, вывод из запоя на дому приобретает все большее значение. Это решение позволяет человеку получить необходимую помощь, не покидая дома, и избежать стресса, связанного с госпитализацией.
Получить больше информации – вывод из запоя на дому цена в краснодаре
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, необходимая для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Это состояние, часто характеризующееся физическими и психоэмоциональными нарушениями, требует профессионального вмешательства. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть разнообразными и варьироваться от лёгкой тревожности до серьёзных нарушений в функционировании внутренних органов. Квалифицированная помощь в этот период позволяет минимизировать риски и значительно ускорить процесс выздоровления.
Подробнее тут – narkologiya vyvod iz zapoya anonimno voronezh
Запой — это состояние, при котором человек не может прекратить употребление алкоголя на протяжении длительного времени, что вызывает физическую и психологическую зависимость. Это крайне опасное состояние, требующее немедленного вмешательства специалистов. Наркологическая клиника «Преображение» в Екатеринбурге предоставляет профессиональную помощь в лечении запоя, используя самые эффективные и безопасные методы.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-20.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-ekaterinburge/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в екатеринбурге[/url]
Стоимость вывода из запоя зависит от ряда факторов, таких как состояние пациента, выбранная программа лечения и место проведения процедуры. Мы предлагаем прозрачное ценообразование, чтобы вы могли заранее ознакомиться с возможными затратами на лечение.
Выяснить больше – srochny vyvod iz zapoya na domu
диплом ссср купить
Запой — это одно из наиболее тяжелых проявлений алкогольной зависимости, которое требует немедленного и квалифицированного вмешательства. В такие моменты близкие зачастую теряются и не знают, как помочь своему родному человеку. На помощь приходит наркологическая клиника «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, которая предоставляет профессиональную помощь в выводе из запоя. Мы понимаем, что лечение запоя требует не только медицинского подхода, но и психологической поддержки. Именно поэтому в нашей клинике пациент получает комплексную помощь, основанную на самых современных методах лечения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – vyvod iz zapoya na domu kruglosutochno chelyabinsk
Алкогольная зависимость — это серьезная проблема, требующая немедленного вмешательства. Если вы или ваши близкие столкнулись с запоем, важно получить профессиональную помощь как можно скорее, чтобы избежать ухудшения здоровья. Наркологическая клиника «Шаг к Трезвости» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вывода из запоя на дому, что является удобным и эффективным решением для тех, кто не может или не хочет посещать стационар.
Подробнее – вывод из запоя
Запой представляет собой состояние, связанное с длительным употреблением алкогольных напитков, что приводит к значительным физическим и психическим расстройствам. Это явление формирует зависимость, оказывая негативное воздействие на здоровье. Вывод из запоя в стационаре становится необходимостью для восстановительных мероприятий, направленных на реабилитацию пациента. В этой статье рассматриваются аспекты анонимного вывода, скорость процедур, а также роль нарколога в процессе лечения.
Детальнее – анонимный вывод из запоя на дому краснодар
Алкогольный запой представляет собой критическое состояние, требующее немедленного вмешательства квалифицированных специалистов. Клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже предлагает круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить своевременное и эффективное лечение. Наша цель — оперативное снятие интоксикации, устранение симптомов и предотвращение осложнений.
Выяснить больше – вывод из запоя на дому цена в воронеже
Алкогольный запой — это тяжелое состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над количеством потребляемого алкоголя. Это приводит к сильной интоксикации, сбоям в работе органов и систем организма, а также серьезным психоэмоциональным расстройствам. Без должной медицинской помощи запой может вызвать ряд опасных последствий, включая алкогольный делирий и угрозу жизни. Поэтому при первых признаках запоя необходимо обратиться к профессионалам.
Подробнее тут – нарколог вывод из запоя цена в твери
купить диплом о высшем в уфе 2orik-diploms.ru .
Пробуйте удачу https://discord.com/invite/B5fF6pW8Cm CS:GO! Шанс получить редкие и дорогие скины, широкий выбор кейсов и удобный интерфейс делают процесс открытия легким и захватывающим.
Запой представляет собой состояние, характеризующееся длительным непрерывным употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к физической и психической зависимости. Этот процесс может длиться от нескольких дней до недель. Алкогольные напитки негативно влияют на функционирование внутренних органов, вызывая серьёзные нарушения, включая алкоголизм. При необходимости вывода из запоя важно обратиться за медицинской помощью, что можно осуществить на дому. В данной статье рассмотрим ключевые аспекты данной процедуры.
Получить дополнительные сведения – vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno narkologiya chelyabinsk
Запой — это одно из наиболее тяжелых проявлений алкогольной зависимости, которое требует немедленного и квалифицированного вмешательства. В такие моменты близкие зачастую теряются и не знают, как помочь своему родному человеку. На помощь приходит наркологическая клиника «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, которая предоставляет профессиональную помощь в выводе из запоя. Мы понимаем, что лечение запоя требует не только медицинского подхода, но и психологической поддержки. Именно поэтому в нашей клинике пациент получает комплексную помощь, основанную на самых современных методах лечения.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – вывод из запоя на дому недорого капельница
https://ritual-gbu.ru/
В современном мире проблема зависимостей остаётся одной из наиболее острых. Всё больше людей сталкиваются с трудностями, связанными с алкоголизмом, наркоманией и другими формами зависимости, что разрушительно сказывается как на их жизни, так и на взаимоотношениях с окружающими. Это сложное явление, затрагивающее не только физическое здоровье, но и психоэмоциональное состояние, требует профессионального подхода для эффективного решения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno narkologiya voronezh
Gpchealth http://onlinepharmacynoprescription.com/ Polar meds
Алкогольные запои — это одно из самых сложных проявлений зависимости, требующее профессионального подхода и незамедлительных действий. В такие периоды близкие люди часто не знают, как помочь, но своевременное обращение за медицинской помощью может стать ключом к восстановлению. В Челябинске клиника «Перекресток Надежды» предоставляет квалифицированные услуги по выводу из запоя, сочетая современные методики лечения с поддержкой на психологическом уровне.
Выяснить больше – narkologicheskij centr chelyabinsk
Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся утратой контроля над употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к тяжелой интоксикации организма. Вывод из запоя — это комплексный процесс, направленный на устранение последствий интоксикации и восстановление нормального функционирования организма. Цена данной процедуры может значительно различаться в зависимости от нескольких факторов, и в этой статье мы подробно рассмотрим, что влияет на стоимость вывода из запоя в Краснодаре, в том числе в клинике «Шаг к Трезвости».
Выяснить больше – narkolog na dom vyvod iz zapoya
Купить недорого дженерики на сайте https://u-farm.ru с доставкой
по городу и области
Admiring the dedication you put into your site and in depth information you provide.
It’s great to come across a blog every once in a while that
isn’t the same unwanted rehashed information. Excellent read!
I’ve saved your site and I’m including your RSS feeds to
my Google account.
online pharmacy no prescription canada Canada Pharmacy 24 Hour Drug Store Cialis kaufen billig
В клинике «Излечение» мы предлагаем широкий спектр услуг по выводу из запоя, включая как стационарное лечение, так и помощь на дому. В этой статье мы подробно рассмотрим, от чего зависит цена вывода из запоя и какие услуги входят в стоимость.
Подробнее – вывод из запоя на дому цена
Рискни и испытай удачу https://t.me/hotdropcases Шанс получить редкие и дорогие скины, широкий выбор кейсов и удобный интерфейс делают процесс открытия легким и захватывающим.
Стоимость вывода из запоя зависит от ряда факторов, таких как состояние пациента, выбранная программа лечения и место проведения процедуры. Мы предлагаем прозрачное ценообразование, чтобы вы могли заранее ознакомиться с возможными затратами на лечение.
Разобраться лучше – нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в челябинске
В клинике «Излечение» понимают важность анонимности и индивидуального подхода при лечении алкогольной зависимости. Полная конфиденциальность гарантируется как в стационаре, так и при выезде на дом. Это позволяет пациентам чувствовать себя защищенными и уверенными на пути к выздоровлению. Процесс вывода из запоя включает в себя устранение токсического воздействия алкоголя, восстановление нормального функционирования организма и психологическую поддержку.
Разобраться лучше – narkologicheskij centr v-krasnodare
Алкогольный запой представляет собой критическое состояние, требующее немедленного вмешательства квалифицированных специалистов. Клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже предлагает круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить своевременное и эффективное лечение. Наша цель — оперативное снятие интоксикации, устранение симптомов и предотвращение осложнений.
Получить дополнительную информацию – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom na dom voronezh
Полезные советы по безопасной покупке диплома о высшем образовании
Алкогольный запой представляет собой серьезное состояние, которое требует немедленного медицинского вмешательства. Это состояние характеризуется длительным и бесконтрольным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к разрушению как физического, так и психоэмоционального здоровья человека. Для эффективного и безопасного вывода из запоя стационарное лечение является оптимальным решением, особенно при тяжелых случаях интоксикации. В стационаре клиники «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем комплексную программу вывода из запоя, которая включает детоксикацию, восстановление организма и психотерапевтическую помощь.
Получить дополнительные сведения – vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare anonimno
Многие люди избегают обращения за помощью из-за страха утраты конфиденциальности. В клинике строго соблюдается анонимность, что позволяет пациентам чувствовать себя защищёнными и уверенными. Высокий уровень профессионализма и индивидуальный подход создают комфортные условия для выздоровления.
Ознакомиться с деталями – вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно в воронеже
Запой — это тяжелое состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над количеством употребляемого алкоголя, что приводит к серьезным нарушениям здоровья. Процесс вывода из запоя требует профессионального подхода, медицинского контроля и тщательного восстановления организма. Наркологическая клиника «Шаг к Трезвости» в Краснодаре предлагает квалифицированную помощь для тех, кто нуждается в срочном и безопасном выходе из запоя. Мы предоставляем комплексное лечение, ориентированное на каждый этап восстановления, с максимальной заботой о здоровье пациента.
Углубиться в тему – vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno narkologiya krasnodar
Зависимость — это сложное хроническое заболевание, требующее долгосрочной терапии и постоянной поддержки. Мы используем современные подходы, основанные на исследованиях в области наркологии и психотерапии, обеспечивая профессиональное сопровождение от диагностики до полной реабилитации. Наша команда заботится о каждом пациенте, предоставляя индивидуальные решения на всех этапах лечения.
Узнать больше – vyvod iz zapoya kapelnica na domu v-sankt-peterburge
Запой — это одно из наиболее тяжелых проявлений алкогольной зависимости, которое требует немедленного и квалифицированного вмешательства. В такие моменты близкие зачастую теряются и не знают, как помочь своему родному человеку. На помощь приходит наркологическая клиника «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, которая предоставляет профессиональную помощь в выводе из запоя. Мы понимаем, что лечение запоя требует не только медицинского подхода, но и психологической поддержки. Именно поэтому в нашей клинике пациент получает комплексную помощь, основанную на самых современных методах лечения.
Узнать больше – vyvod-iz-zapoya-17.ru
Ваши любимые кейсы CS:GO https://t.me/s/hotdropcases в одном месте! Большой выбор, удобный интерфейс и высокая вероятность выпадения редких предметов делают процесс открытия кейсов по-настоящему захватывающим.
Стоимость вывода из запоя зависит от ряда факторов, таких как состояние пациента, выбранная программа лечения и место проведения процедуры. Мы предлагаем прозрачное ценообразование, чтобы вы могли заранее ознакомиться с возможными затратами на лечение.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno narkologiya
Запойное пьянство характеризуется продолжительным и интенсивным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к серьезным физическим и психологическим последствиям. Часто пациенты сталкиваются с различными заболеваниями, такими как цирроз печени, панкреатит, алкогольный делирий и другие. Алкогольное опьянение не только ухудшает качество жизни, но также может угрожать жизни пациента. В условиях стационара лечение может быть более эффективным, однако многие люди предпочитают проходить данную процедуру на дому, чтобы избежать стигматизации и сохранить чувство приватности.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-20.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-ekaterinburge/]vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom cena v-ekaterinburge[/url]
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой сложное и хроническое заболевание, которое влияет не только на физическое, но и на психологическое состояние пациента. Периоды запоя, влекущие за собой неконтролируемое употребление алкоголя, могут привести к опасным последствиям для здоровья и жизни. Абстинентные симптомы, такие как тремор, тошнота, головная боль и другие проявления, требуют немедленного медицинского вмешательства. В таких ситуациях важно не только быстро устранить физическое воздействие алкоголя, но и предоставить пациенту психологическую поддержку.
Выяснить больше – vyvod iz zapoya
как зайти на мегу – мега даркнет, мега купить
Запой — это состояние, при котором человек на протяжении нескольких дней или даже недель непрерывно употребляет алкоголь, что приводит к серьезным физическим и психоэмоциональным последствиям. Этот процесс вызывает тяжелую зависимость, нарушает работу внутренних органов и угрожает общему здоровью. В такой ситуации требуется не только медицинская детоксикация, но и комплексное восстановление организма. Оптимальным решением может стать стационарное лечение, где пациент получает помощь под постоянным наблюдением специалистов.
Выяснить больше – вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно челябинск
Запой — это тяжелое состояние, возникающее вследствие длительного и непрерывного употребления алкоголя, которое сопровождается физической и психической зависимостью. Это опасное явление требует незамедлительного вмешательства специалистов. Вывод из запоя — это комплексный процесс медицинской детоксикации, который включает в себя очищение организма от токсинов, нормализацию функций внутренних органов и поддержку психоэмоционального состояния пациента. В случае тяжелого запоя стационарное лечение становится оптимальным решением для безопасного и эффективного вывода из этого состояния. В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как проходит вывод из запоя в стационаре клиники «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, а также особенности анонимности, скорости лечения и участия нарколога.
Углубиться в тему – вывод из запоя анонимно недорого челябинск
online pharmacy no prescription
Алкогольный запой – это серьёзное состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к тяжёлой интоксикации организма. Во время запоя нарушаются функции внутренних органов, страдает нервная система, и повышается риск развития опасных осложнений, таких как алкогольный делирий. Это состояние требует незамедлительного медицинского вмешательства.
Изучить вопрос глубже – срочный вывод из запоя на дому
В таких ситуациях вывод из запоя на дому становится оптимальным решением, особенно если пациент не может или не хочет посещать стационар. Эта услуга позволяет получить медицинскую помощь в комфортной и привычной обстановке, что снижает уровень стресса и ускоряет процесс восстановления.
Выяснить больше – vyvod iz zapoya na domu nedorogo kapelnica v-voronezhe
Многие люди избегают обращения за помощью из-за страха утраты конфиденциальности. В клинике строго соблюдается анонимность, что позволяет пациентам чувствовать себя защищёнными и уверенными. Высокий уровень профессионализма и индивидуальный подход создают комфортные условия для выздоровления.
Получить дополнительные сведения – vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno narkologiya voronezh
Сервис бытовых услуг https://gidrostok-servis.ru это удобное решение для любых домашних задач. Уборка, ремонт, сантехника, установка техники и многое другое. Надежные специалисты, быстрое выполнение и доступные цены!
Запойное пьянство характеризуется продолжительным и интенсивным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к серьезным физическим и психологическим последствиям. Часто пациенты сталкиваются с различными заболеваниями, такими как цирроз печени, панкреатит, алкогольный делирий и другие. Алкогольное опьянение не только ухудшает качество жизни, но также может угрожать жизни пациента. В условиях стационара лечение может быть более эффективным, однако многие люди предпочитают проходить данную процедуру на дому, чтобы избежать стигматизации и сохранить чувство приватности.
Углубиться в тему – vyvod iz zapoya srochno kruglosutochno v-ekaterinburge
Мы предлагаем варианты лечения, которые учитывают индивидуальное состояние пациента: от комфортного домашнего выезда до комплексной помощи в стационаре. Стоимость процедур определяется исходя из необходимого объёма вмешательства и всегда остаётся прозрачной, чтобы пациенты могли сосредоточиться на главном — возвращении к полноценной жизни.
Детальнее – наркологическая клиника в санкт-петербурге
Клиника «Преображение» предлагает услуги анонимного вывода из запоя в Екатеринбурге, обеспечивая высокое качество медицинской помощи и соблюдение всех этических норм.
Изучить вопрос глубже – narkologicheski centr
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой актуальную медицинскую проблему, требующую тщательного подхода. Запой характеризуется длительным, непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что ведёт к физической и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния могут возникнуть тяжёлые нарушения функций органов, увеличивается риск развития таких состояний, как алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя становится ключевым этапом в лечении зависимостей, который может осуществляться как в стационарных условиях, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента. В клинике «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске мы предлагаем круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить максимально эффективное и безопасное лечение при любом варианте вывода из запоя.
Выяснить больше – вывод из запоя цена
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся длительным и непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к формированию как физической, так и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния часто наблюдаются нарушения работы внутренних органов, что может привести к тяжелым последствиям, включая алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя — важный этап в процессе лечения зависимости, и его можно осуществлять как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от конкретных обстоятельств.
Получить дополнительную информацию – narkologicheskij centr v-sankt-peterburge
Алкогольный запой — это состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к токсической нагрузке на организм. Это опасное состояние требует не только быстрого медицинского вмешательства, но и внимательного подхода к восстановлению здоровья пациента. Процесс вывода из запоя включает в себя комплекс процедур, направленных на устранение последствий интоксикации и восстановление нормального функционирования организма. Важно учитывать, что стоимость этой процедуры может значительно варьироваться в зависимости от нескольких факторов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – анонимный вывод из запоя на дому
Гарантированная анонимность при выводе из запоя в Челябинске. В клинике «Перекресток Надежды» мы строго соблюдаем политику конфиденциальности. Информация о пациенте и его состоянии здоровья остаётся закрытой. Это особенно важно для тех, кто ценит свою репутацию и не хочет разглашения. Мы обеспечиваем анонимность как в стационаре, так и при оказании услуг на дому, сохраняя высокий уровень медицинской помощи.
Ознакомиться с деталями – вывод из запоя с выездом на дом
Алкоголизм — это хроническое прогрессирующее заболевание, связанное с физической и психической зависимостью от этанола. Запой, как его крайнее проявление, представляет собой длительное употребление алкоголя, сопровождающееся тяжелыми нарушениями работы организма, включая абстинентный синдром и потенциальные угрозы для жизни. Лечение запоя требует комплексного подхода, включающего медицинские процедуры, психотерапию и реабилитационные меры.
Разобраться лучше – вывод из запоя цена
Индийские дженерики купить на сайте https://uptab.ru с доставкой
по выгодной цене высокое качество производства Индии
Запой — это тяжелое состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над количеством употребляемого алкоголя, что приводит к серьезным нарушениям здоровья. Процесс вывода из запоя требует профессионального подхода, медицинского контроля и тщательного восстановления организма. Наркологическая клиника «Шаг к Трезвости» в Краснодаре предлагает квалифицированную помощь для тех, кто нуждается в срочном и безопасном выходе из запоя. Мы предоставляем комплексное лечение, ориентированное на каждый этап восстановления, с максимальной заботой о здоровье пациента.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-12.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-krasnodare/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в краснодаре[/url]
Процедура вывода из запоя направлена на очищение организма от токсинов, нормализацию работы внутренних органов и стабилизацию психоэмоционального состояния. Она может быть проведена как в условиях стационара, так и на дому, в зависимости от степени тяжести состояния. При этом анонимность лечения играет важную роль. Клиника «Перекресток Надежды» гарантирует полную конфиденциальность, что особенно важно для тех, кто ценит приватность. Независимо от выбранного варианта, каждый пациент получает высококачественную помощь, соответствующую современным стандартам медицины.
Узнать больше – vyvod iz zapoya na domu nedorogo kapelnica v-chelyabinske
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, необходимая для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Это состояние, часто характеризующееся физическими и психоэмоциональными нарушениями, требует профессионального вмешательства. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть разнообразными и варьироваться от легкой тревожности до серьезных нарушений в функционировании внутренних органов. Квалифицированная помощь в этот период позволяет минимизировать риски и значительно ускорить процесс выздоровления.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – вывод из запоя вызов на дом челябинск
Гарантированная анонимность при выводе из запоя в Челябинске. В клинике «Перекресток Надежды» мы строго соблюдаем политику конфиденциальности. Информация о пациенте и его состоянии здоровья остаётся закрытой. Это особенно важно для тех, кто ценит свою репутацию и не хочет разглашения. Мы обеспечиваем анонимность как в стационаре, так и при оказании услуг на дому, сохраняя высокий уровень медицинской помощи.
Получить дополнительные сведения – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom na dom chelyabinsk
Клиника «Преображение» предлагает услуги анонимного вывода из запоя в Екатеринбурге, обеспечивая высокое качество медицинской помощи и соблюдение всех этических норм.
Детальнее – vyvod iz zapoya na domu kruglosutochno
Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся утратой контроля над употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к тяжелой интоксикации организма. Вывод из запоя — это комплексный процесс, направленный на устранение последствий интоксикации и восстановление нормального функционирования организма. Цена данной процедуры может значительно различаться в зависимости от нескольких факторов, и в этой статье мы подробно рассмотрим, что влияет на стоимость вывода из запоя в Краснодаре, в том числе в клинике «Шаг к Трезвости».
Детальнее – vyvod iz zapoya srochno kruglosutochno v-krasnodare
Алкогольный запой — это состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над своим потреблением алкоголя, что может вызвать серьезные физические и психологические проблемы. В таких ситуациях крайне важно получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь как можно скорее. Однако многие люди опасаются обращаться за помощью, переживая за свою репутацию и возможное раскрытие личной информации. В клинике «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже мы гарантируем анонимность на всех этапах лечения, сохраняя высокий уровень медицинской помощи и заботясь о каждом пациенте.
Разобраться лучше – vyvod iz zapoya srochno kruglosutochno v-voronezhe
Алкогольная зависимость — это серьезная проблема, требующая немедленного вмешательства. Если вы или ваши близкие столкнулись с запоем, важно получить профессиональную помощь как можно скорее, чтобы избежать ухудшения здоровья. Наркологическая клиника «Шаг к Трезвости» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вывода из запоя на дому, что является удобным и эффективным решением для тех, кто не может или не хочет посещать стационар.
Изучить вопрос глубже – narkologiya vyvod iz zapoya anonimno v-krasnodare
В современном мире проблема зависимостей остаётся одной из наиболее острых. Всё больше людей сталкиваются с трудностями, связанными с алкоголизмом, наркоманией и другими формами зависимости, что разрушительно сказывается как на их жизни, так и на взаимоотношениях с окружающими. Это сложное явление, затрагивающее не только физическое здоровье, но и психоэмоциональное состояние, требует профессионального подхода для эффективного решения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – anonimny vyvod iz zapoya na domu v-voronezhe
Мы предлагаем варианты лечения, которые учитывают индивидуальное состояние пациента: от комфортного домашнего выезда до комплексной помощи в стационаре. Стоимость процедур определяется исходя из необходимого объёма вмешательства и всегда остаётся прозрачной, чтобы пациенты могли сосредоточиться на главном — возвращении к полноценной жизни.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – наркологическая клиника санкт-петербург
Canadian Pharmacy No Prescription Cialis online prices Fluoxetine healthy man viagra Buy retin a without prescription
Гарантированная анонимность при выводе из запоя в Челябинске. В клинике «Перекресток Надежды» мы строго соблюдаем политику конфиденциальности. Информация о пациенте и его состоянии здоровья остаётся закрытой. Это особенно важно для тех, кто ценит свою репутацию и не хочет разглашения. Мы обеспечиваем анонимность как в стационаре, так и при оказании услуг на дому, сохраняя высокий уровень медицинской помощи.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – вывод из запоя вызов на дом
Запой представляет собой состояние, характеризующееся длительным непрерывным употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к физической и психической зависимости. Этот процесс может длиться от нескольких дней до недель. Алкогольные напитки негативно влияют на функционирование внутренних органов, вызывая серьёзные нарушения, включая алкоголизм. При необходимости вывода из запоя важно обратиться за медицинской помощью, что можно осуществить на дому. В данной статье рассмотрим ключевые аспекты данной процедуры.
Подробнее тут – vyvod iz zapoya na domu nedorogo kapelnica
canada pharmacy online
Алкогольный запой — это серьезное заболевание, которое требует немедленного и профессионального вмешательства. Запой сопровождается не только физическими страданиями, но и эмоциональными трудностями. Процесс выведения из запоя требует срочного внимания, так как состояние пациента может ухудшиться, если не получить квалифицированную помощь вовремя. Наркологическая клиника «Излечение» в Краснодаре предоставляет круглосуточную помощь при алкогольном запое, чтобы восстановить здоровье пациента в самых сложных ситуациях.
Детальнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-16.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-v-kruglosutochno-v-krasnodare/
Алкогольный запой представляет собой крайне опасное состояние, характеризующееся неконтролируемым употреблением алкоголя, что в свою очередь приводит к тяжелой интоксикации организма. Восстановление после такого состояния требует профессионального вмешательства, включающего не только физическую детоксикацию, но и психологическую поддержку. Стоимость процедуры вывода из запоя может значительно различаться в зависимости от множества факторов, включая метод лечения, тяжесть состояния пациента и место проведения лечения. Рассмотрим более подробно основные аспекты, влияющие на цену вывода из запоя.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – вывод из запоя круглосуточно в санкт-петербурге
В клинике «Рассвет» в Твери мы предлагаем круглосуточную помощь при алкогольных запоях, обеспечивая быстрый вывод токсинов из организма с помощью капельниц и других эффективных методик.
Узнать больше – вывод из запоя анонимно недорого в твери
Запойное пьянство характеризуется продолжительным и интенсивным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к серьезным физическим и психологическим последствиям. Часто пациенты сталкиваются с различными заболеваниями, такими как цирроз печени, панкреатит, алкогольный делирий и другие. Алкогольное опьянение не только ухудшает качество жизни, но также может угрожать жизни пациента. В условиях стационара лечение может быть более эффективным, однако многие люди предпочитают проходить данную процедуру на дому, чтобы избежать стигматизации и сохранить чувство приватности.
Углубиться в тему – анонимный вывод из запоя на дому
Стоимость вывода из запоя зависит от ряда факторов, таких как состояние пациента, выбранная программа лечения и место проведения процедуры. Мы предлагаем прозрачное ценообразование, чтобы вы могли заранее ознакомиться с возможными затратами на лечение.
Подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya cena narkologiya
Запой — это тяжелое состояние, возникающее вследствие длительного и непрерывного употребления алкоголя, которое сопровождается физической и психической зависимостью. Это опасное явление требует незамедлительного вмешательства специалистов. Вывод из запоя — это комплексный процесс медицинской детоксикации, который включает в себя очищение организма от токсинов, нормализацию функций внутренних органов и поддержку психоэмоционального состояния пациента. В случае тяжелого запоя стационарное лечение становится оптимальным решением для безопасного и эффективного вывода из этого состояния. В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как проходит вывод из запоя в стационаре клиники «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, а также особенности анонимности, скорости лечения и участия нарколога.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-17.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-chelyabinske/]вывод из запоя на дому цена [/url]
Клиника «Преображение» предлагает услуги анонимного вывода из запоя в Екатеринбурге, обеспечивая высокое качество медицинской помощи и соблюдение всех этических норм.
Изучить вопрос глубже – анонимный вывод из запоя на дому в екатеринбурге
Алкогольные запои — это одно из самых сложных проявлений зависимости, требующее профессионального подхода и незамедлительных действий. В такие периоды близкие люди часто не знают, как помочь, но своевременное обращение за медицинской помощью может стать ключом к восстановлению. В Челябинске клиника «Перекресток Надежды» предоставляет квалифицированные услуги по выводу из запоя, сочетая современные методики лечения с поддержкой на психологическом уровне.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom cena v-chelyabinske
Запой — это одно из наиболее тяжелых проявлений алкогольной зависимости, которое требует немедленного и квалифицированного вмешательства. В такие моменты близкие зачастую теряются и не знают, как помочь своему родному человеку. На помощь приходит наркологическая клиника «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, которая предоставляет профессиональную помощь в выводе из запоя. Мы понимаем, что лечение запоя требует не только медицинского подхода, но и психологической поддержки. Именно поэтому в нашей клинике пациент получает комплексную помощь, основанную на самых современных методах лечения.
Выяснить больше – srochny vyvod iz zapoya na domu v-chelyabinske
Запойное состояние — это серьёзная проблема, возникающая из-за длительного употребления алкоголя и приводящая к потере контроля над ситуацией. Оно сопровождается тяжёлыми последствиями для организма и психики, поэтому медицинское вмешательство в таких случаях крайне необходимо. Для удобства пациентов доступна услуга вывода из запоя на дому, что позволяет получить профессиональную помощь в привычной обстановке, снижая уровень стресса и ускоряя процесс восстановления.
Получить больше информации – vyvod iz zapoya srochno kruglosutochno
Алкогольная зависимость остаётся серьёзной проблемой, требующей квалифицированного медицинского вмешательства. Капельница от запоя — это ключевой этап в процессе лечения, направленный на стабилизацию состояния пациента и его возвращение к полноценной жизни. Профессиональная помощь позволяет эффективно справиться с последствиями длительного употребления алкоголя и восстановить физическое и психологическое здоровье.
Детальнее – быстрый вывод из запоя в стационаре тверь
Приобретение диплома ПТУ с сокращенной программой обучения в Москве
В таких ситуациях вывод из запоя на дому становится оптимальным решением, особенно если пациент не может или не хочет посещать стационар. Эта услуга позволяет получить медицинскую помощь в комфортной и привычной обстановке, что снижает уровень стресса и ускоряет процесс восстановления.
Детальнее – вывод из запоя цена наркология воронеж
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой серьёзную медицинскую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запойное состояние характеризуется длительным и бесконтрольным потреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к возникновению как физической, так и психической зависимости. Данное явление может вызвать нарушения в работе внутренних органов, значительно увеличивая вероятность развития алкогольного делирия, который представляет собой острое состояние, требующее неотложной медицинской помощи. Вывод из запоя это ключевая часть лечения зависимости, которая может осуществляться как в стационаре, так и в амбулаторных условиях, в зависимости от конкретной ситуации и состояния пациента.
Получить дополнительные сведения – нарколог на дом вывод из запоя
Запой — это одно из наиболее тяжелых проявлений алкогольной зависимости, которое требует немедленного и квалифицированного вмешательства. В такие моменты близкие зачастую теряются и не знают, как помочь своему родному человеку. На помощь приходит наркологическая клиника «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, которая предоставляет профессиональную помощь в выводе из запоя. Мы понимаем, что лечение запоя требует не только медицинского подхода, но и психологической поддержки. Именно поэтому в нашей клинике пациент получает комплексную помощь, основанную на самых современных методах лечения.
Разобраться лучше – вывод из запоя анонимно недорого в челябинске
Алкогольный запой — это состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к токсической нагрузке на организм. Это опасное состояние требует не только быстрого медицинского вмешательства, но и внимательного подхода к восстановлению здоровья пациента. Процесс вывода из запоя включает в себя комплекс процедур, направленных на устранение последствий интоксикации и восстановление нормального функционирования организма. Важно учитывать, что стоимость этой процедуры может значительно варьироваться в зависимости от нескольких факторов.
Углубиться в тему – вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Стоимость вывода из запоя зависит от ряда факторов, таких как состояние пациента, выбранная программа лечения и место проведения процедуры. Мы предлагаем прозрачное ценообразование, чтобы вы могли заранее ознакомиться с возможными затратами на лечение.
Узнать больше – вывод из запоя анонимно в челябинске
canada pharmacy 24h Methocarbamol
Продажа качественный дженериков на сайте https://viagra-deshevo.ru для мужчин
с бесплатной доставкой производства Индия
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой крайне опасное состояние, при котором организм страдает от токсического воздействия алкоголя. Это ведет к нарушению нормальных физиологических процессов и ухудшению общего состояния здоровья. Капельница от запоя — это медицинская процедура, направленная на выведение токсинов из организма и восстановление нормальной функции организма при соблюдении полной конфиденциальности.
Подробнее – вывод из запоя на дому цена в твери
Для эффективного лечения важно обратиться к профессионалам. Наркологическая клиника «Излечение» в Краснодаре предлагает помощь в безопасном и комфортном выведении из запоя, применяя индивидуальный подход к каждому случаю. Алкогольная зависимость разрушает не только физическое здоровье, но и психику, заставляя человека терять волю и становиться заложником собственной зависимости. Запой является одним из самых тяжелых этапов этой болезни: он сопровождается глубокой интоксикацией, нарушением жизненно важных функций организма, психическими расстройствами и обострением хронических заболеваний.
Ознакомиться с деталями – bystry vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare
Сувенирная продукция под нанесение оптом и мегагифт сувениры в Суздале: реклама сувениры оптом
Алкогольный запой — это тяжелое состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над количеством потребляемого алкоголя. Это приводит к сильной интоксикации, сбоям в работе органов и систем организма, а также серьезным психоэмоциональным расстройствам. Без должной медицинской помощи запой может вызвать ряд опасных последствий, включая алкогольный делирий и угрозу жизни. Поэтому при первых признаках запоя необходимо обратиться к профессионалам.
Получить дополнительные сведения – vyvod iz zapoya kapelnica na domu v-tveri
Запой — это тяжелое состояние, возникающее вследствие длительного и непрерывного употребления алкоголя, которое сопровождается физической и психической зависимостью. Это опасное явление требует незамедлительного вмешательства специалистов. Вывод из запоя — это комплексный процесс медицинской детоксикации, который включает в себя очищение организма от токсинов, нормализацию функций внутренних органов и поддержку психоэмоционального состояния пациента. В случае тяжелого запоя стационарное лечение становится оптимальным решением для безопасного и эффективного вывода из этого состояния. В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как проходит вывод из запоя в стационаре клиники «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, а также особенности анонимности, скорости лечения и участия нарколога.
Детальнее – наркологическая клиника
Можно ли купить аттестат о среднем образовании, основные моменты и вопросы
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, необходимая для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Это состояние, часто характеризующееся физическими и психоэмоциональными нарушениями, требует профессионального вмешательства. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть разнообразными и варьироваться от легкой тревожности до серьезных нарушений в функционировании внутренних органов. Квалифицированная помощь в этот период позволяет минимизировать риски и значительно ускорить процесс выздоровления.
Выяснить больше – наркологическая клиника челябинск
Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся утратой контроля над употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к тяжелой интоксикации организма. Вывод из запоя — это комплексный процесс, направленный на устранение последствий интоксикации и восстановление нормального функционирования организма. Цена данной процедуры может значительно различаться в зависимости от нескольких факторов, и в этой статье мы подробно рассмотрим, что влияет на стоимость вывода из запоя в Краснодаре, в том числе в клинике «Шаг к Трезвости».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya na domu nedorogo krasnodar
Стоимость процедур зависит от множества факторов: формы лечения, состояния пациента и индивидуальных потребностей. Клиника «Излечение» предлагает как стационарное лечение, так и помощь на дому, обеспечивая высокий уровень сервиса и безопасности.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – нарколог вывод из запоя цена краснодар
Выведение из запоя — это важный шаг на пути к восстановлению. Состояние, сопровождаемое как физическими, так и эмоциональными нарушениями, требует внимательного профессионального подхода. Квалифицированная медицинская помощь помогает эффективно устранить симптомы абстиненции и ускорить процесс реабилитации, давая пациентам возможность вернуться к полноценной жизни.
Углубиться в тему – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom cena v-voronezhe
Клиника “Второй Шанс” предоставляет круглосуточную помощь в лечении алкогольной зависимости. Мы готовы прийти на помощь в любое время суток, используя современные и проверенные методы, которые обеспечивают безопасность и высокую эффективность лечения. Полная анонимность лечения позволяет пациентам чувствовать себя уверенно и сосредоточиться на своём восстановлении.
Узнать больше – srochny vyvod iz zapoya na domu
Стоимость процедур зависит от состояния пациента, программы терапии и выбранных условий — стационар или вызов врача на дом. Клиника предоставляет прозрачную информацию о ценах, чтобы вы могли заранее оценить предстоящие затраты. Профессиональный подход и индивидуальные решения для каждого пациента помогают не только выйти из запойного состояния, но и сделать шаг к полноценной жизни.
Разобраться лучше – наркологический центр в челябинске
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой крайне опасное состояние, при котором организм страдает от токсического воздействия алкоголя. Это ведет к нарушению нормальных физиологических процессов и ухудшению общего состояния здоровья. Капельница от запоя — это медицинская процедура, направленная на выведение токсинов из организма и восстановление нормальной функции организма при соблюдении полной конфиденциальности.
Ознакомиться с деталями – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom na dom v-tveri
Запой представляет собой состояние, характеризующееся длительным непрерывным употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к физической и психической зависимости. Этот процесс может длиться от нескольких дней до недель. Алкогольные напитки негативно влияют на функционирование внутренних органов, вызывая серьёзные нарушения, включая алкоголизм. При необходимости вывода из запоя важно обратиться за медицинской помощью, что можно осуществить на дому. В данной статье рассмотрим ключевые аспекты данной процедуры.
Подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom na dom
Запой — это одно из наиболее тяжелых проявлений алкогольной зависимости, которое требует немедленного и квалифицированного вмешательства. В такие моменты близкие зачастую теряются и не знают, как помочь своему родному человеку. На помощь приходит наркологическая клиника «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, которая предоставляет профессиональную помощь в выводе из запоя. Мы понимаем, что лечение запоя требует не только медицинского подхода, но и психологической поддержки. Именно поэтому в нашей клинике пациент получает комплексную помощь, основанную на самых современных методах лечения.
Подробнее тут – вывод из запоя с выездом цена челябинск
Диплом пту купить официально с упрощенным обучением в Москве
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, необходимая для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Это состояние, часто характеризующееся физическими и психоэмоциональными нарушениями, требует профессионального вмешательства. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть разнообразными и варьироваться от лёгкой тревожности до серьёзных нарушений в функционировании внутренних органов. Квалифицированная помощь в этот период позволяет минимизировать риски и значительно ускорить процесс выздоровления.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – vyvod iz zapoya vrach na dom
диплом судового повара купить
Алкогольная зависимость — коварное заболевание, которое захватывает не только физическое здоровье, но и разрушает психику, лишает человека воли и заставляет его жить в плену у собственной зависимости. Запой — один из наиболее тяжелых периодов в жизни человека, столкнувшегося с алкоголизмом. Он характеризуется длительным и интенсивным употреблением спиртных напитков, приводящим к глубокой интоксикации организма, нарушению физиологических функций, психическим расстройствам, а также обострению сопутствующих заболеваний.
Детальнее – vyvod iz zapoya vyzov na dom krasnodar
Покупка диплома о среднем полном образовании: как избежать мошенничества?
Запой представляет собой сложное состояние, связанное с длительным употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к формированию зависимости. Это явление не только нарушает нормальную жизнедеятельность, но также вызывает серьезные физические и психологические расстройства. Стационарное лечение становится необходимым для восстановления здоровья и профилактики осложнений. В стационаре клиники «Шаг к Трезвости» в Краснодаре мы предлагаем комплексный подход, включающий медикаментозное лечение, психотерапию и постоянный контроль со стороны квалифицированных специалистов.
Разобраться лучше – нарколог на дом вывод из запоя
Клиника “Второй Шанс” предоставляет круглосуточную помощь в лечении алкогольной зависимости. Мы готовы прийти на помощь в любое время суток, используя современные и проверенные методы, которые обеспечивают безопасность и высокую эффективность лечения. Полная анонимность лечения позволяет пациентам чувствовать себя уверенно и сосредоточиться на своём восстановлении.
Разобраться лучше – вывод из запоя на дому недорого капельница санкт-петербург
Запой — это серьезное состояние, при котором человек не может прекратить употребление алкоголя на протяжении длительного времени, что вызывает физическую и психологическую зависимость. Это крайне опасное состояние, требующее немедленного вмешательства специалистов. Для безопасного и эффективного вывода из запоя необходима квалифицированная медицинская помощь, которую предоставляет наркологическая клиника «Рассвет» в Твери. Наши опытные специалисты используют современные методы детоксикации и восстановления организма, обеспечивая полный медицинский контроль и поддержку на всех этапах лечения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – vyvod iz zapoya gorod tver
Стоимость процедур зависит от множества факторов: формы лечения, состояния пациента и индивидуальных потребностей. Клиника «Излечение» предлагает как стационарное лечение, так и помощь на дому, обеспечивая высокий уровень сервиса и безопасности.
Выяснить больше – vyvod iz zapoya na domu kruglosutochno
Мы предлагаем варианты лечения, которые учитывают индивидуальное состояние пациента: от комфортного домашнего выезда до комплексной помощи в стационаре. Стоимость процедур определяется исходя из необходимого объёма вмешательства и всегда остаётся прозрачной, чтобы пациенты могли сосредоточиться на главном — возвращении к полноценной жизни.
Узнать больше – narkologiya vyvod iz zapoya na domu sankt-peterburg
Запой представляет собой состояние, характеризующееся длительным непрерывным употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к физической и психической зависимости. Этот процесс может длиться от нескольких дней до недель. Алкогольные напитки негативно влияют на функционирование внутренних органов, вызывая серьёзные нарушения, включая алкоголизм. При необходимости вывода из запоя важно обратиться за медицинской помощью, что можно осуществить на дому. В данной статье рассмотрим ключевые аспекты данной процедуры.
Ознакомиться с деталями – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom na dom
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, необходимая для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Это состояние, часто характеризующееся физическими и психоэмоциональными нарушениями, требует профессионального вмешательства. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть разнообразными и варьироваться от легкой тревожности до серьезных нарушений в функционировании внутренних органов. Квалифицированная помощь в этот период позволяет минимизировать риски и значительно ускорить процесс выздоровления.
Детальнее – narkolog na dom vyvod iz zapoya chelyabinsk
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой актуальную медицинскую проблему, требующую тщательного подхода. Запой характеризуется длительным, непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что ведёт к физической и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния могут возникнуть тяжёлые нарушения функций органов, увеличивается риск развития таких состояний, как алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя становится ключевым этапом в лечении зависимостей, который может осуществляться как в стационарных условиях, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента. В клинике «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске мы предлагаем круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить максимально эффективное и безопасное лечение при любом варианте вывода из запоя.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – вывод из запоя с выездом на дом в челябинске
В клинике «Излечение» понимают важность анонимности и индивидуального подхода при лечении алкогольной зависимости. Полная конфиденциальность гарантируется как в стационаре, так и при выезде на дом. Это позволяет пациентам чувствовать себя защищенными и уверенными на пути к выздоровлению. Процесс вывода из запоя включает в себя устранение токсического воздействия алкоголя, восстановление нормального функционирования организма и психологическую поддержку.
Узнать больше – vyvod iz zapoya na domu nedorogo
Запойное пьянство характеризуется продолжительным и интенсивным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к серьезным физическим и психологическим последствиям. Часто пациенты сталкиваются с различными заболеваниями, такими как цирроз печени, панкреатит, алкогольный делирий и другие. Алкогольное опьянение не только ухудшает качество жизни, но также может угрожать жизни пациента. В условиях стационара лечение может быть более эффективным, однако многие люди предпочитают проходить данную процедуру на дому, чтобы избежать стигматизации и сохранить чувство приватности.
Получить больше информации – vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare anonimno
купить диплом горного инженера купить диплом горного инженера .
В Воронеже специалисты клиники «Союз Здоровья» оказывают профессиональную помощь пациентам, страдающим от алкогольной зависимости, включая выведение из запоя. Особое внимание уделяется созданию атмосферы доверия и комфорта, что помогает пациентам быстрее адаптироваться к процессу лечения.
Углубиться в тему – vyvod iz zapoya na domu nedorogo voronezh
Запой — это одно из наиболее тяжелых проявлений алкогольной зависимости, которое требует немедленного и квалифицированного вмешательства. В такие моменты близкие зачастую теряются и не знают, как помочь своему родному человеку. На помощь приходит наркологическая клиника «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, которая предоставляет профессиональную помощь в выводе из запоя. Мы понимаем, что лечение запоя требует не только медицинского подхода, но и психологической поддержки. Именно поэтому в нашей клинике пациент получает комплексную помощь, основанную на самых современных методах лечения.
Выяснить больше – narkologiya vyvod iz zapoya anonimno v-chelyabinske
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, необходимая для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Это состояние, часто характеризующееся физическими и психоэмоциональными нарушениями, требует профессионального вмешательства. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть разнообразными и варьироваться от легкой тревожности до серьезных нарушений в функционировании внутренних органов. Квалифицированная помощь в этот период позволяет минимизировать риски и значительно ускорить процесс выздоровления.
Подробнее тут – вывод из запоя срочно круглосуточно
В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы понимаем, насколько важен своевременный и профессиональный подход к лечению зависимости. Наши специалисты готовы оказать квалифицированную помощь прямо у вас дома, обеспечивая полную безопасность и конфиденциальность на каждом этапе лечения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – вывод из запоя вызов на дом санкт-петербург
Запойное состояние сопряжено с множеством рисков, включая вероятность возникновения алкогольного делирия и других опасных осложнений. Поэтому своевременное обращение к наркологу помогает минимизировать эти угрозы. Круглосуточная доступность специалистов клиники позволяет оперативно реагировать на любые ситуации, обеспечивая пациентам безопасность и комфорт на всех этапах лечения.
Подробнее тут – vyvod iz zapoya vrach na dom v-chelyabinske
Быстрая покупка диплома старого образца: возможные риски
Вывод из запоя – это важнейший шаг на пути к избавлению от алкогольной зависимости, требующий комплексного подхода и поддержки специалистов. В современных условиях все больше людей предпочитают услуги вывода из запоя на дому, что позволяет избежать стресса от госпитализации и сохранить привычный ритм жизни. Такой подход делает процесс более комфортным и анонимным, что особенно важно для тех, кто стремится сохранить конфиденциальность.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – вывод из запоя вызов на дом
В этой статье мы расскажем о возможностях клиники для лечения алкогольной интоксикации круглосуточно, включая вывод из запоя в стационаре и на дому, а также о роли профессионалов, таких как нарколог, в процессе лечения.
Разобраться лучше – narkologicheski centr
Запой – это состояние, которое возникает вследствие длительного употребления алкоголя, приводящее к потере контроля над количеством выпиваемого и формированию как физической, так и психологической зависимости. Оно сопровождается серьёзными последствиями для здоровья и требует немедленного вмешательства.
Ознакомиться с деталями – vyvod iz zapoya na domu kruglosutochno voronezh
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой актуальную медицинскую проблему, требующую тщательного подхода. Запой характеризуется длительным, непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что ведёт к физической и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния могут возникнуть тяжёлые нарушения функций органов, увеличивается риск развития таких состояний, как алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя становится ключевым этапом в лечении зависимостей, который может осуществляться как в стационарных условиях, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента. В клинике «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске мы предлагаем круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить максимально эффективное и безопасное лечение при любом варианте вывода из запоя.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – вывод из запоя цена наркология челябинск
Продажа Индийских дженериков на сайте https://viagragood.ru по выгодной цене
с бесплатной доставкой
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой актуальную медицинскую проблему, требующую тщательного подхода. Запой характеризуется длительным, непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что ведёт к физической и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния могут возникнуть тяжёлые нарушения функций органов, увеличивается риск развития таких состояний, как алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя становится ключевым этапом в лечении зависимостей, который может осуществляться как в стационарных условиях, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента. В клинике «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске мы предлагаем круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить максимально эффективное и безопасное лечение при любом варианте вывода из запоя.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – narkolog na dom vyvod iz zapoya v-chelyabinske
В клинике «Рассвет» в Твери мы предлагаем круглосуточную помощь при алкогольных запоях, обеспечивая быстрый вывод токсинов из организма с помощью капельниц и других эффективных методик.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – vyvod iz zapoya vrach na dom tver
Клиника «Преображение» предлагает услуги анонимного вывода из запоя в Екатеринбурге, обеспечивая высокое качество медицинской помощи и соблюдение всех этических норм.
Получить больше информации – вывод из запоя анонимно
диплом в кирове купить
Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся утратой контроля над употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к тяжелой интоксикации организма. Вывод из запоя — это комплексный процесс, направленный на устранение последствий интоксикации и восстановление нормального функционирования организма. Цена данной процедуры может значительно различаться в зависимости от нескольких факторов, и в этой статье мы подробно рассмотрим, что влияет на стоимость вывода из запоя в Краснодаре, в том числе в клинике «Шаг к Трезвости».
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-12.ru/]вывод из запоя с выездом в краснодаре[/url]
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой состояние, при котором организм человека испытывает серьезное воздействие этанола, что приводит к нарушению нормальной физиологической деятельности. Это состояние сопровождается сильными физическими и психологическими расстройствами, которые требуют профессионального вмешательства. Однако многие люди, страдающие алкогольной зависимостью, сталкиваются с трудностью признания своей проблемы, опасаясь утраты репутации и конфиденциальности. В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем анонимный вывод из запоя в Санкт-Петербурге, предоставляя высококачественное лечение с гарантией сохранения личной информации.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-19.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-anonimno-v-sankt-peterburge/]vyvod iz zapoya anonimno sankt-peterburg[/url]
Состояние запоя характеризуется многодневным или недельным употреблением алкоголя в больших количествах без способности контролировать процесс. Это приводит к тяжелым последствиям для организма: обезвоживанию, интоксикации продуктами распада алкоголя, нарушениям работы нервной системы и полной потере контроля над ситуацией. Процедура вывода из запоя направлена на прекращение употребления алкоголя и восстановление здоровья пациента.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-16.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-krasnodare/]https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-16.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-krasnodare/[/url]
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой состояние, при котором организм человека испытывает серьезное воздействие этанола, что приводит к нарушению нормальной физиологической деятельности. Это состояние сопровождается сильными физическими и психологическими расстройствами, которые требуют профессионального вмешательства. Однако многие люди, страдающие алкогольной зависимостью, сталкиваются с трудностью признания своей проблемы, опасаясь утраты репутации и конфиденциальности. В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем анонимный вывод из запоя в Санкт-Петербурге, предоставляя высококачественное лечение с гарантией сохранения личной информации.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-19.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-anonimno-v-sankt-peterburge/]наркология вывод из запоя анонимно санкт-петербург[/url]
Запой — это серьезное состояние, при котором человек не может прекратить употребление алкоголя на протяжении длительного времени, что вызывает физическую и психологическую зависимость. Это крайне опасное состояние, требующее немедленного вмешательства специалистов. Для безопасного и эффективного вывода из запоя необходима квалифицированная медицинская помощь, которую предоставляет наркологическая клиника «Рассвет» в Твери. Наши опытные специалисты используют современные методы детоксикации и восстановления организма, обеспечивая полный медицинский контроль и поддержку на всех этапах лечения.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya na domu nedorogo tver
смотреть кино бесплатно Netflix 2025 новые фантастические фильмы в хорошем качестве
Запой представляет собой состояние, характеризующееся длительным непрерывным употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к физической и психической зависимости. Этот процесс может длиться от нескольких дней до недель. Алкогольные напитки негативно влияют на функционирование внутренних органов, вызывая серьёзные нарушения, включая алкоголизм. При необходимости вывода из запоя важно обратиться за медицинской помощью, что можно осуществить на дому. В данной статье рассмотрим ключевые аспекты данной процедуры.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-17.ru/]наркологический центр челябинск[/url]
Клиника “Второй Шанс” предоставляет круглосуточную помощь в лечении алкогольной зависимости. Мы готовы прийти на помощь в любое время суток, используя современные и проверенные методы, которые обеспечивают безопасность и высокую эффективность лечения. Полная анонимность лечения позволяет пациентам чувствовать себя уверенно и сосредоточиться на своём восстановлении.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – нарколог вывод из запоя цена в санкт-петербурге
В современном мире проблема зависимостей остаётся одной из наиболее острых. Всё больше людей сталкиваются с трудностями, связанными с алкоголизмом, наркоманией и другими формами зависимости, что разрушительно сказывается как на их жизни, так и на взаимоотношениях с окружающими. Это сложное явление, затрагивающее не только физическое здоровье, но и психоэмоциональное состояние, требует профессионального подхода для эффективного решения.
Узнать больше – вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно воронеж
новинки Netflix 2025 HD 1080p фильмы в хорошем качестве без регистрации
В клинике «Излечение» мы предлагаем широкий спектр услуг по выводу из запоя, включая как стационарное лечение, так и помощь на дому. В этой статье мы подробно рассмотрим, от чего зависит цена вывода из запоя и какие услуги входят в стоимость.
Узнать больше – vyvod iz zapoya na domu
Запойное состояние сопряжено с множеством рисков, включая вероятность возникновения алкогольного делирия и других опасных осложнений. Поэтому своевременное обращение к наркологу помогает минимизировать эти угрозы. Круглосуточная доступность специалистов клиники позволяет оперативно реагировать на любые ситуации, обеспечивая пациентам безопасность и комфорт на всех этапах лечения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – vyvod iz zapoya na domu kruglosutochno v-chelyabinske
Гарантированная анонимность при выводе из запоя в Челябинске. В клинике «Перекресток Надежды» мы строго соблюдаем политику конфиденциальности. Информация о пациенте и его состоянии здоровья остаётся закрытой. Это особенно важно для тех, кто ценит свою репутацию и не хочет разглашения. Мы обеспечиваем анонимность как в стационаре, так и при оказании услуг на дому, сохраняя высокий уровень медицинской помощи.
Разобраться лучше – наркология вывод из запоя анонимно челябинск
Запойное состояние представляет собой серьёзную угрозу для здоровья, поскольку сопровождается тяжёлой интоксикацией организма и нарушением психоэмоционального состояния. Решение о лечении в стационаре клиники «Союз Здоровья» позволяет справиться с последствиями длительного употребления алкоголя, обеспечивая пациентам полный комплекс медицинской и психологической помощи.
Получить дополнительные сведения – vyvod iz zapoya anonimno
Нужны деньги срочно заим с быстрым одобрением и моментальным переводом на карту. Минимум документов, удобные условия и прозрачные ставки. Оформите займ прямо сейчас!
Гарантированная анонимность при выводе из запоя в Челябинске. В клинике «Перекресток Надежды» мы строго соблюдаем политику конфиденциальности. Информация о пациенте и его состоянии здоровья остаётся закрытой. Это особенно важно для тех, кто ценит свою репутацию и не хочет разглашения. Мы обеспечиваем анонимность как в стационаре, так и при оказании услуг на дому, сохраняя высокий уровень медицинской помощи.
Изучить вопрос глубже – narkologicheskaya klinika chelyabinsk
В современном мире зависимость стала серьёзным вызовом, с которым сталкиваются многие. Жизненные трудности, постоянный стресс, финансовые проблемы — всё это способствует развитию таких заболеваний, как алкоголизм, наркомания и игромания. Клиника “Второй Шанс” специализируется на оказании медицинской помощи людям, страдающим от этих проблем, и помогает восстановить здоровье, адаптироваться к нормальной жизни и предотвратить рецидивы.
Изучить вопрос глубже – вывод из запоя вызов на дом в санкт-петербурге
Стоимость вывода из запоя зависит от ряда факторов, таких как состояние пациента, выбранная программа лечения и место проведения процедуры. Мы предлагаем прозрачное ценообразование, чтобы вы могли заранее ознакомиться с возможными затратами на лечение.
Подробнее тут – вывод из запоя анонимно челябинск
Catcasino — это площадка для азартных игр, которая предлагает множество возможностей для развлечений. На платформе можно найти разнообразные слоты, настольные игры, такие как блэкджек, а также захватывающие сессии с живыми дилерами. Сайт выполнен в привлекательном стиле, что удобно для игроков.
https://catcasino-25kas.buzz/
Одно из основных преимуществ Catcasino — это щедрые бонусы: приветственные пакеты для новичков, регулярные турниры, акции и программу лояльности для преданных пользователей. Казино поддерживает удобные способы пополнения счета и вывода средств, обеспечивая надежность и скорость операций.
Сайт адаптирован для мобильных устройств, а круглосуточная служба поддержки всегда готова ответить на вопросы. Catcasino станет отличным выбором для тех, кто хочет испытать яркие эмоции!
Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся утратой контроля над употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к тяжелой интоксикации организма. Вывод из запоя — это комплексный процесс, направленный на устранение последствий интоксикации и восстановление нормального функционирования организма. Цена данной процедуры может значительно различаться в зависимости от нескольких факторов, и в этой статье мы подробно рассмотрим, что влияет на стоимость вывода из запоя в Краснодаре, в том числе в клинике «Шаг к Трезвости».
Получить дополнительную информацию – anonimny vyvod iz zapoya na domu v-krasnodare
Запой является крайней стадией зависимости, требующей немедленного вмешательства специалистов. В клинике «Союз Здоровья» организована круглосуточная помощь, что позволяет оперативно устранять симптомы интоксикации, предотвращать осложнения и облегчать состояние пациента.
Ознакомиться с деталями – анонимный вывод из запоя на дому в воронеже
Состояние запоя характеризуется многодневным или недельным употреблением алкоголя в больших количествах без способности контролировать процесс. Это приводит к тяжелым последствиям для организма: обезвоживанию, интоксикации продуктами распада алкоголя, нарушениям работы нервной системы и полной потере контроля над ситуацией. Процедура вывода из запоя направлена на прекращение употребления алкоголя и восстановление здоровья пациента.
Подробнее тут – vyvod-iz-zapoya-16.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-anonimno-v-krasnodare/
Продажа дженериков с доставкой на сайте https://viagra-india.ru большой ассортимент
по низким ценам
Круглосуточная медицинская помощь при алкогольном запое играет важнейшую роль в спасении жизни пациентов и их возвращении к нормальному состоянию. В данной статье рассмотрим ключевые аспекты вывода из запоя в домашних условиях, срочной помощи и работы нарколога.
Получить дополнительные сведения – vyvod iz zapoya vrach na dom ekaterinburg
В клинике «Излечение» мы предлагаем широкий спектр услуг по выводу из запоя, включая как стационарное лечение, так и помощь на дому. В этой статье мы подробно рассмотрим, от чего зависит цена вывода из запоя и какие услуги входят в стоимость.
Детальнее – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom na dom v-krasnodare
В клинике «Излечение» понимают важность анонимности и индивидуального подхода при лечении алкогольной зависимости. Полная конфиденциальность гарантируется как в стационаре, так и при выезде на дом. Это позволяет пациентам чувствовать себя защищенными и уверенными на пути к выздоровлению. Процесс вывода из запоя включает в себя устранение токсического воздействия алкоголя, восстановление нормального функционирования организма и психологическую поддержку.
Подробнее тут – vyvod iz zapoya na domu
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой актуальную медицинскую проблему, требующую тщательного подхода. Запой характеризуется длительным, непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что ведёт к физической и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния могут возникнуть тяжёлые нарушения функций органов, увеличивается риск развития таких состояний, как алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя становится ключевым этапом в лечении зависимостей, который может осуществляться как в стационарных условиях, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента. В клинике «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске мы предлагаем круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить максимально эффективное и безопасное лечение при любом варианте вывода из запоя.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-17.ru/]narkologicheskij centr chelyabinsk[/url]
Запой — это тяжелое состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над количеством употребляемого алкоголя, что приводит к серьезным нарушениям здоровья. Процесс вывода из запоя требует профессионального подхода, медицинского контроля и тщательного восстановления организма. Наркологическая клиника «Шаг к Трезвости» в Краснодаре предлагает квалифицированную помощь для тех, кто нуждается в срочном и безопасном выходе из запоя. Мы предоставляем комплексное лечение, ориентированное на каждый этап восстановления, с максимальной заботой о здоровье пациента.
Получить дополнительные сведения – vyvod iz zapoya vrach na dom krasnodar
Алкогольная зависимость — одна из самых разрушительных форм аддикции, способная нанести непоправимый вред здоровью. Запой, как крайнее проявление этой зависимости, требует немедленного вмешательства, чтобы избежать серьёзных последствий, включая интоксикацию организма и психические расстройства. Обращение за профессиональной помощью становится ключевым шагом на пути к выздоровлению.
Ознакомиться с деталями – вывод из запоя в стационаре
Алкогольный запой представляет собой критическое состояние, требующее немедленного вмешательства квалифицированных специалистов. Клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже предлагает круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить своевременное и эффективное лечение. Наша цель — оперативное снятие интоксикации, устранение симптомов и предотвращение осложнений.
Углубиться в тему – vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno v-voronezhe
Процедура вывода из запоя направлена на очищение организма от токсинов, нормализацию работы внутренних органов и стабилизацию психоэмоционального состояния. Она может быть проведена как в условиях стационара, так и на дому, в зависимости от степени тяжести состояния. При этом анонимность лечения играет важную роль. Клиника «Перекресток Надежды» гарантирует полную конфиденциальность, что особенно важно для тех, кто ценит приватность. Независимо от выбранного варианта, каждый пациент получает высококачественную помощь, соответствующую современным стандартам медицины.
Получить дополнительную информацию – вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно в челябинске
Самой дорогой технологией имплантации считается классическая двухэтапная операция, которая почти всегда требует предварительной костной пластики имплантация зубов 2024
Запой — это тяжелое состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над количеством употребляемого алкоголя, что приводит к серьезным нарушениям здоровья. Процесс вывода из запоя требует профессионального подхода, медицинского контроля и тщательного восстановления организма. Наркологическая клиника «Шаг к Трезвости» в Краснодаре предлагает квалифицированную помощь для тех, кто нуждается в срочном и безопасном выходе из запоя. Мы предоставляем комплексное лечение, ориентированное на каждый этап восстановления, с максимальной заботой о здоровье пациента.
Детальнее – vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno narkologiya v-krasnodare
Самой дорогой технологией имплантации считается классическая двухэтапная операция, которая почти всегда требует предварительной костной пластики имплантация зубов отзывы пациентов
Лучшие игровые промокоды куда вводить промокод на ggdrop в одном месте! Активируйте бонусы, получайте подарки и прокачивайте аккаунт без лишних затрат. Следите за обновлениями, чтобы не пропустить новые промо!
Самой дорогой технологией имплантации считается классическая двухэтапная операция, которая почти всегда требует предварительной костной пластики имплантация зубов в спб
Промокоды для игр https://esportpromo.com/standoff/ это бесплатные бонусы, скидки и эксклюзивные награды! Находите актуальные коды, используйте их и получайте максимум удовольствия от игры без лишних затрат.
купить диплом с занесением в госреестр
Круглосуточная медицинская помощь при алкогольном запое играет важнейшую роль в спасении жизни пациентов и их возвращении к нормальному состоянию. В данной статье рассмотрим ключевые аспекты вывода из запоя в домашних условиях, срочной помощи и работы нарколога.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-20.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-anonimno-v-ekaterinburge/]вывод из запоя анонимно недорого [/url]
Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся утратой контроля над употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к тяжелой интоксикации организма. Вывод из запоя — это комплексный процесс, направленный на устранение последствий интоксикации и восстановление нормального функционирования организма. Цена данной процедуры может значительно различаться в зависимости от нескольких факторов, и в этой статье мы подробно рассмотрим, что влияет на стоимость вывода из запоя в Краснодаре, в том числе в клинике «Шаг к Трезвости».
Ознакомиться с деталями – narkolog na dom vyvod iz zapoya krasnodar
Открытки в интернете позволяют людям отправлять поздравления и приветы в любое время, независимо от расстояния и времени суток Новые открытки
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой серьёзную медицинскую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запойное состояние характеризуется длительным и бесконтрольным потреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к возникновению как физической, так и психической зависимости. Данное явление может вызвать нарушения в работе внутренних органов, значительно увеличивая вероятность развития алкогольного делирия, который представляет собой острое состояние, требующее неотложной медицинской помощи. Вывод из запоя это ключевая часть лечения зависимости, которая может осуществляться как в стационаре, так и в амбулаторных условиях, в зависимости от конкретной ситуации и состояния пациента.
Получить дополнительные сведения – наркология вывод из запоя на дому краснодар
Запой — это состояние, при котором человек продолжает употреблять алкоголь на протяжении нескольких дней или даже недель, не контролируя объемы потребляемого напитка. Этот процесс сопровождается тяжелыми физическими и психическими последствиями, такими как обезвоживание организма, отравление продуктами распада алкоголя, нервные расстройства и потеря контроля над ситуацией. Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, направленная на прекращение употребления алкоголя и восстановление организма пациента.
Узнать больше – vyvod iz zapoya vyzov na dom v-krasnodare
Открытки в интернете позволяют людям отправлять поздравления и приветы в любое время, независимо от расстояния и времени суток Новые открытки
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой состояние, при котором организм человека испытывает серьёзное воздействие этанола. Это приводит к нарушениям нормальной физиологической деятельности и ухудшению состояния здоровья. Анонимный вывод из запоя — это медицинская помощь, направленная на устранение последствий чрезмерного употребления алкоголя с соблюдением строгой конфиденциальности.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно в екатеринбурге
Проблема зависимостей остаётся актуальной в современном обществе. С каждым годом увеличивается число людей, страдающих от алкоголизма, наркомании и других форм зависимостей, что негативно отражается на их жизни и благополучии близких. Зависимость — это не просто физическое заболевание, но и глубокая психологическая проблема. Для эффективного лечения требуется помощь профессионалов, способных обеспечить комплексный подход.
Ознакомиться с деталями – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom cena v-voronezhe
Запой представляет собой сложное состояние, связанное с длительным употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к формированию зависимости. Это явление не только нарушает нормальную жизнедеятельность, но также вызывает серьезные физические и психологические расстройства. Стационарное лечение становится необходимым для восстановления здоровья и профилактики осложнений. В стационаре клиники «Шаг к Трезвости» в Краснодаре мы предлагаем комплексный подход, включающий медикаментозное лечение, психотерапию и постоянный контроль со стороны квалифицированных специалистов.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-12.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-anonimno-v-krasnodare/]наркология вывод из запоя анонимно в краснодаре[/url]
Открытки в интернете позволяют людям отправлять поздравления и приветы в любое время, независимо от расстояния и времени суток Новые открытки
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, необходимая для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Это состояние, часто характеризующееся физическими и психоэмоциональными нарушениями, требует профессионального вмешательства. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть разнообразными и варьироваться от легкой тревожности до серьезных нарушений в функционировании внутренних органов. Квалифицированная помощь в этот период позволяет минимизировать риски и значительно ускорить процесс выздоровления.
Узнать больше – наркологическая клиника
Wow, amazing blog layout! How long have you been blogging for?
you made blogging look easy. The overall look of your website is magnificent, as well
as the content!
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой серьезную медицинскую проблему, которая влечет за собой не только физические, но и психологические проблемы. Периоды запоя, характеризующиеся бесконтрольным употреблением алкоголя, могут привести к тяжелым последствиям. Симптомы абстиненции требуют незамедлительного вмешательства. Анонимность в процессе реабилитации становится важным аспектом, помогающим пациентам избежать стыда и социального осуждения.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – вывод из запоя врач на дом в краснодаре
Алкоголизм — это хроническое прогрессирующее заболевание, связанное с физической и психической зависимостью от этанола. Запой, как его крайнее проявление, представляет собой длительное употребление алкоголя, сопровождающееся тяжелыми нарушениями работы организма, включая абстинентный синдром и потенциальные угрозы для жизни. Лечение запоя требует комплексного подхода, включающего медицинские процедуры, психотерапию и реабилитационные меры.
Получить больше информации – narkolog na dom vyvod iz zapoya v-ekaterinburge
Заказать дженерики на сайте https://viagra-ru.ru с доставкой по низкой цене
можно ли купить диплом об образовании можно ли купить диплом об образовании .
Лучшие игровые промокоды промокод на кейс гг стандофф в одном месте! Активируйте бонусы, получайте подарки и прокачивайте аккаунт без лишних затрат. Следите за обновлениями, чтобы не пропустить новые промо!
https://byvshye.ru/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/cropped-large_property-food-production-1-768×247.jpg
Доменная почта — корпоративный почтовый сервис email для организаций 2025 почта на своём домене
Доменная почта — корпоративный почтовый сервис email для организаций 2025 доменная почта
Как купить диплом о высшем образовании с минимальными рисками
Доменная почта — корпоративный почтовый сервис email для организаций 2025 доменная почта
https://profritualsamara.ru/
В нашем интернет магазине по продаже дженериков https://viagrasells.ru
представлен широкий ассортимент по низким ценам
skypharmacy online
cialis without a doctor’s prescription
Бесплатные промокоды https://playpromocode.com/cs2/forcedrop/ для ваших любимых игр! Получайте монеты, бустеры, скины и другие ценные награды. Мы собираем только проверенные коды и обновляем их каждый день.
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой состояние, при котором организм человека испытывает серьезное воздействие этанола, что приводит к нарушению нормальной физиологической деятельности. Это состояние сопровождается сильными физическими и психологическими расстройствами, которые требуют профессионального вмешательства. Однако многие люди, страдающие алкогольной зависимостью, сталкиваются с трудностью признания своей проблемы, опасаясь утраты репутации и конфиденциальности. В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем анонимный вывод из запоя в Санкт-Петербурге, предоставляя высококачественное лечение с гарантией сохранения личной информации.
Получить дополнительные сведения – вывод из запоя на дому санкт-петербург
Купить диплом магистра в Екатеринбурге
Алкогольная зависимость остаётся серьёзной проблемой, требующей квалифицированного медицинского вмешательства. Капельница от запоя — это ключевой этап в процессе лечения, направленный на стабилизацию состояния пациента и его возвращение к полноценной жизни. Профессиональная помощь позволяет эффективно справиться с последствиями длительного употребления алкоголя и восстановить физическое и психологическое здоровье.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-21.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-tveri/]vyvod iz zapoya kapelnica na domu v-tveri[/url]
Алкогольный запой представляет собой серьезное состояние, которое требует немедленного медицинского вмешательства. Это состояние характеризуется длительным и бесконтрольным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к разрушению как физического, так и психоэмоционального здоровья человека. Для эффективного и безопасного вывода из запоя стационарное лечение является оптимальным решением, особенно при тяжелых случаях интоксикации. В стационаре клиники «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем комплексную программу вывода из запоя, которая включает детоксикацию, восстановление организма и психотерапевтическую помощь.
Выяснить больше – vyvod iz zapoya vyzov na dom v-sankt-peterburge
Хотите проверить компанию https://innproverka.ru по ИНН? Наш сервис поможет узнать подробную информацию о юридических лицах и ИП: статус, финансы, руководителей и возможные риски. Защищайте себя от ненадежных партнеров!
Запой — это тяжелое состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над количеством употребляемого алкоголя, что приводит к серьезным нарушениям здоровья. Процесс вывода из запоя требует профессионального подхода, медицинского контроля и тщательного восстановления организма. Наркологическая клиника «Шаг к Трезвости» в Краснодаре предлагает квалифицированную помощь для тех, кто нуждается в срочном и безопасном выходе из запоя. Мы предоставляем комплексное лечение, ориентированное на каждый этап восстановления, с максимальной заботой о здоровье пациента.
Получить больше информации – вывод из запоя вызов на дом
Недвижимость на Северном Кипре https://iberiaproperty.ru выгодные инвестиции и комфортная жизнь у моря. Апартаменты, виллы и пентхаусы по доступным ценам. Поможем выбрать лучший вариант и оформить покупку.
удобный маркетплейс blacksprut сайт с высоким уровнем анонимности и надежной системой защиты. Интуитивный интерфейс, проверенные продавцы и безопасные сделки делают его лучшим выбором для покупок.
Услуги дренажа по Озёрскому району Работаем без выходных.
В современном обществе проблема зависимостей приобретает всё большую актуальность. Сложные обстоятельства жизни, стресс, финансовые трудности становятся факторами, способствующими развитию таких расстройств, как алкоголизм, наркомания, игромания. Наркологическая клиника “Второй Шанс” создана для предоставления комплексной медицинской помощи людям, страдающим от этих заболеваний. Наша задача заключается в восстановлении здоровья пациентов, их социальной адаптации, а также профилактике рецидивов.
Получить больше информации – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom cena
https://vminske.by/fashion/regulirovka-okon-pvh-vazhnost-i-osnovnye-aspekty/
Медицинская помощь при запоях направлена не только на устранение симптомов интоксикации, но и на предотвращение рецидивов. Современные методики лечения включают медикаментозную терапию, психологическую поддержку и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту. Одним из ключевых аспектов эффективного лечения является анонимность, позволяющая избежать социального осуждения и дискомфорта, связанного с обращением к наркологам.
Углубиться в тему – vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare anonimno v-krasnodare
look at here rabby wallet
С первого клика, впечатление было таким, словно перешагнул грань реальности. Эта игровая платформа будто спроектировано для тех, кто любит прогресс.
Интерфейс напоминает технологию будущего: всё гладко, моментальный отклик. Пополнение счёта — почти моментальны, вывод средств по высшим стандартам.
Но самое важное — азарт, каждый раунд здесь заряжен энергией. скачать 7К казино — это больше, чем игра, это портал в мир чистого адреналина.
visit this web-site keplr Extension
Процедура вывода из запоя включает очищение организма от токсинов, восстановление работы жизненно важных органов и стабилизацию нервной системы. В зависимости от тяжести состояния пациента лечение может проводиться как в клинике, так и на дому. Для многих людей крайне важно сохранить конфиденциальность, поэтому анонимность таких услуг играет ключевую роль. Современные медицинские центры, предоставляющие помощь при запоях, обеспечивают высокий уровень приватности и профессионального подхода.
Ознакомиться с деталями – вывод из запоя капельница челябинск
Алкогольная зависимость – одно из самых разрушительных заболеваний, наносящее серьёзный ущерб организму. Запойные состояния представляют особую опасность, так как ведут к сильной интоксикации, нарушениям психики и необратимым последствиям. Чем раньше будет оказана медицинская помощь, тем выше шанс избежать тяжёлых осложнений и быстрее вернуться к нормальной жизни.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-14.ru/]https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-14.ru[/url]
Продвижение сайтов — это искусство и наука, направленные на повышение видимости интернет-ресурсов в поисковых системах ссылка В современных условиях, когда конкуренция в сети растет с каждым днем, деятельность по оптимизации и продвижению становится особенно актуальной. Основными инструментами продвижения являются поисковая оптимизация (SEO), контент-маркетинг, работа с социальными сетями и рекламные кампании.
Клиника «Шаг к Трезвости» в Краснодаре предлагает анонимный вывод из запоя, обеспечивая полную конфиденциальность и безопасность на каждом этапе лечения. Мы понимаем, что для многих людей важно сохранить свою личную информацию в тайне, и гарантируем, что все данные о пациенте и его состоянии здоровья останутся закрытыми. Независимо от того, выбрал ли пациент стационарное лечение или вывод из запоя на дому, мы обеспечиваем высококачественную медицинскую помощь с полным соблюдением принципов конфиденциальности.
Получить больше информации – нарколог на дом вывод из запоя краснодар
Стоило мне только зарегистрироваться, впечатление было таким, словно совершил гиперпрыжок. Этот сайт будто создано для тех, кто ищет новые горизонты.
Оформление выглядит как футуристическую консоль: всё плавно, реакция мгновенная. Депозиты — как мгновенный телепорт, получение выигрышей оперативный.
Но самое важное — азарт, каждый раунд здесь заряжен энергией. 7К казино скачать на андроид — это больше, чем игра, это мост в игровое будущее.
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, необходимая для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Это состояние, часто характеризующееся физическими и психоэмоциональными нарушениями, требует профессионального вмешательства. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть разнообразными и варьироваться от лёгкой тревожности до серьёзных нарушений в функционировании внутренних органов. Квалифицированная помощь в этот период позволяет минимизировать риски и значительно ускорить процесс выздоровления.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – вывод из запоя с выездом на дом
С первого клика, ощущение было таким, словно открыл портал в новый мир. Эта игровая платформа будто создано для тех, кто любит прогресс.
Навигация напоминает панель управления звездолёта: всё плавно, моментальный отклик. Пополнение счёта — почти моментальны, получение выигрышей оперативный.
Но самое важное — игры, каждый спин здесь заряжен энергией. 7К игровые — это не просто казино, это мост в новую эру.
Запой – это тяжелое состояние, возникающее из-за длительного и неконтролируемого употребления алкоголя. Оно характеризуется физической и психологической зависимостью, что приводит к серьезным последствиям для организма и психики. Для восстановления нормального самочувствия и здоровья необходимо профессиональное лечение. Одним из наиболее удобных и эффективных методов является вывод из запоя на дому.
Углубиться в тему – вывод из запоя анонимно недорого
Раскрутка в соцсетях https://nakrytka.com без лишних затрат! Привлекаем реальную аудиторию, повышаем охваты и активность. Эффективные инструменты для роста вашего бренда.
additional hints phantom Download
Алкогольное злоупотребление, перетекающее в длительные запои, представляет серьезную угрозу как физическому, так и психическому здоровью. Потеря контроля над количеством выпитого приводит к глубокой интоксикации организма, ухудшению самочувствия и развитию зависимости. В таких случаях необходима срочная медицинская помощь, чтобы избежать тяжелых последствий и стабилизировать состояние пациента.
Получить дополнительные сведения – bystry vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare krasnodar
Процедура вывода из запоя — это не просто очищение организма от токсинов, а комплекс мер, направленных на восстановление физического состояния и психического равновесия. Специалисты клиники помогают минимизировать последствия длительного употребления алкоголя, снижая риск осложнений и помогая пациенту вернуться к нормальной жизни. Чем быстрее начато лечение, тем выше шансы на успешное восстановление и отказ от пагубной привычки.
Ознакомиться с деталями – vyvod iz zapoya kapelnica na domu ryazan
Стоимость процедур формируется в зависимости от состояния пациента, выбранного способа лечения и дополнительных медицинских услуг. Прозрачность ценообразования позволяет заранее оценить предстоящие расходы и выбрать оптимальный вариант. Комплексный подход, профессионализм врачей и индивидуальные схемы терапии помогают не только выйти из запойного состояния, но и сделать уверенный шаг к здоровой и полноценной жизни.
Получить больше информации – вывод из запоя врач на дом челябинск
browse this site keplr Download
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой серьезную медицинскую проблему, которая влечет за собой не только физические, но и психологические проблемы. Периоды запоя, характеризующиеся бесконтрольным употреблением алкоголя, могут привести к тяжелым последствиям. Симптомы абстиненции требуют незамедлительного вмешательства. Анонимность в процессе реабилитации становится важным аспектом, помогающим пациентам избежать стыда и социального осуждения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – вывод из запоя врач на дом в краснодаре
Запой – это состояние, которое возникает вследствие длительного употребления алкоголя, приводящее к потере контроля над количеством выпиваемого и формированию как физической, так и психологической зависимости. Оно сопровождается серьёзными последствиями для здоровья и требует немедленного вмешательства.
Изучить вопрос глубже – наркологическая клиника
Стоимость процедуры зависит от множества факторов, включая тяжесть состояния пациента, необходимость дополнительных медицинских манипуляций и выбранный формат лечения. Однако главное – не откладывать обращение за помощью, поскольку запойное состояние несет серьезные риски для жизни и здоровья.
Разобраться лучше – анонимный вывод из запоя на дому
Запой – это тяжелое состояние, возникающее из-за длительного и неконтролируемого употребления алкоголя. Оно характеризуется физической и психологической зависимостью, что приводит к серьезным последствиям для организма и психики. Для восстановления нормального самочувствия и здоровья необходимо профессиональное лечение. Одним из наиболее удобных и эффективных методов является вывод из запоя на дому.
Получить дополнительные сведения – вывод из запоя с выездом в рязани
купить диплом массажиста
купить диплом в магадане
Процедура вывода из запоя включает очищение организма от токсинов, восстановление работы жизненно важных органов и стабилизацию нервной системы. В зависимости от тяжести состояния пациента лечение может проводиться как в клинике, так и на дому. Для многих людей крайне важно сохранить конфиденциальность, поэтому анонимность таких услуг играет ключевую роль. Современные медицинские центры, предоставляющие помощь при запоях, обеспечивают высокий уровень приватности и профессионального подхода.
Подробнее тут – вывод из запоя круглосуточно наркология
canadian pharmacy online no script
Запой представляет серьёзную угрозу, поэтому откладывать обращение за медицинской помощью нельзя. Чем раньше будет проведена детоксикация и поддерживающая терапия, тем ниже риск осложнений. В клинике «Освобождение» работают круглосуточно, оперативно реагируя на экстренные случаи и предлагая как стационарное лечение, так и выездные услуги — в зависимости от состояния пациента и его пожеланий.
Получить дополнительные сведения – vyvod iz zapoya na domu cena
Функциональное тестирование программного обеспечения: как мобильные приложения, сайты и веб-сервисы проверяют на соответствие требованиям бизнеса и пользователей? Виды, задачи, этапы и примеры сценариев тестов, которые позволяют исправить ошибки разработчиков: https://vc.ru/u/3791103-infa-v-dele/1777821-funkcionalnoe-testirovanie-na-primerah-celi-vidy-instrumenty-i-trudnosti
Алкогольная зависимость – одно из самых разрушительных заболеваний, наносящее серьёзный ущерб организму. Запойные состояния представляют особую опасность, так как ведут к сильной интоксикации, нарушениям психики и необратимым последствиям. Чем раньше будет оказана медицинская помощь, тем выше шанс избежать тяжёлых осложнений и быстрее вернуться к нормальной жизни.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно санкт-петербург
купить диплом радиомеханика
Для тех, кто по разным причинам не может поехать в стационар, предлагается услуга вывода из запоя на дому. Опытные специалисты проводят детоксикацию в комфортных условиях, применяя современные препараты, снижающие нагрузку на организм и уменьшающие неприятные симптомы. Однако при наличии осложнений или тяжёлого состояния может потребоваться круглосуточный медицинский контроль в стационаре, где пациенту будет обеспечена всесторонняя поддержка.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – вывод из запоя на дому цена
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой серьезную медицинскую проблему, которая влечет за собой не только физические, но и психологические проблемы. Периоды запоя, характеризующиеся бесконтрольным употреблением алкоголя, могут привести к тяжелым последствиям. Симптомы абстиненции требуют незамедлительного вмешательства. Анонимность в процессе реабилитации становится важным аспектом, помогающим пациентам избежать стыда и социального осуждения.
Получить больше информации – быстрый вывод из запоя в стационаре
Большой выбор дженериков на сайте https://apteka-russia.ru с доставкой
во все регионы России по выгодным ценам
Алкогольный запой представляет собой критическое состояние, требующее немедленного вмешательства квалифицированных специалистов. Клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже предлагает круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить своевременное и эффективное лечение. Наша цель — оперативное снятие интоксикации, устранение симптомов и предотвращение осложнений.
Углубиться в тему – нарколог на дом вывод из запоя воронеж
Особую опасность представляет алкогольный запой – состояние, сопровождающееся многодневным бесконтрольным употреблением спиртного. Оно разрушает здоровье, негативно влияет на нервную систему, печень и другие органы, а также может привести к тяжёлым осложнениям. Чтобы минимизировать риски, необходимо медицинское вмешательство. Вывести человека из запоя самостоятельно крайне сложно и небезопасно, поэтому важно вовремя обратиться за квалифицированной помощью.
Подробнее тут – наркологический центр
обложка диплом купить спб prema-diploms.ru .
Для тех, кто по разным причинам не может поехать в стационар, предлагается услуга вывода из запоя на дому. Опытные специалисты проводят детоксикацию в комфортных условиях, применяя современные препараты, снижающие нагрузку на организм и уменьшающие неприятные симптомы. Однако при наличии осложнений или тяжёлого состояния может потребоваться круглосуточный медицинский контроль в стационаре, где пациенту будет обеспечена всесторонняя поддержка.
Разобраться лучше – narkologicheskaya klinika
Медицинская помощь при запоях направлена не только на устранение симптомов интоксикации, но и на предотвращение рецидивов. Современные методики лечения включают медикаментозную терапию, психологическую поддержку и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту. Одним из ключевых аспектов эффективного лечения является анонимность, позволяющая избежать социального осуждения и дискомфорта, связанного с обращением к наркологам.
Изучить вопрос глубже – vyvod iz zapoya na domu cena krasnodar
Современное общество сталкивается с серьёзными вызовами, связанными с зависимостями. Алкоголизм, как одна из самых распространённых проблем, оказывает разрушительное воздействие на здоровье человека, разрушая семейные отношения и затрудняя социальную адаптацию. В такие моменты крайне важно обратиться за квалифицированной помощью.
Получить больше информации – vyvod-iz-zapoya-13.ru
Одним из наиболее опасных проявлений алкогольной зависимости является запой — состояние, при котором употребление спиртного становится неконтролируемым и продолжается в течение нескольких дней или даже недель. Это не просто психологическая тяга, а серьёзное нарушение, приводящее к истощению организма и тяжелым последствиям для внутренних органов. Единственный надёжный способ выйти из этого состояния — обратиться за профессиональной помощью. В клинике «Освобождение» доступна услуга вывода из запоя на дому, которая позволяет стабилизировать состояние пациента без необходимости госпитализации, обеспечивая ему комфорт и снижая уровень стресса.
Изучить вопрос глубже – вывод из запоя с выездом цена в рязани
Для тех, кто по разным причинам не может поехать в стационар, предлагается услуга вывода из запоя на дому. Опытные специалисты проводят детоксикацию в комфортных условиях, применяя современные препараты, снижающие нагрузку на организм и уменьшающие неприятные симптомы. Однако при наличии осложнений или тяжёлого состояния может потребоваться круглосуточный медицинский контроль в стационаре, где пациенту будет обеспечена всесторонняя поддержка.
Получить дополнительные сведения – вывод из запоя цена наркология в санкт-петербурге
Игнорирование проблемы запоев может привести к серьезным осложнениям, включая алкогольный делирий и другие опасные состояния, угрожающие жизни. Именно поэтому так важно обратиться за помощью своевременно. Круглосуточная работа специалистов позволяет оперативно реагировать на экстренные случаи, обеспечивая пациенту безопасность и комфорт на каждом этапе лечения.
Детальнее – анонимный вывод из запоя на дому
Особую опасность представляет алкогольный запой – состояние, сопровождающееся многодневным бесконтрольным употреблением спиртного. Оно разрушает здоровье, негативно влияет на нервную систему, печень и другие органы, а также может привести к тяжёлым осложнениям. Чтобы минимизировать риски, необходимо медицинское вмешательство. Вывести человека из запоя самостоятельно крайне сложно и небезопасно, поэтому важно вовремя обратиться за квалифицированной помощью.
Разобраться лучше – vyvod iz zapoya kapelnica v-sankt-peterburge
https://vip-parisescort.com/
Запой — это тяжелое состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над количеством употребляемого алкоголя, что приводит к серьезным нарушениям здоровья. Процесс вывода из запоя требует профессионального подхода, медицинского контроля и тщательного восстановления организма. Наркологическая клиника «Шаг к Трезвости» в Краснодаре предлагает квалифицированную помощь для тех, кто нуждается в срочном и безопасном выходе из запоя. Мы предоставляем комплексное лечение, ориентированное на каждый этап восстановления, с максимальной заботой о здоровье пациента.
Углубиться в тему – вывод из запоя с выездом цена
Furosemide http://canadianpharmacymall.net/ Cytotec online
Медицинская помощь при запоях направлена не только на устранение симптомов интоксикации, но и на предотвращение рецидивов. Современные методики лечения включают медикаментозную терапию, психологическую поддержку и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту. Одним из ключевых аспектов эффективного лечения является анонимность, позволяющая избежать социального осуждения и дискомфорта, связанного с обращением к наркологам.
Углубиться в тему – vyvod iz zapoya na domu cena
Дженерики для повышения потенции на сайте https://aptekaviagry.ru
высокое качество по доступной цене с доставкой
Особую опасность представляет алкогольный запой – состояние, сопровождающееся многодневным бесконтрольным употреблением спиртного. Оно разрушает здоровье, негативно влияет на нервную систему, печень и другие органы, а также может привести к тяжёлым осложнениям. Чтобы минимизировать риски, необходимо медицинское вмешательство. Вывести человека из запоя самостоятельно крайне сложно и небезопасно, поэтому важно вовремя обратиться за квалифицированной помощью.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – вывод из запоя цена наркология санкт-петербург
Алкогольные запои представляют собой сложное состояние, при котором человек на протяжении нескольких дней или даже недель бесконтрольно употребляет спиртное. Это не просто вредная привычка, а серьезная зависимость, ведущая к разрушению организма и психики. Родные и близкие зачастую оказываются в растерянности, не зная, как помочь. В такие моменты важно как можно скорее обратиться за квалифицированной медицинской помощью, так как своевременное вмешательство может предотвратить тяжелые последствия.
Ознакомиться с деталями – vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare v-chelyabinske
Процесс вывода из запоя включает несколько этапов. Абстинентный синдром может выражаться как в лёгком беспокойстве, так и в серьёзных психических расстройствах. Только грамотный подход и современные медицинские методики позволяют снизить нагрузку на организм, избежать осложнений и обеспечить стабильное состояние.
Получить дополнительную информацию – vyvod iz zapoya anonimno v-sankt-peterburge
Запой — это тяжелое состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над количеством употребляемого алкоголя, что приводит к серьезным нарушениям здоровья. Процесс вывода из запоя требует профессионального подхода, медицинского контроля и тщательного восстановления организма. Наркологическая клиника «Шаг к Трезвости» в Краснодаре предлагает квалифицированную помощь для тех, кто нуждается в срочном и безопасном выходе из запоя. Мы предоставляем комплексное лечение, ориентированное на каждый этап восстановления, с максимальной заботой о здоровье пациента.
Получить дополнительные сведения – анонимный вывод из запоя на дому
диплом ссср купить
Check, please: dag-techservice.ru
click reference phantom Download
Алкогольный запой представляет собой критическое состояние, требующее немедленного вмешательства квалифицированных специалистов. Клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже предлагает круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить своевременное и эффективное лечение. Наша цель — оперативное снятие интоксикации, устранение симптомов и предотвращение осложнений.
Ознакомиться с деталями – вывод из запоя с выездом в воронеже
увлекательный сериал подробнее о жизни сказочных персонажей в реальном мире. Интригующий сюжет, волшебные события и неожиданные тайны. Смотрите онлайн в высоком качестве прямо сейчас!
Медицинская помощь при запоях направлена не только на устранение симптомов интоксикации, но и на предотвращение рецидивов. Современные методики лечения включают медикаментозную терапию, психологическую поддержку и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту. Одним из ключевых аспектов эффективного лечения является анонимность, позволяющая избежать социального осуждения и дискомфорта, связанного с обращением к наркологам.
Получить больше информации – narkolog vyvod iz zapoya cena
Алкогольные запои представляют собой сложное состояние, при котором человек на протяжении нескольких дней или даже недель бесконтрольно употребляет спиртное. Это не просто вредная привычка, а серьезная зависимость, ведущая к разрушению организма и психики. Родные и близкие зачастую оказываются в растерянности, не зная, как помочь. В такие моменты важно как можно скорее обратиться за квалифицированной медицинской помощью, так как своевременное вмешательство может предотвратить тяжелые последствия.
Изучить вопрос глубже – vyvod iz zapoya na domu
Запой – это состояние, которое возникает вследствие длительного употребления алкоголя, приводящее к потере контроля над количеством выпиваемого и формированию как физической, так и психологической зависимости. Оно сопровождается серьёзными последствиями для здоровья и требует немедленного вмешательства.
Детальнее – вывод из запоя капельница на дому воронеж
Одним из наиболее опасных проявлений алкогольной зависимости является запой — состояние, при котором употребление спиртного становится неконтролируемым и продолжается в течение нескольких дней или даже недель. Это не просто психологическая тяга, а серьёзное нарушение, приводящее к истощению организма и тяжелым последствиям для внутренних органов. Единственный надёжный способ выйти из этого состояния — обратиться за профессиональной помощью. В клинике «Освобождение» доступна услуга вывода из запоя на дому, которая позволяет стабилизировать состояние пациента без необходимости госпитализации, обеспечивая ему комфорт и снижая уровень стресса.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya vyzov na dom
Запойное состояние представляет собой серьёзную угрозу для здоровья, поскольку сопровождается тяжёлой интоксикацией организма и нарушением психоэмоционального состояния. Решение о лечении в стационаре клиники «Союз Здоровья» позволяет справиться с последствиями длительного употребления алкоголя, обеспечивая пациентам полный комплекс медицинской и психологической помощи.
Узнать больше – bystry vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare v-voronezhe
Купить дженерики недорого с доставкой https://apteka-x.ru/ высокое качество
по выгодным ценам гарантия от производителя
Thank you for sharing this!
https://teen-lesbian-tube.com
It’s ever after attractive to finance different perspectives on this topic.
I rate the creation and itemize spell out into this notify – it provides valuable insights and definitely gives me something to think about.
Looking head to more content like this!
onlinepharmacy
В Рязани помощь людям, страдающим от алкогольной зависимости, оказывает наркологическая клиника «Освобождение». Здесь понимают, что борьба с этим заболеванием требует не только медицинского вмешательства, но и комплексной поддержки, учитывающей как состояние самого пациента, так и влияние зависимости на его окружение.
Получить дополнительные сведения – вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно
В центре доступны различные программы лечения, от амбулаторного наблюдения до интенсивного стационарного курса. Основные принципы работы – анонимность, оперативность и персонализированный подход. Независимо от сложности ситуации, каждый пациент получает квалифицированную помощь, направленную на восстановление физического и психического здоровья.
Подробнее – anonimny vyvod iz zapoya na domu v-sankt-peterburge
Официальное получение диплома техникума с упрощенным обучением в Москве
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой состояние, при котором организм человека испытывает серьёзное воздействие этанола. Это приводит к нарушениям нормальной физиологической деятельности и ухудшению состояния здоровья. Анонимный вывод из запоя — это медицинская помощь, направленная на устранение последствий чрезмерного употребления алкоголя с соблюдением строгой конфиденциальности.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-20.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-v-kruglosutochno-v-ekaterinburge/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно наркология [/url]
Запой — это опасное состояние, которое развивается у людей с алкогольной зависимостью и характеризуется длительным непрерывным потреблением алкоголя. Это состояние приводит к серьезным нарушениям в организме, как физическим, так и психоэмоциональным. Длительный запой может вызвать множество осложнений, таких как поражение внутренних органов, нервной системы, а также проблемы в социальной и семейной жизни. Однако современная медицина предоставляет эффективные методы вывода из запоя, и одним из наиболее удобных и востребованных является вывод из запоя на дому.
Узнать больше – вывод из запоя круглосуточно наркология санкт-петербург
Большой выбор дженериков в магазине https://best-viagra.ru с доставкой
по городу и области
find Metamask Extension
Сейчас расскажем про ревизионные люки Shagma. Представляем вашему вниманию пресс-релиз представителей бренда https://ogorod-bez-hlopot.ru/top-5-proizvoditeley-iskusstvennogo-kamnya-dlya-stoleshnits.html
https://moviefiles.fun
Сейчас расскажем про ревизионные люки Shagma. Представляем вашему вниманию пресс-релиз представителей бренда http://www.vpgazeta.ru/article/_27627
onlinepharmacy Cialis without a doctors prescription
Сейчас расскажем про ревизионные люки Shagma. Представляем вашему вниманию пресс-релиз представителей бренда https://ssa.ru/articles/proryv-v-obustroistve-interera-mebel-iz-iskusstvennogo-kamnja.html
Актуальная ссылка на сайт mega
Стоимость дипломов высшего и среднего образования и как избежать подделок
Продажа качественных дженериков на сайте https://buytablets.ru/ с бесплатной
доставкой в день покупки
more info here phantom wallet
Алкогольный запой сопровождается опасной интоксикацией, которая без своевременной помощи может привести к необратимым последствиям, включая поражение печени, сердца, почек и психические расстройства. В критических случаях промедление может стоить жизни. Именно поэтому специалисты клиники готовы оказывать поддержку круглосуточно.
Детальнее – быстрый вывод из запоя в стационаре
Алкогольный запой — это состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над своим потреблением алкоголя, что может вызвать серьезные физические и психологические проблемы. В таких ситуациях крайне важно получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь как можно скорее. Однако многие люди опасаются обращаться за помощью, переживая за свою репутацию и возможное раскрытие личной информации. В клинике «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже мы гарантируем анонимность на всех этапах лечения, сохраняя высокий уровень медицинской помощи и заботясь о каждом пациенте.
Ознакомиться с деталями – вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно воронеж
Когда включаешь «Однажды в сказке 1 сезон», попадаешь в удивительный мир, где реальность сплетается с фантазией так тесно, что невозможно сразу понять, где заканчивается одно и начинается другое. Сюжет первой главы этой истории строится вокруг Эммы Свон, обычной на первый взгляд женщины с непростым прошлым https://odnazhdy-v-skazke-1-sezon.ru/
Продажа русских сувениров — наш основной бизнес. Интернет-магазин «Ай, Матрешки» собрал одну из крупнейших и интереснейших в стране коллекций жостово подносы купить
Когда включаешь «Однажды в сказке 1 сезон», попадаешь в удивительный мир, где реальность сплетается с фантазией так тесно, что невозможно сразу понять, где заканчивается одно и начинается другое. Сюжет первой главы этой истории строится вокруг Эммы Свон, обычной на первый взгляд женщины с непростым прошлым https://odnazhdy-v-skazke-1-sezon.ru/
Алкогольный запой — это состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к токсической нагрузке на организм. Это опасное состояние требует не только быстрого медицинского вмешательства, но и внимательного подхода к восстановлению здоровья пациента. Процесс вывода из запоя включает в себя комплекс процедур, направленных на устранение последствий интоксикации и восстановление нормального функционирования организма. Важно учитывать, что стоимость этой процедуры может значительно варьироваться в зависимости от нескольких факторов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – наркологическая клиника в краснодаре
Продажа русских сувениров — наш основной бизнес. Интернет-магазин «Ай, Матрешки» собрал одну из крупнейших и интереснейших в стране коллекций шкатулка палех
Когда включаешь «Однажды в сказке 1 сезон», попадаешь в удивительный мир, где реальность сплетается с фантазией так тесно, что невозможно сразу понять, где заканчивается одно и начинается другое. Сюжет первой главы этой истории строится вокруг Эммы Свон, обычной на первый взгляд женщины с непростым прошлым смотреть сериал однажды в сказке 1 сезон
Продажа русских сувениров — наш основной бизнес. Интернет-магазин «Ай, Матрешки» собрал одну из крупнейших и интереснейших в стране коллекций магазин подарков в москве
морские перевозки грузов перевозчики https://bvs-logistica.com/perevozka-gruzov-morem.html
Стоимость вывода из запоя зависит от ряда факторов, таких как состояние пациента, выбранная программа лечения и место проведения процедуры. Мы предлагаем прозрачное ценообразование, чтобы вы могли заранее ознакомиться с возможными затратами на лечение.
Узнать больше – vyvod iz zapoya cena narkologiya v-chelyabinske
Зависимость — это серьёзная проблема, которая затрагивает не только человека, но и его семью и окружение. Алкоголизм, наркомания и другие виды зависимостей могут разрушить жизнь, но с профессиональной помощью можно вернуть её в русло нормального функционирования. Наркологическая клиника «Заря Будущего» в Санкт-Петербурге предлагает уникальные программы лечения зависимостей, которые сочетает медико-психологический подход, индивидуальные методики и квалифицированную поддержку.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – вывод из запоя капельница на дому
Вывод из запоя представляет собой важный этап в процессе лечения алкогольной зависимости. Это медицинская процедура, необходимая для устранения токсических веществ, накопленных в организме в результате длительного употребления алкоголя. Алкогольная зависимость может вызывать множество проблем, включая физические и психоэмоциональные расстройства. Своевременное вмешательство специалистов помогает минимизировать риски и способствует восстановлению здоровья пациента.
Подробнее тут – vyvod iz zapoya na domu nedorogo kapelnica v-ryazani
Интернет-магазин товаров https://vitasleep.ru для здорового сна. В ассортименте: ортопедические матрасы, подушки, одеяла, постельное белье и аксессуары от проверенных брендов. Удобный выбор, доставка по России, гарантия качества. Забота о вашем комфорте и здоровом сне!
Casino is not just a game of luck; it’s a thrilling challenge that can be mastered with the right strategy. Imagine the excitement of hitting 21 and beating the dealer with confidence. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced player, learning best slot machine casino can transform your gaming experience and lead to significant wins. Don’t miss out on the opportunity to improve your skills and enjoy the rewards. Start playing blackjack today and take the first step towards becoming a pro!
Алкогольная зависимость — это длительное и прогрессирующее заболевание, при котором развивается как физическая, так и психическая зависимость от алкоголя. Одним из самых тяжелых проявлений болезни является запой — длительное употребление алкоголя, которое может сопровождаться нарушениями работы организма и абстинентным синдромом, представляющим серьезную угрозу для здоровья. Эффективное лечение запоя требует комплексного подхода, включающего медикаментозную терапию, психотерапию и реабилитационные мероприятия.
Углубиться в тему – срочный вывод из запоя на дому тверь
Алкогольный запой сопровождается опасной интоксикацией, которая без своевременной помощи может привести к необратимым последствиям, включая поражение печени, сердца, почек и психические расстройства. В критических случаях промедление может стоить жизни. Именно поэтому специалисты клиники готовы оказывать поддержку круглосуточно.
Узнать больше – vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno narkologiya v-sankt-peterburge
Запой – это состояние, которое возникает вследствие длительного употребления алкоголя, приводящее к потере контроля над количеством выпиваемого и формированию как физической, так и психологической зависимости. Оно сопровождается серьёзными последствиями для здоровья и требует немедленного вмешательства.
Получить больше информации – vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare voronezh
Сопровождение мужчин — это особая услуга, которая может включать в себя как деловые, так и личные аспекты.
В современном мире многие мужчины ищут профессионалов, которые могут помочь им в различных сферах жизни:
от бизнес-мероприятий до социальных встреч – элитный эскорт москвы
мрт санкт-петербург мрт санкт-петербург .
Широкий выбор дженериков на сайте https://cialis24.ru с доставкой курьером
в день заказа отправка в регионы России
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся длительным и непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к формированию как физической, так и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния часто наблюдаются нарушения работы внутренних органов, что может привести к тяжелым последствиям, включая алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя — важный этап в процессе лечения зависимости, и его можно осуществлять как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от конкретных обстоятельств.
Ознакомиться с деталями – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom na dom v-sankt-peterburge
Запой представляет собой сложное состояние, связанное с длительным употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к формированию зависимости. Это явление не только нарушает нормальную жизнедеятельность, но также вызывает серьезные физические и психологические расстройства. Стационарное лечение становится необходимым для восстановления здоровья и профилактики осложнений. В стационаре клиники «Шаг к Трезвости» в Краснодаре мы предлагаем комплексный подход, включающий медикаментозное лечение, психотерапию и постоянный контроль со стороны квалифицированных специалистов.
Выяснить больше – вывод из запоя с выездом цена
see phantom wallet
Запой – это тяжелое состояние, возникающее из-за длительного и неконтролируемого употребления алкоголя. Оно характеризуется физической и психологической зависимостью, что приводит к серьезным последствиям для организма и психики. Для восстановления нормального самочувствия и здоровья необходимо профессиональное лечение. Одним из наиболее удобных и эффективных методов является вывод из запоя на дому.
Ознакомиться с деталями – anonimny vyvod iz zapoya na domu v-ryazani
Алкогольный запой представляет собой серьезное состояние, которое требует немедленного медицинского вмешательства. Это состояние характеризуется длительным и бесконтрольным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к разрушению как физического, так и психоэмоционального здоровья человека. Для эффективного и безопасного вывода из запоя стационарное лечение является оптимальным решением, особенно при тяжелых случаях интоксикации. В стационаре клиники «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем комплексную программу вывода из запоя, которая включает детоксикацию, восстановление организма и психотерапевтическую помощь.
Выяснить больше – вывод из запоя капельница санкт-петербург
клиника мрт спб клиника мрт спб .
Алкогольная зависимость становится всё более распространенной проблемой, требующей внимания как со стороны медицинского сообщества, так и общества в целом. Вывод из запоя — это сложный и ответственный процесс, необходимый для восстановления здоровья пациента и его интеграции в нормальную жизнь. Профессиональное вмешательство позволяет минимизировать последствия длительного употребления алкоголя и нормализовать состояние организма.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – anonimny vyvod iz zapoya na domu v-ekaterinburge
Запой нарушает привычный ритм жизни, вызывая серьезные физические и эмоциональные проблемы. Для его лечения требуется не только медикаментозное вмешательство, но и постоянное наблюдение специалистов. Стационарное лечение в клинике позволяет обеспечить полный контроль над состоянием пациента, что минимизирует риски и способствует более эффективной реабилитации.
Получить дополнительную информацию – вывод из запоя цена наркология санкт-петербург
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, необходимая для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Это состояние, часто характеризующееся физическими и психоэмоциональными нарушениями, требует профессионального вмешательства. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть разнообразными и варьироваться от лёгкой тревожности до серьёзных нарушений в функционировании внутренних органов. Квалифицированная помощь в этот период позволяет минимизировать риски и значительно ускорить процесс выздоровления.
Узнать больше – быстрый вывод из запоя в стационаре воронеж
Запой — это опасное состояние, которое развивается у людей с алкогольной зависимостью и характеризуется длительным непрерывным потреблением алкоголя. Это состояние приводит к серьезным нарушениям в организме, как физическим, так и психоэмоциональным. Длительный запой может вызвать множество осложнений, таких как поражение внутренних органов, нервной системы, а также проблемы в социальной и семейной жизни. Однако современная медицина предоставляет эффективные методы вывода из запоя, и одним из наиболее удобных и востребованных является вывод из запоя на дому.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom cena sankt-peterburg
Алкоголизм — это хроническое заболевание, которое характеризуется патологической зависимостью от этанола. Периоды запоя, когда человек неконтролируемо потребляет алкоголь, могут привести к разнообразным медицинским осложнениям, как физическим, так и психологическим. Запой становится не только причиной ухудшения здоровья, но и причиной множества социальных и личных проблем. На этом фоне возникает необходимость вывода из запоя, процесс, который должен учитывать индивидуальные особенности пациента. Важно, что анонимность в реабилитации играет ключевую роль, помогая избежать стигматизации и увеличивая шансы на успешное восстановление.
Получить дополнительные сведения – vyvod iz zapoya na domu cena ryazan
Процесс выхода из запоя имеет большое значение в борьбе с алкоголизмом. Он требует не только профессионального медицинского вмешательства, но и внутренней мотивации пациента. Важным моментом является создание комфортных и анонимных условий лечения, особенно для тех, кто опасается осуждения со стороны окружающих. Одним из удобных решений является выведение из запоя на дому, что позволяет пациенту находиться в привычной обстановке и избегать стресса от госпитализации.
Получить дополнительные сведения – vyvod iz zapoya na domu krasnodar
Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся утратой контроля над употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к тяжелой интоксикации организма. Вывод из запоя — это комплексный процесс, направленный на устранение последствий интоксикации и восстановление нормального функционирования организма. Цена данной процедуры может значительно различаться в зависимости от нескольких факторов, и в этой статье мы подробно рассмотрим, что влияет на стоимость вывода из запоя в Краснодаре, в том числе в клинике «Шаг к Трезвости».
Детальнее – narkologicheskaya klinika
Для преодоления запоя применяются современные медицинские методики, позволяющие быстро очистить организм от токсинов, нормализовать его работу и снизить вероятность осложнений. В ходе лечения используются специальные растворы для внутривенного введения и лекарственные препараты, направленные на восстановление обменных процессов. Для тех, кто не может или не хочет обращаться в стационар, существует возможность проведения всех необходимых процедур на дому, что обеспечивает комфорт и полную конфиденциальность.
Узнать больше – anonimny vyvod iz zapoya na domu v-tveri
центр мрт спб центр мрт спб .
смотреть онлайн сериалы подряд бесплатно https://lordseriall.org
сериалы онлайн 2024 lordserial4 top
Команда опытных врачей обеспечивает качественный вывод из запоя, полностью контролируя состояние пациента и устраняя негативные последствия алкоголизма. Запойное состояние характеризуется беспрерывным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к тяжелым нарушениям в работе организма, включая заболевания печени, поджелудочной железы, а также риску развития алкогольного делирия. Такое состояние не только ухудшает качество жизни, но и несет прямую угрозу для жизни. Стационарное лечение может быть более результативным, но многие предпочитают проходить процедуру дома, сохраняя конфиденциальность.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom na dom v-ekaterinburge
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся длительным и непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к формированию как физической, так и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния часто наблюдаются нарушения работы внутренних органов, что может привести к тяжелым последствиям, включая алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя — важный этап в процессе лечения зависимости, и его можно осуществлять как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от конкретных обстоятельств.
Получить больше информации – вывод из запоя капельница в санкт-петербурге
смотреть лучшие сериалы первым https://lordserials2.net
Магазин дженериков https://cialisbrand.ru/ большой выбор низкие
цены быстрая доставка по городу отправка в регионы почтой России
купить диплом логопеда 2orik-diploms.ru .
Клиника “Второй Шанс” в Санкт-Петербурге предлагает услугу вывода из запоя, как в стационаре, так и на дому. Для пациентов, не желающих посещать клинику, квалифицированные врачи готовы предоставить помощь в комфортных домашних условиях. Используя современные методы, специалисты обеспечивают безопасность, анонимность и высокий уровень медицинской поддержки.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya na domu cena sankt-peterburg
check that phantom Download
Выход из запоя — это важнейший этап на пути к избавлению от алкогольной зависимости. Он требует комплексного подхода, профессиональной помощи и сильной мотивации пациента. В условиях, когда анонимность и комфорт становятся ключевыми факторами для многих людей, вывод из запоя на дому приобретает все большее значение. Это решение позволяет человеку получить необходимую помощь, не покидая дома, и избежать стресса, связанного с госпитализацией.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – narkologicheskaya klinika v-krasnodare
Алкогольный запой представляет собой критическое состояние, требующее немедленного вмешательства квалифицированных специалистов. Клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже предлагает круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить своевременное и эффективное лечение. Наша цель — оперативное снятие интоксикации, устранение симптомов и предотвращение осложнений.
Углубиться в тему – вывод из запоя с выездом на дом воронеж
Запой — это опасное состояние, которое развивается у людей с алкогольной зависимостью и характеризуется длительным непрерывным потреблением алкоголя. Это состояние приводит к серьезным нарушениям в организме, как физическим, так и психоэмоциональным. Длительный запой может вызвать множество осложнений, таких как поражение внутренних органов, нервной системы, а также проблемы в социальной и семейной жизни. Однако современная медицина предоставляет эффективные методы вывода из запоя, и одним из наиболее удобных и востребованных является вывод из запоя на дому.
Получить дополнительные сведения – vyvod iz zapoya na domu kruglosutochno sankt-peterburg
Запой — это продолжительное, неконтролируемое потребление алкоголя, которое часто приводит к серьезным физическим и психологическим проблемам. Во время запоя организм подвергается интоксикации, обезвоживанию, нарушениям работы нервной системы, а также утрате способности к самоконтролю. Для успешного преодоления этого состояния необходима профессиональная медицинская помощь, направленная на прекращение употребления алкоголя и восстановление нормального функционирования организма.
Подробнее тут – vyvod iz zapoya srochno kruglosutochno krasnodar
Круглосуточная медицинская помощь при алкогольном запое играет важнейшую роль в спасении жизни пациентов и их возвращении к нормальному состоянию. В данной статье рассмотрим ключевые аспекты вывода из запоя в домашних условиях, срочной помощи и работы нарколога.
Углубиться в тему – наркологический центр екатеринбург
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой актуальную медицинскую проблему, требующую тщательного подхода. Запой характеризуется длительным, непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что ведёт к физической и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния могут возникнуть тяжёлые нарушения функций органов, увеличивается риск развития таких состояний, как алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя становится ключевым этапом в лечении зависимостей, который может осуществляться как в стационарных условиях, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента. В клинике «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске мы предлагаем круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить максимально эффективное и безопасное лечение при любом варианте вывода из запоя.
Получить больше информации – vyvod iz zapoya na domu kruglosutochno v-chelyabinske
Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся утратой контроля над употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к тяжелой интоксикации организма. Вывод из запоя — это комплексный процесс, направленный на устранение последствий интоксикации и восстановление нормального функционирования организма. Цена данной процедуры может значительно различаться в зависимости от нескольких факторов, и в этой статье мы подробно рассмотрим, что влияет на стоимость вывода из запоя в Краснодаре, в том числе в клинике «Шаг к Трезвости».
Выяснить больше – vyvod iz zapoya cena narkologiya krasnodar
Выход из запоя — это важнейший этап на пути к избавлению от алкогольной зависимости. Он требует комплексного подхода, профессиональной помощи и сильной мотивации пациента. В условиях, когда анонимность и комфорт становятся ключевыми факторами для многих людей, вывод из запоя на дому приобретает все большее значение. Это решение позволяет человеку получить необходимую помощь, не покидая дома, и избежать стресса, связанного с госпитализацией.
Углубиться в тему – вывод из запоя на дому недорого капельница краснодар
Запой — это продолжительное, неконтролируемое потребление алкоголя, которое часто приводит к серьезным физическим и психологическим проблемам. Во время запоя организм подвергается интоксикации, обезвоживанию, нарушениям работы нервной системы, а также утрате способности к самоконтролю. Для успешного преодоления этого состояния необходима профессиональная медицинская помощь, направленная на прекращение употребления алкоголя и восстановление нормального функционирования организма.
Углубиться в тему – vyvod iz zapoya na domu
on line pharmacy
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся длительным и непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к формированию как физической, так и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния часто наблюдаются нарушения работы внутренних органов, что может привести к тяжелым последствиям, включая алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя — важный этап в процессе лечения зависимости, и его можно осуществлять как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от конкретных обстоятельств.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-19.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница санкт-петербург[/url]
Для преодоления запоя применяются современные медицинские методики, позволяющие быстро очистить организм от токсинов, нормализовать его работу и снизить вероятность осложнений. В ходе лечения используются специальные растворы для внутривенного введения и лекарственные препараты, направленные на восстановление обменных процессов. Для тех, кто не может или не хочет обращаться в стационар, существует возможность проведения всех необходимых процедур на дому, что обеспечивает комфорт и полную конфиденциальность.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – вывод из запоя с выездом на дом в твери
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой сложное и хроническое заболевание, которое влияет не только на физическое, но и на психологическое состояние пациента. Периоды запоя, влекущие за собой неконтролируемое употребление алкоголя, могут привести к опасным последствиям для здоровья и жизни. Абстинентные симптомы, такие как тремор, тошнота, головная боль и другие проявления, требуют немедленного медицинского вмешательства. В таких ситуациях важно не только быстро устранить физическое воздействие алкоголя, но и предоставить пациенту психологическую поддержку.
Изучить вопрос глубже – наркологический центр краснодар
смотреть сериалы 2019 сериалы смотреть онлайн бесплатно
Запой — это тяжелое состояние, возникающее вследствие длительного и непрерывного употребления алкоголя, которое сопровождается физической и психической зависимостью. Это опасное явление требует незамедлительного вмешательства специалистов. Вывод из запоя — это комплексный процесс медицинской детоксикации, который включает в себя очищение организма от токсинов, нормализацию функций внутренних органов и поддержку психоэмоционального состояния пациента. В случае тяжелого запоя стационарное лечение становится оптимальным решением для безопасного и эффективного вывода из этого состояния. В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как проходит вывод из запоя в стационаре клиники «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, а также особенности анонимности, скорости лечения и участия нарколога.
Изучить вопрос глубже – vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare anonimno
В современном мире зависимость становится все более распространенной проблемой. Стресс, жизненные трудности и финансовые проблемы часто провоцируют развитие таких серьезных состояний, как алкоголизм, наркомания и игромания. Наркологическая клиника “Второй Шанс” предоставляет помощь людям, столкнувшимся с этими заболеваниями. Основное направление работы клиники — восстановление здоровья пациентов, их социальная адаптация и предотвращение повторных рецидивов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – наркология вывод из запоя на дому
смотреть лучшие сериалы 2023 lordserialss.life
смотреть сериалы 2024 https://lordserials.cc
Запой представляет собой состояние, связанное с длительным употреблением алкогольных напитков, что приводит к значительным физическим и психическим расстройствам. Это явление формирует зависимость, оказывая негативное воздействие на здоровье. Вывод из запоя в стационаре становится необходимостью для восстановительных мероприятий, направленных на реабилитацию пациента. В этой статье рассматриваются аспекты анонимного вывода, скорость процедур, а также роль нарколога в процессе лечения.
Узнать больше – вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно в краснодаре
Запой – это тяжелое состояние, возникающее из-за длительного и неконтролируемого употребления алкоголя. Оно характеризуется физической и психологической зависимостью, что приводит к серьезным последствиям для организма и психики. Для восстановления нормального самочувствия и здоровья необходимо профессиональное лечение. Одним из наиболее удобных и эффективных методов является вывод из запоя на дому.
Ознакомиться с деталями – vyvod iz zapoya cena v-ryazani
this hyperlink Metamask Extension
Запойное состояние представляет собой серьёзную угрозу для здоровья, поскольку сопровождается тяжёлой интоксикацией организма и нарушением психоэмоционального состояния. Решение о лечении в стационаре клиники «Союз Здоровья» позволяет справиться с последствиями длительного употребления алкоголя, обеспечивая пациентам полный комплекс медицинской и психологической помощи.
Разобраться лучше – вывод из запоя круглосуточно наркология в воронеже
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся длительным и непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к формированию как физической, так и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния часто наблюдаются нарушения работы внутренних органов, что может привести к тяжелым последствиям, включая алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя — важный этап в процессе лечения зависимости, и его можно осуществлять как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от конкретных обстоятельств.
Изучить вопрос глубже – наркологический центр
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой сложное и хроническое заболевание, которое влияет не только на физическое, но и на психологическое состояние пациента. Периоды запоя, влекущие за собой неконтролируемое употребление алкоголя, могут привести к опасным последствиям для здоровья и жизни. Абстинентные симптомы, такие как тремор, тошнота, головная боль и другие проявления, требуют немедленного медицинского вмешательства. В таких ситуациях важно не только быстро устранить физическое воздействие алкоголя, но и предоставить пациенту психологическую поддержку.
Разобраться лучше – вывод из запоя врач на дом в краснодаре
Процесс вывода из запоя требует быстрого реагирования. Запой, особенно в его тяжелых формах, представляет угрозу не только для психического состояния пациента, но и для его физического здоровья. Чтобы минимизировать риски и предотвратить осложнения, важно начинать лечение как можно скорее. Клинике «Освобождение» в Рязани доступна круглосуточная помощь — мы работаем 24/7, чтобы оперативно вмешаться в любой момент, когда это необходимо. Врачебная помощь может быть предоставлена как в стационаре клиники, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента и его предпочтений.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – narkologiya vyvod iz zapoya na domu v-ryazani
Процесс выхода из запоя имеет большое значение в борьбе с алкоголизмом. Он требует не только профессионального медицинского вмешательства, но и внутренней мотивации пациента. Важным моментом является создание комфортных и анонимных условий лечения, особенно для тех, кто опасается осуждения со стороны окружающих. Одним из удобных решений является выведение из запоя на дому, что позволяет пациенту находиться в привычной обстановке и избегать стресса от госпитализации.
Выяснить больше – нарколог на дом вывод из запоя
Современное общество сталкивается с серьёзными вызовами, связанными с зависимостями. Алкоголизм, как одна из самых распространённых проблем, оказывает разрушительное воздействие на здоровье человека, разрушая семейные отношения и затрудняя социальную адаптацию. В такие моменты крайне важно обратиться за квалифицированной помощью.
Получить больше информации – вывод из запоя капельница рязань
Клиника «Преображение» предлагает услуги анонимного вывода из запоя в Екатеринбурге, обеспечивая высокое качество медицинской помощи и соблюдение всех этических норм.
Изучить вопрос глубже – vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno v-ekaterinburge
Запой представляет собой состояние, характеризующееся длительным непрерывным употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к физической и психической зависимости. Этот процесс может длиться от нескольких дней до недель. Алкогольные напитки негативно влияют на функционирование внутренних органов, вызывая серьёзные нарушения, включая алкоголизм. При необходимости вывода из запоя важно обратиться за медицинской помощью, что можно осуществить на дому. В данной статье рассмотрим ключевые аспекты данной процедуры.
Разобраться лучше – vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno narkologiya chelyabinsk
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой актуальную медицинскую проблему, требующую тщательного подхода. Запой характеризуется длительным, непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что ведёт к физической и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния могут возникнуть тяжёлые нарушения функций органов, увеличивается риск развития таких состояний, как алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя становится ключевым этапом в лечении зависимостей, который может осуществляться как в стационарных условиях, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента. В клинике «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске мы предлагаем круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить максимально эффективное и безопасное лечение при любом варианте вывода из запоя.
Разобраться лучше – вывод из запоя с выездом цена
Алкогольная зависимость — коварное заболевание, которое захватывает не только физическое здоровье, но и разрушает психику, лишает человека воли и заставляет его жить в плену у собственной зависимости. Запой — один из наиболее тяжелых периодов в жизни человека, столкнувшегося с алкоголизмом. Он характеризуется длительным и интенсивным употреблением спиртных напитков, приводящим к глубокой интоксикации организма, нарушению физиологических функций, психическим расстройствам, а также обострению сопутствующих заболеваний.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-16.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-krasnodare/
Процесс выхода из запоя имеет большое значение в борьбе с алкоголизмом. Он требует не только профессионального медицинского вмешательства, но и внутренней мотивации пациента. Важным моментом является создание комфортных и анонимных условий лечения, особенно для тех, кто опасается осуждения со стороны окружающих. Одним из удобных решений является выведение из запоя на дому, что позволяет пациенту находиться в привычной обстановке и избегать стресса от госпитализации.
Изучить вопрос глубже – вывод из запоя капельница на дому челябинск
Зависимость — это серьёзная проблема, которая затрагивает не только человека, но и его семью и окружение. Алкоголизм, наркомания и другие виды зависимостей могут разрушить жизнь, но с профессиональной помощью можно вернуть её в русло нормального функционирования. Наркологическая клиника «Заря Будущего» в Санкт-Петербурге предлагает уникальные программы лечения зависимостей, которые сочетает медико-психологический подход, индивидуальные методики и квалифицированную поддержку.
Ознакомиться с деталями – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom cena
Алкогольная зависимость — это длительное и прогрессирующее заболевание, при котором развивается как физическая, так и психическая зависимость от алкоголя. Одним из самых тяжелых проявлений болезни является запой — длительное употребление алкоголя, которое может сопровождаться нарушениями работы организма и абстинентным синдромом, представляющим серьезную угрозу для здоровья. Эффективное лечение запоя требует комплексного подхода, включающего медикаментозную терапию, психотерапию и реабилитационные мероприятия.
Получить дополнительную информацию – vyvod iz zapoya vrach na dom
Запой нарушает привычный ритм жизни, вызывая серьезные физические и эмоциональные проблемы. Для его лечения требуется не только медикаментозное вмешательство, но и постоянное наблюдение специалистов. Стационарное лечение в клинике позволяет обеспечить полный контроль над состоянием пациента, что минимизирует риски и способствует более эффективной реабилитации.
Получить дополнительную информацию – наркологическая клиника
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, необходимая для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Это состояние, часто характеризующееся физическими и психоэмоциональными нарушениями, требует профессионального вмешательства. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть разнообразными и варьироваться от легкой тревожности до серьезных нарушений в функционировании внутренних органов. Квалифицированная помощь в этот период позволяет минимизировать риски и значительно ускорить процесс выздоровления.
Разобраться лучше – vyvod iz zapoya vrach na dom chelyabinsk
Алкогольный запой представляет собой критическое состояние, требующее немедленного вмешательства квалифицированных специалистов. Клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже предлагает круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить своевременное и эффективное лечение. Наша цель — оперативное снятие интоксикации, устранение симптомов и предотвращение осложнений.
Получить дополнительную информацию – вывод из запоя с выездом на дом в воронеже
Специалисты клиники «Рассвет» в Твери оказывают комплексную поддержку людям, страдающим от запоев. Пациенты получают круглосуточное медицинское наблюдение, эффективную детоксикацию и индивидуально подобранные программы восстановления. Гарантируется высокий уровень обслуживания, анонимность и полное сопровождение на пути к выздоровлению.
Подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya anonimno nedorogo v-tveri
Алкогольная зависимость — это серьезная проблема, требующая незамедлительного вмешательства, чтобы избежать тяжелых последствий для здоровья. Запойное пьянство может привести к различным заболеваниям, таким как цирроз печени, панкреатит и другие опасные состояния. К счастью, современная медицина предлагает эффективные методы решения этой проблемы. Для тех, кто не хочет или не может посетить стационар, есть возможность пройти процедуру капельницы от запоя на дому в Твери.
Получить дополнительные сведения – вывод из запоя круглосуточно наркология тверь
Стоимость вывода из запоя зависит от ряда факторов, таких как состояние пациента, выбранная программа лечения и место проведения процедуры. Мы предлагаем прозрачное ценообразование, чтобы вы могли заранее ознакомиться с возможными затратами на лечение.
Детальнее – вывод из запоя на дому недорого
Алкогольная зависимость — это хроническое заболевание, которое требует комплексного подхода и квалифицированного лечения. В клинике «Излечение» гарантируют полную анонимность на всех этапах лечения, что особенно важно для тех, кто хочет избежать общественного осуждения. Пациенты могут получить помощь как в стационаре, так и на дому, при этом обеспечивается максимальный комфорт и конфиденциальность.
Получить больше информации – narkologiya vyvod iz zapoya anonimno v-krasnodare
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся длительным и непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к формированию как физической, так и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния часто наблюдаются нарушения работы внутренних органов, что может привести к тяжелым последствиям, включая алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя — важный этап в процессе лечения зависимости, и его можно осуществлять как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от конкретных обстоятельств.
Подробнее тут – vyvod iz zapoya na domu kruglosutochno v-sankt-peterburge
купить диплом хирурга
Запой сопровождается сильной интоксикацией организма, что негативно сказывается на внутренних органах и нервной системе, повышая вероятность осложнений, таких как алкогольный делирий. Это требует немедленного медицинского вмешательства, так как своевременная помощь способна спасти жизнь пациента.
Разобраться лучше – vyvod iz zapoya cena narkologiya v-ekaterinburge
Запой – это состояние, возникающее из-за длительного употребления алкоголя и характеризующееся физической и психологической зависимостью. Оно требует комплексного медицинского вмешательства для устранения последствий и предотвращения дальнейшего ухудшения здоровья. Стационарное лечение в клинике «Освобождение» в Рязани – это эффективный способ вернуть пациента к нормальной жизни, предоставляя ему комфортные условия и круглосуточную помощь специалистов.
Подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya na domu v-ryazani
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой серьезную медицинскую проблему, которая влечет за собой не только физические, но и психологические проблемы. Периоды запоя, характеризующиеся бесконтрольным употреблением алкоголя, могут привести к тяжелым последствиям. Симптомы абстиненции требуют незамедлительного вмешательства. Анонимность в процессе реабилитации становится важным аспектом, помогающим пациентам избежать стыда и социального осуждения.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – нарколог вывод из запоя цена краснодар
Алкогольная зависимость — это серьезная проблема, требующая незамедлительного вмешательства, чтобы избежать тяжелых последствий для здоровья. Запойное пьянство может привести к различным заболеваниям, таким как цирроз печени, панкреатит и другие опасные состояния. К счастью, современная медицина предлагает эффективные методы решения этой проблемы. Для тех, кто не хочет или не может посетить стационар, есть возможность пройти процедуру капельницы от запоя на дому в Твери.
Получить больше информации – вывод из запоя круглосуточно наркология в твери
купить диплом о высшем образовании в новосибирске 4russkiy365-diplomy.ru .
Запой представляет собой состояние, связанное с длительным употреблением алкогольных напитков, что приводит к значительным физическим и психическим расстройствам. Это явление формирует зависимость, оказывая негативное воздействие на здоровье. Вывод из запоя в стационаре становится необходимостью для восстановительных мероприятий, направленных на реабилитацию пациента. В этой статье рассматриваются аспекты анонимного вывода, скорость процедур, а также роль нарколога в процессе лечения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom v-krasnodare
Команда опытных врачей обеспечивает качественный вывод из запоя, полностью контролируя состояние пациента и устраняя негативные последствия алкоголизма. Запойное состояние характеризуется беспрерывным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к тяжелым нарушениям в работе организма, включая заболевания печени, поджелудочной железы, а также риску развития алкогольного делирия. Такое состояние не только ухудшает качество жизни, но и несет прямую угрозу для жизни. Стационарное лечение может быть более результативным, но многие предпочитают проходить процедуру дома, сохраняя конфиденциальность.
Получить дополнительную информацию – вывод из запоя с выездом екатеринбург
Алкогольный запой представляет собой серьезное состояние, которое требует немедленного медицинского вмешательства. Это состояние характеризуется длительным и бесконтрольным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к разрушению как физического, так и психоэмоционального здоровья человека. Для эффективного и безопасного вывода из запоя стационарное лечение является оптимальным решением, особенно при тяжелых случаях интоксикации. В стационаре клиники «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем комплексную программу вывода из запоя, которая включает детоксикацию, восстановление организма и психотерапевтическую помощь.
Выяснить больше – вывод из запоя с выездом
Процесс выхода из запоя имеет большое значение в борьбе с алкоголизмом. Он требует не только профессионального медицинского вмешательства, но и внутренней мотивации пациента. Важным моментом является создание комфортных и анонимных условий лечения, особенно для тех, кто опасается осуждения со стороны окружающих. Одним из удобных решений является выведение из запоя на дому, что позволяет пациенту находиться в привычной обстановке и избегать стресса от госпитализации.
Узнать больше – вывод из запоя круглосуточно челябинск
В современном мире зависимость становится все более распространенной проблемой. Стресс, жизненные трудности и финансовые проблемы часто провоцируют развитие таких серьезных состояний, как алкоголизм, наркомания и игромания. Наркологическая клиника “Второй Шанс” предоставляет помощь людям, столкнувшимся с этими заболеваниями. Основное направление работы клиники — восстановление здоровья пациентов, их социальная адаптация и предотвращение повторных рецидивов.
Узнать больше – нарколог на дом вывод из запоя санкт-петербург
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой сложное и хроническое заболевание, которое влияет не только на физическое, но и на психологическое состояние пациента. Периоды запоя, влекущие за собой неконтролируемое употребление алкоголя, могут привести к опасным последствиям для здоровья и жизни. Абстинентные симптомы, такие как тремор, тошнота, головная боль и другие проявления, требуют немедленного медицинского вмешательства. В таких ситуациях важно не только быстро устранить физическое воздействие алкоголя, но и предоставить пациенту психологическую поддержку.
Разобраться лучше – vyvod iz zapoya anonimno nedorogo
Алкогольный запой — это тяжелое состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над количеством потребляемого алкоголя. Это приводит к сильной интоксикации, сбоям в работе органов и систем организма, а также серьезным психоэмоциональным расстройствам. Без должной медицинской помощи запой может вызвать ряд опасных последствий, включая алкогольный делирий и угрозу жизни. Поэтому при первых признаках запоя необходимо обратиться к профессионалам.
Выяснить больше – vyvod iz zapoya cena
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой серьёзную медицинскую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запойное состояние характеризуется длительным и бесконтрольным потреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к возникновению как физической, так и психической зависимости. Данное явление может вызвать нарушения в работе внутренних органов, значительно увеличивая вероятность развития алкогольного делирия, который представляет собой острое состояние, требующее неотложной медицинской помощи. Вывод из запоя это ключевая часть лечения зависимости, которая может осуществляться как в стационаре, так и в амбулаторных условиях, в зависимости от конкретной ситуации и состояния пациента.
Подробнее тут – вывод из запоя на дому недорого капельница краснодар
Клиника «Шаг к Трезвости» в Краснодаре предлагает анонимный вывод из запоя, обеспечивая полную конфиденциальность и безопасность на каждом этапе лечения. Мы понимаем, что для многих людей важно сохранить свою личную информацию в тайне, и гарантируем, что все данные о пациенте и его состоянии здоровья останутся закрытыми. Независимо от того, выбрал ли пациент стационарное лечение или вывод из запоя на дому, мы обеспечиваем высококачественную медицинскую помощь с полным соблюдением принципов конфиденциальности.
Получить дополнительные сведения – анонимный вывод из запоя на дому
Наркологическая клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже специализируется на лечении алкогольной зависимости и предлагает профессиональные услуги по выводу из запоя. Мы стремимся создать атмосферу доверия, где каждый пациент сможет получить необходимую поддержку.
Подробнее тут – вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно воронеж
Команда опытных врачей обеспечивает качественный вывод из запоя, полностью контролируя состояние пациента и устраняя негативные последствия алкоголизма. Запойное состояние характеризуется беспрерывным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к тяжелым нарушениям в работе организма, включая заболевания печени, поджелудочной железы, а также риску развития алкогольного делирия. Такое состояние не только ухудшает качество жизни, но и несет прямую угрозу для жизни. Стационарное лечение может быть более результативным, но многие предпочитают проходить процедуру дома, сохраняя конфиденциальность.
Узнать больше – narkolog vyvod iz zapoya cena
Запой — это продолжительное, неконтролируемое потребление алкоголя, которое часто приводит к серьезным физическим и психологическим проблемам. Во время запоя организм подвергается интоксикации, обезвоживанию, нарушениям работы нервной системы, а также утрате способности к самоконтролю. Для успешного преодоления этого состояния необходима профессиональная медицинская помощь, направленная на прекращение употребления алкоголя и восстановление нормального функционирования организма.
Ознакомиться с деталями – narkolog vyvod iz zapoya cena v-krasnodare
Клиника «Освобождение» в Рязани предоставляет услугу круглосуточного вывода из запоя на дому, что позволяет пациенту получить медицинскую помощь в привычной обстановке, избегая лишнего стресса, связанного с госпитализацией.
Получить дополнительную информацию – vyvod iz zapoya cena narkologiya
online pharmacy
Запой — это тяжелое состояние, возникающее вследствие длительного и непрерывного употребления алкоголя, которое сопровождается физической и психической зависимостью. Это опасное явление требует незамедлительного вмешательства специалистов. Вывод из запоя — это комплексный процесс медицинской детоксикации, который включает в себя очищение организма от токсинов, нормализацию функций внутренних органов и поддержку психоэмоционального состояния пациента. В случае тяжелого запоя стационарное лечение становится оптимальным решением для безопасного и эффективного вывода из этого состояния. В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как проходит вывод из запоя в стационаре клиники «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, а также особенности анонимности, скорости лечения и участия нарколога.
Изучить вопрос глубже – vyvod iz zapoya anonimno chelyabinsk
Зависимость — это серьёзная проблема, которая затрагивает не только человека, но и его семью и окружение. Алкоголизм, наркомания и другие виды зависимостей могут разрушить жизнь, но с профессиональной помощью можно вернуть её в русло нормального функционирования. Наркологическая клиника «Заря Будущего» в Санкт-Петербурге предлагает уникальные программы лечения зависимостей, которые сочетает медико-психологический подход, индивидуальные методики и квалифицированную поддержку.
Выяснить больше – vyvod iz zapoya cena v-sankt-peterburge
Круглосуточная поддержка при алкогольной зависимости помогает восстановить нормальное состояние здоровья и вернуться к полноценной жизни. Анонимное выведение из запоя позволяет получить необходимую медицинскую помощь с соблюдением конфиденциальности, минимизируя последствия алкоголизма и нормализуя общее состояние пациента.
Детальнее – вывод из запоя на дому недорого екатеринбург
Алкогольная зависимость — это длительное и прогрессирующее заболевание, при котором развивается как физическая, так и психическая зависимость от алкоголя. Одним из самых тяжелых проявлений болезни является запой — длительное употребление алкоголя, которое может сопровождаться нарушениями работы организма и абстинентным синдромом, представляющим серьезную угрозу для здоровья. Эффективное лечение запоя требует комплексного подхода, включающего медикаментозную терапию, психотерапию и реабилитационные мероприятия.
Выяснить больше – вывод из запоя с выездом цена в твери
Online pharmacies http://canadianpharmacymall.net/ Where to buy metronidazole
Стоимость вывода из запоя зависит от ряда факторов, таких как состояние пациента, выбранная программа лечения и место проведения процедуры. Мы предлагаем прозрачное ценообразование, чтобы вы могли заранее ознакомиться с возможными затратами на лечение.
Детальнее – вывод из запоя
Специалисты клиники «Рассвет» в Твери оказывают комплексную поддержку людям, страдающим от запоев. Пациенты получают круглосуточное медицинское наблюдение, эффективную детоксикацию и индивидуально подобранные программы восстановления. Гарантируется высокий уровень обслуживания, анонимность и полное сопровождение на пути к выздоровлению.
Узнать больше – вывод из запоя анонимно недорого
prescription free pharmacy
Современное общество сталкивается с серьёзными вызовами, связанными с зависимостями. Алкоголизм, как одна из самых распространённых проблем, оказывает разрушительное воздействие на здоровье человека, разрушая семейные отношения и затрудняя социальную адаптацию. В такие моменты крайне важно обратиться за квалифицированной помощью.
Ознакомиться с деталями – вывод из запоя цена наркология в рязани
Круглосуточная поддержка при алкогольной зависимости помогает восстановить нормальное состояние здоровья и вернуться к полноценной жизни. Анонимное выведение из запоя позволяет получить необходимую медицинскую помощь с соблюдением конфиденциальности, минимизируя последствия алкоголизма и нормализуя общее состояние пациента.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – вывод из запоя в екатеринбурге
Клиника «Рассвет» в Твери предоставляет услугу анонимного вывода из запоя, обеспечивая высокое качество медицинского обслуживания и строгое соблюдение всех этических норм.
Выяснить больше – вывод из запоя с выездом
Процедура вывода из запоя направлена на устранение последствий длительного употребления алкоголя и восстановления работы организма. Этот процесс включает не только медикаментозное лечение, но и психологическую поддержку, что позволяет минимизировать симптомы абстиненции и предотвратить возможные осложнения.
Детальнее – вывод из запоя с выездом цена санкт-петербург
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся длительным и непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к формированию как физической, так и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния часто наблюдаются нарушения работы внутренних органов, что может привести к тяжелым последствиям, включая алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя — важный этап в процессе лечения зависимости, и его можно осуществлять как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от конкретных обстоятельств.
Изучить вопрос глубже – вывод из запоя санкт-петербург
canadian pharmacy
Процесс получения диплома стоматолога: реально ли это сделать быстро?
Generic Cialis Online Pharmacy Reviews northwest pharmacy canada
Запой — это состояние, при котором человек не может прекратить употребление алкоголя на протяжении длительного времени, что вызывает физическую и психологическую зависимость. Это крайне опасное состояние, требующее немедленного вмешательства специалистов. Наркологическая клиника «Преображение» в Екатеринбурге предоставляет профессиональную помощь в лечении запоя, используя самые эффективные и безопасные методы.
Детальнее – vyvod iz zapoya srochno kruglosutochno
Наркологическая клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже специализируется на лечении алкогольной зависимости и предлагает профессиональные услуги по выводу из запоя. Мы стремимся создать атмосферу доверия, где каждый пациент сможет получить необходимую поддержку.
Разобраться лучше – вывод из запоя на дому в воронеже
Продолжительное употребление алкоголя приводит к состоянию, при котором человек теряет способность самостоятельно остановиться, оказываясь в плену физической и психологической зависимости. Такое положение дел представляет серьёзную угрозу для здоровья и требует незамедлительного вмешательства профессионалов. В Екатеринбурге наркологическая клиника «Преображение» предлагает специализированную помощь, используя проверенные и безопасные методы лечения.
Получить больше информации – vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno narkologiya
Vendita cialis usa online overnight pharmacy 247 Overnight Pharmacy Canadian
Алкогольная зависимость — это хроническое заболевание, которое требует комплексного подхода и квалифицированного лечения. В клинике «Излечение» гарантируют полную анонимность на всех этапах лечения, что особенно важно для тех, кто хочет избежать общественного осуждения. Пациенты могут получить помощь как в стационаре, так и на дому, при этом обеспечивается максимальный комфорт и конфиденциальность.
Узнать больше – vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare
Loveshop Снова Работает !!!!!
Подробнее https://telegra.ph/Pushistye-ldinki-kak-NFT-Kak-Shop1-biz-prevrashchaet-iskusstvo-v-cifrovye-aktivy-01-08
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой состояние, при котором организм человека испытывает серьезное воздействие этанола, что приводит к нарушению нормальной физиологической деятельности. Это состояние сопровождается сильными физическими и психологическими расстройствами, которые требуют профессионального вмешательства. Однако многие люди, страдающие алкогольной зависимостью, сталкиваются с трудностью признания своей проблемы, опасаясь утраты репутации и конфиденциальности. В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем анонимный вывод из запоя в Санкт-Петербурге, предоставляя высококачественное лечение с гарантией сохранения личной информации.
Разобраться лучше – вывод из запоя
перевозки заказать в Минске
Алкогольная зависимость становится всё более распространенной проблемой, требующей внимания как со стороны медицинского сообщества, так и общества в целом. Вывод из запоя — это сложный и ответственный процесс, необходимый для восстановления здоровья пациента и его интеграции в нормальную жизнь. Профессиональное вмешательство позволяет минимизировать последствия длительного употребления алкоголя и нормализовать состояние организма.
Разобраться лучше – вывод из запоя цена в екатеринбурге
Алкогольный запой – это серьёзное состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к тяжёлой интоксикации организма. Во время запоя нарушаются функции внутренних органов, страдает нервная система, и повышается риск развития опасных осложнений, таких как алкогольный делирий. Это состояние требует незамедлительного медицинского вмешательства.
Разобраться лучше – вывод из запоя с выездом цена в екатеринбурге
When it pertains to relaxation and rejuvenation in the fast-paced city of New York, few experiences measure up to the extravagance of an elite bodyrub. NEW YORK CITY, referred to as a worldwide hub for deluxe and class, uses a few of the finest bodyrub solutions developed to melt away anxiety, rejuvenate your detects, and restore equilibrium to your body and mind. Whether you’re a hectic expert, a site visitor to the city, or merely a person seeking a premium indulging experience, elite bodyrub solutions in New York City are your entrance to exceptional relaxation.
In this guide, we’ll delve into what makes elite bodyrub solutions in NYC so one-of-a-kind, their benefits, exactly how to pick the very best service providers, and everything you require to understand to make certain a costs experience.
We work in Midtown West. Specialists Emily – nurumassagesex
Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся утратой контроля над употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к тяжелой интоксикации организма. Вывод из запоя — это комплексный процесс, направленный на устранение последствий интоксикации и восстановление нормального функционирования организма. Цена данной процедуры может значительно различаться в зависимости от нескольких факторов, и в этой статье мы подробно рассмотрим, что влияет на стоимость вывода из запоя в Краснодаре, в том числе в клинике «Шаг к Трезвости».
Узнать больше – наркология вывод из запоя на дому в краснодаре
Запой нарушает привычный ритм жизни, вызывая серьезные физические и эмоциональные проблемы. Для его лечения требуется не только медикаментозное вмешательство, но и постоянное наблюдение специалистов. Стационарное лечение в клинике позволяет обеспечить полный контроль над состоянием пациента, что минимизирует риски и способствует более эффективной реабилитации.
Подробнее тут – наркологический центр
лучшие сериалы онлайн https://lordsserial.xyz
Алкоголизм — это хроническое заболевание, которое характеризуется патологической зависимостью от этанола. Периоды запоя, когда человек неконтролируемо потребляет алкоголь, могут привести к разнообразным медицинским осложнениям, как физическим, так и психологическим. Запой становится не только причиной ухудшения здоровья, но и причиной множества социальных и личных проблем. На этом фоне возникает необходимость вывода из запоя, процесс, который должен учитывать индивидуальные особенности пациента. Важно, что анонимность в реабилитации играет ключевую роль, помогая избежать стигматизации и увеличивая шансы на успешное восстановление.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – наркология вывод из запоя на дому в рязани
Запой – это состояние, которое возникает вследствие длительного употребления алкоголя, приводящее к потере контроля над количеством выпиваемого и формированию как физической, так и психологической зависимости. Оно сопровождается серьёзными последствиями для здоровья и требует немедленного вмешательства.
Выяснить больше – narkologiya vyvod iz zapoya anonimno
Длительное запойное состояние крайне опасно, поскольку провоцирует серьезные заболевания, включая цирроз печени, воспаление поджелудочной железы и нарушения работы нервной системы. В тяжелых случаях возможно развитие алкогольного делирия – состояния, угрожающего жизни. Именно поэтому важно своевременно обратиться за медицинской помощью при первых признаках ухудшения самочувствия.
Детальнее – vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno narkologiya v-tveri
Процесс вывода из запоя включает несколько этапов, направленных на детоксикацию и восстановление нормальной работы организма. Для этого необходимы высококвалифицированные специалисты, которые помогают избавиться от последствий токсического воздействия алкоголя и восстанавливают здоровье пациента. Стоимость лечения зависит от необходимого объема услуг и условий их предоставления. В клинике «Излечение» предлагаются доступные цены, с учетом индивидуальных потребностей каждого пациента.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – вывод из запоя анонимно
Запой — это опасное состояние, которое развивается у людей с алкогольной зависимостью и характеризуется длительным непрерывным потреблением алкоголя. Это состояние приводит к серьезным нарушениям в организме, как физическим, так и психоэмоциональным. Длительный запой может вызвать множество осложнений, таких как поражение внутренних органов, нервной системы, а также проблемы в социальной и семейной жизни. Однако современная медицина предоставляет эффективные методы вывода из запоя, и одним из наиболее удобных и востребованных является вывод из запоя на дому.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-19.ru
Команда опытных врачей обеспечивает качественный вывод из запоя, полностью контролируя состояние пациента и устраняя негативные последствия алкоголизма. Запойное состояние характеризуется беспрерывным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к тяжелым нарушениям в работе организма, включая заболевания печени, поджелудочной железы, а также риску развития алкогольного делирия. Такое состояние не только ухудшает качество жизни, но и несет прямую угрозу для жизни. Стационарное лечение может быть более результативным, но многие предпочитают проходить процедуру дома, сохраняя конфиденциальность.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom cena v-ekaterinburge
Логистические услуги в Москве https://bvs-logistica.com доставка, хранение, грузоперевозки. Надежные решения для бизнеса и частных клиентов. Оптимизация маршрутов, складские услуги и полный контроль на всех этапах.
В клинике «Рассвет» в Твери мы предлагаем круглосуточную помощь при алкогольных запоях, обеспечивая быстрый вывод токсинов из организма с помощью капельниц и других эффективных методик.
Разобраться лучше – вывод из запоя на дому недорого тверь
Алкогольная зависимость — это хроническое заболевание, которое требует комплексного подхода и квалифицированного лечения. В клинике «Излечение» гарантируют полную анонимность на всех этапах лечения, что особенно важно для тех, кто хочет избежать общественного осуждения. Пациенты могут получить помощь как в стационаре, так и на дому, при этом обеспечивается максимальный комфорт и конфиденциальность.
Получить дополнительную информацию – vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare anonimno
сериалы онлайн 2024 https://lordserialss.life
купить диплом оригинал гознак купить диплом оригинал гознак .
Процесс вывода из запоя включает несколько этапов, направленных на детоксикацию и восстановление нормальной работы организма. Для этого необходимы высококвалифицированные специалисты, которые помогают избавиться от последствий токсического воздействия алкоголя и восстанавливают здоровье пациента. Стоимость лечения зависит от необходимого объема услуг и условий их предоставления. В клинике «Излечение» предлагаются доступные цены, с учетом индивидуальных потребностей каждого пациента.
Изучить вопрос глубже – narkologiya vyvod iz zapoya na domu v-chelyabinske
healthy man viagra Cialis India Pharmacy Pharmacy express canada
Диплом с занесением в реестр
Первый сезон — это не просто история о противостоянии добра и зла, это настоящий квест, полный загадок, неожиданных поворотов и встреч с героями сказок, которые предстали в совершенно новом свете https://odnazhdy-v-skazke-1-sezon.ru/
Интернет-магазин русских сувениров и подарков по низким ценам в Москве. Более 20 лет на рынке оптом и в розницу приходите выбирайте покупайте ждем вас русские сувениры
Первый сезон — это не просто история о противостоянии добра и зла, это настоящий квест, полный загадок, неожиданных поворотов и встреч с героями сказок, которые предстали в совершенно новом свете https://odnazhdy-v-skazke-1-sezon.ru/
Интернет-магазин русских сувениров и подарков по низким ценам в Москве. Более 20 лет на рынке оптом и в розницу приходите выбирайте покупайте ждем вас русские подарки
книга выдачи аттестатов нового образца купить
Хотите почувствовать азарт? arkada casino промокод за регистрацию предлагает широкий выбор игр, честную систему выигрышей и мгновенные выплаты. Захватывающие слоты и бонусы ждут вас!
Первый сезон — это не просто история о противостоянии добра и зла, это настоящий квест, полный загадок, неожиданных поворотов и встреч с героями сказок, которые предстали в совершенно новом свете https://odnazhdy-v-skazke-1-sezon.ru/
Интернет-магазин русских сувениров и подарков по низким ценам в Москве. Более 20 лет на рынке оптом и в розницу приходите выбирайте покупайте ждем вас шкатулка палех
Полезная информация как официально купить диплом о высшем образовании
online pharmacies canada Buy citalopram online uk
диплом купить о среднем образовании
canadian pharmacy
Many social networking websites permit users to create profiles totally free.
cheapest canadian online pharmacy medications
This sweeping laws finally opened up native and lengthy-distance phone service, in addition to cable television markets, to extra competitors.
Regular maintenance, inspections, and consulting your owner’s manual will make sure you maximize your GMC truck’s towing potential, allowing you to tow safely and efficiently in any state of affairs.
Проблема зависимостей остаётся актуальной в современном обществе. С каждым годом увеличивается число людей, страдающих от алкоголизма, наркомании и других форм зависимостей, что негативно отражается на их жизни и благополучии близких. Зависимость — это не просто физическое заболевание, но и глубокая психологическая проблема. Для эффективного лечения требуется помощь профессионалов, способных обеспечить комплексный подход.
Выяснить больше – srochny vyvod iz zapoya na domu v-voronezhe
В клинике “Восстановление души” работает команда высококвалифицированных специалистов, готовых предложить современное и эффективное лечение зависимостей. Наши врачи-наркологи обладают обширным опытом работы и постоянно совершенствуют свои навыки, чтобы использовать самые передовые методы терапии.
Разобраться лучше – капельница от запоя круглосуточно наркология воронеж
This solved a problem common with standard frames, whose flexing and deflection — brought on by the excessive kick-ups being weak in torsion (bending) — allowed the shifting rear axle to interrupt free on gravel or undulating street surfaces.
While Rall was in Trenton, he and some of his top officers spent Christmas evening at the house of Abraham Hunt, Trenton’s postmaster, the place Hunt performed the position of a Loyalist and placated Rall and his officers with meals and loads of drink into the late hours of the night and morning, which, by many accounts, compromised Rall’s skill to answer Washington’s shock attack at daybreak.
Darth Traya (Kreia) is a mentor to the “Jedi Exile” and the hidden major antagonist of Star Wars: Knights of the Previous Republic II – The Sith Lords.
Сколько стоит диплом высшего и среднего образования и как это происходит?
Even if a robotic with a gun have been allowed to function on its own, and it did go out of management, the push of a button on the management unit is all that would be wanted to reboot the robotic to protected mode.
Современное общество сталкивается с серьёзными вызовами, связанными с зависимостями. Алкоголизм, как одна из самых распространённых проблем, оказывает разрушительное воздействие на здоровье человека, разрушая семейные отношения и затрудняя социальную адаптацию. В такие моменты крайне важно обратиться за квалифицированной помощью.
Получить больше информации – vyvod iz zapoya vrach na dom v-ryazani
When you find yourself purchasing look round for the alternate rates that are provided.
Реально ли приобрести диплом стоматолога? Основные этапы
смотреть сериалы качестве https://lordseriall6.org
Depending on context, the term may also refer to listed company (quarterly) earnings guidance.
The one entered the UK Singles Chart on download gross sales alone at number 18.
It’s additionally straightforward to read, which is perfect for followers looking for a lightweight feel-good read.
смотреть сериалы 2024 https://lordsserials.org
смотреть сериалы качестве https://lordserial5.pet
Запой — это тяжелое состояние, возникающее вследствие длительного и непрерывного употребления алкоголя, которое сопровождается физической и психической зависимостью. Это опасное явление требует незамедлительного вмешательства специалистов. Вывод из запоя — это комплексный процесс медицинской детоксикации, который включает в себя очищение организма от токсинов, нормализацию функций внутренних органов и поддержку психоэмоционального состояния пациента. В случае тяжелого запоя стационарное лечение становится оптимальным решением для безопасного и эффективного вывода из этого состояния. В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как проходит вывод из запоя в стационаре клиники «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, а также особенности анонимности, скорости лечения и участия нарколога.
Получить дополнительную информацию – narkolog vyvod iz zapoya cena chelyabinsk
When a business decides to handle its sources intelligently, it will certainly realise its targets.
Алкогольный запой сопровождается опасной интоксикацией, которая без своевременной помощи может привести к необратимым последствиям, включая поражение печени, сердца, почек и психические расстройства. В критических случаях промедление может стоить жизни. Именно поэтому специалисты клиники готовы оказывать поддержку круглосуточно.
Подробнее тут – vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno narkologiya sankt-peterburg
Проблема зависимостей остаётся актуальной в современном обществе. С каждым годом увеличивается число людей, страдающих от алкоголизма, наркомании и других форм зависимостей, что негативно отражается на их жизни и благополучии близких. Зависимость — это не просто физическое заболевание, но и глубокая психологическая проблема. Для эффективного лечения требуется помощь профессионалов, способных обеспечить комплексный подход.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://www.vyvod-iz-zapoya-11.ru
Зависимость от алкоголя – серьезная проблема, требующая системного подхода и профессионального лечения. В клинике «Излечение» гарантируется полная конфиденциальность на всех этапах процесса, что позволяет пациентам чувствовать себя в безопасности. Лечение может проходить как в стационаре, так и на дому, при этом соблюдаются все условия для максимального комфорта.
Получить дополнительную информацию – bystry vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare
Алкогольный запой представляет собой крайне опасное состояние, характеризующееся неконтролируемым употреблением алкоголя, что в свою очередь приводит к тяжелой интоксикации организма. Восстановление после такого состояния требует профессионального вмешательства, включающего не только физическую детоксикацию, но и психологическую поддержку. Стоимость процедуры вывода из запоя может значительно различаться в зависимости от множества факторов, включая метод лечения, тяжесть состояния пациента и место проведения лечения. Рассмотрим более подробно основные аспекты, влияющие на цену вывода из запоя.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya na domu nedorogo sankt-peterburg
Алкогольный запой – это серьёзное состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к тяжёлой интоксикации организма. Во время запоя нарушаются функции внутренних органов, страдает нервная система, и повышается риск развития опасных осложнений, таких как алкогольный делирий. Это состояние требует незамедлительного медицинского вмешательства.
Подробнее тут – narkolog vyvod iz zapoya cena
EIAs are unique in that they do not require adherence to a predetermined environmental outcome, but rather they require decision-makers to account for environmental values in their decisions and to justify those decisions in light of detailed environmental studies and public comments on the potential environmental impacts.
Choosing the Right Online Tool
Inputting My Measurements and Preferences
technogran.ru
B5XvZR9ny
For a deeper clean‚ dedicate time each week to a more thorough cleaning. Use appropriate cleaning products for each surface. Avoid harsh chemicals that could damage delicate materials like marble or granite. Always test any new cleaning product in an inconspicuous area first. Pay close attention to grout lines‚ as these areas tend to accumulate dirt and mildew. A grout brush and appropriate cleaner are invaluable tools for maintaining clean grout lines. Regularly inspect faucets and showerheads for mineral deposits. Descaling these fixtures regularly prevents clogging and maintains optimal water flow.
Understanding the Importance of Flushing
можно ли купить диплом настоящий 2orik-diploms.ru .
Throuples are sometimes referred to as triad relationships or group relationships.
Although he expects the bill to be unpopular, he wants to hear what people think of such a measure.
Алкогольный запой сопровождается опасной интоксикацией, которая без своевременной помощи может привести к необратимым последствиям, включая поражение печени, сердца, почек и психические расстройства. В критических случаях промедление может стоить жизни. Именно поэтому специалисты клиники готовы оказывать поддержку круглосуточно.
Углубиться в тему – вывод из запоя врач на дом в санкт-петербурге
Запой представляет собой состояние, характеризующееся длительным непрерывным употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к физической и психической зависимости. Этот процесс может длиться от нескольких дней до недель. Алкогольные напитки негативно влияют на функционирование внутренних органов, вызывая серьёзные нарушения, включая алкоголизм. При необходимости вывода из запоя важно обратиться за медицинской помощью, что можно осуществить на дому. В данной статье рассмотрим ключевые аспекты данной процедуры.
Углубиться в тему – вывод из запоя срочно круглосуточно челябинск
Just keep feelings out of the combo so you do not end up flaming the fireplace vs placing it out.
He surreptitiously engaged Individuals in supporting the Loyalist cause.
These companies make their money from interest paid by clients who cannot repay their statements every month.
Клиника «Преображение» предлагает услуги анонимного вывода из запоя в Екатеринбурге, обеспечивая высокое качество медицинской помощи и соблюдение всех этических норм.
Углубиться в тему – вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно
It offers tools for invoicing, expense tracking, payroll, inventory management, and financial reporting.
F.J. ( Dock ) Harrison, aged 82, retired resident of Lockesburg, died at 2:30 a.m.
Наркологическая клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже специализируется на лечении алкогольной зависимости и предлагает профессиональные услуги по выводу из запоя. Мы стремимся создать атмосферу доверия, где каждый пациент сможет получить необходимую поддержку.
Получить больше информации – вывод из запоя врач на дом в воронеже
В этой статье мы расскажем о возможностях клиники для лечения алкогольной интоксикации круглосуточно, включая вывод из запоя в стационаре и на дому, а также о роли профессионалов, таких как нарколог, в процессе лечения.
Углубиться в тему – vyvod iz zapoya na domu nedorogo kapelnica v-krasnodare
Алкогольный запой представляет собой критическое состояние, требующее немедленного вмешательства квалифицированных специалистов. Клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже предлагает круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить своевременное и эффективное лечение. Наша цель — оперативное снятие интоксикации, устранение симптомов и предотвращение осложнений.
Разобраться лучше – vyvod iz zapoya na domu v-voronezhe
Алкогольный запой представляет собой крайне опасное состояние, характеризующееся неконтролируемым употреблением алкоголя, что в свою очередь приводит к тяжелой интоксикации организма. Восстановление после такого состояния требует профессионального вмешательства, включающего не только физическую детоксикацию, но и психологическую поддержку. Стоимость процедуры вывода из запоя может значительно различаться в зависимости от множества факторов, включая метод лечения, тяжесть состояния пациента и место проведения лечения. Рассмотрим более подробно основные аспекты, влияющие на цену вывода из запоя.
Ознакомиться с деталями – vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare sankt-peterburg
Зависимость — это хроническое заболевание, требующее долгосрочного лечения и регулярной поддержки. В клинике используют современные научные методы в наркологии и психотерапии, предлагая помощь на всех этапах — от диагностики до реабилитации. Команда профессионалов работает с каждым пациентом индивидуально, обеспечивая комплексный подход к терапии.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – srochny vyvod iz zapoya na domu sankt-peterburg
В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы понимаем, насколько важен своевременный и профессиональный подход к лечению зависимости. Наши специалисты готовы оказать квалифицированную помощь прямо у вас дома, обеспечивая полную безопасность и конфиденциальность на каждом этапе лечения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – нарколог вывод из запоя цена в санкт-петербурге
Алкогольный запой представляет собой серьезное состояние, которое требует немедленного медицинского вмешательства. Это состояние характеризуется длительным и бесконтрольным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к разрушению как физического, так и психоэмоционального здоровья человека. Для эффективного и безопасного вывода из запоя стационарное лечение является оптимальным решением, особенно при тяжелых случаях интоксикации. В стационаре клиники «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем комплексную программу вывода из запоя, которая включает детоксикацию, восстановление организма и психотерапевтическую помощь.
Получить дополнительную информацию – вывод из запоя в санкт-петербурге
canada pharmacy
Клиника “Восстановление души” предлагает услугу капельницы от запоя на дому в Иркутске и Иркутской области, что является удобным решением для тех, кто не может или не хочет лечиться в стационаре. Мы понимаем, как важно поддерживать пациента в момент, когда его организм нуждается в быстрой и квалифицированной помощи.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – srochnaya kapelnica ot zapoya na domu
healthymale
Алкогольная зависимость — коварное заболевание, которое захватывает не только физическое здоровье, но и разрушает психику, лишает человека воли и заставляет его жить в плену у собственной зависимости. Запой — один из наиболее тяжелых периодов в жизни человека, столкнувшегося с алкоголизмом. Он характеризуется длительным и интенсивным употреблением спиртных напитков, приводящим к глубокой интоксикации организма, нарушению физиологических функций, психическим расстройствам, а также обострению сопутствующих заболеваний.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya na domu nedorogo kapelnica v-krasnodare
Запой представляет собой состояние, характеризующееся длительным непрерывным употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к физической и психической зависимости. Этот процесс может длиться от нескольких дней до недель. Алкогольные напитки негативно влияют на функционирование внутренних органов, вызывая серьёзные нарушения, включая алкоголизм. При необходимости вывода из запоя важно обратиться за медицинской помощью, что можно осуществить на дому. В данной статье рассмотрим ключевые аспекты данной процедуры.
Углубиться в тему – vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare v-chelyabinske
Мы понимаем, что каждая зависимость уникальна, поэтому основой нашего подхода является индивидуализация лечения. После тщательной диагностики, включающей анализ медицинской истории, психологического состояния и социальных факторов, наши специалисты разрабатывают персонализированный план терапии. Этот план может включать медикаментозную детоксикацию, психотерапевтические методы и социальные программы, направленные на изменение поведения и мышления пациента.
Подробнее тут – kapelnica ot zapoya v stacionare anonimno
В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы понимаем, насколько важен своевременный и профессиональный подход к лечению зависимости. Наши специалисты готовы оказать квалифицированную помощь прямо у вас дома, обеспечивая полную безопасность и конфиденциальность на каждом этапе лечения.
Подробнее тут – vyvod iz zapoya na domu
The Chattanooga Steam plays at Lookout Valley Highschool close to Lookout Mountain.
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой актуальную медицинскую проблему, требующую тщательного подхода. Запой характеризуется длительным, непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что ведёт к физической и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния могут возникнуть тяжёлые нарушения функций органов, увеличивается риск развития таких состояний, как алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя становится ключевым этапом в лечении зависимостей, который может осуществляться как в стационарных условиях, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента. В клинике «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске мы предлагаем круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить максимально эффективное и безопасное лечение при любом варианте вывода из запоя.
Ознакомиться с деталями – narkologiya vyvod iz zapoya na domu chelyabinsk
Запой — это состояние, при котором человек продолжает употреблять алкоголь на протяжении нескольких дней или даже недель, не контролируя объемы потребляемого напитка. Этот процесс сопровождается тяжелыми физическими и психическими последствиями, такими как обезвоживание организма, отравление продуктами распада алкоголя, нервные расстройства и потеря контроля над ситуацией. Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, направленная на прекращение употребления алкоголя и восстановление организма пациента.
Изучить вопрос глубже – srochny vyvod iz zapoya na domu krasnodar
В некоторых ситуациях, когда запой длится несколько дней или приводит к серьезным последствиям для здоровья, необходим срочный вызов нарколога. Среди признаков, при которых требуется неотложная помощь:
Узнать больше – kapelnica ot zapoya anonimno v moskve
Немцы настаивают на том, что это единственный автомобиль на рынке с третьим уровнем автономности. Если вы оказались в пробке на шоссе, просто нажмите кнопку и достаньте книгу для чтения. Компьютер останавливается и запускается, сохраняя вам самые раздражающие части вождения peschanokopskoe.ru
Each time Earning profits On-line OR Online Enterprise IN NIGERIA is mention, people begin considering of rip-off.
Запойное состояние представляет собой серьёзную угрозу для здоровья, поскольку сопровождается тяжёлой интоксикацией организма и нарушением психоэмоционального состояния. Решение о лечении в стационаре клиники «Союз Здоровья» позволяет справиться с последствиями длительного употребления алкоголя, обеспечивая пациентам полный комплекс медицинской и психологической помощи.
Детальнее – vyvod iz zapoya vrach na dom v-voronezhe
Canadian Online Pharmacy cialis black 800mg reviews
Немцы настаивают на том, что это единственный автомобиль на рынке с третьим уровнем автономности. Если вы оказались в пробке на шоссе, просто нажмите кнопку и достаньте книгу для чтения. Компьютер останавливается и запускается, сохраняя вам самые раздражающие части вождения shinaspec.ru
Buying nizagara on line canadian superstore pharmacy reviews 4 Corners Pharmacy
Круглосуточная медицинская помощь при алкогольном запое играет важнейшую роль в спасении жизни пациентов и их возвращении к нормальному состоянию. В данной статье рассмотрим ключевые аспекты вывода из запоя в домашних условиях, срочной помощи и работы нарколога.
Разобраться лучше – narkologiya vyvod iz zapoya anonimno
Немцы настаивают на том, что это единственный автомобиль на рынке с третьим уровнем автономности. Если вы оказались в пробке на шоссе, просто нажмите кнопку и достаньте книгу для чтения. Компьютер останавливается и запускается, сохраняя вам самые раздражающие части вождения march-club.ru
Запойное пьянство характеризуется продолжительным и интенсивным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к серьезным физическим и психологическим последствиям. Часто пациенты сталкиваются с различными заболеваниями, такими как цирроз печени, панкреатит, алкогольный делирий и другие. Алкогольное опьянение не только ухудшает качество жизни, но также может угрожать жизни пациента. В условиях стационара лечение может быть более эффективным, однако многие люди предпочитают проходить данную процедуру на дому, чтобы избежать стигматизации и сохранить чувство приватности.
Разобраться лучше – вывод из запоя на дому
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся длительным и непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к формированию как физической, так и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния часто наблюдаются нарушения работы внутренних органов, что может привести к тяжелым последствиям, включая алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя — важный этап в процессе лечения зависимости, и его можно осуществлять как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от конкретных обстоятельств.
Получить больше информации – вывод из запоя цена наркология в санкт-петербурге
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой сложное и хроническое заболевание, которое влияет не только на физическое, но и на психологическое состояние пациента. Периоды запоя, влекущие за собой неконтролируемое употребление алкоголя, могут привести к опасным последствиям для здоровья и жизни. Абстинентные симптомы, такие как тремор, тошнота, головная боль и другие проявления, требуют немедленного медицинского вмешательства. В таких ситуациях важно не только быстро устранить физическое воздействие алкоголя, но и предоставить пациенту психологическую поддержку.
Подробнее – вывод из запоя анонимно в краснодаре
официальный диплом купить
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся длительным и непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к формированию как физической, так и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния часто наблюдаются нарушения работы внутренних органов, что может привести к тяжелым последствиям, включая алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя — важный этап в процессе лечения зависимости, и его можно осуществлять как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от конкретных обстоятельств.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-19.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-sankt-peterburge/]вывод из запоя врач на дом санкт-петербург[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, необходимая для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Это состояние, часто характеризующееся физическими и психоэмоциональными нарушениями, требует профессионального вмешательства. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть разнообразными и варьироваться от легкой тревожности до серьезных нарушений в функционировании внутренних органов. Квалифицированная помощь в этот период позволяет минимизировать риски и значительно ускорить процесс выздоровления.
Детальнее – vyvod iz zapoya anonimno nedorogo v-chelyabinske
Запой — это опасное состояние, которое развивается у людей с алкогольной зависимостью и характеризуется длительным непрерывным потреблением алкоголя. Это состояние приводит к серьезным нарушениям в организме, как физическим, так и психоэмоциональным. Длительный запой может вызвать множество осложнений, таких как поражение внутренних органов, нервной системы, а также проблемы в социальной и семейной жизни. Однако современная медицина предоставляет эффективные методы вывода из запоя, и одним из наиболее удобных и востребованных является вывод из запоя на дому.
Углубиться в тему – narkologicheski centr
Проблема зависимости от алкоголя, наркотиков и азартных игр остается одной из наиболее острых в современном обществе. Эти состояния оказывают значительное воздействие не только на здоровье самого человека, но и на его семью, друзей и общественные связи. Наркологическая клиника “Восстановление души” предлагает широкий спектр услуг для тех, кто борется с различными формами зависимости, такими как алкоголизм, наркомания и игромания. Наша цель — предоставить комплексный подход к лечению, что обеспечивает высокие показатели успешности среди наших пациентов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://www.kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh2.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-cena-v-voronezhe
Алкогольный запой сопровождается опасной интоксикацией, которая без своевременной помощи может привести к необратимым последствиям, включая поражение печени, сердца, почек и психические расстройства. В критических случаях промедление может стоить жизни. Именно поэтому специалисты клиники готовы оказывать поддержку круглосуточно.
Подробнее тут – vyvod iz zapoya gorod sankt-peterburg
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой крайне опасное состояние, при котором организм страдает от токсического воздействия алкоголя. Это ведет к нарушению нормальных физиологических процессов и ухудшению общего состояния здоровья. Капельница от запоя — это медицинская процедура, направленная на выведение токсинов из организма и восстановление нормальной функции организма при соблюдении полной конфиденциальности.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – narkolog na dom vyvod iz zapoya tver
Зависимость — это серьёзная проблема, которая затрагивает не только человека, но и его семью и окружение. Алкоголизм, наркомания и другие виды зависимостей могут разрушить жизнь, но с профессиональной помощью можно вернуть её в русло нормального функционирования. Наркологическая клиника «Заря Будущего» в Санкт-Петербурге предлагает уникальные программы лечения зависимостей, которые сочетает медико-психологический подход, индивидуальные методики и квалифицированную поддержку.
Подробнее тут – vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno v-sankt-peterburge
Зависимость — это хроническое заболевание, требующее долгосрочного лечения и регулярной поддержки. В клинике используют современные научные методы в наркологии и психотерапии, предлагая помощь на всех этапах — от диагностики до реабилитации. Команда профессионалов работает с каждым пациентом индивидуально, обеспечивая комплексный подход к терапии.
Детальнее – быстрый вывод из запоя в стационаре санкт-петербург
Алкогольный запой сопровождается опасной интоксикацией, которая без своевременной помощи может привести к необратимым последствиям, включая поражение печени, сердца, почек и психические расстройства. В критических случаях промедление может стоить жизни. Именно поэтому специалисты клиники готовы оказывать поддержку круглосуточно.
Углубиться в тему – вывод из запоя с выездом
Запой – это состояние, возникающее из-за длительного употребления алкоголя и характеризующееся физической и психологической зависимостью. Оно требует комплексного медицинского вмешательства для устранения последствий и предотвращения дальнейшего ухудшения здоровья. Стационарное лечение в клинике «Освобождение» в Рязани – это эффективный способ вернуть пациента к нормальной жизни, предоставляя ему комфортные условия и круглосуточную помощь специалистов.
Детальнее – http://www.vyvod-iz-zapoya-13.ru
Запой — это состояние, при котором человек не может прекратить употребление алкоголя на протяжении длительного времени, что вызывает физическую и психологическую зависимость. Это крайне опасное состояние, требующее немедленного вмешательства специалистов. Наркологическая клиника «Преображение» в Екатеринбурге предоставляет профессиональную помощь в лечении запоя, используя самые эффективные и безопасные методы.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno narkologiya v-ekaterinburge
Современное общество сталкивается с серьёзными вызовами, связанными с зависимостями. Алкоголизм, как одна из самых распространённых проблем, оказывает разрушительное воздействие на здоровье человека, разрушая семейные отношения и затрудняя социальную адаптацию. В такие моменты крайне важно обратиться за квалифицированной помощью.
Узнать больше – нарколог на дом вывод из запоя рязань
Check out Sellvia on Instagram for the hottest product ideas, store upgrades, and exclusive deals! Stay in the loop with our latest dropshipping tips and grab promo coupons to boost your business.
Наши массажистки посвятят Вам максимальное время и удивят профессиональными навыками. Все наши девушки овладели различными техниками массажа и готовы удовлетворить любого гостя, исполняя любую программу в нашем салоне «Оазис» Эротический массаж в Сочи
Наши массажистки посвятят Вам максимальное время и удивят профессиональными навыками. Все наши девушки овладели различными техниками массажа и готовы удовлетворить любого гостя, исполняя любую программу в нашем салоне «Оазис» Эротический массаж в Сочи
Алкогольный запой — это тяжелое состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над количеством потребляемого алкоголя. Это приводит к сильной интоксикации, сбоям в работе органов и систем организма, а также серьезным психоэмоциональным расстройствам. Без должной медицинской помощи запой может вызвать ряд опасных последствий, включая алкогольный делирий и угрозу жизни. Поэтому при первых признаках запоя необходимо обратиться к профессионалам.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – вывод из запоя анонимно
Процесс вывода из запоя требует быстрого реагирования. Запой, особенно в его тяжелых формах, представляет угрозу не только для психического состояния пациента, но и для его физического здоровья. Чтобы минимизировать риски и предотвратить осложнения, важно начинать лечение как можно скорее. Клинике «Освобождение» в Рязани доступна круглосуточная помощь — мы работаем 24/7, чтобы оперативно вмешаться в любой момент, когда это необходимо. Врачебная помощь может быть предоставлена как в стационаре клиники, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента и его предпочтений.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya na domu kruglosutochno ryazan
Наши массажистки посвятят Вам максимальное время и удивят профессиональными навыками. Все наши девушки овладели различными техниками массажа и готовы удовлетворить любого гостя, исполняя любую программу в нашем салоне «Оазис» Эротический массаж в Сочи
Процесс возвращения к нормальной жизни после длительного употребления алкоголя играет ключевую роль в избавлении от зависимости. Медицинское сопровождение должно сочетаться с осознанным желанием человека изменить свою жизнь. Важно, чтобы лечение проходило в условиях, исключающих стресс и дискомфорт. Для этого предусмотрены как стационарные программы, так и возможность получить медицинскую помощь на дому. Такой вариант подходит тем, кто предпочитает находиться в привычной обстановке и избегать огласки.
Разобраться лучше – наркология вывод из запоя анонимно краснодар
Наши наркологи приезжают к пациенту в удобное для него время и проводят необходимую терапию. Капельница от запоя помогает:
Углубиться в тему – bystry kapelnica ot zapoya v stacionare
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой крайне опасное состояние, при котором организм страдает от токсического воздействия алкоголя. Это ведет к нарушению нормальных физиологических процессов и ухудшению общего состояния здоровья. Капельница от запоя — это медицинская процедура, направленная на выведение токсинов из организма и восстановление нормальной функции организма при соблюдении полной конфиденциальности.
Получить больше информации – наркологический центр
Вывод из запойного состояния – сложный процесс, включающий несколько последовательных этапов. Основная цель – детоксикация организма и восстановление его нормального функционирования. Важно, чтобы процессом руководили опытные специалисты, способные минимизировать последствия интоксикации и помочь человеку вернуться к здоровой жизни. Стоимость лечения зависит от выбранных методов и уровня медицинского обслуживания, а в клинике «Излечение» предлагаются доступные варианты с учетом индивидуальных потребностей пациентов.
Разобраться лучше – vyvod iz zapoya na domu nedorogo
Зависимость от алкоголя – серьезная проблема, требующая системного подхода и профессионального лечения. В клинике «Излечение» гарантируется полная конфиденциальность на всех этапах процесса, что позволяет пациентам чувствовать себя в безопасности. Лечение может проходить как в стационаре, так и на дому, при этом соблюдаются все условия для максимального комфорта.
Разобраться лучше – vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare
После успешной детоксикации начинается этап реабилитации, который включает восстановление социального статуса пациента и формирование новых здоровых привычек. Мы предлагаем как групповые, так и индивидуальные занятия, направленные на изменение поведения и мышления, что способствует долгосрочному удержанию пациента от возвращения к зависимостям.
Подробнее тут – капельница от запоя круглосуточно наркология в иркутске
В некоторых ситуациях, когда запой длится несколько дней или приводит к серьезным последствиям для здоровья, необходим срочный вызов нарколога. Среди признаков, при которых требуется неотложная помощь:
Детальнее – капельница от запоя анонимно
Одной из распространенных проблем является запой, состояние, при котором человек длительное время бесконтрольно употребляет алкоголь, что приводит к тяжелой физической и психологической зависимости. Такое поведение чревато серьезными последствиями для здоровья, включая поражение внутренних органов, нервные расстройства и другие заболевания. Важно своевременно обратиться за профессиональной помощью, чтобы минимизировать риски и предотвратить осложнения.
Получить больше информации – вывод из запоя в стационаре санкт-петербург
Алкогольный запой представляет собой критическое состояние, требующее немедленного вмешательства квалифицированных специалистов. Клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже предлагает круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить своевременное и эффективное лечение. Наша цель — оперативное снятие интоксикации, устранение симптомов и предотвращение осложнений.
Детальнее – anonimny vyvod iz zapoya na domu voronezh
Запой представляет собой состояние, характеризующееся длительным непрерывным употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к физической и психической зависимости. Этот процесс может длиться от нескольких дней до недель. Алкогольные напитки негативно влияют на функционирование внутренних органов, вызывая серьёзные нарушения, включая алкоголизм. При необходимости вывода из запоя важно обратиться за медицинской помощью, что можно осуществить на дому. В данной статье рассмотрим ключевые аспекты данной процедуры.
Изучить вопрос глубже – наркологическая клиника
Алкогольный запой представляет собой серьезное состояние, которое требует немедленного медицинского вмешательства. Это состояние характеризуется длительным и бесконтрольным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к разрушению как физического, так и психоэмоционального здоровья человека. Для эффективного и безопасного вывода из запоя стационарное лечение является оптимальным решением, особенно при тяжелых случаях интоксикации. В стационаре клиники «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем комплексную программу вывода из запоя, которая включает детоксикацию, восстановление организма и психотерапевтическую помощь.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – наркологический центр в санкт-петербурге
Одним из важнейших аспектов, который помогает пациентам справиться с алкогольной зависимостью, является анонимность в процессе лечения. В клинике «Излечение» мы понимаем, как важно сохранить конфиденциальность и гарантировать защиту личной информации, особенно для тех, кто опасается общественного осуждения. Мы обеспечиваем полную анонимность при выводе из запоя, как в стационарных условиях, так и на дому.
Разобраться лучше – вывод из запоя с выездом цена краснодар
В клинике «Рассвет» в Твери мы предлагаем круглосуточную помощь при алкогольных запоях, обеспечивая быстрый вывод токсинов из организма с помощью капельниц и других эффективных методик.
Изучить вопрос глубже – нарколог на дом вывод из запоя
Наши наркологи приезжают к пациенту в удобное для него время и проводят необходимую терапию. Капельница от запоя помогает:
Получить больше информации – нарколог на дом капельница от запоя в иркутске
Алкогольный запой представляет собой серьезное состояние, которое требует немедленного медицинского вмешательства. Это состояние характеризуется длительным и бесконтрольным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к разрушению как физического, так и психоэмоционального здоровья человека. Для эффективного и безопасного вывода из запоя стационарное лечение является оптимальным решением, особенно при тяжелых случаях интоксикации. В стационаре клиники «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем комплексную программу вывода из запоя, которая включает детоксикацию, восстановление организма и психотерапевтическую помощь.
Получить больше информации – наркологическая клиника
Запой представляет собой состояние, связанное с длительным употреблением алкогольных напитков, что приводит к значительным физическим и психическим расстройствам. Это явление формирует зависимость, оказывая негативное воздействие на здоровье. Вывод из запоя в стационаре становится необходимостью для восстановительных мероприятий, направленных на реабилитацию пациента. В этой статье рассматриваются аспекты анонимного вывода, скорость процедур, а также роль нарколога в процессе лечения.
Узнать больше – vyvod iz zapoya kapelnica v-krasnodare
Запой — это опасное состояние, которое развивается у людей с алкогольной зависимостью и характеризуется длительным непрерывным потреблением алкоголя. Это состояние приводит к серьезным нарушениям в организме, как физическим, так и психоэмоциональным. Длительный запой может вызвать множество осложнений, таких как поражение внутренних органов, нервной системы, а также проблемы в социальной и семейной жизни. Однако современная медицина предоставляет эффективные методы вывода из запоя, и одним из наиболее удобных и востребованных является вывод из запоя на дому.
Детальнее – narkologicheskij centr v-sankt-peterburge
Вывод из запоя представляет собой важный этап в процессе лечения алкогольной зависимости. Это медицинская процедура, необходимая для устранения токсических веществ, накопленных в организме в результате длительного употребления алкоголя. Алкогольная зависимость может вызывать множество проблем, включая физические и психоэмоциональные расстройства. Своевременное вмешательство специалистов помогает минимизировать риски и способствует восстановлению здоровья пациента.
Детальнее – быстрый вывод из запоя в стационаре
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой актуальную медицинскую проблему, требующую тщательного подхода. Запой характеризуется длительным, непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что ведёт к физической и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния могут возникнуть тяжёлые нарушения функций органов, увеличивается риск развития таких состояний, как алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя становится ключевым этапом в лечении зависимостей, который может осуществляться как в стационарных условиях, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента. В клинике «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске мы предлагаем круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить максимально эффективное и безопасное лечение при любом варианте вывода из запоя.
Получить больше информации – вывод из запоя на дому недорого
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой состояние, при котором организм человека испытывает серьезное воздействие этанола, что приводит к нарушению нормальной физиологической деятельности. Это состояние сопровождается сильными физическими и психологическими расстройствами, которые требуют профессионального вмешательства. Однако многие люди, страдающие алкогольной зависимостью, сталкиваются с трудностью признания своей проблемы, опасаясь утраты репутации и конфиденциальности. В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем анонимный вывод из запоя в Санкт-Петербурге, предоставляя высококачественное лечение с гарантией сохранения личной информации.
Подробнее – вывод из запоя цена санкт-петербург
В таких ситуациях вывод из запоя на дому становится оптимальным решением, особенно если пациент не может или не хочет посещать стационар. Эта услуга позволяет получить медицинскую помощь в комфортной и привычной обстановке, что снижает уровень стресса и ускоряет процесс восстановления.
Получить дополнительные сведения – narkolog vyvod iz zapoya cena voronezh
В клинике также уделяется внимание конфиденциальности лечения. Понимая деликатность проблемы, врачи гарантируют полную анонимность на всех этапах терапии. Благодаря профессиональному подходу и использованию проверенных методик пациенты могут восстановить здоровье и вернуться к полноценной жизни.
Детальнее – http://www.vyvod-iz-zapoya-14.ru
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся длительным и непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к формированию как физической, так и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния часто наблюдаются нарушения работы внутренних органов, что может привести к тяжелым последствиям, включая алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя — важный этап в процессе лечения зависимости, и его можно осуществлять как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от конкретных обстоятельств.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya kapelnica na domu sankt-peterburg
Алкогольный запой сопровождается опасной интоксикацией, которая без своевременной помощи может привести к необратимым последствиям, включая поражение печени, сердца, почек и психические расстройства. В критических случаях промедление может стоить жизни. Именно поэтому специалисты клиники готовы оказывать поддержку круглосуточно.
Детальнее – vyvod iz zapoya na domu cena sankt-peterburg
Зависимость от алкоголя – серьезная проблема, требующая системного подхода и профессионального лечения. В клинике «Излечение» гарантируется полная конфиденциальность на всех этапах процесса, что позволяет пациентам чувствовать себя в безопасности. Лечение может проходить как в стационаре, так и на дому, при этом соблюдаются все условия для максимального комфорта.
Разобраться лучше – вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно
Алкогольный запой представляет собой серьезное состояние, которое требует немедленного медицинского вмешательства. Это состояние характеризуется длительным и бесконтрольным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к разрушению как физического, так и психоэмоционального здоровья человека. Для эффективного и безопасного вывода из запоя стационарное лечение является оптимальным решением, особенно при тяжелых случаях интоксикации. В стационаре клиники «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем комплексную программу вывода из запоя, которая включает детоксикацию, восстановление организма и психотерапевтическую помощь.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – наркология вывод из запоя на дому санкт-петербург
Запой — это тяжелое состояние, возникающее вследствие длительного и непрерывного употребления алкоголя, которое сопровождается физической и психической зависимостью. Это опасное явление требует незамедлительного вмешательства специалистов. Вывод из запоя — это комплексный процесс медицинской детоксикации, который включает в себя очищение организма от токсинов, нормализацию функций внутренних органов и поддержку психоэмоционального состояния пациента. В случае тяжелого запоя стационарное лечение становится оптимальным решением для безопасного и эффективного вывода из этого состояния. В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как проходит вывод из запоя в стационаре клиники «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, а также особенности анонимности, скорости лечения и участия нарколога.
Получить больше информации – vyvod iz zapoya na domu cena v-chelyabinske
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой состояние, при котором организм человека испытывает сильное воздействие этанола, что приводит к нарушению нормального функционирования физиологических систем. Это состояние может быть опасным и требует квалифицированной медицинской помощи. Вывод из запоя — важная медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение последствий чрезмерного употребления алкоголя и восстановление здоровья пациента.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – vyvod iz zapoya cena narkologiya chelyabinsk
Алкоголизм — это хроническое прогрессирующее заболевание, связанное с физической и психической зависимостью от этанола. Запой, как его крайнее проявление, представляет собой длительное употребление алкоголя, сопровождающееся тяжелыми нарушениями работы организма, включая абстинентный синдром и потенциальные угрозы для жизни. Лечение запоя требует комплексного подхода, включающего медицинские процедуры, психотерапию и реабилитационные меры.
Получить больше информации – вывод из запоя анонимно недорого
Запойное состояние представляет собой серьёзную угрозу для здоровья, поскольку сопровождается тяжёлой интоксикацией организма и нарушением психоэмоционального состояния. Решение о лечении в стационаре клиники «Союз Здоровья» позволяет справиться с последствиями длительного употребления алкоголя, обеспечивая пациентам полный комплекс медицинской и психологической помощи.
Получить дополнительную информацию – vyvod iz zapoya cena
Проблема зависимостей остаётся актуальной в современном обществе. С каждым годом увеличивается число людей, страдающих от алкоголизма, наркомании и других форм зависимостей, что негативно отражается на их жизни и благополучии близких. Зависимость — это не просто физическое заболевание, но и глубокая психологическая проблема. Для эффективного лечения требуется помощь профессионалов, способных обеспечить комплексный подход.
Получить больше информации – вывод из запоя на дому в воронеже
диплом купить в нальчике
Искали, где заказать монтаж плоской крыши недорого, здесь цены на 15% ниже рынка: https://ploskaya-krovli-zagorodnyh-domov.ru/
Процесс вывода из запоя требует быстрого реагирования. Запой, особенно в его тяжелых формах, представляет угрозу не только для психического состояния пациента, но и для его физического здоровья. Чтобы минимизировать риски и предотвратить осложнения, важно начинать лечение как можно скорее. Клинике «Освобождение» в Рязани доступна круглосуточная помощь — мы работаем 24/7, чтобы оперативно вмешаться в любой момент, когда это необходимо. Врачебная помощь может быть предоставлена как в стационаре клиники, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента и его предпочтений.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-13.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-ryazani/]vyvod iz zapoya vrach na dom [/url]
Запой нарушает привычный ритм жизни, вызывая серьезные физические и эмоциональные проблемы. Для его лечения требуется не только медикаментозное вмешательство, но и постоянное наблюдение специалистов. Стационарное лечение в клинике позволяет обеспечить полный контроль над состоянием пациента, что минимизирует риски и способствует более эффективной реабилитации.
Узнать больше – нарколог вывод из запоя цена санкт-петербург
Алкогольный запой представляет собой серьезное состояние, которое требует немедленного медицинского вмешательства. Это состояние характеризуется длительным и бесконтрольным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к разрушению как физического, так и психоэмоционального здоровья человека. Для эффективного и безопасного вывода из запоя стационарное лечение является оптимальным решением, особенно при тяжелых случаях интоксикации. В стационаре клиники «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем комплексную программу вывода из запоя, которая включает детоксикацию, восстановление организма и психотерапевтическую помощь.
Получить больше информации – вывод из запоя на дому недорого капельница санкт-петербург
Алкоголизм — это хроническое прогрессирующее заболевание, связанное с физической и психической зависимостью от этанола. Запой, как его крайнее проявление, представляет собой длительное употребление алкоголя, сопровождающееся тяжелыми нарушениями работы организма, включая абстинентный синдром и потенциальные угрозы для жизни. Лечение запоя требует комплексного подхода, включающего медицинские процедуры, психотерапию и реабилитационные меры.
Выяснить больше – vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno ekaterinburg
купить диплом минск купить диплом минск .
аттестат купить за 9 класс
Приобретение диплома ПТУ с сокращенной программой обучения в Москве
Вывод из запоя представляет собой важный этап в процессе лечения алкогольной зависимости. Это медицинская процедура, необходимая для устранения токсических веществ, накопленных в организме в результате длительного употребления алкоголя. Алкогольная зависимость может вызывать множество проблем, включая физические и психоэмоциональные расстройства. Своевременное вмешательство специалистов помогает минимизировать риски и способствует восстановлению здоровья пациента.
Изучить вопрос глубже – анонимный вывод из запоя на дому
Качественный сервис аренды дизельных генераторов с профессиональной поддержкой 24/7, все подробности здесь https://www.espguitars.com/users/8642776
Алкогольная зависимость — это серьезная проблема, требующая незамедлительного вмешательства, чтобы избежать тяжелых последствий для здоровья. Запойное пьянство может привести к различным заболеваниям, таким как цирроз печени, панкреатит и другие опасные состояния. К счастью, современная медицина предлагает эффективные методы решения этой проблемы. Для тех, кто не хочет или не может посетить стационар, есть возможность пройти процедуру капельницы от запоя на дому в Твери.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – bystry vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare v-tveri
Вывод из запоя представляет собой важный этап в процессе лечения алкогольной зависимости. Это медицинская процедура, необходимая для устранения токсических веществ, накопленных в организме в результате длительного употребления алкоголя. Алкогольная зависимость может вызывать множество проблем, включая физические и психоэмоциональные расстройства. Своевременное вмешательство специалистов помогает минимизировать риски и способствует восстановлению здоровья пациента.
Разобраться лучше – narkologicheski centr
Алкогольный запой — это серьезное заболевание, которое требует немедленного и профессионального вмешательства. Запой сопровождается не только физическими страданиями, но и эмоциональными трудностями. Процесс выведения из запоя требует срочного внимания, так как состояние пациента может ухудшиться, если не получить квалифицированную помощь вовремя. Наркологическая клиника «Излечение» в Краснодаре предоставляет круглосуточную помощь при алкогольном запое, чтобы восстановить здоровье пациента в самых сложных ситуациях.
Углубиться в тему – быстрый вывод из запоя в стационаре в краснодаре
Алкогольная зависимость — это длительное и прогрессирующее заболевание, при котором развивается как физическая, так и психическая зависимость от алкоголя. Одним из самых тяжелых проявлений болезни является запой — длительное употребление алкоголя, которое может сопровождаться нарушениями работы организма и абстинентным синдромом, представляющим серьезную угрозу для здоровья. Эффективное лечение запоя требует комплексного подхода, включающего медикаментозную терапию, психотерапию и реабилитационные мероприятия.
Узнать больше – вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно в твери
Если затянувшееся употребление алкоголя не прерывается, организм начинает испытывать тяжелые последствия. Возникает абстинентный синдром, проявляющийся в виде тошноты, сильной головной боли, дрожи в теле и других неприятных симптомов. Без своевременной помощи состояние может ухудшиться, поэтому важна быстрая медицинская реакция. Комплексное лечение направлено не только на избавление от физической зависимости, но и на поддержку человека в эмоциональном плане. В случаях, когда требуется постоянное наблюдение, рекомендуется стационарная терапия.
Подробнее тут – вывод из запоя срочно круглосуточно краснодар
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой состояние, при котором организм человека испытывает серьезное воздействие этанола, что приводит к нарушению нормальной физиологической деятельности. Это состояние сопровождается сильными физическими и психологическими расстройствами, которые требуют профессионального вмешательства. Однако многие люди, страдающие алкогольной зависимостью, сталкиваются с трудностью признания своей проблемы, опасаясь утраты репутации и конфиденциальности. В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем анонимный вывод из запоя в Санкт-Петербурге, предоставляя высококачественное лечение с гарантией сохранения личной информации.
Получить дополнительную информацию – вывод из запоя вызов на дом санкт-петербург
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой состояние, при котором организм человека испытывает серьезное воздействие этанола, что приводит к нарушению нормальной физиологической деятельности. Это состояние сопровождается сильными физическими и психологическими расстройствами, которые требуют профессионального вмешательства. Однако многие люди, страдающие алкогольной зависимостью, сталкиваются с трудностью признания своей проблемы, опасаясь утраты репутации и конфиденциальности. В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем анонимный вывод из запоя в Санкт-Петербурге, предоставляя высококачественное лечение с гарантией сохранения личной информации.
Выяснить больше – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom na dom sankt-peterburg
Мы понимаем, что каждая зависимость уникальна, поэтому основой нашего подхода является индивидуализация лечения. После тщательной диагностики, включающей анализ медицинской истории, психологического состояния и социальных факторов, наши специалисты разрабатывают персонализированный план терапии. Этот план может включать медикаментозную детоксикацию, психотерапевтические методы и социальные программы, направленные на изменение поведения и мышления пациента.
Разобраться лучше – https://www.kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva1.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-cena-v-moskve
Запой – это тяжелое состояние, возникающее из-за длительного и неконтролируемого употребления алкоголя. Оно характеризуется физической и психологической зависимостью, что приводит к серьезным последствиям для организма и психики. Для восстановления нормального самочувствия и здоровья необходимо профессиональное лечение. Одним из наиболее удобных и эффективных методов является вывод из запоя на дому.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – вывод из запоя капельница рязань
рамки для сертификатов и дипломов купить 2orik-diploms.ru .
Алкогольный запой представляет собой серьезное состояние, которое требует немедленного медицинского вмешательства. Это состояние характеризуется длительным и бесконтрольным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к разрушению как физического, так и психоэмоционального здоровья человека. Для эффективного и безопасного вывода из запоя стационарное лечение является оптимальным решением, особенно при тяжелых случаях интоксикации. В стационаре клиники «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем комплексную программу вывода из запоя, которая включает детоксикацию, восстановление организма и психотерапевтическую помощь.
Изучить вопрос глубже – vyvod iz zapoya na domu nedorogo kapelnica sankt-peterburg
Если затянувшееся употребление алкоголя не прерывается, организм начинает испытывать тяжелые последствия. Возникает абстинентный синдром, проявляющийся в виде тошноты, сильной головной боли, дрожи в теле и других неприятных симптомов. Без своевременной помощи состояние может ухудшиться, поэтому важна быстрая медицинская реакция. Комплексное лечение направлено не только на избавление от физической зависимости, но и на поддержку человека в эмоциональном плане. В случаях, когда требуется постоянное наблюдение, рекомендуется стационарная терапия.
Ознакомиться с деталями – vyvod iz zapoya vyzov na dom v-krasnodare
sns헬퍼 틱톡 마케팅을 사용한 주요 비즈니스 기능으로는 ‘인스타그램 숍스’가 소개됐다. 인스타그램 숍스는 인스타그램 플랫폼 내에서 온라인 사업자의 브랜드 제품, 행사, 가격 등 아이디어를 제공하는 디지털 매장이다. 사용자는 인스타그램 프로필이나 메인 탐색바의 숍스 탭, 인스타그램 탐색 탭 등을 통해 상점을 방문할 수 있다.
sns헬퍼 소셜미디어 마케팅
Запой нарушает привычный ритм жизни, вызывая серьезные физические и эмоциональные проблемы. Для его лечения требуется не только медикаментозное вмешательство, но и постоянное наблюдение специалистов. Стационарное лечение в клинике позволяет обеспечить полный контроль над состоянием пациента, что минимизирует риски и способствует более эффективной реабилитации.
Подробнее – вывод из запоя анонимно недорого санкт-петербург
Если затянувшееся употребление алкоголя не прерывается, организм начинает испытывать тяжелые последствия. Возникает абстинентный синдром, проявляющийся в виде тошноты, сильной головной боли, дрожи в теле и других неприятных симптомов. Без своевременной помощи состояние может ухудшиться, поэтому важна быстрая медицинская реакция. Комплексное лечение направлено не только на избавление от физической зависимости, но и на поддержку человека в эмоциональном плане. В случаях, когда требуется постоянное наблюдение, рекомендуется стационарная терапия.
Разобраться лучше – наркологическая клиника
Нарколог, приехавший на дом, первым делом проводит осмотр пациента, оценивает его состояние и выбирает подходящие препараты для детоксикации организма. Это может включать капельницы с солевыми растворами, витаминами и глюкозой, которые способствуют очищению организма.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://www.kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva2.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-cena-v-moskve
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся длительным и непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к формированию как физической, так и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния часто наблюдаются нарушения работы внутренних органов, что может привести к тяжелым последствиям, включая алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя — важный этап в процессе лечения зависимости, и его можно осуществлять как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от конкретных обстоятельств.
Выяснить больше – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom na dom
Нарколог, приехавший на дом, первым делом проводит осмотр пациента, оценивает его состояние и выбирает подходящие препараты для детоксикации организма. Это может включать капельницы с солевыми растворами, витаминами и глюкозой, которые способствуют очищению организма.
Поддержка — ключевой элемент на пути к выздоровлению. Мы предлагаем программы, которые продолжаются даже после завершения основного курса лечения. Пациенты имеют возможность участвовать в регулярных встречах с психологами и наркологами, где они могут делиться своими успехами и получать необходимую помощь.
Клиника «Преображение» предлагает услуги анонимного вывода из запоя в Екатеринбурге, обеспечивая высокое качество медицинской помощи и соблюдение всех этических норм.
Ознакомиться с деталями – narkologicheskaya klinika ekaterinburg
Клиника «Преображение» предлагает услуги анонимного вывода из запоя в Екатеринбурге, обеспечивая высокое качество медицинской помощи и соблюдение всех этических норм.
Детальнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-20.ru
Зависимость — это хроническое заболевание, требующее долгосрочного лечения и регулярной поддержки. В клинике используют современные научные методы в наркологии и психотерапии, предлагая помощь на всех этапах — от диагностики до реабилитации. Команда профессионалов работает с каждым пациентом индивидуально, обеспечивая комплексный подход к терапии.
Узнать больше – vyvod iz zapoya na domu kruglosutochno
Одним из главных преимуществ стационарного лечения в нашей клинике является полная анонимность. Мы понимаем, что многие пациенты боятся раскрытия своей зависимости и осуждения со стороны окружающих. В “Восстановление души” мы гарантируем конфиденциальность всех процедур и защиту личных данных пациента. Это создает безопасную и доверительную атмосферу, необходимую для успешного лечения и психологического восстановления.
Получить дополнительные сведения – bystry kapelnica ot zapoya v stacionare
В этой статье мы расскажем о возможностях клиники для лечения алкогольной интоксикации круглосуточно, включая вывод из запоя в стационаре и на дому, а также о роли профессионалов, таких как нарколог, в процессе лечения.
Разобраться лучше – vyvod iz zapoya anonimno
Запой — это тяжелое состояние, возникающее вследствие длительного и непрерывного употребления алкоголя, которое сопровождается физической и психической зависимостью. Это опасное явление требует незамедлительного вмешательства специалистов. Вывод из запоя — это комплексный процесс медицинской детоксикации, который включает в себя очищение организма от токсинов, нормализацию функций внутренних органов и поддержку психоэмоционального состояния пациента. В случае тяжелого запоя стационарное лечение становится оптимальным решением для безопасного и эффективного вывода из этого состояния. В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как проходит вывод из запоя в стационаре клиники «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, а также особенности анонимности, скорости лечения и участия нарколога.
Узнать больше – вывод из запоя на дому недорого в челябинске
no prescription foreign pharmacies Canada Pharmacy 24 Hour Drug Store Tadapox online
Одной из распространенных проблем является запой, состояние, при котором человек длительное время бесконтрольно употребляет алкоголь, что приводит к тяжелой физической и психологической зависимости. Такое поведение чревато серьезными последствиями для здоровья, включая поражение внутренних органов, нервные расстройства и другие заболевания. Важно своевременно обратиться за профессиональной помощью, чтобы минимизировать риски и предотвратить осложнения.
Узнать больше – narkologicheskaya klinika
Если затянувшееся употребление алкоголя не прерывается, организм начинает испытывать тяжелые последствия. Возникает абстинентный синдром, проявляющийся в виде тошноты, сильной головной боли, дрожи в теле и других неприятных симптомов. Без своевременной помощи состояние может ухудшиться, поэтому важна быстрая медицинская реакция. Комплексное лечение направлено не только на избавление от физической зависимости, но и на поддержку человека в эмоциональном плане. В случаях, когда требуется постоянное наблюдение, рекомендуется стационарная терапия.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya srochno kruglosutochno krasnodar
В некоторых ситуациях, когда запой длится несколько дней или приводит к серьезным последствиям для здоровья, необходим срочный вызов нарколога. Среди признаков, при которых требуется неотложная помощь:
Разобраться лучше – капельница от запоя вызов на дом
viagra without prescription.
7К казино представляет собой новый уникальный проект, запущенный в 2023 году. На его официальном сайте пользователей ожидает более двух сотен лицензионных игр, выгодные бонусы и несколько проверенных платежных сервисов для проведения денежных переводов 7К Казино
7К казино представляет собой новый уникальный проект, запущенный в 2023 году. На его официальном сайте пользователей ожидает более двух сотен лицензионных игр, выгодные бонусы и несколько проверенных платежных сервисов для проведения денежных переводов казино 7K
диплом купить в орле
7К казино представляет собой новый уникальный проект, запущенный в 2023 году. На его официальном сайте пользователей ожидает более двух сотен лицензионных игр, выгодные бонусы и несколько проверенных платежных сервисов для проведения денежных переводов казино 7K
site-mega.ru
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой состояние, при котором организм человека испытывает серьезное воздействие этанола, что приводит к нарушению нормальной физиологической деятельности. Это состояние сопровождается сильными физическими и психологическими расстройствами, которые требуют профессионального вмешательства. Однако многие люди, страдающие алкогольной зависимостью, сталкиваются с трудностью признания своей проблемы, опасаясь утраты репутации и конфиденциальности. В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем анонимный вывод из запоя в Санкт-Петербурге, предоставляя высококачественное лечение с гарантией сохранения личной информации.
Получить дополнительные сведения – вывод из запоя срочно круглосуточно санкт-петербург
Наркологическая клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже специализируется на лечении алкогольной зависимости и предлагает профессиональные услуги по выводу из запоя. Мы стремимся создать атмосферу доверия, где каждый пациент сможет получить необходимую поддержку.
Детальнее – вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Клиника “Второй Шанс” в Санкт-Петербурге предлагает услугу вывода из запоя, как в стационаре, так и на дому. Для пациентов, не желающих посещать клинику, квалифицированные врачи готовы предоставить помощь в комфортных домашних условиях. Используя современные методы, специалисты обеспечивают безопасность, анонимность и высокий уровень медицинской поддержки.
Получить дополнительные сведения – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom na dom
После успешной детоксикации начинается этап реабилитации, который включает восстановление социального статуса пациента и формирование новых здоровых привычек. Мы предлагаем как групповые, так и индивидуальные занятия, направленные на изменение поведения и мышления, что способствует долгосрочному удержанию пациента от возвращения к зависимостям.
Узнать больше – narkolog na dom kapelnica ot zapoya moskva
Зависимость — это хроническое заболевание, требующее долгосрочного лечения и регулярной поддержки. В клинике используют современные научные методы в наркологии и психотерапии, предлагая помощь на всех этапах — от диагностики до реабилитации. Команда профессионалов работает с каждым пациентом индивидуально, обеспечивая комплексный подход к терапии.
Подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya na domu v-sankt-peterburge
Для достижения эффективных результатов в лечении запоя необходима квалифицированная помощь специалистов. Наркологическая клиника «Излечение» в Краснодаре предоставляет профессиональные услуги по выводу из запоя, гарантируя безопасность, комфорт и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Изучить вопрос глубже – vyvod iz zapoya vrach na dom
Зависимость — это хроническое заболевание, требующее долгосрочного лечения и регулярной поддержки. В клинике используют современные научные методы в наркологии и психотерапии, предлагая помощь на всех этапах — от диагностики до реабилитации. Команда профессионалов работает с каждым пациентом индивидуально, обеспечивая комплексный подход к терапии.
Выяснить больше – anonimny vyvod iz zapoya na domu v-sankt-peterburge
Алкогольный запой представляет собой крайне опасное состояние, характеризующееся неконтролируемым употреблением алкоголя, что в свою очередь приводит к тяжелой интоксикации организма. Восстановление после такого состояния требует профессионального вмешательства, включающего не только физическую детоксикацию, но и психологическую поддержку. Стоимость процедуры вывода из запоя может значительно различаться в зависимости от множества факторов, включая метод лечения, тяжесть состояния пациента и место проведения лечения. Рассмотрим более подробно основные аспекты, влияющие на цену вывода из запоя.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – вывод из запоя анонимно недорого в санкт-петербурге
7к casino – это новое онлайн казино, которая работает на игровом рынке с 2023 года. Игровой оператор предлагает развитую бонусную систему, оперативный вывод выигрышей, широкое разнообразие слотов и бесперебойный доступ к своему ресурсу за счет развитой системы рабочих зеркал казино 7K
7к casino – это новое онлайн казино, которая работает на игровом рынке с 2023 года. Игровой оператор предлагает развитую бонусную систему, оперативный вывод выигрышей, широкое разнообразие слотов и бесперебойный доступ к своему ресурсу за счет развитой системы рабочих зеркал 7К Казино
Клиника предлагает гибкие варианты лечения, включая стационарное и амбулаторное. Стоимость услуг зависит от индивидуальных потребностей пациента, степени тяжести состояния и объемов необходимых процедур. Специалисты стремятся создать максимально комфортные условия для каждого пациента, обеспечивая прозрачное ценообразование и высокое качество обслуживания.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – наркология вывод из запоя на дому санкт-петербург
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, необходимая для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Это состояние, часто характеризующееся физическими и психоэмоциональными нарушениями, требует профессионального вмешательства. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть разнообразными и варьироваться от легкой тревожности до серьезных нарушений в функционировании внутренних органов. Квалифицированная помощь в этот период позволяет минимизировать риски и значительно ускорить процесс выздоровления.
Получить больше информации – narkologiya vyvod iz zapoya anonimno
7к casino – это новое онлайн казино, которая работает на игровом рынке с 2023 года. Игровой оператор предлагает развитую бонусную систему, оперативный вывод выигрышей, широкое разнообразие слотов и бесперебойный доступ к своему ресурсу за счет развитой системы рабочих зеркал 7K Casino
Алкогольный запой представляет собой крайне опасное состояние, характеризующееся неконтролируемым употреблением алкоголя, что в свою очередь приводит к тяжелой интоксикации организма. Восстановление после такого состояния требует профессионального вмешательства, включающего не только физическую детоксикацию, но и психологическую поддержку. Стоимость процедуры вывода из запоя может значительно различаться в зависимости от множества факторов, включая метод лечения, тяжесть состояния пациента и место проведения лечения. Рассмотрим более подробно основные аспекты, влияющие на цену вывода из запоя.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom na dom v-sankt-peterburge
Запой — это тяжелое состояние, возникающее вследствие длительного и непрерывного употребления алкоголя, которое сопровождается физической и психической зависимостью. Это опасное явление требует незамедлительного вмешательства специалистов. Вывод из запоя — это комплексный процесс медицинской детоксикации, который включает в себя очищение организма от токсинов, нормализацию функций внутренних органов и поддержку психоэмоционального состояния пациента. В случае тяжелого запоя стационарное лечение становится оптимальным решением для безопасного и эффективного вывода из этого состояния. В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как проходит вывод из запоя в стационаре клиники «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, а также особенности анонимности, скорости лечения и участия нарколога.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – narkologicheskaya klinika v-chelyabinske
Запой представляет собой состояние, характеризующееся длительным непрерывным употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к физической и психической зависимости. Этот процесс может длиться от нескольких дней до недель. Алкогольные напитки негативно влияют на функционирование внутренних органов, вызывая серьёзные нарушения, включая алкоголизм. При необходимости вывода из запоя важно обратиться за медицинской помощью, что можно осуществить на дому. В данной статье рассмотрим ключевые аспекты данной процедуры.
Подробнее – вывод из запоя в стационаре в челябинске
Алкогольный запой — это тяжелое состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над количеством потребляемого алкоголя. Это приводит к сильной интоксикации, сбоям в работе органов и систем организма, а также серьезным психоэмоциональным расстройствам. Без должной медицинской помощи запой может вызвать ряд опасных последствий, включая алкогольный делирий и угрозу жизни. Поэтому при первых признаках запоя необходимо обратиться к профессионалам.
Подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom cena v-tveri
биржа аккаунтов инстаграм – лолз купить аккаунт вк, купить аккаунт гугл фанпей
Запой — это опасное состояние, которое развивается у людей с алкогольной зависимостью и характеризуется длительным непрерывным потреблением алкоголя. Это состояние приводит к серьезным нарушениям в организме, как физическим, так и психоэмоциональным. Длительный запой может вызвать множество осложнений, таких как поражение внутренних органов, нервной системы, а также проблемы в социальной и семейной жизни. Однако современная медицина предоставляет эффективные методы вывода из запоя, и одним из наиболее удобных и востребованных является вывод из запоя на дому.
Выяснить больше – vyvod iz zapoya na domu v-sankt-peterburge
Targetologist. Advertising on Facebook and Instagram.
Professional services for launching targeted advertising on social networks Facebook and Instagram.
Advertising on Facebook and Instagram
on line pharmacy Viagra 100
Наркологическая клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже специализируется на лечении алкогольной зависимости и предлагает профессиональные услуги по выводу из запоя. Мы стремимся создать атмосферу доверия, где каждый пациент сможет получить необходимую поддержку.
Получить дополнительную информацию – narkologicheskaya klinika
Запой — это одно из наиболее тяжелых проявлений алкогольной зависимости, которое требует немедленного и квалифицированного вмешательства. В такие моменты близкие зачастую теряются и не знают, как помочь своему родному человеку. На помощь приходит наркологическая клиника «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, которая предоставляет профессиональную помощь в выводе из запоя. Мы понимаем, что лечение запоя требует не только медицинского подхода, но и психологической поддержки. Именно поэтому в нашей клинике пациент получает комплексную помощь, основанную на самых современных методах лечения.
Детальнее – narkologiya vyvod iz zapoya anonimno v-chelyabinske
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, необходимая для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Это состояние, часто характеризующееся физическими и психоэмоциональными нарушениями, требует профессионального вмешательства. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть разнообразными и варьироваться от лёгкой тревожности до серьёзных нарушений в функционировании внутренних органов. Квалифицированная помощь в этот период позволяет минимизировать риски и значительно ускорить процесс выздоровления.
Детальнее – вывод из запоя вызов на дом воронеж
Запойное состояние представляет собой серьёзную угрозу для здоровья, поскольку сопровождается тяжёлой интоксикацией организма и нарушением психоэмоционального состояния. Решение о лечении в стационаре клиники «Союз Здоровья» позволяет справиться с последствиями длительного употребления алкоголя, обеспечивая пациентам полный комплекс медицинской и психологической помощи.
Ознакомиться с деталями – вывод из запоя круглосуточно в воронеже
кракен официальная ссылка – кра сайт, кракен войти
Галерея Девелоперов — это агентство недвижимости, которое поможет с подбором и покупкой новостройки в Москве и Московской Области абсолютно бесплатно, поскольку сотрудничает с застройщиками напрямую.
На сайте Developers.Gallery доступен каталог новостроек и статьи на тему покупки недвижимости в административных округах Москвы: ЦАО, САО, СВАО, ВАО, ЮВАО, ЮАО, ЮЗАО, СЗАО, ЗАО, НАО, ТАО, а также Московской Области: Зеленоград, Мытищи, Красногорск, Люберцы, Видное, Жуковский.
Приобретая новостройку на этапе котлована, имеется уникальная возможность извлечь из этого прибыль и рассмотреть покупку в качестве инвестиций. После ввода дома в эксплуатацию стоимость значительно прирастёт, что позволит перепродать её по переуступке, либо сдавать в аренду и извлекать из этого актива доходность.
Заказать звонок можно, перейдя по ссылке: Ростокино Новостройки и менеджер составит индивидуальный каталог новостроек абсолютно бесплатно, поможет с записью в офис продаж застройщика, окажет юридическое сопровождение сделки: Проверит договор ДДУ, поможет с открытием счёта эскроу и аккредитива, а также направит инструкцию по выпуску электронной цифровой подписи для удалённой покупки в онлайн-формате.
Воспользовавшись услугами от Галереи Девелоперов вы экономите время и деньги, поскольку для вас согласуют персональные скидки и условия по покупки в рассрочку, базовую ипотеку, семейную ипотеку, IT-ипотеку и 100% оплату наличными, а ещё доступна покупка по программе trade-in — когда вы сдаёте свою текущую квартиру в обмен на новостройку.
Покупка недвижимости — это важный шаг, поэтому не менее важно подойти к ней максимально ответственно и положиться на опыт профессионалов, которые подберут жилой комплекс в непосредственной близости к станции метро, БКЛ, МЦК, МЦД, выездами на магистраль: СВХ, ЮВХ, МСД, Ленинградский Проспект, ТТК, МКАД и с большими лесными массивами, парками, детскими площадками, закрытыми от автомобилей дворами, сквозными подъездами, спортивными площадками, качественным озеленением с многолетними деревьями, солнечной стороной.
Зависимость — это серьёзная проблема, которая затрагивает не только человека, но и его семью и окружение. Алкоголизм, наркомания и другие виды зависимостей могут разрушить жизнь, но с профессиональной помощью можно вернуть её в русло нормального функционирования. Наркологическая клиника «Заря Будущего» в Санкт-Петербурге предлагает уникальные программы лечения зависимостей, которые сочетает медико-психологический подход, индивидуальные методики и квалифицированную поддержку.
Узнать больше – narkolog na dom vyvod iz zapoya v-sankt-peterburge
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой состояние, при котором организм человека испытывает сильное воздействие этанола, что приводит к нарушению нормального функционирования физиологических систем. Это состояние может быть опасным и требует квалифицированной медицинской помощи. Вывод из запоя — важная медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение последствий чрезмерного употребления алкоголя и восстановление здоровья пациента.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – быстрый вывод из запоя в стационаре в челябинске
новые порно фильмы новые порно фильмы .
дом инвалидов в симферополе дом инвалидов в симферополе .
вывод из запоя цена вывод из запоя цена .
Алкогольный запой представляет собой критическое состояние, требующее немедленного вмешательства квалифицированных специалистов. Клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже предлагает круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить своевременное и эффективное лечение. Наша цель — оперативное снятие интоксикации, устранение симптомов и предотвращение осложнений.
Изучить вопрос глубже – вывод из запоя капельница на дому в воронеже
Зависимость — это серьёзная проблема, которая затрагивает не только человека, но и его семью и окружение. Алкоголизм, наркомания и другие виды зависимостей могут разрушить жизнь, но с профессиональной помощью можно вернуть её в русло нормального функционирования. Наркологическая клиника «Заря Будущего» в Санкт-Петербурге предлагает уникальные программы лечения зависимостей, которые сочетает медико-психологический подход, индивидуальные методики и квалифицированную поддержку.
Узнать больше – vyvod iz zapoya kapelnica
дом престарелых симферополь цены дом престарелых симферополь цены .
В клинике “Восстановление души” работает команда высококвалифицированных специалистов, готовых предложить современное и эффективное лечение зависимостей. Наши врачи-наркологи обладают обширным опытом работы и постоянно совершенствуют свои навыки, чтобы использовать самые передовые методы терапии.
Подробнее тут – капельница от запоя капельница иркутск
кодировка от алкоголя кодировка от алкоголя .
Алкогольный запой — это серьезное заболевание, которое требует немедленного и профессионального вмешательства. Запой сопровождается не только физическими страданиями, но и эмоциональными трудностями. Процесс выведения из запоя требует срочного внимания, так как состояние пациента может ухудшиться, если не получить квалифицированную помощь вовремя. Наркологическая клиника «Излечение» в Краснодаре предоставляет круглосуточную помощь при алкогольном запое, чтобы восстановить здоровье пациента в самых сложных ситуациях.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno narkologiya krasnodar
The full special bip39 Word List consists of 2048 words used to protect cryptocurrency wallets. Allows you to create backups and restore access to digital assets. Check out the full list.
Finest news for all us
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, необходимая для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Это состояние, часто характеризующееся физическими и психоэмоциональными нарушениями, требует профессионального вмешательства. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть разнообразными и варьироваться от лёгкой тревожности до серьёзных нарушений в функционировании внутренних органов. Квалифицированная помощь в этот период позволяет минимизировать риски и значительно ускорить процесс выздоровления.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom cena
В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы понимаем, насколько важен своевременный и профессиональный подход к лечению зависимости. Наши специалисты готовы оказать квалифицированную помощь прямо у вас дома, обеспечивая полную безопасность и конфиденциальность на каждом этапе лечения.
Получить больше информации – vyvod iz zapoya na domu kruglosutochno v-sankt-peterburge
Запой — это опасное состояние, которое развивается у людей с алкогольной зависимостью и характеризуется длительным непрерывным потреблением алкоголя. Это состояние приводит к серьезным нарушениям в организме, как физическим, так и психоэмоциональным. Длительный запой может вызвать множество осложнений, таких как поражение внутренних органов, нервной системы, а также проблемы в социальной и семейной жизни. Однако современная медицина предоставляет эффективные методы вывода из запоя, и одним из наиболее удобных и востребованных является вывод из запоя на дому.
Получить дополнительную информацию – вывод из запоя на дому недорого
Алкогольная зависимость — это длительное и прогрессирующее заболевание, при котором развивается как физическая, так и психическая зависимость от алкоголя. Одним из самых тяжелых проявлений болезни является запой — длительное употребление алкоголя, которое может сопровождаться нарушениями работы организма и абстинентным синдромом, представляющим серьезную угрозу для здоровья. Эффективное лечение запоя требует комплексного подхода, включающего медикаментозную терапию, психотерапию и реабилитационные мероприятия.
Узнать больше – vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare v-tveri
Алкогольный запой сопровождается опасной интоксикацией, которая без своевременной помощи может привести к необратимым последствиям, включая поражение печени, сердца, почек и психические расстройства. В критических случаях промедление может стоить жизни. Именно поэтому специалисты клиники готовы оказывать поддержку круглосуточно.
Подробнее тут – vyvod iz zapoya na domu nedorogo sankt-peterburg
Алкоголизм — это хроническое прогрессирующее заболевание, связанное с физической и психической зависимостью от этанола. Запой, как его крайнее проявление, представляет собой длительное употребление алкоголя, сопровождающееся тяжелыми нарушениями работы организма, включая абстинентный синдром и потенциальные угрозы для жизни. Лечение запоя требует комплексного подхода, включающего медицинские процедуры, психотерапию и реабилитационные меры.
Разобраться лучше – вывод из запоя круглосуточно наркология
Поддержка — ключевой элемент на пути к выздоровлению. Мы предлагаем программы, которые продолжаются даже после завершения основного курса лечения. Пациенты имеют возможность участвовать в регулярных встречах с психологами и наркологами, где они могут делиться своими успехами и получать необходимую помощь.
Получить дополнительные сведения – наркологическая клиника в москве
Алкоголизм — это хроническое заболевание, которое характеризуется патологической зависимостью от этанола. Периоды запоя, когда человек неконтролируемо потребляет алкоголь, могут привести к разнообразным медицинским осложнениям, как физическим, так и психологическим. Запой становится не только причиной ухудшения здоровья, но и причиной множества социальных и личных проблем. На этом фоне возникает необходимость вывода из запоя, процесс, который должен учитывать индивидуальные особенности пациента. Важно, что анонимность в реабилитации играет ключевую роль, помогая избежать стигматизации и увеличивая шансы на успешное восстановление.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – наркология вывод из запоя на дому в рязани
Выберите способ доставки и оплаты, заполните все поля необходимые для доставки заказа, учитывая, что поля, помеченные символом *, обязательны для заполнения https://zapchasti-remont.ru/shop/trosyi_upravleniya/
Клиника “Восстановление души” предлагает услугу капельницы от запоя на дому в Иркутске и Иркутской области, что является удобным решением для тех, кто не может или не хочет лечиться в стационаре. Мы понимаем, как важно поддерживать пациента в момент, когда его организм нуждается в быстрой и квалифицированной помощи.
Получить дополнительную информацию – kapelnica ot zapoya srochno kruglosutochno moskva
В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы понимаем, насколько важен своевременный и профессиональный подход к лечению зависимости. Наши специалисты готовы оказать квалифицированную помощь прямо у вас дома, обеспечивая полную безопасность и конфиденциальность на каждом этапе лечения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – вывод из запоя на дому санкт-петербург
Одним из важнейших аспектов, который помогает пациентам справиться с алкогольной зависимостью, является анонимность в процессе лечения. В клинике «Излечение» мы понимаем, как важно сохранить конфиденциальность и гарантировать защиту личной информации, особенно для тех, кто опасается общественного осуждения. Мы обеспечиваем полную анонимность при выводе из запоя, как в стационарных условиях, так и на дому.
Получить дополнительные сведения – vyvod iz zapoya anonimno
Мы понимаем, что каждая зависимость уникальна, поэтому основой нашего подхода является индивидуализация лечения. После тщательной диагностики, включающей анализ медицинской истории, психологического состояния и социальных факторов, наши специалисты разрабатывают персонализированный план терапии. Этот план может включать медикаментозную детоксикацию, психотерапевтические методы и социальные программы, направленные на изменение поведения и мышления пациента.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – narkologicheski centr v moskve
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, необходимая для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Это состояние, часто характеризующееся физическими и психоэмоциональными нарушениями, требует профессионального вмешательства. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть разнообразными и варьироваться от легкой тревожности до серьезных нарушений в функционировании внутренних органов. Квалифицированная помощь в этот период позволяет минимизировать риски и значительно ускорить процесс выздоровления.
Подробнее тут – vyvod iz zapoya srochno kruglosutochno v-chelyabinske
Алкоголизм — это хроническое заболевание, которое характеризуется патологической зависимостью от этанола. Периоды запоя, когда человек неконтролируемо потребляет алкоголь, могут привести к разнообразным медицинским осложнениям, как физическим, так и психологическим. Запой становится не только причиной ухудшения здоровья, но и причиной множества социальных и личных проблем. На этом фоне возникает необходимость вывода из запоя, процесс, который должен учитывать индивидуальные особенности пациента. Важно, что анонимность в реабилитации играет ключевую роль, помогая избежать стигматизации и увеличивая шансы на успешное восстановление.
Разобраться лучше – vyvod iz zapoya cena
В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы понимаем, насколько важен своевременный и профессиональный подход к лечению зависимости. Наши специалисты готовы оказать квалифицированную помощь прямо у вас дома, обеспечивая полную безопасность и конфиденциальность на каждом этапе лечения.
Получить больше информации – vyvod iz zapoya anonimno nedorogo
canadian pharmacy online no script
Алкогольный запой — это тяжелое состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над количеством потребляемого алкоголя. Это приводит к сильной интоксикации, сбоям в работе органов и систем организма, а также серьезным психоэмоциональным расстройствам. Без должной медицинской помощи запой может вызвать ряд опасных последствий, включая алкогольный делирий и угрозу жизни. Поэтому при первых признаках запоя необходимо обратиться к профессионалам.
Выяснить больше – вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в твери
Алкоголизм — это хроническое заболевание, которое характеризуется патологической зависимостью от этанола. Периоды запоя, когда человек неконтролируемо потребляет алкоголь, могут привести к разнообразным медицинским осложнениям, как физическим, так и психологическим. Запой становится не только причиной ухудшения здоровья, но и причиной множества социальных и личных проблем. На этом фоне возникает необходимость вывода из запоя, процесс, который должен учитывать индивидуальные особенности пациента. Важно, что анонимность в реабилитации играет ключевую роль, помогая избежать стигматизации и увеличивая шансы на успешное восстановление.
Углубиться в тему – быстрый вывод из запоя в стационаре
Клиника “Второй Шанс” в Санкт-Петербурге предлагает услугу вывода из запоя, как в стационаре, так и на дому. Для пациентов, не желающих посещать клинику, квалифицированные врачи готовы предоставить помощь в комфортных домашних условиях. Используя современные методы, специалисты обеспечивают безопасность, анонимность и высокий уровень медицинской поддержки.
Получить больше информации – vyvod iz zapoya vrach na dom
Клиника “Восстановление души” предлагает услугу капельницы от запоя на дому в Иркутске и Иркутской области, что является удобным решением для тех, кто не может или не хочет лечиться в стационаре. Мы понимаем, как важно поддерживать пациента в момент, когда его организм нуждается в быстрой и квалифицированной помощи.
Углубиться в тему – bystry kapelnica ot zapoya v stacionare voronezh
Сопровождение мужчин — это особая услуга, которая может включать в себя как деловые, так и личные аспекты.
В современном мире многие мужчины ищут профессионалов, которые могут помочь им в различных сферах жизни:
от бизнес-мероприятий до социальных встреч – эскорт москвы
Запой нарушает привычный ритм жизни, вызывая серьезные физические и эмоциональные проблемы. Для его лечения требуется не только медикаментозное вмешательство, но и постоянное наблюдение специалистов. Стационарное лечение в клинике позволяет обеспечить полный контроль над состоянием пациента, что минимизирует риски и способствует более эффективной реабилитации.
Углубиться в тему – vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare v-sankt-peterburge
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой состояние, при котором организм человека испытывает сильное воздействие этанола, что приводит к нарушению нормального функционирования физиологических систем. Это состояние может быть опасным и требует квалифицированной медицинской помощи. Вывод из запоя — важная медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение последствий чрезмерного употребления алкоголя и восстановление здоровья пациента.
Получить больше информации – вывод из запоя в челябинске
Зависимость — это хроническое заболевание, требующее долгосрочного лечения и регулярной поддержки. В клинике используют современные научные методы в наркологии и психотерапии, предлагая помощь на всех этапах — от диагностики до реабилитации. Команда профессионалов работает с каждым пациентом индивидуально, обеспечивая комплексный подход к терапии.
Узнать больше – быстрый вывод из запоя в стационаре в санкт-петербурге
Вывод из запоя представляет собой важный этап в процессе лечения алкогольной зависимости. Это медицинская процедура, необходимая для устранения токсических веществ, накопленных в организме в результате длительного употребления алкоголя. Алкогольная зависимость может вызывать множество проблем, включая физические и психоэмоциональные расстройства. Своевременное вмешательство специалистов помогает минимизировать риски и способствует восстановлению здоровья пациента.
Подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya na domu kruglosutochno v-ryazani
В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы понимаем, насколько важен своевременный и профессиональный подход к лечению зависимости. Наши специалисты готовы оказать квалифицированную помощь прямо у вас дома, обеспечивая полную безопасность и конфиденциальность на каждом этапе лечения.
Получить больше информации – вывод из запоя с выездом цена
Наркологическая клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже специализируется на лечении алкогольной зависимости и предлагает профессиональные услуги по выводу из запоя. Мы стремимся создать атмосферу доверия, где каждый пациент сможет получить необходимую поддержку.
Получить дополнительную информацию – vyvod iz zapoya gorod voronezh
Le meilleur code bonus 1xBet et obtenez plus de 100% de bonus de 100€. Les amateurs de sport seront ravis de decouvrir une vaste gamme de marches sportifs, englobant des choix tres apprecies tels que le cricket, le football, le tennis et bien d’autres.
Code Promo 1xBet
https://underatexassky.com/pages/2code_promo_163.html
Code promo de 1xBet – l’utilisation de ce code vous permettra d’obtenir un bonus de 30% supplementaire, allant jusqu’a 100$. Le bonus est accorde sous la forme de 130% du montant de votre premier depot. Cette offre est reservee aux nouveaux utilisateurs majeurs apres leur inscription. Profitez du code promo pour augmenter votre bonus de bienvenue de 100% a 130%. Les fonds seront credites sur votre solde de jeu, et le bonus devra etre mise sur des paris sportifs. Ce code promo est valable jusqu’au 31 decembre 2025. Utiliser le code promo 1xBet lors de l’inscription avec 1xBet 2025. Cela vous permettra d’obtenir leur excellent bonus de bienvenue allant sous forme de paris gratuits.
купить диплом о среднем образовании в балашихе prema-diploms.ru .
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой состояние, при котором организм человека испытывает серьёзное воздействие этанола. Это приводит к нарушениям нормальной физиологической деятельности и ухудшению состояния здоровья. Анонимный вывод из запоя — это медицинская помощь, направленная на устранение последствий чрезмерного употребления алкоголя с соблюдением строгой конфиденциальности.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – вывод из запоя на дому недорого капельница екатеринбург
Зависимость — это серьёзная проблема, которая затрагивает не только человека, но и его семью и окружение. Алкоголизм, наркомания и другие виды зависимостей могут разрушить жизнь, но с профессиональной помощью можно вернуть её в русло нормального функционирования. Наркологическая клиника «Заря Будущего» в Санкт-Петербурге предлагает уникальные программы лечения зависимостей, которые сочетает медико-психологический подход, индивидуальные методики и квалифицированную поддержку.
Разобраться лучше – vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno sankt-peterburg
Запой представляет собой состояние, характеризующееся длительным непрерывным употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к физической и психической зависимости. Этот процесс может длиться от нескольких дней до недель. Алкогольные напитки негативно влияют на функционирование внутренних органов, вызывая серьёзные нарушения, включая алкоголизм. При необходимости вывода из запоя важно обратиться за медицинской помощью, что можно осуществить на дому. В данной статье рассмотрим ключевые аспекты данной процедуры.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-17.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-chelyabinske/]vyvod iz zapoya cena chelyabinsk[/url]
Процесс вывода из запоя требует быстрого реагирования. Запой, особенно в его тяжелых формах, представляет угрозу не только для психического состояния пациента, но и для его физического здоровья. Чтобы минимизировать риски и предотвратить осложнения, важно начинать лечение как можно скорее. Клинике «Освобождение» в Рязани доступна круглосуточная помощь — мы работаем 24/7, чтобы оперативно вмешаться в любой момент, когда это необходимо. Врачебная помощь может быть предоставлена как в стационаре клиники, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента и его предпочтений.
Детальнее – вывод из запоя рязань
Зависимость от алкоголя – серьезная проблема, требующая системного подхода и профессионального лечения. В клинике «Излечение» гарантируется полная конфиденциальность на всех этапах процесса, что позволяет пациентам чувствовать себя в безопасности. Лечение может проходить как в стационаре, так и на дому, при этом соблюдаются все условия для максимального комфорта.
Разобраться лучше – vyvod iz zapoya kapelnica na domu v-krasnodare
Запойное пьянство характеризуется продолжительным и интенсивным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к серьезным физическим и психологическим последствиям. Часто пациенты сталкиваются с различными заболеваниями, такими как цирроз печени, панкреатит, алкогольный делирий и другие. Алкогольное опьянение не только ухудшает качество жизни, но также может угрожать жизни пациента. В условиях стационара лечение может быть более эффективным, однако многие люди предпочитают проходить данную процедуру на дому, чтобы избежать стигматизации и сохранить чувство приватности.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – вывод из запоя на дому недорого капельница
Клиника предлагает гибкие варианты лечения, включая стационарное и амбулаторное. Стоимость услуг зависит от индивидуальных потребностей пациента, степени тяжести состояния и объемов необходимых процедур. Специалисты стремятся создать максимально комфортные условия для каждого пациента, обеспечивая прозрачное ценообразование и высокое качество обслуживания.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – vyvod iz zapoya na domu cena
Алкогольный запой сопровождается опасной интоксикацией, которая без своевременной помощи может привести к необратимым последствиям, включая поражение печени, сердца, почек и психические расстройства. В критических случаях промедление может стоить жизни. Именно поэтому специалисты клиники готовы оказывать поддержку круглосуточно.
Углубиться в тему – vyvod iz zapoya kapelnica na domu
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой состояние, при котором организм человека испытывает серьёзное воздействие этанола. Это приводит к нарушениям нормальной физиологической деятельности и ухудшению состояния здоровья. Анонимный вывод из запоя — это медицинская помощь, направленная на устранение последствий чрезмерного употребления алкоголя с соблюдением строгой конфиденциальности.
Получить больше информации – vyvod iz zapoya na domu kruglosutochno v-ekaterinburge
Алкогольный запой — это состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над своим потреблением алкоголя, что может вызвать серьезные физические и психологические проблемы. В таких ситуациях крайне важно получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь как можно скорее. Однако многие люди опасаются обращаться за помощью, переживая за свою репутацию и возможное раскрытие личной информации. В клинике «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже мы гарантируем анонимность на всех этапах лечения, сохраняя высокий уровень медицинской помощи и заботясь о каждом пациенте.
Углубиться в тему – narkologicheskij centr voronezh
Алкогольный запой представляет собой крайне опасное состояние, характеризующееся неконтролируемым употреблением алкоголя, что в свою очередь приводит к тяжелой интоксикации организма. Восстановление после такого состояния требует профессионального вмешательства, включающего не только физическую детоксикацию, но и психологическую поддержку. Стоимость процедуры вывода из запоя может значительно различаться в зависимости от множества факторов, включая метод лечения, тяжесть состояния пациента и место проведения лечения. Рассмотрим более подробно основные аспекты, влияющие на цену вывода из запоя.
Получить дополнительную информацию – vyvod iz zapoya anonimno
Клиника “Второй Шанс” в Санкт-Петербурге предлагает услугу вывода из запоя, как в стационаре, так и на дому. Для пациентов, не желающих посещать клинику, квалифицированные врачи готовы предоставить помощь в комфортных домашних условиях. Используя современные методы, специалисты обеспечивают безопасность, анонимность и высокий уровень медицинской поддержки.
Узнать больше – vyvod iz zapoya vyzov na dom sankt-peterburg
Клиника “Восстановление души” предлагает услугу капельницы от запоя на дому в Иркутске и Иркутской области, что является удобным решением для тех, кто не может или не хочет лечиться в стационаре. Мы понимаем, как важно поддерживать пациента в момент, когда его организм нуждается в быстрой и квалифицированной помощи.
Изучить вопрос глубже – bystry kapelnica ot zapoya v stacionare moskva
Запой представляет собой состояние, характеризующееся длительным непрерывным употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к физической и психической зависимости. Этот процесс может длиться от нескольких дней до недель. Алкогольные напитки негативно влияют на функционирование внутренних органов, вызывая серьёзные нарушения, включая алкоголизм. При необходимости вывода из запоя важно обратиться за медицинской помощью, что можно осуществить на дому. В данной статье рассмотрим ключевые аспекты данной процедуры.
Изучить вопрос глубже – вывод из запоя круглосуточно наркология
Вывод из запойного состояния – сложный процесс, включающий несколько последовательных этапов. Основная цель – детоксикация организма и восстановление его нормального функционирования. Важно, чтобы процессом руководили опытные специалисты, способные минимизировать последствия интоксикации и помочь человеку вернуться к здоровой жизни. Стоимость лечения зависит от выбранных методов и уровня медицинского обслуживания, а в клинике «Излечение» предлагаются доступные варианты с учетом индивидуальных потребностей пациентов.
Выяснить больше – вывод из запоя анонимно недорого краснодар
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой актуальную медицинскую проблему, требующую тщательного подхода. Запой характеризуется длительным, непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что ведёт к физической и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния могут возникнуть тяжёлые нарушения функций органов, увеличивается риск развития таких состояний, как алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя становится ключевым этапом в лечении зависимостей, который может осуществляться как в стационарных условиях, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента. В клинике «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске мы предлагаем круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить максимально эффективное и безопасное лечение при любом варианте вывода из запоя.
Ознакомиться с деталями – анонимный вывод из запоя на дому в челябинске
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся длительным и непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к формированию как физической, так и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния часто наблюдаются нарушения работы внутренних органов, что может привести к тяжелым последствиям, включая алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя — важный этап в процессе лечения зависимости, и его можно осуществлять как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от конкретных обстоятельств.
Изучить вопрос глубже – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom na dom sankt-peterburg
Запойное состояние представляет собой серьёзную угрозу для здоровья, поскольку сопровождается тяжёлой интоксикацией организма и нарушением психоэмоционального состояния. Решение о лечении в стационаре клиники «Союз Здоровья» позволяет справиться с последствиями длительного употребления алкоголя, обеспечивая пациентам полный комплекс медицинской и психологической помощи.
Выяснить больше – vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare voronezh
Магазин дженериков по адресу https://cialis-deshevo.ru предлагает
широкий выбор препаратов для повышения потенции с доставкой
Когда человек сталкивается с затяжными алкогольными эпизодами, ему необходима квалифицированная помощь. Специалисты наркологической клиники «Излечение» в Краснодаре разрабатывают индивидуальные методы вывода из этого состояния, создавая комфортные и безопасные условия для пациентов. Длительное употребление спиртного оказывает разрушительное воздействие на внутренние органы, приводит к психическим нарушениям и обостряет хронические болезни. В таких случаях медицинское вмешательство становится неотложной необходимостью.
Получить больше информации – вывод из запоя на дому в краснодаре
Запой – это тяжелое состояние, возникающее из-за длительного и неконтролируемого употребления алкоголя. Оно характеризуется физической и психологической зависимостью, что приводит к серьезным последствиям для организма и психики. Для восстановления нормального самочувствия и здоровья необходимо профессиональное лечение. Одним из наиболее удобных и эффективных методов является вывод из запоя на дому.
Выяснить больше – vyvod iz zapoya cena narkologiya
Запой — это одно из наиболее тяжелых проявлений алкогольной зависимости, которое требует немедленного и квалифицированного вмешательства. В такие моменты близкие зачастую теряются и не знают, как помочь своему родному человеку. На помощь приходит наркологическая клиника «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, которая предоставляет профессиональную помощь в выводе из запоя. Мы понимаем, что лечение запоя требует не только медицинского подхода, но и психологической поддержки. Именно поэтому в нашей клинике пациент получает комплексную помощь, основанную на самых современных методах лечения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – вывод из запоя капельница челябинск
Проблема зависимости от алкоголя, наркотиков и азартных игр остается одной из наиболее острых в современном обществе. Эти состояния оказывают значительное воздействие не только на здоровье самого человека, но и на его семью, друзей и общественные связи. Наркологическая клиника “Восстановление души” предлагает широкий спектр услуг для тех, кто борется с различными формами зависимости, такими как алкоголизм, наркомания и игромания. Наша цель — предоставить комплексный подход к лечению, что обеспечивает высокие показатели успешности среди наших пациентов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – kapelnica ot zapoya v stacionare
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой состояние, при котором организм человека испытывает серьёзное воздействие этанола. Это приводит к нарушениям нормальной физиологической деятельности и ухудшению состояния здоровья. Анонимный вывод из запоя — это медицинская помощь, направленная на устранение последствий чрезмерного употребления алкоголя с соблюдением строгой конфиденциальности.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – vyvod iz zapoya
Reliable and unique bip39 Word List contains 2048 words needed to create seed phrases in crypto wallets. Allows you to safely manage private keys and guarantees the possibility of recovering funds.
Когда человек сталкивается с затяжными алкогольными эпизодами, ему необходима квалифицированная помощь. Специалисты наркологической клиники «Излечение» в Краснодаре разрабатывают индивидуальные методы вывода из этого состояния, создавая комфортные и безопасные условия для пациентов. Длительное употребление спиртного оказывает разрушительное воздействие на внутренние органы, приводит к психическим нарушениям и обостряет хронические болезни. В таких случаях медицинское вмешательство становится неотложной необходимостью.
Получить дополнительную информацию – vyvod iz zapoya na domu nedorogo krasnodar
В клинике также уделяется внимание конфиденциальности лечения. Понимая деликатность проблемы, врачи гарантируют полную анонимность на всех этапах терапии. Благодаря профессиональному подходу и использованию проверенных методик пациенты могут восстановить здоровье и вернуться к полноценной жизни.
Выяснить больше – vyvod iz zapoya kapelnica
Одним из главных преимуществ стационарного лечения в нашей клинике является полная анонимность. Мы понимаем, что многие пациенты боятся раскрытия своей зависимости и осуждения со стороны окружающих. В “Восстановление души” мы гарантируем конфиденциальность всех процедур и защиту личных данных пациента. Это создает безопасную и доверительную атмосферу, необходимую для успешного лечения и психологического восстановления.
Углубиться в тему – kapelnica ot zapoya kruglosutochno
Выход из запоя — это важнейший этап на пути к избавлению от алкогольной зависимости. Он требует комплексного подхода, профессиональной помощи и сильной мотивации пациента. В условиях, когда анонимность и комфорт становятся ключевыми факторами для многих людей, вывод из запоя на дому приобретает все большее значение. Это решение позволяет человеку получить необходимую помощь, не покидая дома, и избежать стресса, связанного с госпитализацией.
Получить больше информации – наркология вывод из запоя на дому
аккаунт криптовалюты
Запой – это состояние, которое возникает вследствие длительного употребления алкоголя, приводящее к потере контроля над количеством выпиваемого и формированию как физической, так и психологической зависимости. Оно сопровождается серьёзными последствиями для здоровья и требует немедленного вмешательства.
Получить больше информации – vyvod iz zapoya na domu nedorogo kapelnica
В таких ситуациях вывод из запоя на дому становится оптимальным решением, особенно если пациент не может или не хочет посещать стационар. Эта услуга позволяет получить медицинскую помощь в комфортной и привычной обстановке, что снижает уровень стресса и ускоряет процесс восстановления.
Получить больше информации – срочный вывод из запоя на дому воронеж
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой состояние, при котором организм человека испытывает серьёзное воздействие этанола. Это приводит к нарушениям нормальной физиологической деятельности и ухудшению состояния здоровья. Анонимный вывод из запоя — это медицинская помощь, направленная на устранение последствий чрезмерного употребления алкоголя с соблюдением строгой конфиденциальности.
Выяснить больше – вывод из запоя с выездом екатеринбург
В современном мире зависимость становится все более распространенной проблемой. Стресс, жизненные трудности и финансовые проблемы часто провоцируют развитие таких серьезных состояний, как алкоголизм, наркомания и игромания. Наркологическая клиника “Второй Шанс” предоставляет помощь людям, столкнувшимся с этими заболеваниями. Основное направление работы клиники — восстановление здоровья пациентов, их социальная адаптация и предотвращение повторных рецидивов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – vyvod-iz-zapoya-14.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-sankt-peterburge/
Вывод из запойного состояния – сложный процесс, включающий несколько последовательных этапов. Основная цель – детоксикация организма и восстановление его нормального функционирования. Важно, чтобы процессом руководили опытные специалисты, способные минимизировать последствия интоксикации и помочь человеку вернуться к здоровой жизни. Стоимость лечения зависит от выбранных методов и уровня медицинского обслуживания, а в клинике «Излечение» предлагаются доступные варианты с учетом индивидуальных потребностей пациентов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – вывод из запоя на дому недорого капельница в краснодаре
Клиника «Рассвет» в Твери предоставляет услугу анонимного вывода из запоя, обеспечивая высокое качество медицинского обслуживания и строгое соблюдение всех этических норм.
Получить больше информации – вывод из запоя срочно круглосуточно
Запойное состояние представляет собой серьёзную угрозу для здоровья, поскольку сопровождается тяжёлой интоксикацией организма и нарушением психоэмоционального состояния. Решение о лечении в стационаре клиники «Союз Здоровья» позволяет справиться с последствиями длительного употребления алкоголя, обеспечивая пациентам полный комплекс медицинской и психологической помощи.
Узнать больше – vyvod iz zapoya na domu kruglosutochno
После успешной детоксикации начинается этап реабилитации, который включает восстановление социального статуса пациента и формирование новых здоровых привычек. Мы предлагаем как групповые, так и индивидуальные занятия, направленные на изменение поведения и мышления, что способствует долгосрочному удержанию пациента от возвращения к зависимостям.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh2.ru
Алкогольный запой представляет собой серьезное состояние, которое требует немедленного медицинского вмешательства. Это состояние характеризуется длительным и бесконтрольным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к разрушению как физического, так и психоэмоционального здоровья человека. Для эффективного и безопасного вывода из запоя стационарное лечение является оптимальным решением, особенно при тяжелых случаях интоксикации. В стационаре клиники «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем комплексную программу вывода из запоя, которая включает детоксикацию, восстановление организма и психотерапевтическую помощь.
Ознакомиться с деталями – vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno narkologiya
купить диплом ссср в омске
Запой нарушает привычный ритм жизни, вызывая серьезные физические и эмоциональные проблемы. Для его лечения требуется не только медикаментозное вмешательство, но и постоянное наблюдение специалистов. Стационарное лечение в клинике позволяет обеспечить полный контроль над состоянием пациента, что минимизирует риски и способствует более эффективной реабилитации.
Получить дополнительные сведения – anonimny vyvod iz zapoya na domu sankt-peterburg
купить аттестат за 9 класс в алматы
Выход из запоя — это важнейший этап на пути к избавлению от алкогольной зависимости. Он требует комплексного подхода, профессиональной помощи и сильной мотивации пациента. В условиях, когда анонимность и комфорт становятся ключевыми факторами для многих людей, вывод из запоя на дому приобретает все большее значение. Это решение позволяет человеку получить необходимую помощь, не покидая дома, и избежать стресса, связанного с госпитализацией.
Получить дополнительные сведения – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom na dom v-krasnodare
Запой — это тяжелое состояние, возникающее вследствие длительного и непрерывного употребления алкоголя, которое сопровождается физической и психической зависимостью. Это опасное явление требует незамедлительного вмешательства специалистов. Вывод из запоя — это комплексный процесс медицинской детоксикации, который включает в себя очищение организма от токсинов, нормализацию функций внутренних органов и поддержку психоэмоционального состояния пациента. В случае тяжелого запоя стационарное лечение становится оптимальным решением для безопасного и эффективного вывода из этого состояния. В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как проходит вывод из запоя в стационаре клиники «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, а также особенности анонимности, скорости лечения и участия нарколога.
Подробнее – вывод из запоя с выездом цена в челябинске
Одним из главных преимуществ стационарного лечения в нашей клинике является полная анонимность. Мы понимаем, что многие пациенты боятся раскрытия своей зависимости и осуждения со стороны окружающих. В “Восстановление души” мы гарантируем конфиденциальность всех процедур и защиту личных данных пациента. Это создает безопасную и доверительную атмосферу, необходимую для успешного лечения и психологического восстановления.
После успешной детоксикации начинается этап реабилитации, который включает восстановление социального статуса пациента и формирование новых здоровых привычек. Мы предлагаем как групповые, так и индивидуальные занятия, направленные на изменение поведения и мышления, что способствует долгосрочному удержанию пациента от возвращения к зависимостям.
Дженерики на сайте https://cialis-hit.ru/ с доставкой по городу курьером
в день заказа отличное качество по низкой цене
Как купить диплом о высшем образовании с минимальными рисками
Когда человек сталкивается с затяжными алкогольными эпизодами, ему необходима квалифицированная помощь. Специалисты наркологической клиники «Излечение» в Краснодаре разрабатывают индивидуальные методы вывода из этого состояния, создавая комфортные и безопасные условия для пациентов. Длительное употребление спиртного оказывает разрушительное воздействие на внутренние органы, приводит к психическим нарушениям и обостряет хронические болезни. В таких случаях медицинское вмешательство становится неотложной необходимостью.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – вывод из запоя вызов на дом краснодар
купить диплом без занесения в реестр
Нарколог, приехавший на дом, первым делом проводит осмотр пациента, оценивает его состояние и выбирает подходящие препараты для детоксикации организма. Это может включать капельницы с солевыми растворами, витаминами и глюкозой, которые способствуют очищению организма.
Получить дополнительную информацию – капельница от запоя с выездом в москве
Зависимость — это хроническое заболевание, требующее долгосрочного лечения и регулярной поддержки. В клинике используют современные научные методы в наркологии и психотерапии, предлагая помощь на всех этапах — от диагностики до реабилитации. Команда профессионалов работает с каждым пациентом индивидуально, обеспечивая комплексный подход к терапии.
Подробнее – наркология вывод из запоя анонимно в санкт-петербурге
Алкогольная зависимость остаётся серьёзной проблемой, требующей квалифицированного медицинского вмешательства. Капельница от запоя — это ключевой этап в процессе лечения, направленный на стабилизацию состояния пациента и его возвращение к полноценной жизни. Профессиональная помощь позволяет эффективно справиться с последствиями длительного употребления алкоголя и восстановить физическое и психологическое здоровье.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – вывод из запоя тверь
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся длительным и непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к формированию как физической, так и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния часто наблюдаются нарушения работы внутренних органов, что может привести к тяжелым последствиям, включая алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя — важный этап в процессе лечения зависимости, и его можно осуществлять как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от конкретных обстоятельств.
Выяснить больше – вывод из запоя на дому недорого
В клинике также уделяется внимание конфиденциальности лечения. Понимая деликатность проблемы, врачи гарантируют полную анонимность на всех этапах терапии. Благодаря профессиональному подходу и использованию проверенных методик пациенты могут восстановить здоровье и вернуться к полноценной жизни.
Подробнее тут – вывод из запоя круглосуточно наркология
Алкогольная зависимость — это серьезное хроническое заболевание, которое характеризуется непреодолимым стремлением к употреблению спиртных напитков, потерей контроля над их потреблением и развитием толерантности. Запойное состояние, при котором человек продолжает пить без перерыва в течение нескольких дней, приводит к серьезной интоксикации организма и может вызвать опасные осложнения. Капельница от запоя — один из наиболее эффективных методов лечения, направленный на быструю детоксикацию и стабилизацию состояния пациента. В наркологической клинике “Восстановление души” в Иркутске мы предлагаем профессиональную медицинскую помощь с учетом индивидуальных потребностей каждого пациента.
Подробнее – kapelnica ot zapoya v irkutske
После успешной детоксикации начинается этап реабилитации, который включает восстановление социального статуса пациента и формирование новых здоровых привычек. Мы предлагаем как групповые, так и индивидуальные занятия, направленные на изменение поведения и мышления, что способствует долгосрочному удержанию пациента от возвращения к зависимостям.
Подробнее – kapelnica ot zapoya srochno kruglosutochno irkutsk
Запой – это состояние, которое возникает вследствие длительного употребления алкоголя, приводящее к потере контроля над количеством выпиваемого и формированию как физической, так и психологической зависимости. Оно сопровождается серьёзными последствиями для здоровья и требует немедленного вмешательства.
Разобраться лучше – вывод из запоя вызов на дом
Запой — это опасное состояние, которое развивается у людей с алкогольной зависимостью и характеризуется длительным непрерывным потреблением алкоголя. Это состояние приводит к серьезным нарушениям в организме, как физическим, так и психоэмоциональным. Длительный запой может вызвать множество осложнений, таких как поражение внутренних органов, нервной системы, а также проблемы в социальной и семейной жизни. Однако современная медицина предоставляет эффективные методы вывода из запоя, и одним из наиболее удобных и востребованных является вывод из запоя на дому.
Подробнее тут – вывод из запоя срочно круглосуточно в санкт-петербурге
обложка на аттестат купить красный
Компания 1хБет предоставляет всем 100% бонус за первый депозит до 32500 рублей (или эквивалент в другой валюте по актуальному курсу). Кроме того, вас ожидает приветственный пакет в 1xBet казино до €1950 +150 фриспинов для игры в слоты и игровые автоматы. 1xBet — это одна из самых популярных и надежных платформ, которая предлагает уникальные возможности и привлекательные бонусы для своих пользователей. Независимо от того, являетесь ли вы новичком в мире ставок или опытным игроком, промокоды 1xBet — это отличный способ повысить свои шансы на выигрыш.
Промокод 1xBet
https://www.neukoelln-online.de/include/pages/promokod_1xbet_bonus_pri_registracii_2020.html
Промокод 1хБет на сегодня – предоставляет вам возможность получить 100%-й бонус до 32 500 ? и Приветственный пакет до 1500 евро + 150 фриспинов для игры в разделе азартных игр 1хБет. 1xBet — это известная онлайн-платформа для ставок, которая славится своими щедрыми бонусами и привлекательными предложениями. Если вы ищете уникальный игровой опыт и дополнительные шансы на успех, то бонусы 1xBet станут отличным выбором для вас.
Бонусы являются одной из главных особенностей, которые делают 1xBet привлекательной для множества игроков. Как новый, так и постоянный пользователь, вы сможете воспользоваться различными видами бонусов, которые помогут увеличить ваши шансы на выигрыш. От приветственных бонусов до регулярных акций, 1xBet предлагает множество вариантов, чтобы удовлетворить ваши потребности и предпочтения.
Один из самых популярных бонусов, предоставляемых 1xBet, – это приветственный бонус для новых игроков. Как только вы зарегистрируетесь на платформе, вам будет предложен щедрый приветственный пакет, который включает в себя бонус на первый депозит. Это означает, что вы получите дополнительные средства на свой игровой счет, чтобы увеличить свои возможности для ставок. Такой бонус является отличным стартом в вашем игровом путешествии и помогает вам исследовать различные игры и спортивные события.
Наши наркологи приезжают к пациенту в удобное для него время и проводят необходимую терапию. Капельница от запоя помогает:
Углубиться в тему – капельница от запоя капельница в воронеже
Алкогольный запой — это серьезное заболевание, которое требует немедленного и профессионального вмешательства. Запой сопровождается не только физическими страданиями, но и эмоциональными трудностями. Процесс выведения из запоя требует срочного внимания, так как состояние пациента может ухудшиться, если не получить квалифицированную помощь вовремя. Наркологическая клиника «Излечение» в Краснодаре предоставляет круглосуточную помощь при алкогольном запое, чтобы восстановить здоровье пациента в самых сложных ситуациях.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно
Мы понимаем, что каждая зависимость уникальна, поэтому основой нашего подхода является индивидуализация лечения. После тщательной диагностики, включающей анализ медицинской истории, психологического состояния и социальных факторов, наши специалисты разрабатывают персонализированный план терапии. Этот план может включать медикаментозную детоксикацию, психотерапевтические методы и социальные программы, направленные на изменение поведения и мышления пациента.
Детальнее – kapelnica ot zapoya anonimno
Запойное пьянство характеризуется продолжительным и интенсивным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к серьезным физическим и психологическим последствиям. Часто пациенты сталкиваются с различными заболеваниями, такими как цирроз печени, панкреатит, алкогольный делирий и другие. Алкогольное опьянение не только ухудшает качество жизни, но также может угрожать жизни пациента. В условиях стационара лечение может быть более эффективным, однако многие люди предпочитают проходить данную процедуру на дому, чтобы избежать стигматизации и сохранить чувство приватности.
Ознакомиться с деталями – анонимный вывод из запоя на дому екатеринбург
Магазин дженериков https://cialismoscow.ru высокое качество по доступной цене
производство Индии в наличии
Запой — это состояние, при котором человек продолжает употреблять алкоголь на протяжении нескольких дней или даже недель, не контролируя объемы потребляемого напитка. Этот процесс сопровождается тяжелыми физическими и психическими последствиями, такими как обезвоживание организма, отравление продуктами распада алкоголя, нервные расстройства и потеря контроля над ситуацией. Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, направленная на прекращение употребления алкоголя и восстановление организма пациента.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – anonimny vyvod iz zapoya na domu
Процесс вывода из запоя требует быстрого реагирования. Запой, особенно в его тяжелых формах, представляет угрозу не только для психического состояния пациента, но и для его физического здоровья. Чтобы минимизировать риски и предотвратить осложнения, важно начинать лечение как можно скорее. Клинике «Освобождение» в Рязани доступна круглосуточная помощь — мы работаем 24/7, чтобы оперативно вмешаться в любой момент, когда это необходимо. Врачебная помощь может быть предоставлена как в стационаре клиники, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента и его предпочтений.
Получить дополнительные сведения – вывод из запоя на дому в рязани
Алкогольный запой — это серьезное заболевание, которое требует немедленного и профессионального вмешательства. Запой сопровождается не только физическими страданиями, но и эмоциональными трудностями. Процесс выведения из запоя требует срочного внимания, так как состояние пациента может ухудшиться, если не получить квалифицированную помощь вовремя. Наркологическая клиника «Излечение» в Краснодаре предоставляет круглосуточную помощь при алкогольном запое, чтобы восстановить здоровье пациента в самых сложных ситуациях.
Подробнее тут – srochny vyvod iz zapoya na domu krasnodar
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой актуальную медицинскую проблему, требующую тщательного подхода. Запой характеризуется длительным, непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что ведёт к физической и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния могут возникнуть тяжёлые нарушения функций органов, увеличивается риск развития таких состояний, как алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя становится ключевым этапом в лечении зависимостей, который может осуществляться как в стационарных условиях, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента. В клинике «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске мы предлагаем круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить максимально эффективное и безопасное лечение при любом варианте вывода из запоя.
Подробнее – http://www.vyvod-iz-zapoya-17.ru
Процедура вывода из запоя направлена на устранение последствий длительного употребления алкоголя и восстановления работы организма. Этот процесс включает не только медикаментозное лечение, но и психологическую поддержку, что позволяет минимизировать симптомы абстиненции и предотвратить возможные осложнения.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – bystry vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare
В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы понимаем, насколько важен своевременный и профессиональный подход к лечению зависимости. Наши специалисты готовы оказать квалифицированную помощь прямо у вас дома, обеспечивая полную безопасность и конфиденциальность на каждом этапе лечения.
Получить больше информации – вывод из запоя капельница санкт-петербург
Мы понимаем, что каждая зависимость уникальна, поэтому основой нашего подхода является индивидуализация лечения. После тщательной диагностики, включающей анализ медицинской истории, психологического состояния и социальных факторов, наши специалисты разрабатывают персонализированный план терапии. Этот план может включать медикаментозную детоксикацию, психотерапевтические методы и социальные программы, направленные на изменение поведения и мышления пациента.
Изучить вопрос глубже – narkolog kapelnica ot zapoya cena voronezh
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой состояние, при котором организм человека испытывает серьёзное воздействие этанола. Это приводит к нарушениям нормальной физиологической деятельности и ухудшению состояния здоровья. Анонимный вывод из запоя — это медицинская помощь, направленная на устранение последствий чрезмерного употребления алкоголя с соблюдением строгой конфиденциальности.
Разобраться лучше – vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare anonimno v-ekaterinburge
Алкогольный запой сопровождается опасной интоксикацией, которая без своевременной помощи может привести к необратимым последствиям, включая поражение печени, сердца, почек и психические расстройства. В критических случаях промедление может стоить жизни. Именно поэтому специалисты клиники готовы оказывать поддержку круглосуточно.
Получить дополнительную информацию – vyvod iz zapoya na domu kruglosutochno sankt-peterburg
Мы понимаем, что каждая зависимость уникальна, поэтому основой нашего подхода является индивидуализация лечения. После тщательной диагностики, включающей анализ медицинской истории, психологического состояния и социальных факторов, наши специалисты разрабатывают персонализированный план терапии. Этот план может включать медикаментозную детоксикацию, психотерапевтические методы и социальные программы, направленные на изменение поведения и мышления пациента.
Получить больше информации – narkologicheskaya klinika irkutsk
кино онлайн – фильмы вышедшие онлайн, мультфильмы онлайн
Мы понимаем, что каждая зависимость уникальна, поэтому основой нашего подхода является индивидуализация лечения. После тщательной диагностики, включающей анализ медицинской истории, психологического состояния и социальных факторов, наши специалисты разрабатывают персонализированный план терапии. Этот план может включать медикаментозную детоксикацию, психотерапевтические методы и социальные программы, направленные на изменение поведения и мышления пациента.
Получить дополнительную информацию – srochnaya kapelnica ot zapoya na domu v irkutske
Алкогольный запой представляет собой критическое состояние, требующее немедленного вмешательства квалифицированных специалистов. Клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже предлагает круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить своевременное и эффективное лечение. Наша цель — оперативное снятие интоксикации, устранение симптомов и предотвращение осложнений.
Ознакомиться с деталями – вывод из запоя в стационаре в воронеже
Круглосуточная медицинская помощь при алкогольном запое играет важнейшую роль в спасении жизни пациентов и их возвращении к нормальному состоянию. В данной статье рассмотрим ключевые аспекты вывода из запоя в домашних условиях, срочной помощи и работы нарколога.
Подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya srochno kruglosutochno v-ekaterinburge
Алкогольный запой представляет собой крайне опасное состояние, характеризующееся неконтролируемым употреблением алкоголя, что в свою очередь приводит к тяжелой интоксикации организма. Восстановление после такого состояния требует профессионального вмешательства, включающего не только физическую детоксикацию, но и психологическую поддержку. Стоимость процедуры вывода из запоя может значительно различаться в зависимости от множества факторов, включая метод лечения, тяжесть состояния пациента и место проведения лечения. Рассмотрим более подробно основные аспекты, влияющие на цену вывода из запоя.
Узнать больше – вывод из запоя в стационаре санкт-петербург
Запой — это опасное состояние, которое развивается у людей с алкогольной зависимостью и характеризуется длительным непрерывным потреблением алкоголя. Это состояние приводит к серьезным нарушениям в организме, как физическим, так и психоэмоциональным. Длительный запой может вызвать множество осложнений, таких как поражение внутренних органов, нервной системы, а также проблемы в социальной и семейной жизни. Однако современная медицина предоставляет эффективные методы вывода из запоя, и одним из наиболее удобных и востребованных является вывод из запоя на дому.
Ознакомиться с деталями – быстрый вывод из запоя в стационаре
Наркологическая клиника «Освобождение» в Рязани предлагает профессиональные услуги по выводу из запоя и комплексной реабилитации. Мы понимаем, что зависимость — это болезнь, требующая индивидуального подхода и поддержки не только для пациента, но и для его близких.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – анонимный вывод из запоя на дому
Эти меры позволяют пациенту быстро и безопасно восстановиться, минимизируя негативные последствия запойного состояния.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – нарколог капельница от запоя цена москва
Запой — это тяжелое состояние, возникающее вследствие длительного и непрерывного употребления алкоголя, которое сопровождается физической и психической зависимостью. Это опасное явление требует незамедлительного вмешательства специалистов. Вывод из запоя — это комплексный процесс медицинской детоксикации, который включает в себя очищение организма от токсинов, нормализацию функций внутренних органов и поддержку психоэмоционального состояния пациента. В случае тяжелого запоя стационарное лечение становится оптимальным решением для безопасного и эффективного вывода из этого состояния. В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как проходит вывод из запоя в стационаре клиники «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, а также особенности анонимности, скорости лечения и участия нарколога.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – vyvod iz zapoya vrach na dom chelyabinsk
Одним из важнейших аспектов, который помогает пациентам справиться с алкогольной зависимостью, является анонимность в процессе лечения. В клинике «Излечение» мы понимаем, как важно сохранить конфиденциальность и гарантировать защиту личной информации, особенно для тех, кто опасается общественного осуждения. Мы обеспечиваем полную анонимность при выводе из запоя, как в стационарных условиях, так и на дому.
Получить дополнительные сведения – вывод из запоя капельница на дому
Качественные дженерики в магазине https://dapoxetine-60mg.ru/ с доставкой
по городу и области в день покупки
Order synthetic viagra http://pharmwithoutadoctorsprescription.com/ When will alli be available
Запой представляет собой состояние, характеризующееся длительным непрерывным употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к физической и психической зависимости. Этот процесс может длиться от нескольких дней до недель. Алкогольные напитки негативно влияют на функционирование внутренних органов, вызывая серьёзные нарушения, включая алкоголизм. При необходимости вывода из запоя важно обратиться за медицинской помощью, что можно осуществить на дому. В данной статье рассмотрим ключевые аспекты данной процедуры.
Детальнее – vyvod iz zapoya na domu cena v-chelyabinske
Современное общество сталкивается с серьёзными вызовами, связанными с зависимостями. Алкоголизм, как одна из самых распространённых проблем, оказывает разрушительное воздействие на здоровье человека, разрушая семейные отношения и затрудняя социальную адаптацию. В такие моменты крайне важно обратиться за квалифицированной помощью.
Детальнее – vyvod iz zapoya kapelnica na domu ryazan
Алкогольный запой представляет собой крайне опасное состояние, характеризующееся неконтролируемым употреблением алкоголя, что в свою очередь приводит к тяжелой интоксикации организма. Восстановление после такого состояния требует профессионального вмешательства, включающего не только физическую детоксикацию, но и психологическую поддержку. Стоимость процедуры вывода из запоя может значительно различаться в зависимости от множества факторов, включая метод лечения, тяжесть состояния пациента и место проведения лечения. Рассмотрим более подробно основные аспекты, влияющие на цену вывода из запоя.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – наркология вывод из запоя на дому в санкт-петербурге
Злоупотребление алкоголем в течение продолжительного времени приводит к состоянию, при котором человек теряет контроль над собой, а его организм подвергается серьезным нагрузкам. Последствия такого состояния проявляются на физическом и психическом уровнях: организм страдает от отравления, обезвоживания и сбоев в работе нервной системы, а человек теряет способность адекватно оценивать ситуацию. Выйти из этого состояния без медицинской помощи крайне сложно, так как требуется не только прекратить употребление алкоголя, но и восстановить нормальные функции организма.
Получить дополнительные сведения – вывод из запоя вызов на дом в краснодаре
Клиника предлагает гибкие варианты лечения, включая стационарное и амбулаторное. Стоимость услуг зависит от индивидуальных потребностей пациента, степени тяжести состояния и объемов необходимых процедур. Специалисты стремятся создать максимально комфортные условия для каждого пациента, обеспечивая прозрачное ценообразование и высокое качество обслуживания.
Получить дополнительную информацию – вывод из запоя анонимно недорого в санкт-петербурге
В современном мире зависимость становится все более распространенной проблемой. Стресс, жизненные трудности и финансовые проблемы часто провоцируют развитие таких серьезных состояний, как алкоголизм, наркомания и игромания. Наркологическая клиника “Второй Шанс” предоставляет помощь людям, столкнувшимся с этими заболеваниями. Основное направление работы клиники — восстановление здоровья пациентов, их социальная адаптация и предотвращение повторных рецидивов.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-14.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-sankt-peterburge/]быстрый вывод из запоя в стационаре в санкт-петербурге[/url]
купить диплом вуза
Алкогольный запой – это серьёзное состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к тяжёлой интоксикации организма. Во время запоя нарушаются функции внутренних органов, страдает нервная система, и повышается риск развития опасных осложнений, таких как алкогольный делирий. Это состояние требует незамедлительного медицинского вмешательства.
Углубиться в тему – вывод из запоя анонимно в екатеринбурге
Запойное пьянство характеризуется продолжительным и интенсивным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к серьезным физическим и психологическим последствиям. Часто пациенты сталкиваются с различными заболеваниями, такими как цирроз печени, панкреатит, алкогольный делирий и другие. Алкогольное опьянение не только ухудшает качество жизни, но также может угрожать жизни пациента. В условиях стационара лечение может быть более эффективным, однако многие люди предпочитают проходить данную процедуру на дому, чтобы избежать стигматизации и сохранить чувство приватности.
Получить больше информации – vyvod-iz-zapoya-20.ru
Гизбо Казино ориентировано на игроков с различными предпочтениями и бюджетами. В казино представлены игры с различными ставками, что позволяет выбирать развлечения в соответствии с индивидуальными возможностями казино Gizbo
Запой – это состояние, возникающее из-за длительного употребления алкоголя и характеризующееся физической и психологической зависимостью. Оно требует комплексного медицинского вмешательства для устранения последствий и предотвращения дальнейшего ухудшения здоровья. Стационарное лечение в клинике «Освобождение» в Рязани – это эффективный способ вернуть пациента к нормальной жизни, предоставляя ему комфортные условия и круглосуточную помощь специалистов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно рязань
Запой — это одно из наиболее тяжелых проявлений алкогольной зависимости, которое требует немедленного и квалифицированного вмешательства. В такие моменты близкие зачастую теряются и не знают, как помочь своему родному человеку. На помощь приходит наркологическая клиника «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, которая предоставляет профессиональную помощь в выводе из запоя. Мы понимаем, что лечение запоя требует не только медицинского подхода, но и психологической поддержки. Именно поэтому в нашей клинике пациент получает комплексную помощь, основанную на самых современных методах лечения.
Получить больше информации – вывод из запоя на дому цена челябинск
Гизбо Казино ориентировано на игроков с различными предпочтениями и бюджетами. В казино представлены игры с различными ставками, что позволяет выбирать развлечения в соответствии с индивидуальными возможностями казино Gizbo
Индивидуальный дизайн: Мы создаем кухни по вашим размерам и пожеланиям, учитывая особенности вашего пространства http://otdel.com.ua/index.php?subaction=userinfo&user=ydawy
Индивидуальный дизайн: Мы создаем кухни по вашим размерам и пожеланиям, учитывая особенности вашего пространства http://jordirocas.com/node/4422
Клиника «Рассвет» в Твери предоставляет услугу анонимного вывода из запоя, обеспечивая высокое качество медицинского обслуживания и строгое соблюдение всех этических норм.
Подробнее – вывод из запоя срочно круглосуточно в твери
Клиника «Преображение» предлагает услуги анонимного вывода из запоя в Екатеринбурге, обеспечивая высокое качество медицинской помощи и соблюдение всех этических норм.
Получить дополнительную информацию – наркологическая клиника екатеринбург
Гизбо Казино ориентировано на игроков с различными предпочтениями и бюджетами. В казино представлены игры с различными ставками, что позволяет выбирать развлечения в соответствии с индивидуальными возможностями Гизбо Казино
Запой – это состояние, которое возникает вследствие длительного употребления алкоголя, приводящее к потере контроля над количеством выпиваемого и формированию как физической, так и психологической зависимости. Оно сопровождается серьёзными последствиями для здоровья и требует немедленного вмешательства.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – вывод из запоя анонимно недорого воронеж
Индивидуальный дизайн: Мы создаем кухни по вашим размерам и пожеланиям, учитывая особенности вашего пространства http://dev.may-green.ru/forum/user/19262/
Мы понимаем, что каждая зависимость уникальна, поэтому основой нашего подхода является индивидуализация лечения. После тщательной диагностики, включающей анализ медицинской истории, психологического состояния и социальных факторов, наши специалисты разрабатывают персонализированный план терапии. Этот план может включать медикаментозную детоксикацию, психотерапевтические методы и социальные программы, направленные на изменение поведения и мышления пациента.
Изучить вопрос глубже – нарколог капельница от запоя цена в москве
Алкогольный запой представляет собой критическое состояние, требующее немедленного вмешательства квалифицированных специалистов. Клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже предлагает круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить своевременное и эффективное лечение. Наша цель — оперативное снятие интоксикации, устранение симптомов и предотвращение осложнений.
Получить больше информации – вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно воронеж
Reliable and unique bip39 Word List contains 2048 words needed to create seed phrases in crypto wallets. Allows you to safely manage private keys and guarantees the possibility of recovering funds.
Наркологическая клиника «Освобождение» в Рязани предлагает профессиональные услуги по выводу из запоя и комплексной реабилитации. Мы понимаем, что зависимость — это болезнь, требующая индивидуального подхода и поддержки не только для пациента, но и для его близких.
Изучить вопрос глубже – bystry vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare
Аттестат 9 классов
Вывод из запойного состояния – сложный процесс, включающий несколько последовательных этапов. Основная цель – детоксикация организма и восстановление его нормального функционирования. Важно, чтобы процессом руководили опытные специалисты, способные минимизировать последствия интоксикации и помочь человеку вернуться к здоровой жизни. Стоимость лечения зависит от выбранных методов и уровня медицинского обслуживания, а в клинике «Излечение» предлагаются доступные варианты с учетом индивидуальных потребностей пациентов.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-16.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-krasnodare/]bystry vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare [/url]
Приобретение школьного аттестата с официальным упрощенным обучением в Москве
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, необходимая для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Это состояние, часто характеризующееся физическими и психоэмоциональными нарушениями, требует профессионального вмешательства. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть разнообразными и варьироваться от лёгкой тревожности до серьёзных нарушений в функционировании внутренних органов. Квалифицированная помощь в этот период позволяет минимизировать риски и значительно ускорить процесс выздоровления.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-11.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-voronezhe/]наркология вывод из запоя на дому воронеж[/url]
Большой выбор дженериков на сайте https://dickfix.ru/ доступная цена
высокое качество производства Индии
В клинике “Восстановление души” работает команда высококвалифицированных специалистов, готовых предложить современное и эффективное лечение зависимостей. Наши врачи-наркологи обладают обширным опытом работы и постоянно совершенствуют свои навыки, чтобы использовать самые передовые методы терапии.
Получить дополнительные сведения – капельница от запоя на дому цена
Зависимость — это серьёзная проблема, которая затрагивает не только человека, но и его семью и окружение. Алкоголизм, наркомания и другие виды зависимостей могут разрушить жизнь, но с профессиональной помощью можно вернуть её в русло нормального функционирования. Наркологическая клиника «Заря Будущего» в Санкт-Петербурге предлагает уникальные программы лечения зависимостей, которые сочетает медико-психологический подход, индивидуальные методики и квалифицированную поддержку.
Получить дополнительные сведения – вывод из запоя вызов на дом в санкт-петербурге
Зависимость — это хроническое заболевание, требующее долгосрочного лечения и регулярной поддержки. В клинике используют современные научные методы в наркологии и психотерапии, предлагая помощь на всех этапах — от диагностики до реабилитации. Команда профессионалов работает с каждым пациентом индивидуально, обеспечивая комплексный подход к терапии.
Выяснить больше – bystry vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare sankt-peterburg
Зависимость — это хроническое заболевание, требующее долгосрочного лечения и регулярной поддержки. В клинике используют современные научные методы в наркологии и психотерапии, предлагая помощь на всех этапах — от диагностики до реабилитации. Команда профессионалов работает с каждым пациентом индивидуально, обеспечивая комплексный подход к терапии.
Получить дополнительные сведения – быстрый вывод из запоя в стационаре санкт-петербург
https://xphone.tel/learn-how-to-get-a-promo-code-for-1xbet-easily-2/
Клиника «Рассвет» в Твери предоставляет услугу анонимного вывода из запоя, обеспечивая высокое качество медицинского обслуживания и строгое соблюдение всех этических норм.
Узнать больше – vyvod iz zapoya na domu
Если затянувшееся употребление алкоголя не прерывается, организм начинает испытывать тяжелые последствия. Возникает абстинентный синдром, проявляющийся в виде тошноты, сильной головной боли, дрожи в теле и других неприятных симптомов. Без своевременной помощи состояние может ухудшиться, поэтому важна быстрая медицинская реакция. Комплексное лечение направлено не только на избавление от физической зависимости, но и на поддержку человека в эмоциональном плане. В случаях, когда требуется постоянное наблюдение, рекомендуется стационарная терапия.
Подробнее тут – vyvod iz zapoya kapelnica
Одним из главных преимуществ стационарного лечения в нашей клинике является полная анонимность. Мы понимаем, что многие пациенты боятся раскрытия своей зависимости и осуждения со стороны окружающих. В “Восстановление души” мы гарантируем конфиденциальность всех процедур и защиту личных данных пациента. Это создает безопасную и доверительную атмосферу, необходимую для успешного лечения и психологического восстановления.
Детальнее – анонимная капельница от запоя на дому иркутск
В клинике также уделяется внимание конфиденциальности лечения. Понимая деликатность проблемы, врачи гарантируют полную анонимность на всех этапах терапии. Благодаря профессиональному подходу и использованию проверенных методик пациенты могут восстановить здоровье и вернуться к полноценной жизни.
Подробнее тут – вывод из запоя цена санкт-петербург
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся длительным и непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к формированию как физической, так и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния часто наблюдаются нарушения работы внутренних органов, что может привести к тяжелым последствиям, включая алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя — важный этап в процессе лечения зависимости, и его можно осуществлять как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от конкретных обстоятельств.
Детальнее – vyvod iz zapoya na domu cena
Как получить диплом стоматолога быстро и официально
buy marijuana in prague https://sale-weed-prague.com
Процесс возвращения к нормальной жизни после длительного употребления алкоголя играет ключевую роль в избавлении от зависимости. Медицинское сопровождение должно сочетаться с осознанным желанием человека изменить свою жизнь. Важно, чтобы лечение проходило в условиях, исключающих стресс и дискомфорт. Для этого предусмотрены как стационарные программы, так и возможность получить медицинскую помощь на дому. Такой вариант подходит тем, кто предпочитает находиться в привычной обстановке и избегать огласки.
Подробнее – вывод из запоя с выездом на дом краснодар
В клинике работает команда квалифицированных специалистов, которые осуществляют вывод из запоя, обеспечивая полный контроль над состоянием пациента и устраняя все последствия длительного употребления алкоголя.
Подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare anonimno v-ekaterinburge
Устанавливаем заборы из металлопрофиля, евроштакетника на дачном участке http://cascaderpark.pl/witaj-swiecie/comment-page-6094/#comment-820222
Запой — это тяжелое состояние, возникающее вследствие длительного и непрерывного употребления алкоголя, которое сопровождается физической и психической зависимостью. Это опасное явление требует незамедлительного вмешательства специалистов. Вывод из запоя — это комплексный процесс медицинской детоксикации, который включает в себя очищение организма от токсинов, нормализацию функций внутренних органов и поддержку психоэмоционального состояния пациента. В случае тяжелого запоя стационарное лечение становится оптимальным решением для безопасного и эффективного вывода из этого состояния. В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как проходит вывод из запоя в стационаре клиники «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, а также особенности анонимности, скорости лечения и участия нарколога.
Детальнее – вывод из запоя круглосуточно наркология в челябинске
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой состояние, при котором организм человека испытывает серьезное воздействие этанола, что приводит к нарушению нормальной физиологической деятельности. Это состояние сопровождается сильными физическими и психологическими расстройствами, которые требуют профессионального вмешательства. Однако многие люди, страдающие алкогольной зависимостью, сталкиваются с трудностью признания своей проблемы, опасаясь утраты репутации и конфиденциальности. В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем анонимный вывод из запоя в Санкт-Петербурге, предоставляя высококачественное лечение с гарантией сохранения личной информации.
Ознакомиться с деталями – срочный вывод из запоя на дому санкт-петербург
Устанавливаем заборы из металлопрофиля, евроштакетника на дачном участке http://www.swolesource.com/forum/showthread.php?t=166838&p=243484#post243484
Наркологическая клиника «Освобождение» в Рязани предлагает профессиональные услуги по выводу из запоя и комплексной реабилитации. Мы понимаем, что зависимость — это болезнь, требующая индивидуального подхода и поддержки не только для пациента, но и для его близких.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-13.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-anonimno-v-ryazani/]вывод из запоя анонимно недорого рязань[/url]
Алкогольная зависимость — это серьезное заболевание, при котором человек теряет контроль над потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к его физической и психологической зависимости. Одним из наиболее выраженных проявлений алкоголизма является состояние запоя — длительное и неконтролируемое употребление спиртных напитков. В таких случаях капельница от запоя становится не только быстрым, но и безопасным методом для избавления от последствий интоксикации.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – kapelnica ot zapoya kruglosutochno narkologiya
1xBet promo code https://taisei-ts.co.jp/1xbet-promocodes/top-advantages-of-the-1xbet-promo-code-free-bet-3/ your chance to get bonuses on bets, free bets and exclusive promotions! Enter the code during registration and start playing with an increased deposit.
Устанавливаем заборы из металлопрофиля, евроштакетника на дачном участке http://greaterhillcrest.com/filipino-bistro-comes-to-hillcrest/?unapproved=213832&moderation-hash=153377fcced340adb9bc2e61f6fcd918#comment-213832
Выход из запоя — это важнейший этап на пути к избавлению от алкогольной зависимости. Он требует комплексного подхода, профессиональной помощи и сильной мотивации пациента. В условиях, когда анонимность и комфорт становятся ключевыми факторами для многих людей, вывод из запоя на дому приобретает все большее значение. Это решение позволяет человеку получить необходимую помощь, не покидая дома, и избежать стресса, связанного с госпитализацией.
Ознакомиться с деталями – vyvod iz zapoya cena narkologiya
Запой — это одно из наиболее тяжелых проявлений алкогольной зависимости, которое требует немедленного и квалифицированного вмешательства. В такие моменты близкие зачастую теряются и не знают, как помочь своему родному человеку. На помощь приходит наркологическая клиника «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, которая предоставляет профессиональную помощь в выводе из запоя. Мы понимаем, что лечение запоя требует не только медицинского подхода, но и психологической поддержки. Именно поэтому в нашей клинике пациент получает комплексную помощь, основанную на самых современных методах лечения.
Подробнее тут – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom cena chelyabinsk
I learnt a lot from this, thanks so much. Nice clear and explanations too. 티비몬
купить 10 11 класс аттестат
Зависимость от алкоголя – серьезная проблема, требующая системного подхода и профессионального лечения. В клинике «Излечение» гарантируется полная конфиденциальность на всех этапах процесса, что позволяет пациентам чувствовать себя в безопасности. Лечение может проходить как в стационаре, так и на дому, при этом соблюдаются все условия для максимального комфорта.
Получить дополнительные сведения – вывод из запоя капельница на дому в краснодаре
Приобретение диплома ПТУ с сокращенной программой обучения в Москве
Узнайте стоимость диплома высшего и среднего образования и процесс получения
Алкоголизм — это хроническое заболевание, которое характеризуется патологической зависимостью от этанола. Периоды запоя, когда человек неконтролируемо потребляет алкоголь, могут привести к разнообразным медицинским осложнениям, как физическим, так и психологическим. Запой становится не только причиной ухудшения здоровья, но и причиной множества социальных и личных проблем. На этом фоне возникает необходимость вывода из запоя, процесс, который должен учитывать индивидуальные особенности пациента. Важно, что анонимность в реабилитации играет ключевую роль, помогая избежать стигматизации и увеличивая шансы на успешное восстановление.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-13.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-ryazani/]narkologiya vyvod iz zapoya na domu ryazan[/url]
На нашем сайте https://doctorpills.ru представлен широкий выбор
дженериков производства Индии с доставкой во все регионы России
После успешной детоксикации начинается этап реабилитации, который включает восстановление социального статуса пациента и формирование новых здоровых привычек. Мы предлагаем как групповые, так и индивидуальные занятия, направленные на изменение поведения и мышления, что способствует долгосрочному удержанию пациента от возвращения к зависимостям.
Углубиться в тему – kapelnica ot zapoya v stacionare voronezh
Наши наркологи приезжают к пациенту в удобное для него время и проводят необходимую терапию. Капельница от запоя помогает:
Подробнее тут – капельница от запоя с выездом
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, необходимая для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Это состояние, часто характеризующееся физическими и психоэмоциональными нарушениями, требует профессионального вмешательства. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть разнообразными и варьироваться от лёгкой тревожности до серьёзных нарушений в функционировании внутренних органов. Квалифицированная помощь в этот период позволяет минимизировать риски и значительно ускорить процесс выздоровления.
Ознакомиться с деталями – вывод из запоя врач на дом
과도한 소비는 자원 소모와 환경 파괴를 초래할 수 있으며, 상품권 신용카드 소비주의적인 가치관은 소수의 소비에만 초점을 맞추어 사회적 불평등을 증가시킬 수 있을 것이다. 따라서, 쇼핑을 할 때는 지속 가능한 소비를 실천하고, 고유의 욕구에 따라 무난히 고르는 것이 중요합니다.
상품권 소액결제
supreme suppliers viagra
После успешной детоксикации начинается этап реабилитации, который включает восстановление социального статуса пациента и формирование новых здоровых привычек. Мы предлагаем как групповые, так и индивидуальные занятия, направленные на изменение поведения и мышления, что способствует долгосрочному удержанию пациента от возвращения к зависимостям.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – капельница от запоя с выездом цена воронеж
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой сложное и хроническое заболевание, которое влияет не только на физическое, но и на психологическое состояние пациента. Периоды запоя, влекущие за собой неконтролируемое употребление алкоголя, могут привести к опасным последствиям для здоровья и жизни. Абстинентные симптомы, такие как тремор, тошнота, головная боль и другие проявления, требуют немедленного медицинского вмешательства. В таких ситуациях важно не только быстро устранить физическое воздействие алкоголя, но и предоставить пациенту психологическую поддержку.
Подробнее – наркологический центр в краснодаре
Процесс вывода из запоя требует быстрого реагирования. Запой, особенно в его тяжелых формах, представляет угрозу не только для психического состояния пациента, но и для его физического здоровья. Чтобы минимизировать риски и предотвратить осложнения, важно начинать лечение как можно скорее. Клинике «Освобождение» в Рязани доступна круглосуточная помощь — мы работаем 24/7, чтобы оперативно вмешаться в любой момент, когда это необходимо. Врачебная помощь может быть предоставлена как в стационаре клиники, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента и его предпочтений.
Получить дополнительные сведения – наркологический центр рязань
Запойное состояние представляет собой серьёзную угрозу для здоровья, поскольку сопровождается тяжёлой интоксикацией организма и нарушением психоэмоционального состояния. Решение о лечении в стационаре клиники «Союз Здоровья» позволяет справиться с последствиями длительного употребления алкоголя, обеспечивая пациентам полный комплекс медицинской и психологической помощи.
Получить дополнительные сведения – vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno narkologiya voronezh
Алкогольный запой — это состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к токсической нагрузке на организм. Это опасное состояние требует не только быстрого медицинского вмешательства, но и внимательного подхода к восстановлению здоровья пациента. Процесс вывода из запоя включает в себя комплекс процедур, направленных на устранение последствий интоксикации и восстановление нормального функционирования организма. Важно учитывать, что стоимость этой процедуры может значительно варьироваться в зависимости от нескольких факторов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – вывод из запоя
В клинике «Излечение» мы предлагаем широкий спектр услуг по выводу из запоя, включая как стационарное лечение, так и помощь на дому. В этой статье мы подробно рассмотрим, от чего зависит цена вывода из запоя и какие услуги входят в стоимость.
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-16.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-anonimno-v-krasnodare/
http://www.vgronlinepharmacy.com
Клиника «Рассвет» в Твери предоставляет услугу анонимного вывода из запоя, обеспечивая высокое качество медицинского обслуживания и строгое соблюдение всех этических норм.
Узнать больше – vyvod iz zapoya vrach na dom
Запой — это одно из наиболее тяжелых проявлений алкогольной зависимости, которое требует немедленного и квалифицированного вмешательства. В такие моменты близкие зачастую теряются и не знают, как помочь своему родному человеку. На помощь приходит наркологическая клиника «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, которая предоставляет профессиональную помощь в выводе из запоя. Мы понимаем, что лечение запоя требует не только медицинского подхода, но и психологической поддержки. Именно поэтому в нашей клинике пациент получает комплексную помощь, основанную на самых современных методах лечения.
Получить больше информации – vyvod iz zapoya anonimno nedorogo v-chelyabinske
Выбирайте эротический массаж в Сочи для уникального и расслабляющего опыта. Этот вид массажа помогает снять стресс и напряжение, даря удовольствие и новые ощущения https://valetinowiki.racing/index.php?title=%20%D0%AD%D1%80%D0%BE%D1%82%D0%B8%D1%87%D0%B5%D1%81%D0%BA%D0%B8%D0%B9%20%D0%BC%D0%B0%D1%81%D1%81%D0%B0%D0%B6:%20%D0%A2%D0%BE%D0%BF-5%20%D0%BC%D0%B5%D1%81%D1%82%20%D0%B2%20%D0%A1%D0%BE%D1%87%D0%B8%20%D0%B4%D0%BB%D1%8F%20%D0%BD%D0%B5%D0%B7%D0%B0%D0%B1%D1%8B%D0%B2%D0%B0%D0%B5%D0%BC%D1%8B%D1%85%20%D0%BE%D1%89%D1%83%D1%89%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%B9
https://digi298sa.netlify.app/research/digi298sa-(40)
They have the chic and simple mom of bride attire out there by way of authenticated retailers or an official online retailer.
Круглосуточная медицинская помощь при алкогольном запое играет важнейшую роль в спасении жизни пациентов и их возвращении к нормальному состоянию. В данной статье рассмотрим ключевые аспекты вывода из запоя в домашних условиях, срочной помощи и работы нарколога.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – наркология вывод из запоя анонимно
Алкогольная зависимость — это серьезная проблема, требующая незамедлительного вмешательства, чтобы избежать тяжелых последствий для здоровья. Запойное пьянство может привести к различным заболеваниям, таким как цирроз печени, панкреатит и другие опасные состояния. К счастью, современная медицина предлагает эффективные методы решения этой проблемы. Для тех, кто не хочет или не может посетить стационар, есть возможность пройти процедуру капельницы от запоя на дому в Твери.
Узнать больше – vyvod iz zapoya kapelnica
Выбирайте эротический массаж в Сочи для уникального и расслабляющего опыта. Этот вид массажа помогает снять стресс и напряжение, даря удовольствие и новые ощущения http://punik.ru/index.php?title=%20%D0%AD%D1%80%D0%BE%D1%82%D0%B8%D1%87%D0%B5%D1%81%D0%BA%D0%B8%D0%B9%20%D0%BC%D0%B0%D1%81%D1%81%D0%B0%D0%B6%20%D0%B8%20%D0%BC%D1%83%D0%B7%D1%8B%D0%BA%D0%B0:%20%D0%9A%D0%B0%D0%BA%20%D0%B7%D0%B2%D1%83%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%BE%D0%B5%20%D1%81%D0%BE%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%BE%D0%B6%D0%B4%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%B5%20%D0%B2%D0%BB%D0%B8%D1%8F%D0%B5%D1%82%20%D0%BD%D0%B0%20%D0%BE%D1%89%D1%83%D1%89%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%B8%D1%8F
online pharmacy europ no prescription Cialis kaufen
Алкогольный запой — это тяжелое состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над количеством потребляемого алкоголя. Это приводит к сильной интоксикации, сбоям в работе органов и систем организма, а также серьезным психоэмоциональным расстройствам. Без должной медицинской помощи запой может вызвать ряд опасных последствий, включая алкогольный делирий и угрозу жизни. Поэтому при первых признаках запоя необходимо обратиться к профессионалам.
Подробнее тут – наркология вывод из запоя на дому в твери
Ремонт компьютеров и ноутбуков https://remcomp89.ru в Новом Уренгое – быстрые и качественные услуги! Диагностика, настройка, замена комплектующих, восстановление данных. Гарантия на работу, доступные цены и выезд мастера!
Современное общество сталкивается с серьёзными вызовами, связанными с зависимостями. Алкоголизм, как одна из самых распространённых проблем, оказывает разрушительное воздействие на здоровье человека, разрушая семейные отношения и затрудняя социальную адаптацию. В такие моменты крайне важно обратиться за квалифицированной помощью.
Подробнее – наркология вывод из запоя анонимно в рязани
Запой нарушает привычный ритм жизни, вызывая серьезные физические и эмоциональные проблемы. Для его лечения требуется не только медикаментозное вмешательство, но и постоянное наблюдение специалистов. Стационарное лечение в клинике позволяет обеспечить полный контроль над состоянием пациента, что минимизирует риски и способствует более эффективной реабилитации.
Получить больше информации – https://www.vyvod-iz-zapoya-14.ru
Поддержка — ключевой элемент на пути к выздоровлению. Мы предлагаем программы, которые продолжаются даже после завершения основного курса лечения. Пациенты имеют возможность участвовать в регулярных встречах с психологами и наркологами, где они могут делиться своими успехами и получать необходимую помощь.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva2.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-na-domu-v-moskve/]капельница от запоя с выездом[/url]
Выбирайте эротический массаж в Сочи для уникального и расслабляющего опыта. Этот вид массажа помогает снять стресс и напряжение, даря удовольствие и новые ощущения http://sabrina-online.su/wiki/index.php?title=%20%D0%9F%D0%BE%D1%87%D0%B5%D0%BC%D1%83%20%D1%8D%D1%80%D0%BE%D1%82%D0%B8%D1%87%D0%B5%D1%81%D0%BA%D0%B8%D0%B9%20%D0%BC%D0%B0%D1%81%D1%81%D0%B0%D0%B6%20%E2%80%94%20%D0%B8%D0%B4%D0%B5%D0%B0%D0%BB%D1%8C%D0%BD%D1%8B%D0%B9%20%D1%81%D0%BF%D0%BE%D1%81%D0%BE%D0%B1%20%D1%81%D0%BD%D1%8F%D1%82%D1%8C%20%D1%81%D1%82%D1%80%D0%B5%D1%81%D1%81%20%D0%B2%20%D0%A1%D0%BE%D1%87%D0%B8
find here https://web-lumiwallet.com/
Bip39 Bip39 .
секс с милфами секс с милфами .
порно с чудовищами порно с чудовищами .
Купить дженерики в магазине https://dzhenerik-dapoksetin.ru/ с доставкой
гарантированное качество от производителя из Индии
Эти меры позволяют пациенту быстро и безопасно восстановиться, минимизируя негативные последствия запойного состояния.
Ознакомиться с деталями – kapelnica ot zapoya s vyezdom cena voronezh
Злоупотребление алкоголем в течение продолжительного времени приводит к состоянию, при котором человек теряет контроль над собой, а его организм подвергается серьезным нагрузкам. Последствия такого состояния проявляются на физическом и психическом уровнях: организм страдает от отравления, обезвоживания и сбоев в работе нервной системы, а человек теряет способность адекватно оценивать ситуацию. Выйти из этого состояния без медицинской помощи крайне сложно, так как требуется не только прекратить употребление алкоголя, но и восстановить нормальные функции организма.
Получить больше информации – narkologiya vyvod iz zapoya na domu
немки порно https://www.trax-nemeckoe1.ru .
Запой — это одно из наиболее тяжелых проявлений алкогольной зависимости, которое требует немедленного и квалифицированного вмешательства. В такие моменты близкие зачастую теряются и не знают, как помочь своему родному человеку. На помощь приходит наркологическая клиника «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, которая предоставляет профессиональную помощь в выводе из запоя. Мы понимаем, что лечение запоя требует не только медицинского подхода, но и психологической поддержки. Именно поэтому в нашей клинике пациент получает комплексную помощь, основанную на самых современных методах лечения.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – наркологический центр челябинск
Одной из распространенных проблем является запой, состояние, при котором человек длительное время бесконтрольно употребляет алкоголь, что приводит к тяжелой физической и психологической зависимости. Такое поведение чревато серьезными последствиями для здоровья, включая поражение внутренних органов, нервные расстройства и другие заболевания. Важно своевременно обратиться за профессиональной помощью, чтобы минимизировать риски и предотвратить осложнения.
Получить больше информации – narkologicheskaya klinika sankt-peterburg
После успешной детоксикации начинается этап реабилитации, который включает восстановление социального статуса пациента и формирование новых здоровых привычек. Мы предлагаем как групповые, так и индивидуальные занятия, направленные на изменение поведения и мышления, что способствует долгосрочному удержанию пациента от возвращения к зависимостям.
Подробнее тут – kapelnica ot zapoya v stacionare anonimno v moskve
Клиника предлагает гибкие варианты лечения, включая стационарное и амбулаторное. Стоимость услуг зависит от индивидуальных потребностей пациента, степени тяжести состояния и объемов необходимых процедур. Специалисты стремятся создать максимально комфортные условия для каждого пациента, обеспечивая прозрачное ценообразование и высокое качество обслуживания.
Получить больше информации – вывод из запоя
В таких ситуациях вывод из запоя на дому становится оптимальным решением, особенно если пациент не может или не хочет посещать стационар. Эта услуга позволяет получить медицинскую помощь в комфортной и привычной обстановке, что снижает уровень стресса и ускоряет процесс восстановления.
Ознакомиться с деталями – bystry vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare voronezh
секс японка https://japanxxx-video1.ru/ .
Вывод из запоя представляет собой важный этап в процессе лечения алкогольной зависимости. Это медицинская процедура, необходимая для устранения токсических веществ, накопленных в организме в результате длительного употребления алкоголя. Алкогольная зависимость может вызывать множество проблем, включая физические и психоэмоциональные расстройства. Своевременное вмешательство специалистов помогает минимизировать риски и способствует восстановлению здоровья пациента.
Подробнее тут – вывод из запоя в стационаре в рязани
диплом об окончании вуза купить
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой сложное и хроническое заболевание, которое влияет не только на физическое, но и на психологическое состояние пациента. Периоды запоя, влекущие за собой неконтролируемое употребление алкоголя, могут привести к опасным последствиям для здоровья и жизни. Абстинентные симптомы, такие как тремор, тошнота, головная боль и другие проявления, требуют немедленного медицинского вмешательства. В таких ситуациях важно не только быстро устранить физическое воздействие алкоголя, но и предоставить пациенту психологическую поддержку.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://www.vyvod-iz-zapoya-16.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-anonimno-v-krasnodare/
В современном мире зависимость становится все более распространенной проблемой. Стресс, жизненные трудности и финансовые проблемы часто провоцируют развитие таких серьезных состояний, как алкоголизм, наркомания и игромания. Наркологическая клиника “Второй Шанс” предоставляет помощь людям, столкнувшимся с этими заболеваниями. Основное направление работы клиники — восстановление здоровья пациентов, их социальная адаптация и предотвращение повторных рецидивов.
Детальнее – вывод из запоя круглосуточно наркология в санкт-петербурге
Вывод из запойного состояния – сложный процесс, включающий несколько последовательных этапов. Основная цель – детоксикация организма и восстановление его нормального функционирования. Важно, чтобы процессом руководили опытные специалисты, способные минимизировать последствия интоксикации и помочь человеку вернуться к здоровой жизни. Стоимость лечения зависит от выбранных методов и уровня медицинского обслуживания, а в клинике «Излечение» предлагаются доступные варианты с учетом индивидуальных потребностей пациентов.
Углубиться в тему – vyvod iz zapoya vyzov na dom v-krasnodare
Алкогольный запой – это серьёзное состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к тяжёлой интоксикации организма. Во время запоя нарушаются функции внутренних органов, страдает нервная система, и повышается риск развития опасных осложнений, таких как алкогольный делирий. Это состояние требует незамедлительного медицинского вмешательства.
Получить больше информации – вывод из запоя на дому недорого
Вывод из запоя представляет собой важный этап в процессе лечения алкогольной зависимости. Это медицинская процедура, необходимая для устранения токсических веществ, накопленных в организме в результате длительного употребления алкоголя. Алкогольная зависимость может вызывать множество проблем, включая физические и психоэмоциональные расстройства. Своевременное вмешательство специалистов помогает минимизировать риски и способствует восстановлению здоровья пациента.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – anonimny vyvod iz zapoya na domu v-ryazani
В таких ситуациях вывод из запоя на дому становится оптимальным решением, особенно если пациент не может или не хочет посещать стационар. Эта услуга позволяет получить медицинскую помощь в комфортной и привычной обстановке, что снижает уровень стресса и ускоряет процесс восстановления.
Ознакомиться с деталями – вывод из запоя круглосуточно в воронеже
Алкогольный запой — это тяжелое состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над количеством потребляемого алкоголя. Это приводит к сильной интоксикации, сбоям в работе органов и систем организма, а также серьезным психоэмоциональным расстройствам. Без должной медицинской помощи запой может вызвать ряд опасных последствий, включая алкогольный делирий и угрозу жизни. Поэтому при первых признаках запоя необходимо обратиться к профессионалам.
Подробнее тут – вывод из запоя круглосуточно наркология тверь
Алкогольный запой – это серьёзное состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к тяжёлой интоксикации организма. Во время запоя нарушаются функции внутренних органов, страдает нервная система, и повышается риск развития опасных осложнений, таких как алкогольный делирий. Это состояние требует незамедлительного медицинского вмешательства.
Подробнее тут – вывод из запоя с выездом цена екатеринбург
В этой статье мы расскажем о возможностях клиники для лечения алкогольной интоксикации круглосуточно, включая вывод из запоя в стационаре и на дому, а также о роли профессионалов, таких как нарколог, в процессе лечения.
Детальнее – вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно в краснодаре
Купить дженерики с доставкой на сайте https://dzhenerik-dapoxetine-kupit.ru/
большой выбор доступные цены
купить диплом о высшем в уфе 2orik-diploms.ru .
Запой — это одно из наиболее тяжелых проявлений алкогольной зависимости, которое требует немедленного и квалифицированного вмешательства. В такие моменты близкие зачастую теряются и не знают, как помочь своему родному человеку. На помощь приходит наркологическая клиника «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, которая предоставляет профессиональную помощь в выводе из запоя. Мы понимаем, что лечение запоя требует не только медицинского подхода, но и психологической поддержки. Именно поэтому в нашей клинике пациент получает комплексную помощь, основанную на самых современных методах лечения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare anonimno v-chelyabinske
Когда человек сталкивается с затяжными алкогольными эпизодами, ему необходима квалифицированная помощь. Специалисты наркологической клиники «Излечение» в Краснодаре разрабатывают индивидуальные методы вывода из этого состояния, создавая комфортные и безопасные условия для пациентов. Длительное употребление спиртного оказывает разрушительное воздействие на внутренние органы, приводит к психическим нарушениям и обостряет хронические болезни. В таких случаях медицинское вмешательство становится неотложной необходимостью.
Подробнее тут – narkologicheskaya klinika
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой состояние, при котором организм человека испытывает серьёзное воздействие этанола. Это приводит к нарушениям нормальной физиологической деятельности и ухудшению состояния здоровья. Анонимный вывод из запоя — это медицинская помощь, направленная на устранение последствий чрезмерного употребления алкоголя с соблюдением строгой конфиденциальности.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – anonimny vyvod iz zapoya na domu ekaterinburg
Клиника «Освобождение» в Рязани предоставляет услугу круглосуточного вывода из запоя на дому, что позволяет пациенту получить медицинскую помощь в привычной обстановке, избегая лишнего стресса, связанного с госпитализацией.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – вывод из запоя с выездом на дом
Запой – это состояние, возникающее из-за длительного употребления алкоголя и характеризующееся физической и психологической зависимостью. Оно требует комплексного медицинского вмешательства для устранения последствий и предотвращения дальнейшего ухудшения здоровья. Стационарное лечение в клинике «Освобождение» в Рязани – это эффективный способ вернуть пациента к нормальной жизни, предоставляя ему комфортные условия и круглосуточную помощь специалистов.
Разобраться лучше – вывод из запоя
Официальная покупка диплома вуза с сокращенной программой обучения в Москве
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой сложное и хроническое заболевание, которое влияет не только на физическое, но и на психологическое состояние пациента. Периоды запоя, влекущие за собой неконтролируемое употребление алкоголя, могут привести к опасным последствиям для здоровья и жизни. Абстинентные симптомы, такие как тремор, тошнота, головная боль и другие проявления, требуют немедленного медицинского вмешательства. В таких ситуациях важно не только быстро устранить физическое воздействие алкоголя, но и предоставить пациенту психологическую поддержку.
Разобраться лучше – вывод из запоя краснодар
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, необходимая для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Это состояние, часто характеризующееся физическими и психоэмоциональными нарушениями, требует профессионального вмешательства. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть разнообразными и варьироваться от легкой тревожности до серьезных нарушений в функционировании внутренних органов. Квалифицированная помощь в этот период позволяет минимизировать риски и значительно ускорить процесс выздоровления.
Подробнее тут – нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в челябинске
купить диплом нгту 2orik-diploms.ru .
Для достижения эффективных результатов в лечении запоя необходима квалифицированная помощь специалистов. Наркологическая клиника «Излечение» в Краснодаре предоставляет профессиональные услуги по выводу из запоя, гарантируя безопасность, комфорт и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Узнать больше – vyvod iz zapoya na domu kruglosutochno
Алкогольный запой — это серьезное заболевание, которое требует немедленного и профессионального вмешательства. Запой сопровождается не только физическими страданиями, но и эмоциональными трудностями. Процесс выведения из запоя требует срочного внимания, так как состояние пациента может ухудшиться, если не получить квалифицированную помощь вовремя. Наркологическая клиника «Излечение» в Краснодаре предоставляет круглосуточную помощь при алкогольном запое, чтобы восстановить здоровье пациента в самых сложных ситуациях.
Детальнее – vyvod iz zapoya na domu nedorogo
Looking for the current spinbetter promo code? Get bonus funds for bets and casino games. Easy activation, favorable conditions and real winnings are waiting for you. Hurry to use it!
Используйте актуальный промокод 1xbet и получите увеличенный бонус на первый депозит! Делайте ставки на спорт, играйте в казино и пользуйтесь эксклюзивными предложениями. Легкая регистрация и моментальные выплаты!
Запой – это состояние, возникающее из-за длительного употребления алкоголя и характеризующееся физической и психологической зависимостью. Оно требует комплексного медицинского вмешательства для устранения последствий и предотвращения дальнейшего ухудшения здоровья. Стационарное лечение в клинике «Освобождение» в Рязани – это эффективный способ вернуть пациента к нормальной жизни, предоставляя ему комфортные условия и круглосуточную помощь специалистов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – вывод из запоя с выездом
Алкогольный запой — это состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над своим потреблением алкоголя, что может вызвать серьезные физические и психологические проблемы. В таких ситуациях крайне важно получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь как можно скорее. Однако многие люди опасаются обращаться за помощью, переживая за свою репутацию и возможное раскрытие личной информации. В клинике «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже мы гарантируем анонимность на всех этапах лечения, сохраняя высокий уровень медицинской помощи и заботясь о каждом пациенте.
Изучить вопрос глубже – вывод из запоя с выездом на дом в воронеже
Злоупотребление алкоголем в течение продолжительного времени приводит к состоянию, при котором человек теряет контроль над собой, а его организм подвергается серьезным нагрузкам. Последствия такого состояния проявляются на физическом и психическом уровнях: организм страдает от отравления, обезвоживания и сбоев в работе нервной системы, а человек теряет способность адекватно оценивать ситуацию. Выйти из этого состояния без медицинской помощи крайне сложно, так как требуется не только прекратить употребление алкоголя, но и восстановить нормальные функции организма.
Получить дополнительные сведения – vyvod iz zapoya cena narkologiya
Алкогольный запой — это состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к токсической нагрузке на организм. Это опасное состояние требует не только быстрого медицинского вмешательства, но и внимательного подхода к восстановлению здоровья пациента. Процесс вывода из запоя включает в себя комплекс процедур, направленных на устранение последствий интоксикации и восстановление нормального функционирования организма. Важно учитывать, что стоимость этой процедуры может значительно варьироваться в зависимости от нескольких факторов.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-16.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-v-kruglosutochno-v-krasnodare/
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой сложное и хроническое заболевание, которое влияет не только на физическое, но и на психологическое состояние пациента. Периоды запоя, влекущие за собой неконтролируемое употребление алкоголя, могут привести к опасным последствиям для здоровья и жизни. Абстинентные симптомы, такие как тремор, тошнота, головная боль и другие проявления, требуют немедленного медицинского вмешательства. В таких ситуациях важно не только быстро устранить физическое воздействие алкоголя, но и предоставить пациенту психологическую поддержку.
Ознакомиться с деталями – narkologiya vyvod iz zapoya anonimno v-krasnodare
Наши наркологи приезжают к пациенту в удобное для него время и проводят необходимую терапию. Капельница от запоя помогает:
Изучить вопрос глубже – narkologiya kapelnica ot zapoya anonimno moskva
Вывод из запоя представляет собой важный этап в процессе лечения алкогольной зависимости. Это медицинская процедура, необходимая для устранения токсических веществ, накопленных в организме в результате длительного употребления алкоголя. Алкогольная зависимость может вызывать множество проблем, включая физические и психоэмоциональные расстройства. Своевременное вмешательство специалистов помогает минимизировать риски и способствует восстановлению здоровья пациента.
Выяснить больше – vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno ryazan
В таких ситуациях вывод из запоя на дому становится оптимальным решением, особенно если пациент не может или не хочет посещать стационар. Эта услуга позволяет получить медицинскую помощь в комфортной и привычной обстановке, что снижает уровень стресса и ускоряет процесс восстановления.
Изучить вопрос глубже – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom na dom v-voronezhe
Гизбо Казино — это платформа, которая привлекает внимание игроков широким ассортиментом азартных развлечений и выгодными бонусами. Здесь вы найдете слоты с прогрессивными джекпотами, настольные игры, а также турниры, которые проходят на регулярной основе Gizbo Casino
Welcome to our club – a place where dance becomes art!
We offer a variety of dance styles for all ages.
For more information, follow the link танго занятия
Group of professional coaches will help you develop skills and love for dance.
Принимать финансовые решения может быть сложно. Но с нашим каталогом финансовых продуктов это стало проще, чем когда-либо!
кредит для бизнеса
Мы собрали все лучшие финансовые продукты в одном месте, чтобы вы могли легко сравнить их и найти те, которые подходят именно вам. Наши экспертные обзоры и рейтинги помогут вам принять обоснованное решение, соответствующее вашим уникальным потребностям.
Независимо от того, ищете ли вы кредит наличными, дебетовую карту или инвестиционный счет, наш каталог финансовых продуктов поможет вам сделать правильный выбор.
Гизбо Казино — это платформа, которая привлекает внимание игроков широким ассортиментом азартных развлечений и выгодными бонусами. Здесь вы найдете слоты с прогрессивными джекпотами, настольные игры, а также турниры, которые проходят на регулярной основе Gizbo Casino
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся длительным и непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к формированию как физической, так и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния часто наблюдаются нарушения работы внутренних органов, что может привести к тяжелым последствиям, включая алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя — важный этап в процессе лечения зависимости, и его можно осуществлять как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от конкретных обстоятельств.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – вывод из запоя на дому цена санкт-петербург
Покупка школьного аттестата с упрощенной программой: что важно знать
Гизбо Казино — это платформа, которая привлекает внимание игроков широким ассортиментом азартных развлечений и выгодными бонусами. Здесь вы найдете слоты с прогрессивными джекпотами, настольные игры, а также турниры, которые проходят на регулярной основе казино Gizbo
Discover the world of comfort with our pools!
We offer a huge selection of pools, their installation and maintenance.
More detailed information on the link построить частный бассейн
Create an oasis at home with high-quality solutions.
Individual approach and guarantees for all work.
Вывод из запойного состояния – сложный процесс, включающий несколько последовательных этапов. Основная цель – детоксикация организма и восстановление его нормального функционирования. Важно, чтобы процессом руководили опытные специалисты, способные минимизировать последствия интоксикации и помочь человеку вернуться к здоровой жизни. Стоимость лечения зависит от выбранных методов и уровня медицинского обслуживания, а в клинике «Излечение» предлагаются доступные варианты с учетом индивидуальных потребностей пациентов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – вывод из запоя на дому цена в краснодаре
Дженерики для мужчин на сайте https://dzheneriki-viagra.ru быстрая доставка
широкий выбор по выгодным ценам
Запой — это тяжелое состояние, возникающее вследствие длительного и непрерывного употребления алкоголя, которое сопровождается физической и психической зависимостью. Это опасное явление требует незамедлительного вмешательства специалистов. Вывод из запоя — это комплексный процесс медицинской детоксикации, который включает в себя очищение организма от токсинов, нормализацию функций внутренних органов и поддержку психоэмоционального состояния пациента. В случае тяжелого запоя стационарное лечение становится оптимальным решением для безопасного и эффективного вывода из этого состояния. В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как проходит вывод из запоя в стационаре клиники «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, а также особенности анонимности, скорости лечения и участия нарколога.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – вывод из запоя на дому недорого в челябинске
Вывод из запоя представляет собой важный этап в процессе лечения алкогольной зависимости. Это медицинская процедура, необходимая для устранения токсических веществ, накопленных в организме в результате длительного употребления алкоголя. Алкогольная зависимость может вызывать множество проблем, включая физические и психоэмоциональные расстройства. Своевременное вмешательство специалистов помогает минимизировать риски и способствует восстановлению здоровья пациента.
Получить дополнительные сведения – наркологическая клиника рязань
Запой представляет собой состояние, характеризующееся длительным непрерывным употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к физической и психической зависимости. Этот процесс может длиться от нескольких дней до недель. Алкогольные напитки негативно влияют на функционирование внутренних органов, вызывая серьёзные нарушения, включая алкоголизм. При необходимости вывода из запоя важно обратиться за медицинской помощью, что можно осуществить на дому. В данной статье рассмотрим ключевые аспекты данной процедуры.
Подробнее – вывод из запоя в челябинске
Запой — это состояние, при котором человек не может прекратить употребление алкоголя на протяжении длительного времени, что вызывает физическую и психологическую зависимость. Это крайне опасное состояние, требующее немедленного вмешательства специалистов. Наркологическая клиника «Преображение» в Екатеринбурге предоставляет профессиональную помощь в лечении запоя, используя самые эффективные и безопасные методы.
Выяснить больше – srochny vyvod iz zapoya na domu v-ekaterinburge
Запой – это тяжелое состояние, возникающее из-за длительного и неконтролируемого употребления алкоголя. Оно характеризуется физической и психологической зависимостью, что приводит к серьезным последствиям для организма и психики. Для восстановления нормального самочувствия и здоровья необходимо профессиональное лечение. Одним из наиболее удобных и эффективных методов является вывод из запоя на дому.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – vyvod iz zapoya anonimno ryazan
Зависимость от алкоголя – серьезная проблема, требующая системного подхода и профессионального лечения. В клинике «Излечение» гарантируется полная конфиденциальность на всех этапах процесса, что позволяет пациентам чувствовать себя в безопасности. Лечение может проходить как в стационаре, так и на дому, при этом соблюдаются все условия для максимального комфорта.
Изучить вопрос глубже – bystry vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare krasnodar
Алкогольная зависимость — коварное заболевание, которое захватывает не только физическое здоровье, но и разрушает психику, лишает человека воли и заставляет его жить в плену у собственной зависимости. Запой — один из наиболее тяжелых периодов в жизни человека, столкнувшегося с алкоголизмом. Он характеризуется длительным и интенсивным употреблением спиртных напитков, приводящим к глубокой интоксикации организма, нарушению физиологических функций, психическим расстройствам, а также обострению сопутствующих заболеваний.
Подробнее тут – вывод из запоя срочно круглосуточно
Запойное состояние представляет собой серьёзную угрозу для здоровья, поскольку сопровождается тяжёлой интоксикацией организма и нарушением психоэмоционального состояния. Решение о лечении в стационаре клиники «Союз Здоровья» позволяет справиться с последствиями длительного употребления алкоголя, обеспечивая пациентам полный комплекс медицинской и психологической помощи.
Разобраться лучше – вывод из запоя круглосуточно в воронеже
sky pharmacy online drugstore review
Вывод из запоя представляет собой важный этап в процессе лечения алкогольной зависимости. Это медицинская процедура, необходимая для устранения токсических веществ, накопленных в организме в результате длительного употребления алкоголя. Алкогольная зависимость может вызывать множество проблем, включая физические и психоэмоциональные расстройства. Своевременное вмешательство специалистов помогает минимизировать риски и способствует восстановлению здоровья пациента.
Получить дополнительную информацию – наркологический центр в рязани
Запой — это состояние, при котором человек не может прекратить употребление алкоголя на протяжении длительного времени, что вызывает физическую и психологическую зависимость. Это крайне опасное состояние, требующее немедленного вмешательства специалистов. Наркологическая клиника «Преображение» в Екатеринбурге предоставляет профессиональную помощь в лечении запоя, используя самые эффективные и безопасные методы.
Получить дополнительную информацию – vyvod iz zapoya gorod ekaterinburg
Запой – это состояние, которое возникает вследствие длительного употребления алкоголя, приводящее к потере контроля над количеством выпиваемого и формированию как физической, так и психологической зависимости. Оно сопровождается серьёзными последствиями для здоровья и требует немедленного вмешательства.
Углубиться в тему – вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно в воронеже
Для достижения эффективных результатов в лечении запоя необходима квалифицированная помощь специалистов. Наркологическая клиника «Излечение» в Краснодаре предоставляет профессиональные услуги по выводу из запоя, гарантируя безопасность, комфорт и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – вывод из запоя с выездом цена в краснодаре
Злоупотребление алкоголем в течение продолжительного времени приводит к состоянию, при котором человек теряет контроль над собой, а его организм подвергается серьезным нагрузкам. Последствия такого состояния проявляются на физическом и психическом уровнях: организм страдает от отравления, обезвоживания и сбоев в работе нервной системы, а человек теряет способность адекватно оценивать ситуацию. Выйти из этого состояния без медицинской помощи крайне сложно, так как требуется не только прекратить употребление алкоголя, но и восстановить нормальные функции организма.
Подробнее тут – вывод из запоя капельница в краснодаре
Вывод из запойного состояния – сложный процесс, включающий несколько последовательных этапов. Основная цель – детоксикация организма и восстановление его нормального функционирования. Важно, чтобы процессом руководили опытные специалисты, способные минимизировать последствия интоксикации и помочь человеку вернуться к здоровой жизни. Стоимость лечения зависит от выбранных методов и уровня медицинского обслуживания, а в клинике «Излечение» предлагаются доступные варианты с учетом индивидуальных потребностей пациентов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – vyvod iz zapoya vrach na dom v-krasnodare
Запой – это тяжелое состояние, возникающее из-за длительного и неконтролируемого употребления алкоголя. Оно характеризуется физической и психологической зависимостью, что приводит к серьезным последствиям для организма и психики. Для восстановления нормального самочувствия и здоровья необходимо профессиональное лечение. Одним из наиболее удобных и эффективных методов является вывод из запоя на дому.
Получить дополнительную информацию – bystry vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare v-ryazani
Алкогольная зависимость — это длительное и прогрессирующее заболевание, при котором развивается как физическая, так и психическая зависимость от алкоголя. Одним из самых тяжелых проявлений болезни является запой — длительное употребление алкоголя, которое может сопровождаться нарушениями работы организма и абстинентным синдромом, представляющим серьезную угрозу для здоровья. Эффективное лечение запоя требует комплексного подхода, включающего медикаментозную терапию, психотерапию и реабилитационные мероприятия.
Углубиться в тему – vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare anonimno
купить аттестат в перми
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой состояние, при котором организм человека испытывает сильное воздействие этанола, что приводит к нарушению нормального функционирования физиологических систем. Это состояние может быть опасным и требует квалифицированной медицинской помощи. Вывод из запоя — важная медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение последствий чрезмерного употребления алкоголя и восстановление здоровья пациента.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom
В этой статье мы расскажем о возможностях клиники для лечения алкогольной интоксикации круглосуточно, включая вывод из запоя в стационаре и на дому, а также о роли профессионалов, таких как нарколог, в процессе лечения.
Разобраться лучше – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom na dom krasnodar
Дженерики на сайте https://ed-apteka.ru/ с доставкой по городу и области
курьером в день заказа по низким ценам
Вывод из запойного состояния – сложный процесс, включающий несколько последовательных этапов. Основная цель – детоксикация организма и восстановление его нормального функционирования. Важно, чтобы процессом руководили опытные специалисты, способные минимизировать последствия интоксикации и помочь человеку вернуться к здоровой жизни. Стоимость лечения зависит от выбранных методов и уровня медицинского обслуживания, а в клинике «Излечение» предлагаются доступные варианты с учетом индивидуальных потребностей пациентов.
Углубиться в тему – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom na dom
article https://myjaxxwallet.us/
Алкогольный запой — это серьезное заболевание, которое требует немедленного и профессионального вмешательства. Запой сопровождается не только физическими страданиями, но и эмоциональными трудностями. Процесс выведения из запоя требует срочного внимания, так как состояние пациента может ухудшиться, если не получить квалифицированную помощь вовремя. Наркологическая клиника «Излечение» в Краснодаре предоставляет круглосуточную помощь при алкогольном запое, чтобы восстановить здоровье пациента в самых сложных ситуациях.
Детальнее – вывод из запоя врач на дом
купить диплом в вологде
Зависимость — это серьёзная проблема, которая затрагивает не только человека, но и его семью и окружение. Алкоголизм, наркомания и другие виды зависимостей могут разрушить жизнь, но с профессиональной помощью можно вернуть её в русло нормального функционирования. Наркологическая клиника «Заря Будущего» в Санкт-Петербурге предлагает уникальные программы лечения зависимостей, которые сочетает медико-психологический подход, индивидуальные методики и квалифицированную поддержку.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – narkologicheskaya klinika
Алкоголизм — это хроническое прогрессирующее заболевание, связанное с физической и психической зависимостью от этанола. Запой, как его крайнее проявление, представляет собой длительное употребление алкоголя, сопровождающееся тяжелыми нарушениями работы организма, включая абстинентный синдром и потенциальные угрозы для жизни. Лечение запоя требует комплексного подхода, включающего медицинские процедуры, психотерапию и реабилитационные меры.
Получить дополнительные сведения – vyvod iz zapoya vrach na dom
Алкогольный запой — это состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над своим потреблением алкоголя, что может вызвать серьезные физические и психологические проблемы. В таких ситуациях крайне важно получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь как можно скорее. Однако многие люди опасаются обращаться за помощью, переживая за свою репутацию и возможное раскрытие личной информации. В клинике «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже мы гарантируем анонимность на всех этапах лечения, сохраняя высокий уровень медицинской помощи и заботясь о каждом пациенте.
Разобраться лучше – вывод из запоя круглосуточно наркология
Процесс возвращения к нормальной жизни после длительного употребления алкоголя играет ключевую роль в избавлении от зависимости. Медицинское сопровождение должно сочетаться с осознанным желанием человека изменить свою жизнь. Важно, чтобы лечение проходило в условиях, исключающих стресс и дискомфорт. Для этого предусмотрены как стационарные программы, так и возможность получить медицинскую помощь на дому. Такой вариант подходит тем, кто предпочитает находиться в привычной обстановке и избегать огласки.
Узнать больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-16.ru
Запой представляет собой состояние, характеризующееся длительным непрерывным употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к физической и психической зависимости. Этот процесс может длиться от нескольких дней до недель. Алкогольные напитки негативно влияют на функционирование внутренних органов, вызывая серьёзные нарушения, включая алкоголизм. При необходимости вывода из запоя важно обратиться за медицинской помощью, что можно осуществить на дому. В данной статье рассмотрим ключевые аспекты данной процедуры.
Получить дополнительную информацию – вывод из запоя цена наркология
Современное общество сталкивается с серьёзными вызовами, связанными с зависимостями. Алкоголизм, как одна из самых распространённых проблем, оказывает разрушительное воздействие на здоровье человека, разрушая семейные отношения и затрудняя социальную адаптацию. В такие моменты крайне важно обратиться за квалифицированной помощью.
Получить дополнительные сведения – вывод из запоя срочно круглосуточно в рязани
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой крайне опасное состояние, при котором организм страдает от токсического воздействия алкоголя. Это ведет к нарушению нормальных физиологических процессов и ухудшению общего состояния здоровья. Капельница от запоя — это медицинская процедура, направленная на выведение токсинов из организма и восстановление нормальной функции организма при соблюдении полной конфиденциальности.
Ознакомиться с деталями – быстрый вывод из запоя в стационаре
Запой — это одно из наиболее тяжелых проявлений алкогольной зависимости, которое требует немедленного и квалифицированного вмешательства. В такие моменты близкие зачастую теряются и не знают, как помочь своему родному человеку. На помощь приходит наркологическая клиника «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, которая предоставляет профессиональную помощь в выводе из запоя. Мы понимаем, что лечение запоя требует не только медицинского подхода, но и психологической поддержки. Именно поэтому в нашей клинике пациент получает комплексную помощь, основанную на самых современных методах лечения.
Узнать больше – наркология вывод из запоя анонимно
Алкогольная зависимость — это длительное и прогрессирующее заболевание, при котором развивается как физическая, так и психическая зависимость от алкоголя. Одним из самых тяжелых проявлений болезни является запой — длительное употребление алкоголя, которое может сопровождаться нарушениями работы организма и абстинентным синдромом, представляющим серьезную угрозу для здоровья. Эффективное лечение запоя требует комплексного подхода, включающего медикаментозную терапию, психотерапию и реабилитационные мероприятия.
Ознакомиться с деталями – наркология вывод из запоя анонимно тверь
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой крайне опасное состояние, при котором организм страдает от токсического воздействия алкоголя. Это ведет к нарушению нормальных физиологических процессов и ухудшению общего состояния здоровья. Капельница от запоя — это медицинская процедура, направленная на выведение токсинов из организма и восстановление нормальной функции организма при соблюдении полной конфиденциальности.
Подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya vyzov na dom v-tveri
Зависимость от алкоголя – серьезная проблема, требующая системного подхода и профессионального лечения. В клинике «Излечение» гарантируется полная конфиденциальность на всех этапах процесса, что позволяет пациентам чувствовать себя в безопасности. Лечение может проходить как в стационаре, так и на дому, при этом соблюдаются все условия для максимального комфорта.
Углубиться в тему – vyvod iz zapoya anonimno
Алкогольный запой – это серьёзное состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к тяжёлой интоксикации организма. Во время запоя нарушаются функции внутренних органов, страдает нервная система, и повышается риск развития опасных осложнений, таких как алкогольный делирий. Это состояние требует незамедлительного медицинского вмешательства.
Подробнее – вывод из запоя на дому цена
Sildenafil generic viagra on line pharmacy Pharmacy Online
Продажа дженериков на сайте https://generic-dapoxetine.ru/ широкий выбор
по доступным ценам быстрая доставка по городу и области
диплом куплю диплом куплю .
https://bip39-phrase.blogspot.com/2025/02/bip39-world-list-2048.html
Online betting has become increasingly popular in the Philippines, with many sports enthusiasts and casual bettors turning to online sportsbooks for their betting needs. One of the leading online bookmakers in the country is 1xBet, which offers a wide range of sports betting options and exciting promotions for its users https://www.hovawart24.de/unlock-exclusive-rewards-with-the-1xbet-official/
1Win first-time bonus is one of the best opportunities for bettors in 2025. With a 500% boost on your first deposit and the ability to start betting https://gabumbi.com/read-blog/14056
Online betting has become increasingly popular in the Philippines, with many sports enthusiasts and casual bettors turning to online sportsbooks for their betting needs. One of the leading online bookmakers in the country is 1xBet, which offers a wide range of sports betting options and exciting promotions for its users http://demo69.com1.vn/2024/09/25/maximize-your-winnings-with-the-1xbet-promo-code-2/
1Win first-time bonus is one of the best opportunities for bettors in 2025. With a 500% boost on your first deposit and the ability to start betting http://malaysiapal.com/read-blog/8170
Online betting has become increasingly popular in the Philippines, with many sports enthusiasts and casual bettors turning to online sportsbooks for their betting needs. One of the leading online bookmakers in the country is 1xBet, which offers a wide range of sports betting options and exciting promotions for its users http://www.simobb.com/top-benefits-of-the-promo-code-1xbet-3/
1Win first-time bonus is one of the best opportunities for bettors in 2025. With a 500% boost on your first deposit and the ability to start betting https://community.wongcw.com/blogs/948063/SpinBetter-Promo-Code-2025-Unlock-Exclusive-Bonuses-for-Your-First
The most comprehensive bip39 world list for securely creating and restoring cryptocurrency wallets. Learn how mnemonic coding works and protect your digital assets!
moving service reviews Prague moving to Czech Republic
купить аттестат об окончании 11 классов
автошкола красноярск цена – Лучшая автошкола Красноярска, Права категории C Красноярск получить
сколько стоит заказать кандидатскую диссертацию – Заказать шпаргалку, заказать научную статью для публикации
Misoprostol sale http://canadianpharmacymall.net/ Viagra us pharmacy fedex delivery
Большой выбор дженериков на сайте https://generic-pills.ru/ быстрая доставка
доступные цены
https://dubllikat.ru/
Portable Balancing & Vibration Analysis with Balanset-1A
Experiencing excessive vibrations in your equipment? This can lead to rapid wear, breakdowns, and costly downtime. We have the solution!
Portable Balancer & Vibration Analyzer Balanset-1A is a compact yet powerful tool for precise rotor, shaft, turbine, and machinery balancing.
Eliminates harmful vibrations and extends equipment lifespan
Easy to use – no special training required
Lightweight & portable – ideal for on-site work
Suitable for multiple industries: agriculture, manufacturing, heavy machinery
Complete set with software and sensors available now.
Order today on eBay!
Invest in reliability and smooth operation of your equipment!
Наслаждайтесь игрой в любое время и в любом месте – Olymp Casino адаптирован под мобильные устройства. Удобный интерфейс и высокая производительность позволяют комфортно играть как со смартфона, так и с планшета без потери качества https://shopster.kz/
Наслаждайтесь игрой в любое время и в любом месте – Olymp Casino адаптирован под мобильные устройства. Удобный интерфейс и высокая производительность позволяют комфортно играть как со смартфона, так и с планшета без потери качества https://shopster.kz/
Промокод 1xBet 2025: 1XFREE777 используйте код при регистрации, внесите депозит от 100 рублей и получите бонус +100% (до 32500 рублей), а также приветственный пакет в казино до 1500 евро + 150 фриспинов для игры в разделе азартных игр 1хБет. Бонусный код 1xBet дает возможность получить бонусы при регистрации на сайте букмекерской конторы https://rotoruanz.ru/pags/sovety_po_prohoghdeniyu_mage_knight_apocalypse_osnovnye_missii_057.html
Наслаждайтесь игрой в любое время и в любом месте – Olymp Casino адаптирован под мобильные устройства. Удобный интерфейс и высокая производительность позволяют комфортно играть как со смартфона, так и с планшета без потери качества olymp casino сайт
Промокод 1xBet 2025: 1XFREE777 используйте код при регистрации, внесите депозит от 100 рублей и получите бонус +100% (до 32500 рублей), а также приветственный пакет в казино до 1500 евро + 150 фриспинов для игры в разделе азартных игр 1хБет. Бонусный код 1xBet дает возможность получить бонусы при регистрации на сайте букмекерской конторы https://www.anak2u.com.my/pages/melbet__valid_2022__promo_code_india.html
диплом купить
Промокод 1xBet 2025: 1XFREE777 используйте код при регистрации, внесите депозит от 100 рублей и получите бонус +100% (до 32500 рублей), а также приветственный пакет в казино до 1500 евро + 150 фриспинов для игры в разделе азартных игр 1хБет. Бонусный код 1xBet дает возможность получить бонусы при регистрации на сайте букмекерской конторы http://skags.ru/doc/pages/promokod_1xbet_na_segodnya_pri_registracii.html
Зависимость — это хроническое заболевание, требующее долгосрочного лечения и регулярной поддержки. В клинике используют современные научные методы в наркологии и психотерапии, предлагая помощь на всех этапах — от диагностики до реабилитации. Команда профессионалов работает с каждым пациентом индивидуально, обеспечивая комплексный подход к терапии.
Детальнее – vyvod iz zapoya
Процедура, как правило, занимает от 1 до 2 часов, и после её завершения большинство пациентов чувствуют заметное улучшение самочувствия. В капельницу входят растворы для восстановления водного баланса, препараты, способствующие очищению печени и почек, а также витамины и антиоксиданты для общего восстановления организма.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – капельница от запоя анонимно недорого в воронеже
Заказать дженерики в нашем магазине https://generikonline.ru/ с доставкой
в день покупки по доступным ценам
Запой представляет собой состояние, связанное с длительным употреблением алкогольных напитков, что приводит к значительным физическим и психическим расстройствам. Это явление формирует зависимость, оказывая негативное воздействие на здоровье. Вывод из запоя в стационаре становится необходимостью для восстановительных мероприятий, направленных на реабилитацию пациента. В этой статье рассматриваются аспекты анонимного вывода, скорость процедур, а также роль нарколога в процессе лечения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – anonimny vyvod iz zapoya na domu
stehovani s garanci bezpecne stehovani
купить диплом высшее старого купить диплом высшее старого .
Алкогольная зависимость — это серьезная проблема, требующая немедленного вмешательства. Если вы или ваши близкие столкнулись с запоем, важно получить профессиональную помощь как можно скорее, чтобы избежать ухудшения здоровья. Наркологическая клиника «Шаг к Трезвости» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вывода из запоя на дому, что является удобным и эффективным решением для тех, кто не может или не хочет посещать стационар.
Углубиться в тему – вывод из запоя анонимно в краснодаре
Алкогольная зависимость — это серьезная проблема, требующая немедленного вмешательства. Если вы или ваши близкие столкнулись с запоем, важно получить профессиональную помощь как можно скорее, чтобы избежать ухудшения здоровья. Наркологическая клиника «Шаг к Трезвости» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вывода из запоя на дому, что является удобным и эффективным решением для тех, кто не может или не хочет посещать стационар.
Получить дополнительные сведения – vyvod iz zapoya kapelnica na domu v-krasnodare
Запойное состояние представляет собой серьёзную угрозу для здоровья, поскольку сопровождается тяжёлой интоксикацией организма и нарушением психоэмоционального состояния. Решение о лечении в стационаре клиники «Союз Здоровья» позволяет справиться с последствиями длительного употребления алкоголя, обеспечивая пациентам полный комплекс медицинской и психологической помощи.
Разобраться лучше – вывод из запоя вызов на дом
Мы понимаем, что успешное лечение невозможно без индивидуального подхода. Каждый случай уникален, поэтому мы разрабатываем персонализированные программы, учитывающие особенности каждого человека. Наши специалисты проводят детальное обследование и подбирают оптимальные методы лечения, обеспечивая комплексное внимание к состоянию пациента.
Изучить вопрос глубже – anonimnaya kapelnica ot zapoya na domu v voronezhe
The basis of any high-quality erotic massage is known to be professional masseuses who are skilled in various massage techniques. Our massage salon provides a wide selection of beautiful and slender models, among which you are certain to find the only one that fully meets your tastes, needs, interests and requirements nude massage new york
The basis of any high-quality erotic massage is known to be professional masseuses who are skilled in various massage techniques. Our massage salon provides a wide selection of beautiful and slender models, among which you are certain to find the only one that fully meets your tastes, needs, interests and requirements https://nuru-massage-ny.com/
Полезная информация как официально купить диплом о высшем образовании
The basis of any high-quality erotic massage is known to be professional masseuses who are skilled in various massage techniques. Our massage salon provides a wide selection of beautiful and slender models, among which you are certain to find the only one that fully meets your tastes, needs, interests and requirements https://nuru-massage-ny.com/
диплом врача купить диплом врача купить .
Клиника «Шаг к Трезвости» в Краснодаре предлагает анонимный вывод из запоя, обеспечивая полную конфиденциальность и безопасность на каждом этапе лечения. Мы понимаем, что для многих людей важно сохранить свою личную информацию в тайне, и гарантируем, что все данные о пациенте и его состоянии здоровья останутся закрытыми. Независимо от того, выбрал ли пациент стационарное лечение или вывод из запоя на дому, мы обеспечиваем высококачественную медицинскую помощь с полным соблюдением принципов конфиденциальности.
Подробнее тут – вывод из запоя цена
Купить дженерики на сайте https://krolik78.ru/ с доставкой курьером
высокое качество производства Индии
Цікавлять новобудови Україна? Сучасні квартири з панорамними вікнами, зачиненими дворами та зручним розташуванням. Вибирайте комфортне житло з найкращими умовами покупки!
Останні актуальні новини світу 2025 цілодобово оперативні події, важливі рішення, міжнародна політика та економіка. Все, що потрібно знати про життя країни, в одному місці!
Вывод из запоя — это не только помощь в улучшении самочувствия, но и важный этап на пути к лечению зависимости. Обратитесь к нам, если:
Подробнее – kapelnica ot zapoya kruglosutochno v voronezhe
navigate to this website https://jaxx-liberty.com
Вывод из запоя представляет собой важный этап в процессе лечения алкогольной зависимости. Это медицинская процедура, необходимая для устранения токсических веществ, накопленных в организме в результате длительного употребления алкоголя. Алкогольная зависимость может вызывать множество проблем, включая физические и психоэмоциональные расстройства. Своевременное вмешательство специалистов помогает минимизировать риски и способствует восстановлению здоровья пациента.
Углубиться в тему – вывод из запоя капельница на дому рязань
В современном обществе проблема алкоголизма остаётся одной из самых острых, требуя профессионального и комплексного подхода к лечению. Наркологическая клиника “Трезвый Мир” в Воронеже и Воронежской области предлагает эффективное решение для тех, кто столкнулся с запоем и стремится вернуть себе ясность ума и здоровье. Одной из ключевых методик, используемых в нашей клинике, является капельница от запоя – безопасный и быстрый способ восстановить организм и начать путь к трезвости.
Изучить вопрос глубже – капельница от запоя в стационаре анонимно
these details https://jaxx-wallet.net
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, необходимая для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Это состояние, часто характеризующееся физическими и психоэмоциональными нарушениями, требует профессионального вмешательства. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть разнообразными и варьироваться от лёгкой тревожности до серьёзных нарушений в функционировании внутренних органов. Квалифицированная помощь в этот период позволяет минимизировать риски и значительно ускорить процесс выздоровления.
Углубиться в тему – narkologiya vyvod iz zapoya anonimno v-voronezhe
Проблема зависимостей остаётся актуальной в современном обществе. С каждым годом увеличивается число людей, страдающих от алкоголизма, наркомании и других форм зависимостей, что негативно отражается на их жизни и благополучии близких. Зависимость — это не просто физическое заболевание, но и глубокая психологическая проблема. Для эффективного лечения требуется помощь профессионалов, способных обеспечить комплексный подход.
Выяснить больше – вывод из запоя капельница на дому воронеж
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, необходимая для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Это состояние, часто характеризующееся физическими и психоэмоциональными нарушениями, требует профессионального вмешательства. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть разнообразными и варьироваться от лёгкой тревожности до серьёзных нарушений в функционировании внутренних органов. Квалифицированная помощь в этот период позволяет минимизировать риски и значительно ускорить процесс выздоровления.
Углубиться в тему – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-11.ru
online pharmacy uk no prescription Buy wellbutrin xl without prescription
Алкоголизм — это хроническое заболевание, которое характеризуется патологической зависимостью от этанола. Периоды запоя, когда человек неконтролируемо потребляет алкоголь, могут привести к разнообразным медицинским осложнениям, как физическим, так и психологическим. Запой становится не только причиной ухудшения здоровья, но и причиной множества социальных и личных проблем. На этом фоне возникает необходимость вывода из запоя, процесс, который должен учитывать индивидуальные особенности пациента. Важно, что анонимность в реабилитации играет ключевую роль, помогая избежать стигматизации и увеличивая шансы на успешное восстановление.
Получить дополнительную информацию – вывод из запоя врач на дом рязань
“Наркозависимость разрушила мою жизнь. Я потратила все силы, и не знала, что делать дальше. В клинике “Пульс жизни” я получила необходимую помощь. Программа лечения действительно работает, и я снова чувствую себя свободной.”— Мария, 29 лет
Ознакомиться с деталями – anonimnaya kapelnica ot zapoya na domu
Выведение из запоя – это процесс, включающий несколько этапов. Симптомы могут варьироваться от тревожности и бессонницы до серьезных психических расстройств. Только профессиональный подход и современные медицинские технологии помогают минимизировать риски, стабилизировать состояние и избежать осложнений.
Подробнее тут – вывод из запоя анонимно недорого санкт-петербург
Купить диплом в Верхней Пышме
Наркологическая клиника «Освобождение» в Рязани предлагает профессиональные услуги по выводу из запоя и комплексной реабилитации. Мы понимаем, что зависимость — это болезнь, требующая индивидуального подхода и поддержки не только для пациента, но и для его близких.
Подробнее – вывод из запоя на дому рязань
Проблема зависимостей остаётся актуальной в современном обществе. С каждым годом увеличивается число людей, страдающих от алкоголизма, наркомании и других форм зависимостей, что негативно отражается на их жизни и благополучии близких. Зависимость — это не просто физическое заболевание, но и глубокая психологическая проблема. Для эффективного лечения требуется помощь профессионалов, способных обеспечить комплексный подход.
Узнать больше – bystry vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare
Процедура, как правило, занимает от 1 до 2 часов, и после её завершения большинство пациентов чувствуют заметное улучшение самочувствия. В капельницу входят растворы для восстановления водного баланса, препараты, способствующие очищению печени и почек, а также витамины и антиоксиданты для общего восстановления организма.
Углубиться в тему – narkologiya kapelnica ot zapoya na domu v voronezhe
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой серьёзную медицинскую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запойное состояние характеризуется длительным и бесконтрольным потреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к возникновению как физической, так и психической зависимости. Данное явление может вызвать нарушения в работе внутренних органов, значительно увеличивая вероятность развития алкогольного делирия, который представляет собой острое состояние, требующее неотложной медицинской помощи. Вывод из запоя это ключевая часть лечения зависимости, которая может осуществляться как в стационаре, так и в амбулаторных условиях, в зависимости от конкретной ситуации и состояния пациента.
Получить дополнительную информацию – вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
Запой – это тяжелое состояние, возникающее из-за длительного и неконтролируемого употребления алкоголя. Оно характеризуется физической и психологической зависимостью, что приводит к серьезным последствиям для организма и психики. Для восстановления нормального самочувствия и здоровья необходимо профессиональное лечение. Одним из наиболее удобных и эффективных методов является вывод из запоя на дому.
Получить больше информации – вывод из запоя цена наркология
Качественные дженерики купить на сайте https://levitralife.ru/ с доставкой
в день покупки отправка в другие регионы
Запой — это тяжелое состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над количеством употребляемого алкоголя, что приводит к серьезным нарушениям здоровья. Процесс вывода из запоя требует профессионального подхода, медицинского контроля и тщательного восстановления организма. Наркологическая клиника «Шаг к Трезвости» в Краснодаре предлагает квалифицированную помощь для тех, кто нуждается в срочном и безопасном выходе из запоя. Мы предоставляем комплексное лечение, ориентированное на каждый этап восстановления, с максимальной заботой о здоровье пациента.
Детальнее – vyvod iz zapoya vrach na dom krasnodar
Алкоголизм — это хроническое заболевание, которое характеризуется патологической зависимостью от этанола. Периоды запоя, когда человек неконтролируемо потребляет алкоголь, могут привести к разнообразным медицинским осложнениям, как физическим, так и психологическим. Запой становится не только причиной ухудшения здоровья, но и причиной множества социальных и личных проблем. На этом фоне возникает необходимость вывода из запоя, процесс, который должен учитывать индивидуальные особенности пациента. Важно, что анонимность в реабилитации играет ключевую роль, помогая избежать стигматизации и увеличивая шансы на успешное восстановление.
Подробнее тут – вывод из запоя на дому цена рязань
Запой — это длительное, неконтролируемое употребление алкоголя, часто сопровождающееся тяжелыми физическими и психоэмоциональными симптомами. Капельница от запоя является неотъемлемой частью выведения пациента из состояния алкогольной интоксикации и восстановления его здоровья. Она помогает быстро восстановить водно-солевой баланс, вывести токсины, снизить симптомы абстиненции и улучшить общее самочувствие пациента.
Подробнее – капельница от запоя в стационаре в воронеже
Продажа инструментов для дома profimaster58.ru/ строительства и ремонта! Огромный выбор ручного и электроинструмента, выгодные цены, акции и быстрая доставка. Найдите все необходимое в одном месте!
elon casino bangladesh elon casino bangladesh .
When it comes to gambling online, understanding the legality and security of platforms like Royal Reels Casino is crucial for players. Royal Reels operates under Australian regulations, ensuring compliance with local laws. Additionally, their advanced encryption technology safeguards your personal and financial information royal reels bonus codes for existing players
elon casino giri? http://eloncasinofun.com .
Free and reliable nudify ai tool to create images with AI? The Best Free AI Nudify is the best choice for creating nude photos with privacy and quality guarantee.
When it comes to gambling online, understanding the legality and security of platforms like Royal Reels Casino is crucial for players. Royal Reels operates under Australian regulations, ensuring compliance with local laws. Additionally, their advanced encryption technology safeguards your personal and financial information https://royalreels101.com/
online pharmacies for generic amoxil
When it comes to gambling online, understanding the legality and security of platforms like Royal Reels Casino is crucial for players. Royal Reels operates under Australian regulations, ensuring compliance with local laws. Additionally, their advanced encryption technology safeguards your personal and financial information https://royalreels101.com/
Современное общество сталкивается с серьёзными вызовами, связанными с зависимостями. Алкоголизм, как одна из самых распространённых проблем, оказывает разрушительное воздействие на здоровье человека, разрушая семейные отношения и затрудняя социальную адаптацию. В такие моменты крайне важно обратиться за квалифицированной помощью.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – быстрый вывод из запоя в стационаре рязань
Алкогольный запой — это состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к токсической нагрузке на организм. Это опасное состояние требует не только быстрого медицинского вмешательства, но и внимательного подхода к восстановлению здоровья пациента. Процесс вывода из запоя включает в себя комплекс процедур, направленных на устранение последствий интоксикации и восстановление нормального функционирования организма. Важно учитывать, что стоимость этой процедуры может значительно варьироваться в зависимости от нескольких факторов.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya vyzov na dom v-krasnodare
Наркологическая клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже специализируется на лечении алкогольной зависимости и предлагает профессиональные услуги по выводу из запоя. Мы стремимся создать атмосферу доверия, где каждый пациент сможет получить необходимую поддержку.
Подробнее тут – narkologicheskaya klinika v-voronezhe
Для достижения эффективных результатов в лечении запоя необходима квалифицированная помощь специалистов. Наркологическая клиника «Излечение» в Краснодаре предоставляет профессиональные услуги по выводу из запоя, гарантируя безопасность, комфорт и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Подробнее тут – vyvod iz zapoya srochno kruglosutochno v-krasnodare
Запойное состояние представляет собой серьёзную угрозу для здоровья, поскольку сопровождается тяжёлой интоксикацией организма и нарушением психоэмоционального состояния. Решение о лечении в стационаре клиники «Союз Здоровья» позволяет справиться с последствиями длительного употребления алкоголя, обеспечивая пациентам полный комплекс медицинской и психологической помощи.
Получить дополнительную информацию – вывод из запоя на дому цена в воронеже
Алкоголизм — это хроническое заболевание, которое характеризуется патологической зависимостью от этанола. Периоды запоя, когда человек неконтролируемо потребляет алкоголь, могут привести к разнообразным медицинским осложнениям, как физическим, так и психологическим. Запой становится не только причиной ухудшения здоровья, но и причиной множества социальных и личных проблем. На этом фоне возникает необходимость вывода из запоя, процесс, который должен учитывать индивидуальные особенности пациента. Важно, что анонимность в реабилитации играет ключевую роль, помогая избежать стигматизации и увеличивая шансы на успешное восстановление.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – вывод из запоя анонимно недорого рязань
Запой – это состояние, которое возникает вследствие длительного употребления алкоголя, приводящее к потере контроля над количеством выпиваемого и формированию как физической, так и психологической зависимости. Оно сопровождается серьёзными последствиями для здоровья и требует немедленного вмешательства.
Подробнее тут – vyvod iz zapoya kapelnica na domu voronezh
диплом колледжа купить
Компания- фирма-производитель зарабатывает доход только через продажи своей продукции.
Партнеры производителя обретают доход от реализации продукции через людей, которые благодаря им выучились
данному бизнесу.
» https://multi-level-marketing.ru/
» https://t.me/siberian_wellnass_rf
Этот бизнес необычный, непривычный для многих,
но при грамотном подходе надежный, стабильный и интересный.
Основной движущей силой вашего бизнеса должны стать лидерские качества
и умение мотивировать…
Для достижения эффективных результатов в лечении запоя необходима квалифицированная помощь специалистов. Наркологическая клиника «Излечение» в Краснодаре предоставляет профессиональные услуги по выводу из запоя, гарантируя безопасность, комфорт и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Подробнее – вывод из запоя срочно круглосуточно краснодар
Запой – это состояние, которое возникает вследствие длительного употребления алкоголя, приводящее к потере контроля над количеством выпиваемого и формированию как физической, так и психологической зависимости. Оно сопровождается серьёзными последствиями для здоровья и требует немедленного вмешательства.
Выяснить больше – вывод из запоя на дому цена
Алкогольная зависимость — это серьезная проблема, требующая немедленного вмешательства. Если вы или ваши близкие столкнулись с запоем, важно получить профессиональную помощь как можно скорее, чтобы избежать ухудшения здоровья. Наркологическая клиника «Шаг к Трезвости» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вывода из запоя на дому, что является удобным и эффективным решением для тех, кто не может или не хочет посещать стационар.
Детальнее – vyvod iz zapoya kapelnica na domu
Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся утратой контроля над употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к тяжелой интоксикации организма. Вывод из запоя — это комплексный процесс, направленный на устранение последствий интоксикации и восстановление нормального функционирования организма. Цена данной процедуры может значительно различаться в зависимости от нескольких факторов, и в этой статье мы подробно рассмотрим, что влияет на стоимость вывода из запоя в Краснодаре, в том числе в клинике «Шаг к Трезвости».
Подробнее можно узнать тут – вывод из запоя врач на дом краснодар
Desde 2019, a Mostbet Portugal tem se consolidado como uma excelente escolha para os jogadores portugueses que buscam formas seguras e divertidas de apostar e jogar nos casinos online e ao vivo. Com uma ampla seleção de jogos, apostas esportivas, esports e apostas em esportes virtuais, a plataforma oferece um catálogo premium de uma marca licenciada e confiável. Confiança, inteligência e lealdade são os pilares que sustentam a Mostbet Casino, que ainda proporciona bônus e promoções exclusivas, métodos de pagamento locais reconhecidos e ferramentas para um jogo responsável: Mostbet Portugal
Алкогольная зависимость — это серьезная проблема, требующая немедленного вмешательства. Если вы или ваши близкие столкнулись с запоем, важно получить профессиональную помощь как можно скорее, чтобы избежать ухудшения здоровья. Наркологическая клиника «Шаг к Трезвости» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вывода из запоя на дому, что является удобным и эффективным решением для тех, кто не может или не хочет посещать стационар.
Изучить вопрос глубже – vyvod iz zapoya kapelnica na domu
грузчик нанять грузчики срочно
Вывод из запоя представляет собой важный этап в процессе лечения алкогольной зависимости. Это медицинская процедура, необходимая для устранения токсических веществ, накопленных в организме в результате длительного употребления алкоголя. Алкогольная зависимость может вызывать множество проблем, включая физические и психоэмоциональные расстройства. Своевременное вмешательство специалистов помогает минимизировать риски и способствует восстановлению здоровья пациента.
Углубиться в тему – вывод из запоя с выездом на дом
Запой представляет собой состояние, связанное с длительным употреблением алкогольных напитков, что приводит к значительным физическим и психическим расстройствам. Это явление формирует зависимость, оказывая негативное воздействие на здоровье. Вывод из запоя в стационаре становится необходимостью для восстановительных мероприятий, направленных на реабилитацию пациента. В этой статье рассматриваются аспекты анонимного вывода, скорость процедур, а также роль нарколога в процессе лечения.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya na domu nedorogo kapelnica v-krasnodare
диплом купить в белгороде
Качественные дженерики для мужчин на сайте https://medmens.ru большой
выбор доступные цены быстрая доставка
Запой — это тяжелое состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над количеством употребляемого алкоголя, что приводит к серьезным нарушениям здоровья. Процесс вывода из запоя требует профессионального подхода, медицинского контроля и тщательного восстановления организма. Наркологическая клиника «Шаг к Трезвости» в Краснодаре предлагает квалифицированную помощь для тех, кто нуждается в срочном и безопасном выходе из запоя. Мы предоставляем комплексное лечение, ориентированное на каждый этап восстановления, с максимальной заботой о здоровье пациента.
Изучить вопрос глубже – srochny vyvod iz zapoya na domu krasnodar
Особенно опасны длительные запои, когда человек в течение нескольких дней бесконтрольно употребляет алкоголь. Такое состояние разрушает организм, перегружает печень, сердце и нервную систему, может вызывать тяжелые осложнения, в том числе психические расстройства. Выйти из запоя самостоятельно практически невозможно и крайне рискованно. Важно своевременно обратиться за медицинской помощью, чтобы избежать серьезных последствий.
Подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya srochno kruglosutochno v-sankt-peterburge
Вывод из запоя — это не только помощь в улучшении самочувствия, но и важный этап на пути к лечению зависимости. Обратитесь к нам, если:
Получить дополнительную информацию – narkologicheski centr voronezh
Зависимость – это сложное испытание, с которым сталкиваются люди во всём мире. Ежедневные стрессы, проблемы в семье и на работе, финансовые трудности часто становятся почвой для развития пагубных привычек, таких как алкоголизм, наркомания и игромания. Медицинский центр «Второй Шанс» предоставляет помощь тем, кто хочет избавиться от этих состояний, вернуть здоровье и научиться жить без разрушительных зависимостей.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-14.ru
Зависимость – это сложное испытание, с которым сталкиваются люди во всём мире. Ежедневные стрессы, проблемы в семье и на работе, финансовые трудности часто становятся почвой для развития пагубных привычек, таких как алкоголизм, наркомания и игромания. Медицинский центр «Второй Шанс» предоставляет помощь тем, кто хочет избавиться от этих состояний, вернуть здоровье и научиться жить без разрушительных зависимостей.
Подробнее – нарколог на дом вывод из запоя
Запой – это тяжелое состояние, возникающее из-за длительного и неконтролируемого употребления алкоголя. Оно характеризуется физической и психологической зависимостью, что приводит к серьезным последствиям для организма и психики. Для восстановления нормального самочувствия и здоровья необходимо профессиональное лечение. Одним из наиболее удобных и эффективных методов является вывод из запоя на дому.
Углубиться в тему – vyvod iz zapoya na domu cena v-ryazani
Запой представляет собой состояние, связанное с длительным употреблением алкогольных напитков, что приводит к значительным физическим и психическим расстройствам. Это явление формирует зависимость, оказывая негативное воздействие на здоровье. Вывод из запоя в стационаре становится необходимостью для восстановительных мероприятий, направленных на реабилитацию пациента. В этой статье рассматриваются аспекты анонимного вывода, скорость процедур, а также роль нарколога в процессе лечения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – narkologiya vyvod iz zapoya anonimno
Вывод из запоя представляет собой важный этап в процессе лечения алкогольной зависимости. Это медицинская процедура, необходимая для устранения токсических веществ, накопленных в организме в результате длительного употребления алкоголя. Алкогольная зависимость может вызывать множество проблем, включая физические и психоэмоциональные расстройства. Своевременное вмешательство специалистов помогает минимизировать риски и способствует восстановлению здоровья пациента.
Ознакомиться с деталями – narkologiya vyvod iz zapoya na domu
Алкогольная зависимость — коварное заболевание, которое захватывает не только физическое здоровье, но и разрушает психику, лишает человека воли и заставляет его жить в плену у собственной зависимости. Запой — один из наиболее тяжелых периодов в жизни человека, столкнувшегося с алкоголизмом. Он характеризуется длительным и интенсивным употреблением спиртных напитков, приводящим к глубокой интоксикации организма, нарушению физиологических функций, психическим расстройствам, а также обострению сопутствующих заболеваний.
Получить больше информации – vyvod iz zapoya kapelnica v-krasnodare
Как безопасно купить диплом колледжа или ПТУ в России, что важно знать
Use the proven bip39 standard to protect your assets and easily restore access to your finances. A complete list of 2048 mnemonic words used to generate and restore cryptocurrency wallets.
купить аттестат в москве за 11 класс
Для достижения эффективных результатов в лечении запоя необходима квалифицированная помощь специалистов. Наркологическая клиника «Излечение» в Краснодаре предоставляет профессиональные услуги по выводу из запоя, гарантируя безопасность, комфорт и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Разобраться лучше – vyvod iz zapoya na domu nedorogo kapelnica krasnodar
Алкогольная зависимость — это не просто привычка, а серьезная болезнь, требующая внимательного подхода и квалифицированного лечения. Если алкоголизм затягивается, могут возникнуть такие опасные состояния, как длительный запой, физическая и психоэмоциональная зависимость. В таких случаях необходима срочная медицинская помощь, и капельница от запоя является одним из самых эффективных методов, который используется для экстренной помощи пациентам.
Подробнее – капельница от запоя в стационаре
Выведение из запоя – это процесс, включающий несколько этапов. Симптомы могут варьироваться от тревожности и бессонницы до серьезных психических расстройств. Только профессиональный подход и современные медицинские технологии помогают минимизировать риски, стабилизировать состояние и избежать осложнений.
Получить больше информации – vyvod iz zapoya na domu sankt-peterburg
Для достижения эффективных результатов в лечении запоя необходима квалифицированная помощь специалистов. Наркологическая клиника «Излечение» в Краснодаре предоставляет профессиональные услуги по выводу из запоя, гарантируя безопасность, комфорт и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Выяснить больше – vyvod iz zapoya srochno kruglosutochno
Алкогольная зависимость — это серьезная проблема, требующая немедленного вмешательства. Если вы или ваши близкие столкнулись с запоем, важно получить профессиональную помощь как можно скорее, чтобы избежать ухудшения здоровья. Наркологическая клиника «Шаг к Трезвости» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вывода из запоя на дому, что является удобным и эффективным решением для тех, кто не может или не хочет посещать стационар.
Получить больше информации – нарколог вывод из запоя цена краснодар
купить дипломы о высшем образовании купить дипломы о высшем образовании .
Качественные дженерики в магазине https://mister-tvister16.ru/ быстрая доставка
гарантированное качество товара производства Индии
Процесс вывода из запоя требует быстрого реагирования. Запой, особенно в его тяжелых формах, представляет угрозу не только для психического состояния пациента, но и для его физического здоровья. Чтобы минимизировать риски и предотвратить осложнения, важно начинать лечение как можно скорее. Клинике «Освобождение» в Рязани доступна круглосуточная помощь — мы работаем 24/7, чтобы оперативно вмешаться в любой момент, когда это необходимо. Врачебная помощь может быть предоставлена как в стационаре клиники, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента и его предпочтений.
Подробнее – наркологический центр рязань
Source:
– http://school9msk.ru
Наркологическая клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже специализируется на лечении алкогольной зависимости и предлагает профессиональные услуги по выводу из запоя. Мы стремимся создать атмосферу доверия, где каждый пациент сможет получить необходимую поддержку.
Ознакомиться с деталями – narkologicheskij centr voronezh
Наркологическая клиника «Освобождение» в Рязани предлагает профессиональные услуги по выводу из запоя и комплексной реабилитации. Мы понимаем, что зависимость — это болезнь, требующая индивидуального подхода и поддержки не только для пациента, но и для его близких.
Подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya
Вывод из запоя — это не только помощь в улучшении самочувствия, но и важный этап на пути к лечению зависимости. Обратитесь к нам, если:
Получить дополнительную информацию – kapelnica ot zapoya s vyezdom cena v voronezhe
Мы понимаем, что успешное лечение невозможно без индивидуального подхода. Каждый случай уникален, поэтому мы разрабатываем персонализированные программы, учитывающие особенности каждого человека. Наши специалисты проводят детальное обследование и подбирают оптимальные методы лечения, обеспечивая комплексное внимание к состоянию пациента.
Получить дополнительную информацию – наркологическая клиника воронеж
В медицинском центре «Второй Шанс» помощь оказывается круглосуточно. Применяются проверенные и эффективные методы, обеспечивающие безопасность пациента и устойчивый результат. Конфиденциальность гарантирует комфорт и спокойствие тем, кто обратился за поддержкой, позволяя сосредоточиться на выздоровлении.
Получить дополнительные сведения – вывод из запоя с выездом на дом
Алкогольный запой — это состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над своим потреблением алкоголя, что может вызвать серьезные физические и психологические проблемы. В таких ситуациях крайне важно получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь как можно скорее. Однако многие люди опасаются обращаться за помощью, переживая за свою репутацию и возможное раскрытие личной информации. В клинике «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже мы гарантируем анонимность на всех этапах лечения, сохраняя высокий уровень медицинской помощи и заботясь о каждом пациенте.
Изучить вопрос глубже – вывод из запоя срочно круглосуточно в воронеже
В этой статье мы расскажем о возможностях клиники для лечения алкогольной интоксикации круглосуточно, включая вывод из запоя в стационаре и на дому, а также о роли профессионалов, таких как нарколог, в процессе лечения.
Выяснить больше – вывод из запоя капельница на дому в краснодаре
В таких ситуациях вывод из запоя на дому становится оптимальным решением, особенно если пациент не может или не хочет посещать стационар. Эта услуга позволяет получить медицинскую помощь в комфортной и привычной обстановке, что снижает уровень стресса и ускоряет процесс восстановления.
Разобраться лучше – narkologicheskaya klinika v-voronezhe
Зависимость – это сложное испытание, с которым сталкиваются люди во всём мире. Ежедневные стрессы, проблемы в семье и на работе, финансовые трудности часто становятся почвой для развития пагубных привычек, таких как алкоголизм, наркомания и игромания. Медицинский центр «Второй Шанс» предоставляет помощь тем, кто хочет избавиться от этих состояний, вернуть здоровье и научиться жить без разрушительных зависимостей.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://www.vyvod-iz-zapoya-14.ru
Для тех, кто не может приехать в клинику, специалисты проводят детоксикацию на дому. С помощью современных препаратов организм мягко очищается от токсинов, уменьшается нагрузка на внутренние органы, снимаются неприятные симптомы абстиненции. Однако при тяжелом состоянии или наличии осложнений может потребоваться круглосуточное наблюдение в стационаре, где пациенту обеспечивается полная медицинская поддержка.
Получить дополнительные сведения – narkologiya vyvod iz zapoya na domu sankt-peterburg
Проблема зависимостей остаётся актуальной в современном обществе. С каждым годом увеличивается число людей, страдающих от алкоголизма, наркомании и других форм зависимостей, что негативно отражается на их жизни и благополучии близких. Зависимость — это не просто физическое заболевание, но и глубокая психологическая проблема. Для эффективного лечения требуется помощь профессионалов, способных обеспечить комплексный подход.
Подробнее тут – vyvod iz zapoya na domu nedorogo kapelnica
В этой статье мы расскажем о возможностях клиники для лечения алкогольной интоксикации круглосуточно, включая вывод из запоя в стационаре и на дому, а также о роли профессионалов, таких как нарколог, в процессе лечения.
Выяснить больше – vyvod iz zapoya v-krasnodare
Запой – это состояние, которое возникает вследствие длительного употребления алкоголя, приводящее к потере контроля над количеством выпиваемого и формированию как физической, так и психологической зависимости. Оно сопровождается серьёзными последствиями для здоровья и требует немедленного вмешательства.
Выяснить больше – vyvod iz zapoya cena voronezh
viagra samples
Для достижения эффективных результатов в лечении запоя необходима квалифицированная помощь специалистов. Наркологическая клиника «Излечение» в Краснодаре предоставляет профессиональные услуги по выводу из запоя, гарантируя безопасность, комфорт и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Разобраться лучше – вывод из запоя анонимно в краснодаре
Зависимость – это сложное испытание, с которым сталкиваются люди во всём мире. Ежедневные стрессы, проблемы в семье и на работе, финансовые трудности часто становятся почвой для развития пагубных привычек, таких как алкоголизм, наркомания и игромания. Медицинский центр «Второй Шанс» предоставляет помощь тем, кто хочет избавиться от этих состояний, вернуть здоровье и научиться жить без разрушительных зависимостей.
Узнать больше – вывод из запоя
Купить паллеты поддоны на сайте https://palletcom.ru/ с доставкой по Москве
и области большой выбор по выгодным ценам
Алкогольный запой представляет собой критическое состояние, требующее немедленного вмешательства квалифицированных специалистов. Клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже предлагает круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить своевременное и эффективное лечение. Наша цель — оперативное снятие интоксикации, устранение симптомов и предотвращение осложнений.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – нарколог вывод из запоя цена
Используя тепловизоры, вы получаете идеальное сочетание скорости и точности, что значительно упрощает мониторинг и диагностику в самых разных областях. Как выбрать тепловизор для строительного контроля https://ai-db.science/index.php?title=%20%D0%A2%D0%B5%D0%BF%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%B8%D0%B7%D0%BE%D1%80%D1%8B%20%D0%B4%D0%BB%D1%8F%20%D0%BE%D1%85%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%BD%D0%BD%D1%8B%D1%85%20%D1%81%D0%B8%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B5%D0%BC:%20%D0%9A%D0%B0%D0%BA%20%D0%B7%D0%B0%D1%89%D0%B8%D1%82%D0%B8%D1%82%D1%8C%20%D1%81%D0%B2%D0%BE%D1%8E%20%D1%81%D0%BE%D0%B1%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B2%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%BD%D0%BE%D1%81%D1%82%D1%8C
В клинике «Излечение» мы предлагаем широкий спектр услуг по выводу из запоя, включая как стационарное лечение, так и помощь на дому. В этой статье мы подробно рассмотрим, от чего зависит цена вывода из запоя и какие услуги входят в стоимость.
Подробнее тут – vyvod iz zapoya v-krasnodare
free viagra samples in canada
Используя тепловизоры, вы получаете идеальное сочетание скорости и точности, что значительно упрощает мониторинг и диагностику в самых разных областях. Как выбрать тепловизор для строительного контроля http://www.apicarrara.it/modules.php?name=Journal&file=display&jid=7310
Используя тепловизоры, вы получаете идеальное сочетание скорости и точности, что значительно упрощает мониторинг и диагностику в самых разных областях. Как выбрать тепловизор для строительного контроля http://place-e.ru/index.php?title=%20%D0%A2%D0%B5%D0%BF%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%B8%D0%B7%D0%B8%D0%BE%D0%BD%D0%BD%D0%BE%D0%B5%20%D0%BE%D0%B1%D1%81%D0%BB%D0%B5%D0%B4%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%B0%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%B5:%20%D0%A7%D1%82%D0%BE%20%D0%BD%D1%83%D0%B6%D0%BD%D0%BE%20%D0%B7%D0%BD%D0%B0%D1%82%D1%8C
No Prescription Pharmacy Buy priligy dapoxetine united states canadian pharmacy
Generic cialis for sale
skypharmacy
online pharmacy with prescription Generic Cialis Online Pharmacy Reviews Supreme suppliers
купить диплом педагогический
диплом техникума купить
Viagra From Usa Pharmacy Acheter du viagra Rualis 20 super active sky pharmacy store Buy trazodone
All Dogs Sports Park, LLC is located on the beautiful grounds of Sycamore Lane Kennels and Farm, surrounded by orchards and vineyards in the heart of Lodi Wine Country. Our new sports center is for dogs of all shapes, sizes and abilities.
Looking for something fun to do with your dog? Come check out our regulation size competition dock and pool. Sign up for Dock Diving classes, reserve the pool for private dock diving practice or just for a swim.
We also have a 100 x 200 turfed arena where we offer Agility, Flyball and Barnhunt training class.
Our Obedience, Nosework and Trick Dog classes are held inside our matted, temperature controlled building.
alldogssportspark.com
Sitio web oficial https://jude-bellingham.com.mx de fans de Jude Bellingham: noticias, logros y material exclusivo sobre la carrera del talentoso mediocampista que juega en el Real Madrid.
Sitio web de fans rodrigo hernandez de Rodri Hernandez: Descubre la carrera y logros del mediocampista espanol del Manchester City. Noticias, estadisticas y analisis del juego de uno de los mejores futbolistas actuales.
Заказать дженерики в магазине https://pillbar.ru/ с доставкой по городу
курьером отправка в регионы почтой России
Официальная покупка аттестата о среднем образовании в Москве и других городах
Интернет – магазин керамический плитки и керамогранита, для любых поверхностей и помещений Плитка для пола
Интернет – магазин керамический плитки и керамогранита, для любых поверхностей и помещений Плитка керамическая
Интернет – магазин керамический плитки и керамогранита, для любых поверхностей и помещений Плитка для ванной
Проблема зависимостей остаётся актуальной в современном обществе. С каждым годом увеличивается число людей, страдающих от алкоголизма, наркомании и других форм зависимостей, что негативно отражается на их жизни и благополучии близких. Зависимость — это не просто физическое заболевание, но и глубокая психологическая проблема. Для эффективного лечения требуется помощь профессионалов, способных обеспечить комплексный подход.
Подробнее тут – vyvod iz zapoya na domu cena v-voronezhe
Kevin De Bruyne kevin-de-bruyne.com mx es un maestro del futbol moderno, conocido por su vision de juego, precision y liderazgo en el Manchester City. Su talento y trabajo duro lo han convertido en una leyenda del deporte.
Sitio fan de Mohamed Salah https://mohamed-salah.com.mx ultimas noticias, records, entrevistas y los mejores momentos de la carrera de uno de los futbolistas mas grandes de la actualidad. ?Mantente al tanto!
online canadian pharmacy
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Разобраться лучше – https://narko-zakodirovat1.ru/
Обращение к специалисту требуется в ситуациях, когда самостоятельное справление с проблемой становится невозможным или небезопасным. Одной из наиболее распространенных причин вызова нарколога является алкогольная интоксикация, связанная с запоем. В таких случаях состояние пациента может быть опасным, а попытки справиться с ситуацией без профессионального вмешательства чреваты осложнениями.
Детальнее – врач нарколог на дом платный в москве
Кроме того, анонимность является важной составляющей этой услуги. Лечение дома исключает возможность столкновения с посторонними людьми и помогает пациентам сохранить свою репутацию. Клиника «Гармония и Свет» обеспечивает полную конфиденциальность, предоставляя пациентам возможность получать помощь без лишних вопросов и обсуждений.
Разобраться лучше – выезд нарколога на дом цена в екатеринбурге
Запойное состояние представляет собой серьёзную угрозу для здоровья, поскольку сопровождается тяжёлой интоксикацией организма и нарушением психоэмоционального состояния. Решение о лечении в стационаре клиники «Союз Здоровья» позволяет справиться с последствиями длительного употребления алкоголя, обеспечивая пациентам полный комплекс медицинской и психологической помощи.
Получить больше информации – vyvod iz zapoya srochno kruglosutochno
elon casino elon casino .
Fan site de Vinicius Junior https://vinicius-jr.com.mx noticias, logros y detalles sobre su carrera en el Real Madrid. Sigue la evolucion de esta estrella del futbol mundial.
Продажа дженериков для мужчин на сайте https://poxetmsk.ru большой
выбор доступные цены гарантия качества
Запой – это не просто временное состояние, а серьёзная медицинская проблема, требующая своевременного вмешательства. Капельница от запоя в клинике «Пульс жизни» – один из самых эффективных методов восстановления, который помогает решить сразу несколько проблем:
Изучить вопрос глубже – капельница от запоя круглосуточно наркология в воронеже
Запой — это тяжелое состояние, возникающее вследствие длительного и непрерывного употребления алкоголя, которое сопровождается физической и психической зависимостью. Это опасное явление требует незамедлительного вмешательства специалистов. Вывод из запоя — это комплексный процесс медицинской детоксикации, который включает в себя очищение организма от токсинов, нормализацию функций внутренних органов и поддержку психоэмоционального состояния пациента. В случае тяжелого запоя стационарное лечение становится оптимальным решением для безопасного и эффективного вывода из этого состояния. В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как проходит вывод из запоя в стационаре клиники «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, а также особенности анонимности, скорости лечения и участия нарколога.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – нарколог на дом вывод из запоя челябинск
В первую очередь это вывод из запоя, который проводится с применением современных инфузионных растворов. Процедура включает внутривенное введение препаратов, устраняющих абстиненцию, восстанавливающих водно-солевой баланс и нормализующих работу внутренних органов. Это помогает снять тревожность, нормализовать сон и восстановить общее состояние.
Разобраться лучше – нарколог на дом в москве
Запойное состояние представляет собой серьёзную угрозу для здоровья, поскольку сопровождается тяжёлой интоксикацией организма и нарушением психоэмоционального состояния. Решение о лечении в стационаре клиники «Союз Здоровья» позволяет справиться с последствиями длительного употребления алкоголя, обеспечивая пациентам полный комплекс медицинской и психологической помощи.
Получить больше информации – вывод из запоя с выездом
1xbet apk code promo – utilisez-le pour vous inscrire et obtenir un bonus de 130% sur le montant de votre premier depot, pouvant aller jusqu’a 130$. Ces fonds doivent etre mises dans la section sportive, ou vous devez placer des paris avec une cote minimale de 1,4 et un wager x5.
Code Promo 1xBet
https://biggo.com.vn/wp-includes/articles/?kak_otuchity_malysha_ot_ruk.html
Code promo de 1xBet – l’utilisation de ce code vous permettra d’obtenir un bonus de 30% supplementaire, allant jusqu’a 100$. Le bonus est accorde sous la forme de 130% du montant de votre premier depot. Cette offre est reservee aux nouveaux utilisateurs majeurs apres leur inscription. Profitez du code promo pour augmenter votre bonus de bienvenue de 100% a 130%. Les fonds seront credites sur votre solde de jeu, et le bonus devra etre mise sur des paris sportifs. Ce code promo est valable jusqu’au 31 decembre 2025.
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Детальнее – https://narko-zakodirovat1.ru/
При рассмотрении вопроса о наркологической помощи на дому, необходимо четко представлять спектр доступных услуг:
Подробнее – http://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-moskva/
Когда пациент решает обратиться за помощью к наркологу на дом, ему предстоит пройти ряд этапов лечения, каждый из которых будет направлен на устранение последствий алкоголизма. Врач проведет первичный осмотр, выслушает жалобы пациента и на основе собранной информации начнёт индивидуальную программу лечения.
Детальнее – нарколог на дом стоимость екатеринбург
Выведение из запоя — это первый шаг к полноценному восстановлению. Важно не только купировать симптомы абстиненции, но и заложить основу для дальнейшей реабилитации. Квалифицированная медицинская помощь позволяет быстрее нормализовать состояние пациента, помогая ему вернуться к здоровой и полноценной жизни.
Получить дополнительные сведения – вывод из запоя капельница
купить диплом в керчи
Узнайте, как приобрести диплом о высшем образовании без рисков
Как купить аттестат 11 класса с официальным упрощенным обучением в Москве
Проблема зависимостей остаётся актуальной в современном обществе. С каждым годом увеличивается число людей, страдающих от алкоголизма, наркомании и других форм зависимостей, что негативно отражается на их жизни и благополучии близких. Зависимость — это не просто физическое заболевание, но и глубокая психологическая проблема. Для эффективного лечения требуется помощь профессионалов, способных обеспечить комплексный подход.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-11.ru/]http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-11.ru[/url]
casino en ligne captain caz casino en ligne fiable avis
Основой лечения становится индивидуальный подход. Врач-нарколог проводит диагностику, разрабатывает план терапии, подбирает необходимые препараты и внимательно следит за состоянием пациента на всех этапах. Учитывается не только физическое, но и психоэмоциональное состояние человека. Психологическая поддержка и мотивация на отказ от алкоголя играют важную роль, помогая закрепить результат и избежать рецидивов.
Разобраться лучше – капельница от запоя круглосуточно наркология
Запой — это тяжелое состояние, возникающее вследствие длительного и непрерывного употребления алкоголя, которое сопровождается физической и психической зависимостью. Это опасное явление требует незамедлительного вмешательства специалистов. Вывод из запоя — это комплексный процесс медицинской детоксикации, который включает в себя очищение организма от токсинов, нормализацию функций внутренних органов и поддержку психоэмоционального состояния пациента. В случае тяжелого запоя стационарное лечение становится оптимальным решением для безопасного и эффективного вывода из этого состояния. В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как проходит вывод из запоя в стационаре клиники «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, а также особенности анонимности, скорости лечения и участия нарколога.
Получить дополнительную информацию – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom na dom
Современная жизнь в мегаполисе порой становится источником серьезных испытаний для здоровья. Проблемы, связанные с алкоголизмом или наркотической зависимостью, требуют немедленного вмешательства. В таких ситуациях вызов нарколога на дом становится оптимальным решением. Это услуга, которая объединяет оперативность, профессионализм и комфорт, предлагая пациентам возможность получить качественную медицинскую помощь, не покидая собственного жилья.
Подробнее тут – нарколог на дом стоимость в москве
Проблема зависимости в современном обществе становится всё более актуальной. Алкоголизм, наркомания, игромания — все эти расстройства наносят значительный вред как индивидуумам, так и их окружению. В Воронеже и Воронежской области наркологическая клиника «Пульс жизни» предлагает профессиональную помощь в преодолении запоев и зависимостей, помогая вернуть здоровье и ясность ума.
Узнать больше – kapelnica ot zapoya v stacionare anonimno voronezh
Детоксикация организма — еще одна важная процедура, которая позволяет вывести токсины и минимизировать их негативное воздействие на органы. Для этого применяются специальные растворы, содержащие витамины, глюкозу и электролиты. Все компоненты подбираются индивидуально на основе состояния пациента.
Подробнее тут – вызов нарколога на дом цена в москве
Зависимости продолжают оставаться одной из самых серьёзных проблем современности, затрагивая не только здоровье человека, но и его социальные связи. Алкоголизм и наркомания способны разрушить жизнь, приводя к тяжёлым последствиям, требующим профессионального вмешательства. Комплексный подход к лечению подобных состояний позволяет не только справиться с физическими проявлениями зависимости, но и восстановить психоэмоциональное равновесие.
Получить больше информации – наркология вывод из запоя на дому в воронеже
https://cyblab.ru
Детоксикация организма представляет собой комплексное очищение от токсинов. Для этого используются инфузионные растворы, содержащие витамины, антиоксиданты и препараты для поддержки печени. Процедура помогает снизить нагрузку на органы и улучшить общее самочувствие.
Выяснить больше – нарколог екатеринбург
Одним из наиболее удобных вариантов лечения является проведение процедуры в домашних условиях. Это особенно актуально для пациентов, которые чувствуют себя слишком плохо, чтобы отправиться в клинику, или желают сохранить анонимность.Алкогольная зависимость остается одной из самых серьезных проблем современного общества. Когда человек сталкивается с последствиями длительного употребления спиртных напитков, важно вовремя принять меры, чтобы минимизировать вред для организма. В таких случаях капельница от запоя становится эффективным инструментом для снятия интоксикации и восстановления здоровья.
Разобраться лучше – капельница от запоя красноярск
Ситуации, требующие вмешательства нарколога, могут быть различными. Наиболее распространенным поводом является состояние тяжелого алкогольного или наркотического опьянения, при котором пациент уже не может самостоятельно справляться с последствиями интоксикации. Это может быть вызвано передозировкой, длительным употреблением веществ или острой реакцией организма на токсичные соединения.
Узнать больше – http://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-moskva-tseny/
Когда речь идет о лечении зависимостей, многие пациенты испытывают стресс от визита в медицинские учреждения, особенно если это касается такой деликатной темы, как алкоголизм. Лечение на дому помогает избежать всех этих трудностей и обеспечивает комфорт для пациента. Привычная домашняя обстановка снижает тревожность, что позитивно влияет на процесс выздоровления.
Детальнее – вызов нарколога на дом цена екатеринбург
Generic cialis for sale comprare cialis generico in farmacia Canada Pharmacy 24 Hour Drug Store
Дженерики на сайте https://rukamagra.ru/ по доступным ценам с доставкой
в день заказа курьером анонимно
Алкогольный запой представляет собой критическое состояние, требующее немедленного вмешательства квалифицированных специалистов. Клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже предлагает круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить своевременное и эффективное лечение. Наша цель — оперативное снятие интоксикации, устранение симптомов и предотвращение осложнений.
Выяснить больше – vyvod iz zapoya anonimno nedorogo voronezh
Полезные советы по выбору LED ламп во Львове от KabelProКачество света: как выбрать лампы для идеального освещения?. Индекс цветопередачи (CRI): почему он важен?. Выбор ламп с высоким CRI улучшает качество освещения. Как индекс цветопередачи влияет на цветопередачу?. Секреты выбора LED ламп с высоким качеством света
Эта процедура доступна как в условиях клиники, так и на дому, что делает ее универсальным решением для различных жизненных ситуаций. При этом важно доверять свое здоровье только профессиональным врачам, которые могут обеспечить безопасное и качественное лечение.Эта процедура доступна как в условиях клиники, так и на дому, что делает ее универсальным решением для различных жизненных ситуаций. При этом важно доверять свое здоровье только профессиональным врачам, которые могут обеспечить безопасное и качественное лечение.
Детальнее – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-krasnoyarsk55.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-stacionare-krasnoyarsk/
Запойное состояние является крайней стадией зависимости, требующей немедленного медицинского вмешательства. В «Союзе Здоровья» организована круглосуточная помощь, что позволяет оперативно стабилизировать состояние пациента, минимизировать риск осложнений и облегчить процесс восстановления.
Разобраться лучше – вывод из запоя цена
Стоимость вывода из запоя зависит от ряда факторов, таких как состояние пациента, выбранная программа лечения и место проведения процедуры. Мы предлагаем прозрачное ценообразование, чтобы вы могли заранее ознакомиться с возможными затратами на лечение.
Подробнее – вывод из запоя вызов на дом челябинск
Для тех, кто по разным причинам не может посетить медицинский центр, существует возможность вызова нарколога на дом. Такая услуга позволяет получить необходимую помощь в комфортных условиях, сохраняя при этом полную анонимность. Опытные врачи проведут детоксикацию, назначат поддерживающую терапию и дадут рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению.
Детальнее – наркология вывод из запоя анонимно
Многие люди боятся обращаться за помощью, опасаясь нарушения конфиденциальности. В клинике строго соблюдаются правила анонимности, что создаёт атмосферу безопасности и доверия. Высокий уровень профессионализма специалистов и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту способствуют комфортному и эффективному лечению.
Детальнее – вывод из запоя с выездом цена
Как получить диплом техникума с упрощенным обучением в Москве официально
Try your luck at pinup casino! The best slots, roulette, blackjack and live games with real dealers. Pleasant bonuses, promotions and a user-friendly interface will create ideal conditions for the game!
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, необходимая для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Это состояние, часто характеризующееся физическими и психоэмоциональными нарушениями, требует профессионального вмешательства. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть разнообразными и варьироваться от легкой тревожности до серьезных нарушений в функционировании внутренних органов. Квалифицированная помощь в этот период позволяет минимизировать риски и значительно ускорить процесс выздоровления.
Детальнее – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom
Запойное состояние обычно сопровождается тяжелыми симптомами алкогольной интоксикации: головной болью, тошнотой, рвотой, бессонницей и раздражительностью. Эти признаки свидетельствуют о глубоком отравлении организма, требующем комплексного подхода. В таких ситуациях капельница становится незаменимым инструментом, способствующим быстрому снятию симптомов и улучшению самочувствия пациента.Одним из наиболее удобных вариантов лечения является проведение процедуры в домашних условиях. Это особенно актуально для пациентов, которые чувствуют себя слишком плохо, чтобы отправиться в клинику, или желают сохранить анонимность.
Получить дополнительную информацию – капельница от запоя красноярск
Стоимость услуги формируется на основе различных факторов, включая сложность состояния пациента, срочность вызова, квалификацию врача и расстояние до места вызова. Чтобы сделать правильный выбор, важно учитывать все аспекты, влияющие на цену, и понимать, как получить качественную помощь по справедливой стоимости.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – выезд нарколога на дом цена в екатеринбурге
Запой – это не просто временное состояние, а серьёзная медицинская проблема, требующая своевременного вмешательства. Капельница от запоя в клинике «Пульс жизни» – один из самых эффективных методов восстановления, который помогает решить сразу несколько проблем:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – капельница от запоя в стационаре в воронеже
“Наркозависимость разрушила мою жизнь. Я потратила все силы, и не знала, что делать дальше. В клинике “Пульс жизни” я получила необходимую помощь. Программа лечения действительно работает, и я снова чувствую себя свободной.”— Мария, 29 лет
Изучить вопрос глубже – капельница от запоя в стационаре в воронеже
Почта для домена на https://email4domain.ru это корпоративный почтовый сервис email для организаций. Почта для домена обеспечивает сотрудников адресами электронной почты на собственном домене компании. Почта для бизнеса улучшает узнаваемость и повышает имидж бренда.
Комплекты видеонаблюдения – важный элемент системы безопасности дома, офиса, а также других помещений и уличных территорий Заказать видеонаблюдение для охраны
https://long-living.ru/
купить диплом высшем образовании купить диплом высшем образовании .
Как официально купить диплом вуза с упрощенным обучением в Москве
Запойное пьянство представляет серьезную угрозу для здоровья, провоцируя развитие таких заболеваний, как цирроз печени, панкреатит, сердечно-сосудистые нарушения, а также психические расстройства. В запущенных случаях возможны тяжелые последствия, включая алкогольный делирий (белую горячку), который требует экстренной медицинской помощи. Чтобы избежать подобных рисков, необходимо своевременно обратиться к специалистам, которые помогут стабилизировать состояние и провести грамотное лечение.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-21.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-v-kruglosutochno-v-tveri/]vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno narkologiya v-tveri[/url]
Комплекты видеонаблюдения – важный элемент системы безопасности дома, офиса, а также других помещений и уличных территорий Купить камеры видеонаблюдения с доставкой
Одним из наиболее удобных вариантов лечения является проведение процедуры в домашних условиях. Это особенно актуально для пациентов, которые чувствуют себя слишком плохо, чтобы отправиться в клинику, или желают сохранить анонимность.Алкогольная зависимость остается одной из самых серьезных проблем современного общества. Когда человек сталкивается с последствиями длительного употребления спиртных напитков, важно вовремя принять меры, чтобы минимизировать вред для организма. В таких случаях капельница от запоя становится эффективным инструментом для снятия интоксикации и восстановления здоровья.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-krasnoyarsk55.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-stacionare-krasnoyarsk
Комплекты видеонаблюдения – важный элемент системы безопасности дома, офиса, а также других помещений и уличных территорий Установка скрытых камер видеонаблюдения
Еще одной причиной вызова нарколога может быть абстинентный синдром, возникающий после прекращения употребления алкоголя или наркотиков. Это состояние сопровождается физическими и психологическими проявлениями, такими как дрожь, тревога, бессонница, боли в мышцах.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – вызов нарколога на дом москва
Вывод из запоя – это не просто разовое медицинское вмешательство, а важный шаг на пути к полному избавлению от алкогольной зависимости. Комплексный подход, включающий не только устранение симптомов интоксикации, но и последующую психологическую реабилитацию, позволяет добиться устойчивого результата и вернуть человека к полноценной жизни.
Детальнее – вывод из запоя
Процесс вызова специалиста на дом продуман до мелочей, чтобы максимально упростить задачу для пациента и его близких.
Узнать больше – врач нарколог на дом платный москва
В Воронеже специалисты клиники «Союз Здоровья» предлагают квалифицированную помощь людям, столкнувшимся с алкогольной зависимостью. Особое внимание уделяется созданию комфортных условий для пациентов, что способствует успешному прохождению лечения. Одной из востребованных услуг является выведение из запоя, позволяющее оперативно нормализовать состояние человека и предотвратить опасные осложнения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – вывод из запоя с выездом
eu realmente sou apaixonado por demais daquele.
comprar seguidores por 1 real pix
Наркологическая клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже специализируется на лечении алкогольной зависимости и предлагает профессиональные услуги по выводу из запоя. Мы стремимся создать атмосферу доверия, где каждый пациент сможет получить необходимую поддержку.
Углубиться в тему – vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare anonimno voronezh
Запой — это одно из наиболее тяжелых проявлений алкогольной зависимости, которое требует немедленного и квалифицированного вмешательства. В такие моменты близкие зачастую теряются и не знают, как помочь своему родному человеку. На помощь приходит наркологическая клиника «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, которая предоставляет профессиональную помощь в выводе из запоя. Мы понимаем, что лечение запоя требует не только медицинского подхода, но и психологической поддержки. Именно поэтому в нашей клинике пациент получает комплексную помощь, основанную на самых современных методах лечения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – нарколог вывод из запоя цена
Интернет магазин дженериков https://saleviagra.ru большой выбор
по выгодным ценам бесплатная доставка курьером
Диплом вуза купить официально с упрощенным обучением в Москве
Жизнь в мегаполисе, таком как Москва, предъявляет к человеку множество требований и вызовов. В условиях постоянного стресса и давления вероятность столкнуться с проблемами, связанными с алкоголизмом или наркоманией, возрастает. В таких ситуациях вызов нарколога на дом в Москве становится не роскошью, а необходимостью. В этой статье рассмотрим, когда и как можно воспользоваться этой услугой, а также разберем стоимость и основные преимущества.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – выезд нарколога на дом цена москва
Для тех, кто по разным причинам не может посетить медицинский центр, существует возможность вызова нарколога на дом. Такая услуга позволяет получить необходимую помощь в комфортных условиях, сохраняя при этом полную анонимность. Опытные врачи проведут детоксикацию, назначат поддерживающую терапию и дадут рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya vyzov na dom v-tveri
casino en ligne bonus meilleurs casino en ligne avis
Наркологическая помощь на дому необходима в ряде случаев, связанных с острыми состояниями пациента или невозможностью посетить клинику. Часто это ситуации, когда человек испытывает тяжелые последствия запоя, сильную интоксикацию или симптомы, угрожающие здоровью.
Узнать больше – http://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru
Такая терапия помогает подготовить организм к дальнейшему лечению от зависимости, улучшить физическое состояние и предотвратить развитие осложнений, таких как обезвоживание или нарушение работы внутренних органов.
Выяснить больше – narkologiya kapelnica ot zapoya anonimno
отзывы о приворотах кто делал в домашних условиях отзывы – Помог этот маг 89842861265
белая магия приворот отзывы
приворот на скрученные свечи отзывы кто делал отзывы
отзывы приворот на сигарету кто делал отзывы
приворот на любовь с отзывами
кто пробовал приворот отзывы
Сайт мага настоящего https://cmag666.ru
последствия приворота для мужчины отзывы
бесплатный приворот отзывы
приворот форум отзывы
черный сват отзывы приворот кто делал
приворот реальные отзывы
приворот отзывы кому помогло
бесовский приворот отзывы кто делал отзывы
привороты на мужчину отзывы кто
отзывы приворот кто делал
последствия кладбищенских приворотов все отзывы
Контакты мага телефон 89842861265
Наркологическая клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже специализируется на лечении алкогольной зависимости и предлагает профессиональные услуги по выводу из запоя. Мы стремимся создать атмосферу доверия, где каждый пациент сможет получить необходимую поддержку.
Ознакомиться с деталями – вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно
Проблемы с алкоголем или наркотиками могут появиться в самый неподходящий момент, и зачастую требуется срочная помощь специалиста. Нередко необходим срочный вызов врача в следующих ситуациях:
Выяснить больше – нарколог на дом цены в москве
Процесс вызова специалиста на дом продуман до мелочей, чтобы максимально упростить задачу для пациента и его близких.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/
Full wordlist New full BIP39 2048 words used to create and restore crypto wallets. Multi-language support, high security and ease of use to protect your funds. 2048 mnemonic words for seed generation.
Основой лечения становится индивидуальный подход. Врач-нарколог проводит диагностику, разрабатывает план терапии, подбирает необходимые препараты и внимательно следит за состоянием пациента на всех этапах. Учитывается не только физическое, но и психоэмоциональное состояние человека. Психологическая поддержка и мотивация на отказ от алкоголя играют важную роль, помогая закрепить результат и избежать рецидивов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – anonimnaya kapelnica ot zapoya na domu voronezh
Жизнь в мегаполисах, подобных Москве, нередко становится причиной развития различных зависимостей. В критических ситуациях может понадобиться экстренная наркологическая помощь. Это оптимальный вариант для тех, кто нуждается в квалифицированной медицинской поддержке, не выходя из собственного жилья. В данной статье мы детально разберем услуги круглосуточной наркологической помощи на дому в Москве, порядок вызова врача, а также рассмотрим цены и достоинства данного метода лечения.
Детальнее – нарколог на дом стоимость в москве
New full Bip39 2048 words used to create and restore crypto wallets. Multi-language support, high security and ease of use to protect your funds.
ставки на спорт бишкек mabc.com.kg .
1win официальный сайт казино 1win официальный сайт казино .
платье для кормления https://ivadesign.ru .
Основой лечения становится индивидуальный подход. Врач-нарколог проводит диагностику, разрабатывает план терапии, подбирает необходимые препараты и внимательно следит за состоянием пациента на всех этапах. Учитывается не только физическое, но и психоэмоциональное состояние человека. Психологическая поддержка и мотивация на отказ от алкоголя играют важную роль, помогая закрепить результат и избежать рецидивов.
Получить больше информации – нарколог капельница от запоя цена воронеж
Запойное состояние представляет собой серьёзную угрозу для здоровья, поскольку сопровождается тяжёлой интоксикацией организма и нарушением психоэмоционального состояния. Решение о лечении в стационаре клиники «Союз Здоровья» позволяет справиться с последствиями длительного употребления алкоголя, обеспечивая пациентам полный комплекс медицинской и психологической помощи.
Выяснить больше – вывод из запоя капельница воронеж
Клиника работает круглосуточно, предоставляя помощь в любое время. Стоимость услуг зависит от времени вызова и степени срочности, а ночные или праздничные выезды требуют дополнительных затрат. В особо сложных случаях капельница помогает не только снять интоксикацию, но и предотвратить возможные осложнения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – капельница от запоя на дому цена в воронеже
Детоксикация организма представляет собой комплексное очищение от токсинов. Для этого используются инфузионные растворы, содержащие витамины, антиоксиданты и препараты для поддержки печени. Процедура помогает снизить нагрузку на органы и улучшить общее самочувствие.
Получить дополнительную информацию – нарколог екатеринбург
Процесс вызова специалиста на дом продуман до мелочей, чтобы максимально упростить задачу для пациента и его близких.
Получить дополнительные сведения – narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/
Быстрая схема покупки диплома старого образца: что важно знать?
Наркологическая клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже специализируется на лечении алкогольной зависимости и предлагает профессиональные услуги по выводу из запоя. Мы стремимся создать атмосферу доверия, где каждый пациент сможет получить необходимую поддержку.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom voronezh
Процедура необходима в случае появления симптомов алкогольной интоксикации, таких как тошнота, головная боль, слабость, тревожность или нарушения сна. Особенно важно провести детоксикацию, если у человека наблюдаются хронические заболевания, которые могут обостриться под воздействием токсинов.Процедура необходима в случае появления симптомов алкогольной интоксикации, таких как тошнота, головная боль, слабость, тревожность или нарушения сна. Особенно важно провести детоксикацию, если у человека наблюдаются хронические заболевания, которые могут обостриться под воздействием токсинов.
Узнать больше – капельницы от запоя в красноярске
Кроме того, анонимность является важной составляющей этой услуги. Лечение дома исключает возможность столкновения с посторонними людьми и помогает пациентам сохранить свою репутацию. Клиника «Гармония и Свет» обеспечивает полную конфиденциальность, предоставляя пациентам возможность получать помощь без лишних вопросов и обсуждений.
Разобраться лучше – нарколог на дом стоимость в екатеринбурге
Эта процедура доступна как в условиях клиники, так и на дому, что делает ее универсальным решением для различных жизненных ситуаций. При этом важно доверять свое здоровье только профессиональным врачам, которые могут обеспечить безопасное и качественное лечение.Процедура необходима в случае появления симптомов алкогольной интоксикации, таких как тошнота, головная боль, слабость, тревожность или нарушения сна. Особенно важно провести детоксикацию, если у человека наблюдаются хронические заболевания, которые могут обостриться под воздействием токсинов.
Углубиться в тему – капельница от запоя на дому в красноярске
Выбирайте к покупке качественные дженерики на сайте https://sialisbuy.ru
с доставкой курьером в день покупки
Лечение может проходить как дома, так и в стационаре. Амбулаторный вариант удобен для тех, кто предпочитает находиться в привычной обстановке, тогда как стационарное лечение подходит для более сложных случаев, требующих постоянного медицинского наблюдения. В стационаре проводятся все необходимые исследования, включая анализы, ЭКГ и УЗИ, что позволяет минимизировать риски и ускорить восстановление.
Углубиться в тему – капельница от запоя на дому в воронеже
Проблемы с алкоголем или наркотиками могут появиться в самый неподходящий момент, и зачастую требуется срочная помощь специалиста. Нередко необходим срочный вызов врача в следующих ситуациях:
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-moskva-tseny
Алкогольный запой — это состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над своим потреблением алкоголя, что может вызвать серьезные физические и психологические проблемы. В таких ситуациях крайне важно получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь как можно скорее. Однако многие люди опасаются обращаться за помощью, переживая за свою репутацию и возможное раскрытие личной информации. В клинике «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже мы гарантируем анонимность на всех этапах лечения, сохраняя высокий уровень медицинской помощи и заботясь о каждом пациенте.
Углубиться в тему – быстрый вывод из запоя в стационаре воронеж
В Воронеже специалисты клиники «Союз Здоровья» предлагают квалифицированную помощь людям, столкнувшимся с алкогольной зависимостью. Особое внимание уделяется созданию комфортных условий для пациентов, что способствует успешному прохождению лечения. Одной из востребованных услуг является выведение из запоя, позволяющее оперативно нормализовать состояние человека и предотвратить опасные осложнения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – вывод из запоя
Для тех, кто по разным причинам не может посетить медицинский центр, существует возможность вызова нарколога на дом. Такая услуга позволяет получить необходимую помощь в комфортных условиях, сохраняя при этом полную анонимность. Опытные врачи проведут детоксикацию, назначат поддерживающую терапию и дадут рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению.
Разобраться лучше – vyvod iz zapoya na domu nedorogo kapelnica
Вывод из запоя – это не просто разовое медицинское вмешательство, а важный шаг на пути к полному избавлению от алкогольной зависимости. Комплексный подход, включающий не только устранение симптомов интоксикации, но и последующую психологическую реабилитацию, позволяет добиться устойчивого результата и вернуть человека к полноценной жизни.
Изучить вопрос глубже – vyvod iz zapoya vyzov na dom v-tveri
В таких ситуациях вывод из запоя на дому становится оптимальным решением, особенно если пациент не может или не хочет посещать стационар. Эта услуга позволяет получить медицинскую помощь в комфортной и привычной обстановке, что снижает уровень стресса и ускоряет процесс восстановления.
Выяснить больше – vyvod iz zapoya kapelnica voronezh
Запой представляет собой состояние, характеризующееся длительным непрерывным употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к физической и психической зависимости. Этот процесс может длиться от нескольких дней до недель. Алкогольные напитки негативно влияют на функционирование внутренних органов, вызывая серьёзные нарушения, включая алкоголизм. При необходимости вывода из запоя важно обратиться за медицинской помощью, что можно осуществить на дому. В данной статье рассмотрим ключевые аспекты данной процедуры.
Ознакомиться с деталями – vyvod iz zapoya srochno kruglosutochno chelyabinsk
Запой — это серьёзное состояние, вызванное длительным употреблением алкоголя и сопровождающееся утратой контроля над своим поведением. Оно несёт угрозу как для организма, так и для психики, а потому требует своевременного медицинского вмешательства. Для удобства пациентов предусмотрена возможность оказания помощи на дому, что снижает уровень стресса и позволяет провести процедуру в привычной обстановке.
Получить дополнительную информацию – вывод из запоя анонимно недорого в воронеже
Преимущества домашнего лечения также заключаются в индивидуальном подходе. Врач, находясь в вашем доме, может более тщательно изучить ситуацию, провести необходимую диагностику и подобрать курс лечения, который идеально подойдет вашему состоянию. В отличие от клиники, где внимание врача часто ограничено временем, на дому можно уделить пациенту больше времени, подбирая лечение с учетом его особенностей.
Получить больше информации – вызов нарколога на дом цена москва
Клиника «Гармония и Свет» предоставляет качественные услуги нарколога на дому, обеспечивая пациентам комфортное лечение в привычной обстановке. Это позволяет не только своевременно получить квалифицированную помощь, но и сделать процесс лечения максимально непринужденным и анонимным.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narcolog-na-dom-ektb55.ru/
Когда пациент решает обратиться за помощью к наркологу на дом, ему предстоит пройти ряд этапов лечения, каждый из которых будет направлен на устранение последствий алкоголизма. Врач проведет первичный осмотр, выслушает жалобы пациента и на основе собранной информации начнёт индивидуальную программу лечения.
Получить больше информации – нарколог на дом недорого в екатеринбурге
купить диплом ординатуры
“Наркозависимость разрушила мою жизнь. Я потратила все силы, и не знала, что делать дальше. В клинике “Пульс жизни” я получила необходимую помощь. Программа лечения действительно работает, и я снова чувствую себя свободной.”— Мария, 29 лет
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh2.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-na-domu-v-voronezhe/]капельница от запоя в стационаре анонимно воронеж[/url]
Для многих пациентов важным моментом является сохранение конфиденциальности. Врач, приехавший на дом, работает с полной защитой данных. Пациент может быть уверен, что его проблема останется личной и не станет достоянием общественности. Врачи приезжают на неприметных автомобилях и избегают всяческих ситуаций, которые могут привлечь лишнее внимание.
Детальнее – https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-moskva/
Алкогольный запой — это состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над своим потреблением алкоголя, что может вызвать серьезные физические и психологические проблемы. В таких ситуациях крайне важно получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь как можно скорее. Однако многие люди опасаются обращаться за помощью, переживая за свою репутацию и возможное раскрытие личной информации. В клинике «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже мы гарантируем анонимность на всех этапах лечения, сохраняя высокий уровень медицинской помощи и заботясь о каждом пациенте.
Детальнее – srochny vyvod iz zapoya na domu
Наркологическая клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже специализируется на лечении алкогольной зависимости и предлагает профессиональные услуги по выводу из запоя. Мы стремимся создать атмосферу доверия, где каждый пациент сможет получить необходимую поддержку.
Детальнее – наркология вывод из запоя анонимно воронеж
Запой — это тяжелое состояние, возникающее вследствие длительного и непрерывного употребления алкоголя, которое сопровождается физической и психической зависимостью. Это опасное явление требует незамедлительного вмешательства специалистов. Вывод из запоя — это комплексный процесс медицинской детоксикации, который включает в себя очищение организма от токсинов, нормализацию функций внутренних органов и поддержку психоэмоционального состояния пациента. В случае тяжелого запоя стационарное лечение становится оптимальным решением для безопасного и эффективного вывода из этого состояния. В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как проходит вывод из запоя в стационаре клиники «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, а также особенности анонимности, скорости лечения и участия нарколога.
Подробнее – вывод из запоя круглосуточно наркология челябинск
Качественные дженерики для повышения потенции на сайте https://sialis-sell.ru
гарантированное качество производства Индии с доставкой курьером
В таких ситуациях вывод из запоя на дому становится оптимальным решением, особенно если пациент не может или не хочет посещать стационар. Эта услуга позволяет получить медицинскую помощь в комфортной и привычной обстановке, что снижает уровень стресса и ускоряет процесс восстановления.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно
Процесс вызова нарколога достаточно прост и удобен для пациента и его близких.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru
“Наркозависимость разрушила мою жизнь. Я потратила все силы, и не знала, что делать дальше. В клинике “Пульс жизни” я получила необходимую помощь. Программа лечения действительно работает, и я снова чувствую себя свободной.”— Мария, 29 лет
Подробнее можно узнать тут – kapelnica ot zapoya v stacionare anonimno voronezh
Наркологическая клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже специализируется на лечении алкогольной зависимости и предлагает профессиональные услуги по выводу из запоя. Мы стремимся создать атмосферу доверия, где каждый пациент сможет получить необходимую поддержку.
Узнать больше – наркологическая клиника воронеж
Всем привет!
Меня зовут Арий, и я обожаю смотреть мультики онлайн на сайте https://multfilmy.cyou .
Там много интересных мультиков, которые Вам понравятся.
Присоединяйтесь!
canadian pharmacy cialis
Алкогольный запой представляет собой критическое состояние, требующее немедленного вмешательства квалифицированных специалистов. Клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже предлагает круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить своевременное и эффективное лечение. Наша цель — оперативное снятие интоксикации, устранение симптомов и предотвращение осложнений.
Получить дополнительную информацию – нарколог на дом вывод из запоя воронеж
casino en ligne legal en france forum casino en ligne
Full wordlist New full BIP39 2048 words used to create and restore crypto wallets. Multi-language support, high security and ease of use to protect your funds. 2048 mnemonic words for seed generation.
skypharmacy online
Запой – это состояние, которое возникает вследствие длительного употребления алкоголя, приводящее к потере контроля над количеством выпиваемого и формированию как физической, так и психологической зависимости. Оно сопровождается серьёзными последствиями для здоровья и требует немедленного вмешательства.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – vyvod iz zapoya v-voronezhe
Cialis black market price 274 order cipro online supreme suppliers Canadian Pharmacy No Prescription
где можно купить настоящий диплом где можно купить настоящий диплом .
Запойное состояние представляет собой серьёзную угрозу для здоровья, поскольку сопровождается тяжёлой интоксикацией организма и нарушением психоэмоционального состояния. Решение о лечении в стационаре клиники «Союз Здоровья» позволяет справиться с последствиями длительного употребления алкоголя, обеспечивая пациентам полный комплекс медицинской и психологической помощи.
Получить больше информации – bystry vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare v-voronezhe
Use the 1xBet promo code: 1XGIFT130 to receive a welcome bonus in 2025. New players will be eligible for a VIP bonus of 100% up to $130. Once you have obtained the promo code, make sure to use it during the registration process http://autofs.ru/documents/pages/promokod_betwinner_na_segodnya_pri_registracii.html
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Подробнее тут – https://narko-zakodirovat1.ru/
Use the 1xBet promo code: 1XGIFT130 to receive a welcome bonus in 2025. New players will be eligible for a VIP bonus of 100% up to $130. Once you have obtained the promo code, make sure to use it during the registration process https://actnigeria.com/news/code_promotionnel_1xbet_dans.html
Эта статья полна интересного контента, который побудит вас исследовать новые горизонты. Мы собрали полезные факты и удивительные истории, которые обогащают ваше понимание темы. Читайте, погружайтесь в детали и наслаждайтесь процессом изучения!
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narko-zakodirovat1.ru/
https://filedn.eu/lXvDNJGJo3S0aUrNKUTnNkb/marketing-306/research/je-tall-sf-marketing-(61).html
You may think it’s customary for the mom of the bride to put on an over-sized hat, however that’s merely not the case for 2022.
Use the 1xBet promo code: 1XGIFT130 to receive a welcome bonus in 2025. New players will be eligible for a VIP bonus of 100% up to $130. Once you have obtained the promo code, make sure to use it during the registration process https://mebel-3d.ru/libraries/news/?betwinner_promokod_pri_registracii_2020.html
canadian pharmacy cialis 5mg
Запойное состояние представляет собой серьёзную угрозу для здоровья, поскольку сопровождается тяжёлой интоксикацией организма и нарушением психоэмоционального состояния. Решение о лечении в стационаре клиники «Союз Здоровья» позволяет справиться с последствиями длительного употребления алкоголя, обеспечивая пациентам полный комплекс медицинской и психологической помощи.
Подробнее тут – narkolog na dom vyvod iz zapoya v-voronezhe
Магазин качественных дженериков по адресу https://sialis-tadalafil.ru
быстрая доставка высокое качество по низкой цене
Canadianpharmacy Canadian health canadian pharmacies mail order
Healthy man viagra sales
myskypharmacy
sky pharmacy online Onlinepharmacy Retin a without prescription
Pharmacy Online Online pharmacy viagra Maxifort zimax 100 mg canadian pharmacy mall Kamagra
купить диплом в новосибирске отзывы
Алкогольная и наркотическая зависимости — серьезные проблемы, требующие профессионального вмешательства. В Красноярске одной из самых востребованных услуг является вызов нарколога на дом. Этот формат позволяет пациентам получить квалифицированную помощь в комфортной обстановке, избегая стрессов, связанных с посещением клиники.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnoyarsk55.ru/]https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnoyarsk55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-krasnoyarsk-tseny/[/url]
Капельница от запоя – это метод внутривенного введения специальных растворов, направленных на восстановление водно-электролитного баланса организма, выведение токсинов и снижение симптомов абстинентного синдрома. Эта процедура позволяет быстро стабилизировать состояние пациента, ускорить процессы детоксикации и предотвратить возможные осложнения, связанные с длительным употреблением алкоголя.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – капельница от запоя с выездом на дом
Промокод MelBet при Регистрации: FreeBonus777 укажите это код в поле во время регистрации и вы получите бонус до 19 500р, а также автоматически активируете все промо акции мелбет 2025. Зарабатывайте больше с melbet промокодом актуальным сегодня http://bestaff.ru/includes/pages/chto_takoe_i_kak_ukladyvaetsya_teploizolyacionnaya_shlakovata.html
В таких ситуациях вывод из запоя на дому становится оптимальным решением, особенно если пациент не может или не хочет посещать стационар. Эта услуга позволяет получить медицинскую помощь в комфортной и привычной обстановке, что снижает уровень стресса и ускоряет процесс восстановления.
Получить больше информации – narkologicheskaya klinika
Промокод MelBet при Регистрации: FreeBonus777 укажите это код в поле во время регистрации и вы получите бонус до 19 500р, а также автоматически активируете все промо акции мелбет 2025. Зарабатывайте больше с melbet промокодом актуальным сегодня https://restoranoved.ru/molly/pages/lth1gtporsche_918_spyder_2015_3lt_h1gt.html
Алкогольная зависимость — это тяжелое состояние, требующее срочного медицинского вмешательства. В столице растет число пациентов, предпочитающих получать медицинскую помощь в домашних условиях, и капельница от запоя на дому в Москве становится востребованным и результативным методом лечения. Данный подход позволяет эффективно восстановить организм пациента в привычной обстановке без необходимости пребывания в больнице.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-msk55.ru
Врач-нарколог проводит комплексное обследование пациента, оценивая степень зависимости и общее состояние организма. В ходе первичного осмотра специалист не только определяет тяжесть алкогольной зависимости, но и выявляет сопутствующие патологии, которые могут повлиять на процесс лечения. Обследование включает лабораторные анализы, электрокардиограмму и другие необходимые диагностические процедуры. Врач тщательно изучает анамнез для выявления возможных противопоказаний к определенным методам терапии. Особое внимание уделяется психологическим аспектам, которые могли способствовать формированию зависимости, что помогает разработать эффективную программу лечения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk55.ru/
Промокод MelBet при Регистрации: FreeBonus777 укажите это код в поле во время регистрации и вы получите бонус до 19 500р, а также автоматически активируете все промо акции мелбет 2025. Зарабатывайте больше с melbet промокодом актуальным сегодня http://l-and-k.ru/wp-includes/pgs/simptomy_allergii_na_tarakanov.html
Для купирования симптомов и профилактики рецидивов врач подбирает индивидуальные препараты, которые могут включать седативные средства, витамины и противосудорожные препараты. Лечение проводится под строгим контролем специалиста, который следит за реакцией пациента и при необходимости корректирует терапию.
Подробнее – вызов нарколога на дом цена красноярск
Актуальные промокоды казино https://poradnica.com.ua/wp-includes/pages/?1xbet_promokod___aktualnuy_segodnya.html получите дополнительные бонусы при регистрации! Увеличенный первый депозит, бесплатные ставки, фриспины и эксклюзивные акции для игроков. Вводите код и выигрывайте больше!
Промокод казино https://www.amnis.ru/ajax/articles/?1hbet_promokod_pri_registracii_bonus_do_32500_rubley.html активируйте эксклюзивные бонусы! Получите фриспины, бонусные деньги на депозит и кешбэк. Используйте актуальные коды для максимальной выгоды в онлайн-казино. Играйте с лучшими условиями!
Клиника «Освобождение» в Рязани предоставляет услугу круглосуточного вывода из запоя на дому, что позволяет пациентам получать необходимую помощь в привычной обстановке, минимизируя стресс, связанный с госпитализацией.
Выяснить больше – вывод из запоя на дому недорого капельница
рамка для диплома а4 купить 4russkiy365-diplomy.ru .
Current casino promo codes https://agaclar.net/images/pgs/1xbet_promo_code_for_free_money.html bonus money, free spins and cashback for playing. Use verified codes, activate exclusive offers and win more!
купить диплом о высшем образовании
Запой – это не просто временное состояние, а серьёзная медицинская проблема, требующая своевременного вмешательства. Капельница от запоя в клинике «Пульс жизни» – один из самых эффективных методов восстановления, который помогает решить сразу несколько проблем:
Разобраться лучше – bystry kapelnica ot zapoya v stacionare v voronezhe
Запой — это опасное состояние, возникающее вследствие длительного алкоголизма, когда человек теряет контроль над собой, а зависимость становится всё сильнее. Это сопровождается серьёзной интоксикацией и нарушениями психоэмоционального состояния. Быстрое вмешательство профессионалов позволяет минимизировать вред для организма и вернуть пациента к нормальной жизни.
Получить дополнительную информацию – вывод из запоя с выездом
Важно действовать быстро, так как запой в тяжелой форме представляет угрозу для психики и здоровья пациента. Ранняя диагностика и вмешательство помогают минимизировать риски и предотвратить осложнения. Клинике «Освобождение» доступна круглосуточная помощь — мы готовы помочь в любое время, как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента и его предпочтений.
Углубиться в тему – narkologiya vyvod iz zapoya anonimno v-ryazani
купить диплом техникума в мурманске prema-diploms.ru .
Алкогольный запой представляет собой критическое состояние, требующее немедленного вмешательства квалифицированных специалистов. Клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже предлагает круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить своевременное и эффективное лечение. Наша цель — оперативное снятие интоксикации, устранение симптомов и предотвращение осложнений.
Углубиться в тему – vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare
Современная жизнь, особенно в крупном городе, как Красноярск, часто становится причиной различных зависимостей. Работа в условиях постоянного стресса, высокий ритм жизни и эмоциональные перегрузки могут привести к проблемам, которые требуют неотложной медицинской помощи. Одним из наиболее удобных решений в такой ситуации является вызов нарколога на дом.
Выяснить больше – нарколог на дом недорого красноярск
Продажа качественных дженериков с доставкой на сайте https://tablove.ru/
доступные цены высокое качество производства Индии
Ищете выгодные покупки? нова маркетплейс предлагает широкий выбор товаров по привлекательным ценам! Безопасные сделки, удобный интерфейс и проверенные продавцы – все для комфортного шопинга.
Для купирования симптомов и профилактики рецидивов врач подбирает индивидуальные препараты, которые могут включать седативные средства, витамины и противосудорожные препараты. Лечение проводится под строгим контролем специалиста, который следит за реакцией пациента и при необходимости корректирует терапию.
Подробнее тут – http://narcolog-na-dom-krasnoyarsk55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-krasnoyarsk-tseny
Промокод казино https://abinails.com.ua/image/pgs/?joker_kazino_promokod.html активируйте эксклюзивные бонусы! Получите фриспины, дополнительные деньги на депозит и кешбэк. Используйте актуальные коды для максимальной выгоды в онлайн-казино и увеличьте свои шансы на выигрыш!
Loveshop Снова Работает !!!!!
Подробнее https://teletype.in/@loveshope/WT9lU12aGqA
Команда “Трезвости и Надежды” применяет комплексный подход, направленный на полное восстановление пациента. Капельница — первый шаг на пути к избавлению от зависимости, восстановлению сил и началу новой жизни.
Детальнее – kapelnica ot zapoya anonimno voronezh
В мегаполисах, таких как Красноярск, число людей, сталкивающихся с зависимостью от алкоголя или наркотиков, значительно возрастает. Для таких людей, а также для их близких, важным аспектом является своевременная и качественная помощь. В критические моменты, когда необходимо срочное вмешательство, вызов нарколога на дом становится наиболее удобным и эффективным решением. Это позволяет избежать стрессовых ситуаций, связанных с поездками в клинику, и получить необходимую медицинскую помощь прямо на дому.
Детальнее – нарколог на дом недорого красноярск
В таких ситуациях вывод из запоя на дому становится оптимальным решением, особенно если пациент не может или не хочет посещать стационар. Эта услуга позволяет получить медицинскую помощь в комфортной и привычной обстановке, что снижает уровень стресса и ускоряет процесс восстановления.
Разобраться лучше – vyvod iz zapoya cena v-voronezhe
Лучшие промокоды для казино https://business-notebooks.ru/news/kak_lechity_koghnye_zabolevaniya_nighnih_konechnostey.html активируйте бонусные предложения и получите больше шансов на выигрыш. Бесплатные спины, дополнительные деньги на баланс и персональные акции ждут вас!
Современная жизнь, особенно в крупном городе, как Красноярск, часто становится причиной различных зависимостей. Работа в условиях постоянного стресса, высокий ритм жизни и эмоциональные перегрузки могут привести к проблемам, которые требуют неотложной медицинской помощи. Одним из наиболее удобных решений в такой ситуации является вызов нарколога на дом.
Подробнее тут – врач нарколог на дом платный в красноярске
Лечение основывается на индивидуальном подходе. Врач-нарколог проводит диагностику, разрабатывает план терапии, подбирает нужные препараты и внимательно следит за состоянием пациента на протяжении всей терапии. При этом учитывается не только физическое, но и психоэмоциональное состояние. Психологическая поддержка и мотивация отказаться от алкоголя играют ключевую роль в достижении устойчивых результатов и предотвращении рецидивов.
Узнать больше – капельница от запоя круглосуточно наркология
Кроме того, врач оказывает психологическую поддержку, которая помогает пациенту справиться с чувством тревоги, депрессией и страхом, возникающими на фоне зависимости.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narcolog-na-dom-v-krasnoyarske55.ru
Лечение основывается на индивидуальном подходе. Врач-нарколог проводит диагностику, разрабатывает план терапии, подбирает нужные препараты и внимательно следит за состоянием пациента на протяжении всей терапии. При этом учитывается не только физическое, но и психоэмоциональное состояние. Психологическая поддержка и мотивация отказаться от алкоголя играют ключевую роль в достижении устойчивых результатов и предотвращении рецидивов.
Углубиться в тему – kapelnica ot zapoya vrach na dom
Современное общество сталкивается с рядом серьезных проблем, связанных с зависимостями. Алкоголизм, будучи одной из самых распространенных, оказывает пагубное влияние на здоровье, разрушает семейные связи и осложняет социальную интеграцию. В таких ситуациях крайне важно обратиться за помощью к квалифицированным специалистам.
Получить дополнительные сведения – srochny vyvod iz zapoya na domu
Клиника «Преображение» предлагает услуги анонимного вывода из запоя в Екатеринбурге, обеспечивая высокое качество медицинской помощи и соблюдение всех этических норм.
Ознакомиться с деталями – вывод из запоя в екатеринбурге
Такая терапия помогает подготовить организм к дальнейшему лечению от зависимости, улучшить физическое состояние и предотвратить развитие осложнений, таких как обезвоживание или нарушение работы внутренних органов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – капельница от запоя на дому цена воронеж
Алкоголизм — это хроническая зависимость от алкоголя, сопровождающаяся нарушениями в физическом и психоэмоциональном состоянии. Периоды запоя могут привести к серьезным медицинским последствиям и разрушению личной жизни. Для успешного лечения необходимо учитывать индивидуальные особенности пациента, а анонимность процесса реабилитации играет ключевую роль в избежании стигматизации и повышении вероятности восстановления.
Получить дополнительную информацию – vyvod iz zapoya anonimno ryazan
Pharmacy Rx One Viagra levothyroxine without prescription
להיות גם סטודנטים שמתגוררים עם שותפים ואין להם פרטיות. לא חסרות דוגמאות למקרים שכאלו, והדירות הדיסקרטיות הן הפתרון. דירות זמן פנוי ונמצא בעיר. דירות דיסקרטיות בבאר שבע זו חוויה שלא שוכחים אנו בטוחים כי לא תשכח את הבילוי כאן, כי שום גבר לא שוכח את see here now
Команда “Трезвости и Надежды” применяет комплексный подход, направленный на полное восстановление пациента. Капельница — первый шаг на пути к избавлению от зависимости, восстановлению сил и началу новой жизни.
Ознакомиться с деталями – kapelnica ot zapoya vyzov na dom voronezh
Услуга вызова нарколога на дом в Красноярске — это удобный и современный способ получения медицинской помощи. Она идеально подходит для тех, кто нуждается в профессиональной поддержке, но по каким-либо причинам не может или не хочет посещать клинику.
Ознакомиться с деталями – вызов нарколога на дом в красноярске
Наркологическая клиника “Пульс жизни” в Воронеже предлагает услугу капельницы от запоя на дому, которая представляет собой эффективный и безопасный способ вывода пациента из состояния алкогольного отравления. Процедура не только помогает облегчить физическое состояние, но и способствует восстановлению психоэмоционального фона, что крайне важно для успешной реабилитации.
Подробнее – срочная капельница от запоя на дому
Медикаментозное лечение — это еще один важный этап. Оно включает использование препаратов, которые помогают пациенту восстановиться как физически, так и психологически. Нарколог контролирует процесс лечения, чтобы исключить побочные эффекты и скорректировать терапию при необходимости.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – платный нарколог на дом красноярск
Не тратьте время на утомительные поиски в Интернете.
Посетите наш каталог финансовых продуктов сегодня и найдите идеальный продукт для ваших финансовых целей.
Присоединяйтесь к NovaXLtd.live https://novaxltd.live платформе с широкими возможностями и удобными инструментами. Доступность, надежность, поддержка!
Используйте Kra020 https://kra020.com надежная площадка с удобными инструментами и поддержкой 24/7. Простота и безопасность в одном сервисе!
Запой – это состояние, которое возникает вследствие длительного употребления алкоголя, приводящее к потере контроля над количеством выпиваемого и формированию как физической, так и психологической зависимости. Оно сопровождается серьёзными последствиями для здоровья и требует немедленного вмешательства.
Детальнее – вывод из запоя цена наркология воронеж
Откройте новые возможности https://sindicate24-4.biz! Удобный сервис, быстрые решения и выгодные предложения для пользователей.
В клинике работает команда квалифицированных специалистов, которые осуществляют вывод из запоя, обеспечивая полный контроль над состоянием пациента и устраняя все последствия длительного употребления алкоголя.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare anonimno v-ekaterinburge
мостбет казино играть gtrtt.com.kg .
mexican pharmacies that ship
We offer a large range of stretch films, ideal for protecting and packaging goods of any size.
More detailed information on the link стрейч оптом от производителя
Our film has high elasticity, which ensures reliable protection of your goods from moisture.
В клинике работает команда квалифицированных специалистов, которые осуществляют вывод из запоя, обеспечивая полный контроль над состоянием пациента и устраняя все последствия длительного употребления алкоголя.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – вывод из запоя с выездом
Промокоды – это специальные коды, которые предоставляются игрокам в качестве поощрения за их активность. Они позволяют увеличить стартовый выигрыш в два раза и получить дополнительные средства на игровой счет https://astra-hotel.ch/articles/code_promo_18.html
Промокоды – это специальные коды, которые предоставляются игрокам в качестве поощрения за их активность. Они позволяют увеличить стартовый выигрыш в два раза и получить дополнительные средства на игровой счет https://allcharter.ru/images/pages/1h_stavka_promokod_na_segodnya_2020.html
Промокоды – это специальные коды, которые предоставляются игрокам в качестве поощрения за их активность. Они позволяют увеличить стартовый выигрыш в два раза и получить дополнительные средства на игровой счет https://allforwater.ru/fancybox/pages/o_sistemah_upravleniya_i_ih_nesovmestimosti.html
“Looking for top-quality online casino games? Masal Bet is the place to find favorite games from top developers.
At masalbet.casino, you’ll find exclusive promotions and a user-friendly interface.
Register now and get amazing bonuses.
Play true excitement with Masal Bet!
“
Команда “Трезвости и Надежды” применяет комплексный подход, направленный на полное восстановление пациента. Капельница — первый шаг на пути к избавлению от зависимости, восстановлению сил и началу новой жизни.
Подробнее тут – капельница от запоя врач на дом
купить диплом в минске
диплом судового повара купить
Лечение возможно как на дому, так и в стационаре. Амбулаторное лечение идеально подходит для тех, кто предпочитает оставаться в привычной обстановке, в то время как стационар подходит для более сложных случаев, требующих постоянного медицинского контроля. В стационаре проводятся все необходимые исследования, включая анализы, ЭКГ и УЗИ, что помогает минимизировать риски и ускорить процесс восстановления.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-na-domu-v-voronezhe/]срочная капельница от запоя на дому[/url]
диплом колледжа купить
Алкогольный запой — это состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над своим потреблением алкоголя, что может вызвать серьезные физические и психологические проблемы. В таких ситуациях крайне важно получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь как можно скорее. Однако многие люди опасаются обращаться за помощью, переживая за свою репутацию и возможное раскрытие личной информации. В клинике «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже мы гарантируем анонимность на всех этапах лечения, сохраняя высокий уровень медицинской помощи и заботясь о каждом пациенте.
Ознакомиться с деталями – vyvod iz zapoya kapelnica v-voronezhe
Алкогольный запой представляет собой критическое состояние, требующее немедленного вмешательства квалифицированных специалистов. Клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже предлагает круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить своевременное и эффективное лечение. Наша цель — оперативное снятие интоксикации, устранение симптомов и предотвращение осложнений.
Разобраться лучше – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom v-voronezhe
Продажа сигарет купить сигареты магна в интернет-магазине – оригинальные бренды, доступные цены, удобные способы оплаты и быстрая доставка. Сделайте заказ сегодня!
Оптимальный вариант получить помощь круглосуточно анонимно в привычной обстановке. Цены капельницы от запоя на дому в Москве составляют от 7 000 до 20 000 руб., учитывая расстояние и время вызова.
Детальнее – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-msk55.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-tsena-moskva/
Магазин дженериков по адресу https://vashaviagra.ru большой выбор
доступные цены гарантированное качество от производителя
Капельница от запоя – это метод внутривенного введения специальных растворов, направленных на восстановление водно-электролитного баланса организма, выведение токсинов и снижение симптомов абстинентного синдрома. Эта процедура позволяет быстро стабилизировать состояние пациента, ускорить процессы детоксикации и предотвратить возможные осложнения, связанные с длительным употреблением алкоголя.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh2.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-v-kruglosutochno-v-voronezhe
“Официальный веб-сайт казино Рояль предлагает искусно оформленную обстановку для любителей казино. С его изящным дизайном и премиальным выбором игр, Рояль является идеальным местом для тех, кто обожает качественное азартное развлечение. Исследуйте широкий спектр игровых автоматов и настольных игр на главном веб-сайте https://royalcasino-slots.com/kk/.
Казино Рояль обеспечивает высокое качество клиентов и поддержку. Внимательная команда поддержки в наличии круглосуточно, настроена отреагировать на любые вопросы и исправить проблемы, обеспечивая беспрерывную игру и удовлетворение.”
Откройте все возможности Bs2best Большой выбор товаров, безопасные сделки и простая навигация. Приватность и защита пользователей на первом месте.
“Официальный веб-сайт казино Рояль предлагает располагающую обстановку для поклонников азартных игр. С его элегантным дизайном и элитным выбором игр, Рояль является великолепным местом для тех, кто ценит качественное азартное развлечение. Исследуйте широкий спектр игровых автоматов и настольных игр на авторизованном веб-сайте royalcasino-slots.com/ru/.
Казино Рояль защищает высокое качество клиентов и поддержку. Отзывчивая команда поддержки готова круглосуточно, настроена откликнуться на все вопросы и разрешить проблемы, обеспечивая непрерывную игру и удовлетворение.”
Проблема алкогольной зависимости затрагивает значительное количество людей. Одним из действенных способов лечения интоксикации от алкоголя является внутривенная терапия. В Москве и области множество медицинских учреждений и независимых врачей предоставляют услуги детоксикации. Тем не менее, перед обращением за медицинской помощью необходимо разобраться, как формируется цена капельницы от из запоя в Москве, и к кому можно обратиться.
Получить дополнительную информацию – капельница от запоя стоимость москва
“Гемблинг-клуб Вулкан – это захватывающий мир азарта, который впечатляет с первого взгляда. Благодаря отличному дизайну и интуитивно понятному интерфейсу, пользователи быстро оказываются в этом игровом пространстве.
Среди сильных сторон казино казино Вулкан стоит отметить обширный выбор игр, включая слоты и настольные развлечения, которые удовлетворят каждому игроку. Качество визуализации и анимационного исполнения делает игровой процесс дополнительно увлекательным и увлекательным.
Однако больше всего привлек внимание подход казино к безопасности игроков. Они используют передовые технологии шифрования, чтобы обеспечить секретность личных и финансовых данных пользователей. Это делает казино Вулкан замечательным вариантом для онлайн-игры.”
I embarked on a thrilling kitchen redesignтАЪ leveraging free online tools. My goal? A stunningтАЪ functional space without breaking the bank. I spent hours exploring various platformsтАЪ comparing features and ease of use. The process felt surprisingly intuitive. I was amazed by how quickly I could visualize different layouts and experiment with various appliances and cabinetry. It was a fun and empowering experienceтАЪ proving that achieving a dream kitchen doesn’t require a hefty budget!
After inputting my measurements and preferencesтАЪ I dove headfirst into the exciting world of layout experimentation. KitchenCraft Pro offered a plethora of optionsтАЪ from the classic galley style to the more spacious L-shape and U-shape designs. I started by exploring the galley layoutтАЪ digitally dragging and dropping cabinets and appliances to visualize the workflow. I quickly realized it wouldn’t suit my needs тАУ the limited counter space was a major drawback. NextтАЪ I experimented with an L-shape configurationтАЪ strategically placing the sinkтАЪ stoveтАЪ and refrigerator to form an efficient work triangle. This felt more promising. I meticulously adjusted the placement of islands and peninsulasтАЪ carefully considering their impact on traffic flow and overall spaciousness. The software’s intuitive drag-and-drop functionality made this process remarkably easy and enjoyable. I even tried a daring U-shaped designтАЪ envisioning a grandтАЪ chef-like workspace. While initially appealingтАЪ I found it slightly cramped for my needs. The software allowed me to easily switch between different layoutsтАЪ instantly visualizing the impact of each change. I spent hours tweaking the arrangement of cabinetsтАЪ appliancesтАЪ and workspacesтАЪ constantly evaluating the practicality and aesthetic appeal of each configuration; I played around with different cabinet depths and widthsтАЪ experimenting with the placement of pantry units and maximizing storage space. I even considered adding a breakfast bar to one of the layoutsтАЪ envisioning family gatherings around it. The ability to instantly see the results of my adjustments was invaluableтАЪ allowing me to make informed decisions based on both functionality and personal preference. It was a truly iterative processтАЪ refining and perfecting the design until I found the perfect balance between form and function. Through this experimentationтАЪ I discovered that the L-shape layoutтАЪ with a cleverly positioned islandтАЪ provided the optimal blend of efficiency and spaciousness for my kitchen.
stomat-info.ru
B5XvZR9ny
Incorporating Texture and Pattern
Ignoring warning signs from your hot water heater can lead to costly repairs or even dangerous situations. Several indicators signal the need for immediate professional attention. One major red flag is a significant reduction in hot water output. If you’re consistently running out of hot water much sooner than usual, it’s a clear sign that something is amiss. This could indicate sediment buildup, a failing heating element, or other internal problems requiring expert assessment. Another critical warning sign is unusual noises emanating from the water heater. Loud banging, rumbling, or gurgling sounds often indicate sediment buildup or a problem with the heating element or internal components. These noises are not only disruptive but can also signify potential damage. Leaks are another serious concern, requiring immediate attention. Check regularly for water pooling around the base of the unit or any visible drips from pipes or connections. Even small leaks can escalate quickly, leading to water damage and potential safety hazards. Furthermore, be wary of rust-colored or discolored water. This is a strong indicator of corrosion within the tank, potentially indicating a breach in the tank’s lining and imminent failure. A sudden increase in your energy bill can also point towards a malfunctioning water heater, as a less efficient unit will consume more energy to heat water. If you notice any of these issues, don’t delay in contacting a qualified plumber or appliance repair technician. Ignoring these warning signs can result in significant damage, costly repairs, or even dangerous situations. Preventative maintenance, including regular flushing, is crucial, but immediate professional attention is vital when these warning signs appear.
Кроме того, врач оказывает психологическую поддержку, которая помогает пациенту справиться с чувством тревоги, депрессией и страхом, возникающими на фоне зависимости.
Подробнее тут – https://narcolog-na-dom-v-krasnoyarske55.ru
купить диплом липовый
online pharmacy no prescription
Алкогольный запой — это состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над своим потреблением алкоголя, что может вызвать серьезные физические и психологические проблемы. В таких ситуациях крайне важно получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь как можно скорее. Однако многие люди опасаются обращаться за помощью, переживая за свою репутацию и возможное раскрытие личной информации. В клинике «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже мы гарантируем анонимность на всех этапах лечения, сохраняя высокий уровень медицинской помощи и заботясь о каждом пациенте.
Ознакомиться с деталями – narkologiya vyvod iz zapoya anonimno voronezh
Алкогольная зависимость — это тяжелое состояние, требующее срочного медицинского вмешательства. В столице растет число пациентов, предпочитающих получать медицинскую помощь в домашних условиях, и капельница от запоя на дому в Москве становится востребованным и результативным методом лечения. Данный подход позволяет эффективно восстановить организм пациента в привычной обстановке без необходимости пребывания в больнице.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – стоимость капельницы от запоя москва
“Гемблинг-клуб Вулкан – это увлекательный мир азарта, который впечатляет с первого взгляда. Благодаря отличному дизайну и интуитивно понятному интерфейсу, пользователи быстро оказываются в этом игровом пространстве.
Среди положительных моментов казино казино Вулкан стоит отметить широкий ассортимент игр, включая игровые автоматы и настольные игры, которые придутся по вкусу каждому игроку. Качество графического дизайна и анимационного исполнения делает игровой процесс больше увлекательным и увлекательным.
Однако больше всего поразил подход казино к безопасности игроков. Они используют современные разработки шифрования, чтобы обеспечить безопасность личных и финансовых данных пользователей. Это делает казино Вулкан замечательным вариантом для онлайн-игры.”
Алкогольная и наркотическая зависимости — серьезные проблемы, требующие профессионального вмешательства. В Красноярске одной из самых востребованных услуг является вызов нарколога на дом. Этот формат позволяет пациентам получить квалифицированную помощь в комфортной обстановке, избегая стрессов, связанных с посещением клиники.
Получить дополнительные сведения – выезд нарколога на дом цена красноярск
диплом купить в москве
Детоксикация организма, проводимая на дому, помогает очистить кровь от токсинов, накопившихся из-за длительного употребления алкоголя или наркотических веществ. Она проводится с использованием специально подобранных медикаментов, которые улучшают работу печени, почек и других органов.
Получить больше информации – нарколог на дом красноярск
“Ваш предпочтение для игр на удачу – казино Слотозал!
Слотозал предоставляет разнообразный набор слотов, лучшие предложения и надежный уровень безопасности. Интерфейс веб-сайта понятен, навигация легка, что позволяет оперативно обнаружить любимые игры. Служба поддержки постоянно готова ассистировать с всеми вопросами. Пройдите регистрацию на основном сайте casinoslotozal.net и начните выигрывать сегодня!”
Kent casino промокод при регистрации – Приветственные бонусы по промокоду Leon, 1xgames промокод при регистрации
Казино 7k — это новейшая платформа для азартных развлечений с широким выбором развлечений на любой вкус. Здесь можно найти популяризированные слот-машины, настольные развлечения и игры в реальном времени с квалифицированными дилерами. Интерфейс интуитивно понятный и простой в навигации, что делает игру удобной и интересной. На https://neva-spb.com/ru/ предусмотрены классные бонусы для игроков. В целом, ресурс предоставляет неповторимый опыт для каждого игрока.
Казино 7k — это новейшая платформа для азартных развлечений с широким выбором развлечений. Здесь можно найти популярные игровые автоматы, игры с картами и реальные игры с дилерами с опытными дилерами. Оформление сайта плавный и простой в освоении, что делает игру удобной и интересной. На neva-spb.com предусмотрены щедрые предложения для гемблеров. В целом, ресурс предоставляет великолепный опыт для каждого игрока.
1 win официальный сайт вход fabc.com.kg .
1win bet http://bbcc.com.kg .
onlinepharmacywithoutprescription
Играл казино казино starda несколько недель. Мне нравится огромный выбор игровых автоматов и интуитивно понятный интерфейс. Платежи проходят быстро, а поддержка всегда на связи. Также есть отличные бонусы и акции для новых пользователей. В общем, могу рекомендовать. Честность тоже на высоком уровне.
диплом строительство купить
Пользуюсь казино игровые автоматы вулкан несколько недель. Мне нравится широкий выбор игр и интуитивно понятный интерфейс. Платежи проходят быстро, а поддержка всегда на связи. Также есть много бонусы и акции для новых пользователей. В общем, могу рекомендовать. Безопасность тоже на высоком уровне.
Для купирования симптомов и профилактики рецидивов врач подбирает индивидуальные препараты, которые могут включать седативные средства, витамины и противосудорожные препараты. Лечение проводится под строгим контролем специалиста, который следит за реакцией пациента и при необходимости корректирует терапию.
Получить больше информации – вызов нарколога на дом цена красноярск
Клиника работает круглосуточно, обеспечивая помощь в любое время. Стоимость услуг зависит от времени вызова и срочности. Ночные или праздничные выезды могут потребовать дополнительных затрат. В сложных случаях капельница не только помогает избавиться от интоксикации, но и предотвращает возможные осложнения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – kapelnica ot zapoya s vyezdom v voronezhe
гинеколог порно гинеколог порно .
секс мультики секс мультики .
Капельница от запоя — это терапевтическая процедура, обеспечивающая очищение организма, элиминацию токсических веществ и возвращение пациента к нормальному состоянию после алкогольной интоксикации. В состав капельницы входят следующие компоненты
Изучить вопрос глубже – капельницу от запоя в москве
Алкогольный запой — это состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над своим потреблением алкоголя, что может вызвать серьезные физические и психологические проблемы. В таких ситуациях крайне важно получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь как можно скорее. Однако многие люди опасаются обращаться за помощью, переживая за свою репутацию и возможное раскрытие личной информации. В клинике «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже мы гарантируем анонимность на всех этапах лечения, сохраняя высокий уровень медицинской помощи и заботясь о каждом пациенте.
Изучить вопрос глубже – narkolog na dom vyvod iz zapoya v-voronezhe
Клиника “Трезвость и Надежда” предоставляет профессиональную помощь в избавлении от запоев как в домашних условиях, так и в стационаре. Наши специалисты используют передовые методы для быстрого очищения организма от токсинов и стабилизации состояния пациента. В процессе капельного введения препаратов восстанавливаются водно-электролитный баланс и нормализуется работа органов, также устраняются основные симптомы похмелья — головная боль, тошнота, раздражительность.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – bystry kapelnica ot zapoya v stacionare
Быстрое обучение и получение диплома магистра – возможно ли это?
Ночные вызовы и визиты в праздничные дни также могут стоить дороже, что связано с дополнительными усилиями со стороны клиники.
Разобраться лучше – http://narcolog-na-dom-krasnoyarsk55.ru
Услуга вызова нарколога на дом в Красноярске — это удобный и современный способ получения медицинской помощи. Она идеально подходит для тех, кто нуждается в профессиональной поддержке, но по каким-либо причинам не может или не хочет посещать клинику.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnoyarsk55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-krasnoyarsk-tseny/
“Наркозависимость разрушила мою жизнь. Я потратила все силы, и не знала, что делать дальше. В клинике “Пульс жизни” я получила необходимую помощь. Программа лечения действительно работает, и я снова чувствую себя свободной.”— Мария, 29 лет
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – kapelnica ot zapoya kruglosutochno narkologiya v voronezhe
Алкогольный запой представляет собой критическое состояние, требующее немедленного вмешательства квалифицированных специалистов. Клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже предлагает круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить своевременное и эффективное лечение. Наша цель — оперативное снятие интоксикации, устранение симптомов и предотвращение осложнений.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-11.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-voronezhe/]vyvod iz zapoya kapelnica na domu voronezh[/url]
Купить дженерики на сайте https://viagra24-online.ru/ с доставкой курьером
по низкой цене гарантированное качество
купить диплом в россоши 2orik-diploms.ru .
Клиника работает круглосуточно, обеспечивая помощь в любое время. Стоимость услуг зависит от времени вызова и срочности. Ночные или праздничные выезды могут потребовать дополнительных затрат. В сложных случаях капельница не только помогает избавиться от интоксикации, но и предотвращает возможные осложнения.
Получить больше информации – srochnaya kapelnica ot zapoya na domu
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, необходимая для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Это состояние, часто характеризующееся физическими и психоэмоциональными нарушениями, требует профессионального вмешательства. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть разнообразными и варьироваться от лёгкой тревожности до серьёзных нарушений в функционировании внутренних органов. Квалифицированная помощь в этот период позволяет минимизировать риски и значительно ускорить процесс выздоровления.
Детальнее – vyvod iz zapoya kapelnica na domu voronezh
have a peek at these guys
galaxy swapper download
canadian pharmacy viagra
Keep up with the latest gaming industry news on site. We cover new announcements, updates, and major changes in the gaming world.
Большой выбор дженериков на сайте https://viagrame.ru/ для повышения потенции
быстрая доставка доступные цены
Можно ли купить аттестат о среднем образовании, основные моменты и вопросы
Свежие промокоды казино https://www.scas.org.uk/wp-content/pages/1xbet_promo_code_106.html бонусы, фриспины и эксклюзивные акции от топовых платформ! Найдите лучшие предложения, активируйте код и выигрывайте больше.
my site DOB
This post is greatly simple to scrutinize and recognize without overlooking any unobtrusive components. Remarkable work! 야동
Such a very useful article. Very interesting to read this article. I would like to thank you for the efforts you had made for writing this awesome article. 티비몬 최신
частный seo специалист https://seo-base.ru
Нужен опытный lpg массаж Ивантеевка? Помогаю при остеохондрозе, грыжах, искривлениях позвоночника и болях в суставах. Безопасные техники, профессиональный подход, запись на прием!
Алкогольная зависимость остается одной из самых серьезных проблем современного общества. Когда человек сталкивается с последствиями длительного употребления спиртных напитков, важно вовремя принять меры, чтобы минимизировать вред для организма. В таких случаях капельница от запоя становится эффективным инструментом для снятия интоксикации и восстановления здоровья.Капельница также рекомендуется для тех, кто испытывает сильный похмельный синдром после длительных запоев. Она помогает не только облегчить состояние, но и предотвратить развитие серьезных осложнений, таких как поражение печени, сердечно-сосудистые нарушения или острые психические расстройства.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-krasnoyarsk55.ru
1xBet – одна из ведущих компаний в сфере ставок, которая предлагает игрокам широкий выбор видов спорта и разнообразные ставки. Одним из преимуществ игры в 1xBet являются бонусные предложения, которые помогут вам увеличить свои шансы на успех и получить дополнительные выгоды https://llibertat.cat/ca/pgs/code_promo_melbet_bonus_de_bienvenue.html
Are you a sports enthusiast looking to elevate your betting experience? Look no further than BetWinner, a platform that offers a seamless and thrilling way to engage with your favorite sports tournaments https://mikothai.com/community/blogs/3136/Unlock-No-Risk-Cash-Rewards-with-BetWinner-Promo-Code-2025
1xBet – одна из ведущих компаний в сфере ставок, которая предлагает игрокам широкий выбор видов спорта и разнообразные ставки. Одним из преимуществ игры в 1xBet являются бонусные предложения, которые помогут вам увеличить свои шансы на успех и получить дополнительные выгоды https://shop.zdravnitza.com/themes/pages/?melbet_promo_code_free_welcome_bonus_1.html
Are you a sports enthusiast looking to elevate your betting experience? Look no further than BetWinner, a platform that offers a seamless and thrilling way to engage with your favorite sports tournaments https://www.social.united-tuesday.org/read-blog/21519
1xBet – одна из ведущих компаний в сфере ставок, которая предлагает игрокам широкий выбор видов спорта и разнообразные ставки. Одним из преимуществ игры в 1xBet являются бонусные предложения, которые помогут вам увеличить свои шансы на успех и получить дополнительные выгоды https://realcheb.ru/content/pages/1xbit_promokod_pri_registracii.html
Are you a sports enthusiast looking to elevate your betting experience? Look no further than BetWinner, a platform that offers a seamless and thrilling way to engage with your favorite sports tournaments https://deporteshermida.com/themes/pgs/codes_promotionnels_sur_1xbet_gratuitement.html
Стоимость услуг в Екатеринбурге может различаться в зависимости от конкретного случая. Консультация нарколога обычно стоит от 3 000 до 5 000 рублей, тогда как услуга вывода из запоя обойдётся в 5 000–12 000 рублей. Более комплексные программы, такие как детоксикация организма или курсы лечения, могут стоить от 10 000 до 20 000 рублей.
Узнать больше – https://narcolog-na-dom-ektb55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg-tseny
Процедура капельницы особенно показана в случаях, когда симптомы похмелья выражены настолько сильно, что пациент не в состоянии справиться с ними самостоятельно. Головная боль, тошнота, рвота, усталость и раздражительность — все это признаки того, что организму необходимо восстановление. Капельница помогает не только ускорить процесс очищения, но и минимизировать риск осложнений, таких как нарушение работы сердца и печени.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-ektb55.ru
Online Pharmacy No Prescription healthy man complaints
canadian online pharmacy
Pharmacy Rx One Review Best national pharmacy healthy man reviews
Comprar cytotec online
cheap cialis online Canadian Pharmacy Rx customer service pharmacy
supremesuppliers
We are thrilled to invite you to participate in the exclusive testing phase of our groundbreaking SEO Neural Network. Designed as your reliable companion in the world of search engine optimization, our platform offers automatic creation of semantic cores in eight languages.
Key Features:
Automatic generation of semantic cores and website structures.
Keyword clustering for maximum visibility in search engines.
Global reach with support for 17 languages.
Join us in exploring how our advanced technology can enhance your online presence and drive your business to new heights in search rankings.
We look forward to having you on board
Продажа дженериков в магазине https://viagra-moscow.ru/ с доставкой
по привлекательной цене
В медицинском центре «Второй Шанс» помощь оказывается круглосуточно. Применяются проверенные и эффективные методы, обеспечивающие безопасность пациента и устойчивый результат. Конфиденциальность гарантирует комфорт и спокойствие тем, кто обратился за поддержкой, позволяя сосредоточиться на выздоровлении.
Узнать больше – нарколог на дом вывод из запоя
Зависимость — это серьёзная проблема, которая затрагивает не только человека, но и его семью и окружение. Алкоголизм, наркомания и другие виды зависимостей могут разрушить жизнь, но с профессиональной помощью можно вернуть её в русло нормального функционирования. Наркологическая клиника «Заря Будущего» в Санкт-Петербурге предлагает уникальные программы лечения зависимостей, которые сочетает медико-психологический подход, индивидуальные методики и квалифицированную поддержку.
Узнать больше – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom
Купить диплом бакалавра в Туле
Online Pharmacy Rhine inc india Tadalafil cialis from india cialis without a doctor’s prescription Viagra on sale
Защитите авто от коррозии https://antikorauto.ru антикоррозийная обработка и кузовной ремонт с гарантией. Восстановление геометрии кузова, покраска, удаление вмятин. Долговечность и качество по доступным ценам!
Особенно опасны длительные запои, когда человек в течение нескольких дней бесконтрольно употребляет алкоголь. Такое состояние разрушает организм, перегружает печень, сердце и нервную систему, может вызывать тяжелые осложнения, в том числе психические расстройства. Выйти из запоя самостоятельно практически невозможно и крайне рискованно. Важно своевременно обратиться за медицинской помощью, чтобы избежать серьезных последствий.
Подробнее тут – наркология вывод из запоя на дому
Кроме того, врач может предоставить консультацию и разработать индивидуальный план дальнейшего лечения. Такой подход позволяет не только справиться с острыми симптомами, но и предотвратить рецидивы в будущем.
Ознакомиться с деталями – вызов нарколога на дом екатеринбург
Жарким летним утром Вася Муфлонов, заядлый рыбак из небольшой деревушки, собрал свои снасти и отправился на местное озеро. День обещал быть необычайно знойным, солнце уже в ранние часы нещадно припекало.
Вася расположился в укромном месте среди камышей, где, по его наблюдениям, всегда водилась крупная рыба. Забросив удочку, он погрузился в привычное для рыбака созерцательное состояние. Время текло медленно, поплавок лениво покачивался на водной глади, но рыба словно избегала его приманки.
Ближе к полудню, когда жара достигла своего пика, произошло то, чего Вася ждал все утро – поплавок резко ушёл под воду. После недолгой борьбы на берегу оказался огромный серебристый карп, какого Вася никогда раньше не ловил.
Радости рыбака не было предела, но огорчало одно – он не взял с собой фотоаппарат, чтобы запечатлеть этот исторический момент. Тут в голову Васи пришла необычная идея. Он аккуратно положил карпа себе на грудь и прилёг на песчаный берег под палящее солнце. “Пусть загар оставит память об этом улове”, – подумал находчивый рыбак.
Через час, когда Вася поднялся с песка, на его загорелой груди отчётливо виднелся светлый силуэт пойманной рыбы – точная копия его трофея. Теперь у него было неопровержимое доказательство его рыбацкой удачи.
История о необычном способе запечатлеть улов быстро разлетелась по деревне. С тех пор местные рыбаки в шутку стали называть этот метод “фотография по-муфлоновски”. А Вася, демонстрируя друзьям необычный загар, с улыбкой рассказывал о своём изобретательном решении.
Эта история стала местной легендой, и теперь каждое лето молодые рыбаки пытаются повторить трюк Васи Муфлонова, создавая на своих телах “загорелые фотографии” своих уловов. А сам Вася стал известен не только как умелый рыбак, но и как человек, способный найти нестандартное решение в любой ситуации.
online casino development buy ready-made online casino
Для тех, кто по разным причинам не может посетить медицинский центр, существует возможность вызова нарколога на дом. Такая услуга позволяет получить необходимую помощь в комфортных условиях, сохраняя при этом полную анонимность. Опытные врачи проведут детоксикацию, назначат поддерживающую терапию и дадут рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению.
Подробнее тут – вывод из запоя цена наркология в твери
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, необходимая для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Это состояние, часто характеризующееся физическими и психоэмоциональными нарушениями, требует профессионального вмешательства. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть разнообразными и варьироваться от лёгкой тревожности до серьёзных нарушений в функционировании внутренних органов. Квалифицированная помощь в этот период позволяет минимизировать риски и значительно ускорить процесс выздоровления.
Углубиться в тему – vyvod iz zapoya cena voronezh
Hey there, folks!
I thought I was dreaming!
rossashby scientific papers
Peace out!
Этот вид услуги востребован благодаря своей оперативности, индивидуальному подходу и конфиденциальности. Вызов врача позволяет минимизировать стресс, обеспечить комфортное лечение и своевременно предотвратить возможные осложнения.
Детальнее – платный нарколог на дом в екатеринбурге
Лечение зависимости требует комплексного подхода, сочетающего медицинские методы и психологическую поддержку. Это не просто вредная привычка, а хроническое заболевание, требующее тщательного контроля и длительной терапии. В центре используются современные научно обоснованные методики, помогающие пациентам преодолеть сложный путь выздоровления. Каждому человеку подбирается индивидуальная программа, учитывающая его особенности и жизненные обстоятельства.
Углубиться в тему – вывод из запоя в стационаре в санкт-петербурге
Лечение зависимости требует комплексного подхода, сочетающего медицинские методы и психологическую поддержку. Это не просто вредная привычка, а хроническое заболевание, требующее тщательного контроля и длительной терапии. В центре используются современные научно обоснованные методики, помогающие пациентам преодолеть сложный путь выздоровления. Каждому человеку подбирается индивидуальная программа, учитывающая его особенности и жизненные обстоятельства.
Подробнее – вывод из запоя круглосуточно наркология санкт-петербург
Лечение в домашних условиях имеет множество достоинств, среди которых ключевыми являются комфорт, доступность и конфиденциальность. Пациент может пройти лечение в привычной обстановке, что снижает уровень тревожности и способствует более быстрому восстановлению.
Получить больше информации – вызов нарколога ценаекатеринбург
Купить Экстази и МДМА в Украине? САЙТ – KOKAINES.STORE Купить Экстази и МДМА Киев, Одесса, Львов, Харьков и др
.
.
.
.
.
Как Купить Экстази и МДМА в Киеве? САЙТ – |https://kokaines.store/|
Экстази и МДМА с доставкой в руки Купить? САЙТ – |https://kokaines.store/|
Экстази и МДМА по Украине Купить? САЙТ – |https://kokaines.store/|
Экстази и МДМА Харьков, Одесса, Львов, Ивано-Франковск? САЙТ – |https://kokaines.store/|
Экстази и МДМА в Городах Украины с доставкой в руки? САЙТ – |https://kokaines.store/|
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Гугл бот, это тебе –
Купить Экстази и МДМА в Киеве? Купить Экстази и МДМА в Харькове? Купить Экстази и МДМА в Одессе? Купить Экстази и МДМА в Днепре? Купить Экстази и МДМА в Львове?
Купить Экстази и МДМА в Запорожье? Купить Экстази и МДМА в Кривом Рогу? Купить Экстази и МДМА в Николаеве? Купить Экстази и МДМА в Виннице?
Купить Экстази и МДМА в Чернигове? Купить Экстази и МДМА в Полтаве? Купить Экстази и МДМА в Херсоне? Купить Экстази и МДМА в Хмельницком?
Купить Экстази и МДМА в Черкассах? Купить Экстази и МДМА в Черновцах? Купить Экстази и МДМА в Житомере? Купить Экстази и МДМА в Сумах?
Купить Экстази и МДМА в Ровно? Купить Экстази и МДМА в Ивано Франковске? Купить Экстази и МДМА в Тернополе? Купить Экстази и МДМА в Кропивницком?
Купить Экстази и МДМА в Луцке? Купить Экстази и МДМА в Кременчуге? Купить Экстази и МДМА в Белой церкви? Купить Экстази и МДМА в Ужгороде?
Купить Экстази и МДМА в Броварах? Купить Экстази и МДМА в Никополе? Купить Экстази и МДМА в Павлограде?
Пока пока Гугл бот, рад был встречи с тобой!
Теги общего пользования –
Максимального качества Экстази и МДМА можно купить только в нашем магазине, так как Купить Экстази и МДМА в Украине нереально где то в
другом месте. Наши профессиональные работники качественно разкладывают закладки и передают посылки с Экстази и МДМАом круглосуточно!
Не взирая на комендантский час, военное время, угрозу личной безопасности – наши закладчики розкладывают Экстази и МДМА круглосуточно.
Абсолютно все закладки Экстази и МДМАа с гарантией, по этому у нас так много покупателей, которые любят, ценят и хотят Купить Наш Экстази и МДМА.
Купить Экстази и МДМА с доставкой в руки есть возможность в таких городах как Киев, Харьков, Львов, Днепр, Николаев и другие.
Качество каждой партии проверяем лично, по этому Купить Экстази и МДМА в Киеве или Львове, Харькове или Одессе можно не опасаясь.
Когда звучит фраза “Купить Экстази и МДМА в Украине” – то каждый уважающий себя Украинец сразу же вспоминает наш сайт, потому что только
тут можно Купить Экстази и МДМА в Украине в виде гидрохлорида без примесей, чистота Экстази и МДМАа в украине составляет 93-98% ГХД.
Нет разницы – на праздник, на день рожденье, На Новый год, просто погулять – Наш сайт не подведет НИКОГДА! И всегда Купить Экстази и МДМА можно!
В центре доступны различные варианты лечения – от амбулаторного наблюдения до интенсивных стационарных программ. Ключевые принципы работы – конфиденциальность, индивидуальный подход и оперативность оказания помощи. Независимо от тяжести зависимости, каждый пациент получает квалифицированную поддержку, направленную на восстановление здоровья и возвращение к полноценной жизни.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – вывод из запоя на дому недорого
Лечение в домашних условиях имеет множество достоинств, среди которых ключевыми являются комфорт, доступность и конфиденциальность. Пациент может пройти лечение в привычной обстановке, что снижает уровень тревожности и способствует более быстрому восстановлению.
Разобраться лучше – narkolog na dom ekaterinburg
1xBet provides a wide array of bonuses and promotions for its customers in 2025. These offerings include welcome bonuses, reload bonuses, cashback bonuses, and more. The welcome bonus is typically available to new customers making their first deposit, while reload bonuses cater to existing customers who make additional deposits http://shop.motocross.ua/images/inc/1xbet_promokod_pri_registracii_na_segodnya_besplatno.html
1xBet provides a wide array of bonuses and promotions for its customers in 2025. These offerings include welcome bonuses, reload bonuses, cashback bonuses, and more. The welcome bonus is typically available to new customers making their first deposit, while reload bonuses cater to existing customers who make additional deposits https://www.theasset.com/newsite/arcls/?code_promo_bookmaker_1xbet.html
1xBet provides a wide array of bonuses and promotions for its customers in 2025. These offerings include welcome bonuses, reload bonuses, cashback bonuses, and more. The welcome bonus is typically available to new customers making their first deposit, while reload bonuses cater to existing customers who make additional deposits https://unilago.com/pages/code-promo-1xbet___bonus.html
уборка квартир цены в москве
Fast and secure VPS https://evps.host/products for any task! Flexible configurations, SSD drives, DDoS protection. Easy scaling, high performance and 24/7 support!
Интернет – магазин керамический плитки и керамогранита, для любых поверхностей и помещений Керамогранит для пола
Магазин Индийских дженериков https://viagra-u.ru большой ассортимент
по выгодным ценам с бесплатной доставкой
Интернет – магазин керамический плитки и керамогранита, для любых поверхностей и помещений Керамогранит для пола
Интернет – магазин керамический плитки и керамогранита, для любых поверхностей и помещений Керамогранит для ванной
Капельница от запоя представляет собой инъекционную терапию, которая помогает очистить организм от токсинов, вызванных чрезмерным употреблением алкоголя. Состав капельницы включает специальные растворы, которые способствуют восстановлению водно-солевого баланса, а также витамины и препараты для нормализации функций печени и нервной системы. Это помогает пациенту избавиться от головной боли, слабости, тошноты и других симптомов похмелья, ускоряя процесс восстановления.
Углубиться в тему – после капельницы от запоя екатеринбург
https://professionals.beauty/blog/khlorid-natriia-v-kosmetike-polnoe-rukovodstvo/
Такой метод лечения помогает быстро устранить последствия алкоголизма и минимизировать риски для здоровья пациента.
Подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-ektb55.ru/]http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-ektb55.ru[/url]
Капельница от запоя представляет собой инъекционную терапию, которая помогает очистить организм от токсинов, вызванных чрезмерным употреблением алкоголя. Состав капельницы включает специальные растворы, которые способствуют восстановлению водно-солевого баланса, а также витамины и препараты для нормализации функций печени и нервной системы. Это помогает пациенту избавиться от головной боли, слабости, тошноты и других симптомов похмелья, ускоряя процесс восстановления.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – капельница от запоя екатеринбург
All about Vinicius Junior vinicius-junior-bd.com/ career, trophies, highlights and records. Follow the Brazilian winger, his success at Real Madrid and on the international stage!
В центре доступны различные варианты лечения – от амбулаторного наблюдения до интенсивных стационарных программ. Ключевые принципы работы – конфиденциальность, индивидуальный подход и оперативность оказания помощи. Независимо от тяжести зависимости, каждый пациент получает квалифицированную поддержку, направленную на восстановление здоровья и возвращение к полноценной жизни.
Получить дополнительную информацию – vyvod iz zapoya vyzov na dom sankt-peterburg
купить диплом техника
Алкогольный запой — это состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над своим потреблением алкоголя, что может вызвать серьезные физические и психологические проблемы. В таких ситуациях крайне важно получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь как можно скорее. Однако многие люди опасаются обращаться за помощью, переживая за свою репутацию и возможное раскрытие личной информации. В клинике «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже мы гарантируем анонимность на всех этапах лечения, сохраняя высокий уровень медицинской помощи и заботясь о каждом пациенте.
Получить больше информации – вывод из запоя на дому
All about Karim Benzema karim benzema biography, achievements, main goals and career moments. Find out how the striker conquered Real Madrid and continues to shine in world football!
All about Karim Benzema karim-benzema-bd.com/ biography, achievements, main goals and career moments. Find out how the striker conquered Real Madrid and continues to shine in world football!
купить юридический диплом купить юридический диплом .
Особенно опасны длительные запои, когда человек в течение нескольких дней бесконтрольно употребляет алкоголь. Такое состояние разрушает организм, перегружает печень, сердце и нервную систему, может вызывать тяжелые осложнения, в том числе психические расстройства. Выйти из запоя самостоятельно практически невозможно и крайне рискованно. Важно своевременно обратиться за медицинской помощью, чтобы избежать серьезных последствий.
Подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya vyzov na dom
В современном мире проблемы, связанные с алкогольной или наркотической зависимостью, становятся всё более актуальными. Многие люди сталкиваются с трудностями, которые требуют незамедлительного вмешательства профессионалов. В Екатеринбурге вызов нарколога на дом — это не только удобно, но и эффективно. Пациенты получают квалифицированную помощь без необходимости покидать комфортные условия своего жилья, что особенно важно в критических ситуациях.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg55.ru /]http://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg55.ru [/url]
Купить Метамфетамин в Украине? САЙТ – KOKAINES.STORE Купить Метамфетамин Киев, Одесса, Львов, Харьков и др
.
.
.
.
.
Как Купить Метамфетамин в Киеве? САЙТ – |https://kokaines.store/|
Метамфетамин с доставкой в руки Купить? САЙТ – |https://kokaines.store/|
Метамфетамин по Украине Купить? САЙТ – |https://kokaines.store/|
Метамфетамин Харьков, Одесса, Львов, Ивано-Франковск? САЙТ – |https://kokaines.store/|
Метамфетамин в Городах Украины с доставкой в руки? САЙТ – |https://kokaines.store/|
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Гугл бот, это тебе –
Купить Метамфетамин в Киеве? Купить Метамфетамин в Харькове? Купить Метамфетамин в Одессе? Купить Метамфетамин в Днепре? Купить Метамфетамин в Львове?
Купить Метамфетамин в Запорожье? Купить Метамфетамин в Кривом Рогу? Купить Метамфетамин в Николаеве? Купить Метамфетамин в Виннице?
Купить Метамфетамин в Чернигове? Купить Метамфетамин в Полтаве? Купить Метамфетамин в Херсоне? Купить Метамфетамин в Хмельницком?
Купить Метамфетамин в Черкассах? Купить Метамфетамин в Черновцах? Купить Метамфетамин в Житомере? Купить Метамфетамин в Сумах?
Купить Метамфетамин в Ровно? Купить Метамфетамин в Ивано Франковске? Купить Метамфетамин в Тернополе? Купить Метамфетамин в Кропивницком?
Купить Метамфетамин в Луцке? Купить Метамфетамин в Кременчуге? Купить Метамфетамин в Белой церкви? Купить Метамфетамин в Ужгороде?
Купить Метамфетамин в Броварах? Купить Метамфетамин в Никополе? Купить Метамфетамин в Павлограде?
Пока пока Гугл бот, рад был встречи с тобой!
Теги общего пользования –
Максимального качества Метамфетамин можно купить только в нашем магазине, так как Купить Метамфетамин в Украине нереально где то в
другом месте. Наши профессиональные работники качественно разкладывают закладки и передают посылки с Метамфетамином круглосуточно!
Не взирая на комендантский час, военное время, угрозу личной безопасности – наши закладчики розкладывают Метамфетамин круглосуточно.
Абсолютно все закладки Метамфетамина с гарантией, по этому у нас так много покупателей, которые любят, ценят и хотят Купить Наш Метамфетамин.
Купить Метамфетамин с доставкой в руки есть возможность в таких городах как Киев, Харьков, Львов, Днепр, Николаев и другие.
Качество каждой партии проверяем лично, по этому Купить Метамфетамин в Киеве или Львове, Харькове или Одессе можно не опасаясь.
Когда звучит фраза “Купить Метамфетамин в Украине” – то каждый уважающий себя Украинец сразу же вспоминает наш сайт, потому что только
тут можно Купить Метамфетамин в Украине в виде гидрохлорида без примесей, чистота Метамфетамина в украине составляет 93-98% ГХД.
Нет разницы – на праздник, на день рожденье, На Новый год, просто погулять – Наш сайт не подведет НИКОГДА! И всегда Купить Метамфетамин можно!
Запойное пьянство представляет серьезную угрозу для здоровья, провоцируя развитие таких заболеваний, как цирроз печени, панкреатит, сердечно-сосудистые нарушения, а также психические расстройства. В запущенных случаях возможны тяжелые последствия, включая алкогольный делирий (белую горячку), который требует экстренной медицинской помощи. Чтобы избежать подобных рисков, необходимо своевременно обратиться к специалистам, которые помогут стабилизировать состояние и провести грамотное лечение.
Разобраться лучше – vyvod iz zapoya cena narkologiya tver
Кроме того, врач приедет в любое удобное для пациента время, даже ночью, обеспечив круглосуточный доступ к медицинской помощи. Специалист подбирает индивидуальный состав капельницы, что позволяет оптимально поддержать организм в зависимости от состояния пациента.
Получить дополнительную информацию – kapelnica ot zapoya ekaterinburg
Алкогольная зависимость – сложное и опасное состояние, которое сопровождается как физической, так и психологической привязанностью к спиртному. Одним из самых тяжелых проявлений этой проблемы является запой – длительное бесконтрольное употребление алкоголя, которое приводит к серьезным нарушениям в работе организма. Такое состояние требует срочного медицинского вмешательства, поскольку без профессиональной помощи возможны тяжелые осложнения, вплоть до угрозы жизни.
Детальнее – наркология вывод из запоя на дому в твери
Алкоголизм – одно из наиболее разрушительных заболеваний, наносящих серьезный ущерб организму. Запойные состояния особенно опасны, так как приводят к глубокой интоксикации, психическим нарушениям и необратимым последствиям. Чем раньше начато лечение, тем выше вероятность избежать осложнений и быстрее восстановиться.
Подробнее тут – вывод из запоя анонимно санкт-петербург
Особенно опасны длительные запои, когда человек в течение нескольких дней бесконтрольно употребляет алкоголь. Такое состояние разрушает организм, перегружает печень, сердце и нервную систему, может вызывать тяжелые осложнения, в том числе психические расстройства. Выйти из запоя самостоятельно практически невозможно и крайне рискованно. Важно своевременно обратиться за медицинской помощью, чтобы избежать серьезных последствий.
Узнать больше – анонимный вывод из запоя на дому санкт-петербург
Запойное пьянство представляет серьезную угрозу для здоровья, провоцируя развитие таких заболеваний, как цирроз печени, панкреатит, сердечно-сосудистые нарушения, а также психические расстройства. В запущенных случаях возможны тяжелые последствия, включая алкогольный делирий (белую горячку), который требует экстренной медицинской помощи. Чтобы избежать подобных рисков, необходимо своевременно обратиться к специалистам, которые помогут стабилизировать состояние и провести грамотное лечение.
Получить дополнительные сведения – vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno narkologiya tver
В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы понимаем, насколько важен своевременный и профессиональный подход к лечению зависимости. Наши специалисты готовы оказать квалифицированную помощь прямо у вас дома, обеспечивая полную безопасность и конфиденциальность на каждом этапе лечения.
Выяснить больше – vyvod iz zapoya anonimno nedorogo sankt-peterburg
Запой — это опасное состояние, которое развивается у людей с алкогольной зависимостью и характеризуется длительным непрерывным потреблением алкоголя. Это состояние приводит к серьезным нарушениям в организме, как физическим, так и психоэмоциональным. Длительный запой может вызвать множество осложнений, таких как поражение внутренних органов, нервной системы, а также проблемы в социальной и семейной жизни. Однако современная медицина предоставляет эффективные методы вывода из запоя, и одним из наиболее удобных и востребованных является вывод из запоя на дому.
Ознакомиться с деталями – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom na dom
Запойное состояние представляет собой серьёзную угрозу для здоровья, поскольку сопровождается тяжёлой интоксикацией организма и нарушением психоэмоционального состояния. Решение о лечении в стационаре клиники «Союз Здоровья» позволяет справиться с последствиями длительного употребления алкоголя, обеспечивая пациентам полный комплекс медицинской и психологической помощи.
Получить больше информации – вывод из запоя анонимно недорого воронеж
Широкий выбор дженериков по выгодной цене на сайте https://viagra-viagra.ru
быстрая доставка гарантированное качество
Удивительно, но купить диплом кандидата наук оказалось не так сложно
В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы понимаем, насколько важен своевременный и профессиональный подход к лечению зависимости. Наши специалисты готовы оказать квалифицированную помощь прямо у вас дома, обеспечивая полную безопасность и конфиденциальность на каждом этапе лечения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – narkologiya vyvod iz zapoya na domu sankt-peterburg
Наркологическая клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже специализируется на лечении алкогольной зависимости и предлагает профессиональные услуги по выводу из запоя. Мы стремимся создать атмосферу доверия, где каждый пациент сможет получить необходимую поддержку.
Получить дополнительную информацию – вывод из запоя в стационаре
Алкогольная зависимость – сложное и опасное состояние, которое сопровождается как физической, так и психологической привязанностью к спиртному. Одним из самых тяжелых проявлений этой проблемы является запой – длительное бесконтрольное употребление алкоголя, которое приводит к серьезным нарушениям в работе организма. Такое состояние требует срочного медицинского вмешательства, поскольку без профессиональной помощи возможны тяжелые осложнения, вплоть до угрозы жизни.
Изучить вопрос глубже – вывод из запоя на дому недорого капельница тверь
Цена услуги формируется с учётом нескольких факторов. Один из ключевых моментов — квалификация специалиста. Опытный врач, обладающий знаниями и практическими навыками, способен оказать помощь быстро и эффективно, что отражается на стоимости услуги.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg-tseny/
Алкогольная зависимость – это серьёзная проблема, требующая комплексного медицинского вмешательства. Для эффективного лечения и восстановления здоровья пациенты всё чаще выбирают стационарное лечение в наркологической клинике. Капельница от запоя в стационаре в Екатеринбурге представляет собой одно из наиболее популярных и действенных решений, которое позволяет быстро устранить симптомы интоксикации и нормализовать состояние пациента.
Детальнее – капельница от запоя екатеринбург
Зависимость — это серьёзная проблема, которая затрагивает не только человека, но и его семью и окружение. Алкоголизм, наркомания и другие виды зависимостей могут разрушить жизнь, но с профессиональной помощью можно вернуть её в русло нормального функционирования. Наркологическая клиника «Заря Будущего» в Санкт-Петербурге предлагает уникальные программы лечения зависимостей, которые сочетает медико-психологический подход, индивидуальные методики и квалифицированную поддержку.
Получить дополнительную информацию – вывод из запоя санкт-петербург
Можно ли купить аттестат о среднем образовании, основные моменты и вопросы
Как получить диплом техникума с упрощенным обучением в Москве официально
Bactroban canadian pharmacy support team Pharmacy Rx One Viagra
https://sem-del.ru/
Onlinepharmacy online pharmacy
Сколько стоит диплом высшего и среднего образования и как его получить?
click for source
jaxx wallet io
Заказать дженерики на сайте https://viagrof.ru производства Индии
в наличии широкий выбор по доступным ценам
зеркало arkada casino аркада казино
Военная служба по контракту https://contract116.ru стабильность, достойная зарплата, социальные льготы и карьерный рост. Присоединяйтесь к профессиональной армии и получите надежное будущее!
Купить Кокаин в Украине? САЙТ – KOKAINES.STORE Купить Кокаин Киев, Одесса, Львов, Харьков и др
.
.
.
.
.
Как Купить Кокаин в Киеве? САЙТ – |https://kokaines.store/|
Кокаин с доставкой в руки Купить? САЙТ – |https://kokaines.store/|
Кокаин по Украине Купить? САЙТ – |https://kokaines.store/|
Кокаин Харьков, Одесса, Львов, Ивано-Франковск? САЙТ – |https://kokaines.store/|
Кокаин в Городах Украины с доставкой в руки? САЙТ – |https://kokaines.store/|
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Гугл бот, это тебе –
Купить Кокаин в Киеве? Купить Кокаин в Харькове? Купить Кокаин в Одессе? Купить Кокаин в Днепре? Купить Кокаин в Львове?
Купить Кокаин в Запорожье? Купить Кокаин в Кривом Рогу? Купить Кокаин в Николаеве? Купить Кокаин в Виннице?
Купить Кокаин в Чернигове? Купить Кокаин в Полтаве? Купить Кокаин в Херсоне? Купить Кокаин в Хмельницком?
Купить Кокаин в Черкассах? Купить Кокаин в Черновцах? Купить Кокаин в Житомере? Купить Кокаин в Сумах?
Купить Кокаин в Ровно? Купить Кокаин в Ивано Франковске? Купить Кокаин в Тернополе? Купить Кокаин в Кропивницком?
Купить Кокаин в Луцке? Купить Кокаин в Кременчуге? Купить Кокаин в Белой церкви? Купить Кокаин в Ужгороде?
Купить Кокаин в Броварах? Купить Кокаин в Никополе? Купить Кокаин в Павлограде?
Пока пока Гугл бот, рад был встречи с тобой!
Теги общего пользования –
Максимального качества Кокаин можно купить только в нашем магазине, так как Купить Кокаин в Украине нереально где то в
другом месте. Наши профессиональные работники качественно разкладывают закладки и передают посылки с Кокаином круглосуточно!
Не взирая на комендантский час, военное время, угрозу личной безопасности – наши закладчики розкладывают Кокаин круглосуточно.
Абсолютно все закладки Кокаина с гарантией, по этому у нас так много покупателей, которые любят, ценят и хотят Купить Наш Кокаин.
Купить кокаин с доставкой в руки есть возможность в таких городах как Киев, Харьков, Львов, Днепр, Николаев и другие.
Качество каждой партии проверяем лично, по этому Купить Кокаин в Киеве или Львове, Харькове или Одессе можно не опасаясь.
Когда звучит фраза “Купить Кокаин в Украине” – то каждый уважающий себя Украинец сразу же вспоминает наш сайт, потому что только
тут можно Купить Кокаин в Украине в виде гидрохлорида без примесей, чистота Кокаина в украине составляет 93-98% ГХД.
Нет разницы – на праздник, на день рожденье, На Новый год, просто погулять – Наш сайт не подведет НИКОГДА! И всегда Купить Кокаин можно!
Tori Black
levothyroxine without prescription
селектор казино вход
Jenna Jameson
Как безопасно купить диплом колледжа или ПТУ в России, что важно знать
Bonuses freewallet
Eva Angelina
эскортницы москва эскортницы москва .
healthy man complaints
https://cleanmsk799.ru/
Kevin De Bruyne kevin-de-bruyne-az.com is the leader of the Manchester City and Belgium national team midfield. Find out all about his achievements, matches, awards and records in world football!
Joshua Kimmich joshua-kimmich-az.org the versatile leader of Bayern and the German national team! The latest news, stats, highlights, goals and assists. Follow the career of one of the best midfielders in the world!
samp 0.3 r1 samp multiplayer
Процесс детоксикации с помощью капельницы существенно облегчает симптомы похмелья: головную боль, тошноту, слабость, беспокойство и другие неприятные проявления. В результате пациент начинает чувствовать себя значительно лучше в короткие сроки, и процесс восстановления проходит гораздо быстрее.Запойное состояние обычно сопровождается тяжелыми симптомами алкогольной интоксикации: головной болью, тошнотой, рвотой, бессонницей и раздражительностью. Эти признаки свидетельствуют о глубоком отравлении организма, требующем комплексного подхода. В таких ситуациях капельница становится незаменимым инструментом, способствующим быстрому снятию симптомов и улучшению самочувствия пациента.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-krasnoyarsk55.ru/]https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-krasnoyarsk55.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-stacionare-krasnoyarsk/[/url]
https://teletype.in/@blogabout/music_download_listen_2025
В клинике работает команда квалифицированных специалистов, которые осуществляют вывод из запоя, обеспечивая полный контроль над состоянием пациента и устраняя все последствия длительного употребления алкоголя.
Получить больше информации – наркология вывод из запоя на дому
Когда речь идет о лечении зависимостей, многие пациенты испытывают стресс от визита в медицинские учреждения, особенно если это касается такой деликатной темы, как алкоголизм. Лечение на дому помогает избежать всех этих трудностей и обеспечивает комфорт для пациента. Привычная домашняя обстановка снижает тревожность, что позитивно влияет на процесс выздоровления.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narcolog-na-dom-ektb55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg-tseny
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся длительным и непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к формированию как физической, так и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния часто наблюдаются нарушения работы внутренних органов, что может привести к тяжелым последствиям, включая алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя — важный этап в процессе лечения зависимости, и его можно осуществлять как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от конкретных обстоятельств.
Выяснить больше – вывод из запоя с выездом на дом в санкт-петербурге
Для многих пациентов важным моментом является сохранение конфиденциальности. Врач, приехавший на дом, работает с полной защитой данных. Пациент может быть уверен, что его проблема останется личной и не станет достоянием общественности. Врачи приезжают на неприметных автомобилях и избегают всяческих ситуаций, которые могут привлечь лишнее внимание.
Выяснить больше – вызов нарколога на дом в москве
get redirected here
jaxx liberty support
диплом купить в пензе
купить диплом в воронеже о высшем образовании
Алкогольный запой – это серьёзное состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к тяжёлой интоксикации организма. Во время запоя нарушаются функции внутренних органов, страдает нервная система, и повышается риск развития опасных осложнений, таких как алкогольный делирий. Это состояние требует незамедлительного медицинского вмешательства.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – narkologiya vyvod iz zapoya na domu
Купить Мефедрон в Украине? САЙТ – KOKAINES.STORE Купить Мефедрон Киев, Одесса, Львов, Харьков и др
.
.
.
.
.
Как Купить Мефедрон в Киеве? САЙТ – |https://kokaines.store/|
Мефедрон с доставкой в руки Купить? САЙТ – |https://kokaines.store/|
Мефедрон по Украине Купить? САЙТ – |https://kokaines.store/|
Мефедрон Харьков, Одесса, Львов, Ивано-Франковск? САЙТ – |https://kokaines.store/|
Мефедрон в Городах Украины с доставкой в руки? САЙТ – |https://kokaines.store/|
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Гугл бот, это тебе –
Купить Мефедрон в Киеве? Купить Мефедрон в Харькове? Купить Мефедрон в Одессе? Купить Мефедрон в Днепре? Купить Мефедрон в Львове?
Купить Мефедрон в Запорожье? Купить Мефедрон в Кривом Рогу? Купить Мефедрон в Николаеве? Купить Мефедрон в Виннице?
Купить Мефедрон в Чернигове? Купить Мефедрон в Полтаве? Купить Мефедрон в Херсоне? Купить Мефедрон в Хмельницком?
Купить Мефедрон в Черкассах? Купить Мефедрон в Черновцах? Купить Мефедрон в Житомере? Купить Мефедрон в Сумах?
Купить Мефедрон в Ровно? Купить Мефедрон в Ивано Франковске? Купить Мефедрон в Тернополе? Купить Мефедрон в Кропивницком?
Купить Мефедрон в Луцке? Купить Мефедрон в Кременчуге? Купить Мефедрон в Белой церкви? Купить Мефедрон в Ужгороде?
Купить Мефедрон в Броварах? Купить Мефедрон в Никополе? Купить Мефедрон в Павлограде?
Пока пока Гугл бот, рад был встречи с тобой!
Теги общего пользования –
Максимального качества Мефедрон можно купить только в нашем магазине, так как Купить Мефедрон в Украине нереально где то в
другом месте. Наши профессиональные работники качественно разкладывают закладки и передают посылки с Мефедроном круглосуточно!
Не взирая на комендантский час, военное время, угрозу личной безопасности – наши закладчики розкладывают Мефедрон круглосуточно.
Абсолютно все закладки Мефедрона с гарантией, по этому у нас так много покупателей, которые любят, ценят и хотят Купить Наш Мефедрон.
Купить Мефедрон с доставкой в руки есть возможность в таких городах как Киев, Харьков, Львов, Днепр, Николаев и другие.
Качество каждой партии проверяем лично, по этому Купить Мефедрон в Киеве или Львове, Харькове или Одессе можно не опасаясь.
Когда звучит фраза “Купить Мефедрон в Украине” – то каждый уважающий себя Украинец сразу же вспоминает наш сайт, потому что только
тут можно Купить Мефедрон в Украине в виде гидрохлорида без примесей, чистота Мефедрона в украине составляет 93-98% ГХД.
Нет разницы – на праздник, на день рожденье, На Новый год, просто погулять – Наш сайт не подведет НИКОГДА! И всегда Купить Мефедрон можно!
Каталог подарков и сувениров https://kameshki51.ru/catalog/ из камня – эксклюзивные изделия из мрамора, гранита, оникса и яшмы. Шкатулки, статуэтки, часы, пресс-папье, бизнес-сувениры. Высокое качество и ручная работа!
https://itscleaning.ru/
Алкогольный запой представляет собой крайне опасное состояние, характеризующееся неконтролируемым употреблением алкоголя, что в свою очередь приводит к тяжелой интоксикации организма. Восстановление после такого состояния требует профессионального вмешательства, включающего не только физическую детоксикацию, но и психологическую поддержку. Стоимость процедуры вывода из запоя может значительно различаться в зависимости от множества факторов, включая метод лечения, тяжесть состояния пациента и место проведения лечения. Рассмотрим более подробно основные аспекты, влияющие на цену вывода из запоя.
Получить больше информации – vyvod iz zapoya na domu kruglosutochno sankt-peterburg
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся длительным и непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к формированию как физической, так и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния часто наблюдаются нарушения работы внутренних органов, что может привести к тяжелым последствиям, включая алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя — важный этап в процессе лечения зависимости, и его можно осуществлять как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от конкретных обстоятельств.
Ознакомиться с деталями – вывод из запоя капельница
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой состояние, при котором организм человека испытывает серьезное воздействие этанола, что приводит к нарушению нормальной физиологической деятельности. Это состояние сопровождается сильными физическими и психологическими расстройствами, которые требуют профессионального вмешательства. Однако многие люди, страдающие алкогольной зависимостью, сталкиваются с трудностью признания своей проблемы, опасаясь утраты репутации и конфиденциальности. В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем анонимный вывод из запоя в Санкт-Петербурге, предоставляя высококачественное лечение с гарантией сохранения личной информации.
Углубиться в тему – srochny vyvod iz zapoya na domu v-sankt-peterburge
Transform one’s vehicle into a custom with expert car tuning services. At the shop, we provide a full range of customizations to boost speed . Whether you want a modern appearance or top-tier drivetrain adjustments, we’ve got you covered. Explore our packages at https://mckeesportautobody.com/. Upgrade your ride today and experience reliability like never before.
Подарки и сувениры из камня Камнерезная мастерская Виктора Журавлева статуэтки, шкатулки, часы, панно, изделия из мрамора, гранита и оникса. Ручная работа, уникальный дизайн, доставка по России!
лучшие цветы в Томске купить букеты всегда беру тут
247 Overnight Pharmacy Canadian Buy cheap generic cialis uk sky pharmacy online
Sildenafil citrate 100mg plus
online pharmacy with prescription
Современный ритм жизни в Москве, с его постоянным стрессом, высокой интенсивностью и зачастую перегрузками, становится одной из причин, провоцирующих развитие зависимостей. Проблемы с алкоголем и наркотиками не всегда решаются быстро, и чаще всего требуют немедленного вмешательства профессионалов. В таких случаях вызов нарколога на дом становится оптимальным решением, которое сочетает комфорт, безопасность и высокий уровень медицинской поддержки.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой состояние, при котором организм человека испытывает серьезное воздействие этанола, что приводит к нарушению нормальной физиологической деятельности. Это состояние сопровождается сильными физическими и психологическими расстройствами, которые требуют профессионального вмешательства. Однако многие люди, страдающие алкогольной зависимостью, сталкиваются с трудностью признания своей проблемы, опасаясь утраты репутации и конфиденциальности. В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем анонимный вывод из запоя в Санкт-Петербурге, предоставляя высококачественное лечение с гарантией сохранения личной информации.
Получить дополнительные сведения – срочный вывод из запоя на дому санкт-петербург
Алкогольная зависимость становится всё более распространенной проблемой, требующей внимания как со стороны медицинского сообщества, так и общества в целом. Вывод из запоя — это сложный и ответственный процесс, необходимый для восстановления здоровья пациента и его интеграции в нормальную жизнь. Профессиональное вмешательство позволяет минимизировать последствия длительного употребления алкоголя и нормализовать состояние организма.
Выяснить больше – вывод из запоя вызов на дом
https://posle-remonta-uborka.ru/
В клинике работает команда квалифицированных специалистов, которые осуществляют вывод из запоя, обеспечивая полный контроль над состоянием пациента и устраняя все последствия длительного употребления алкоголя.
Разобраться лучше – вывод из запоя цена наркология в екатеринбурге
online pharmacy uk no prescription
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся длительным и непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к формированию как физической, так и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния часто наблюдаются нарушения работы внутренних органов, что может привести к тяжелым последствиям, включая алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя — важный этап в процессе лечения зависимости, и его можно осуществлять как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от конкретных обстоятельств.
Изучить вопрос глубже – наркология вывод из запоя анонимно
Ситуации, требующие вмешательства нарколога, могут быть различными. Наиболее распространенным поводом является состояние тяжелого алкогольного или наркотического опьянения, при котором пациент уже не может самостоятельно справляться с последствиями интоксикации. Это может быть вызвано передозировкой, длительным употреблением веществ или острой реакцией организма на токсичные соединения.
Углубиться в тему – платный нарколог на дом москва
купить диплом с профессией 2orik-diploms.ru .
купить диплом крановщика
candian no script pharmacy Canada Pharmacy 24 Hour Drug Store Healthy men viagra
Алкогольный запой представляет собой крайне опасное состояние, характеризующееся неконтролируемым употреблением алкоголя, что в свою очередь приводит к тяжелой интоксикации организма. Восстановление после такого состояния требует профессионального вмешательства, включающего не только физическую детоксикацию, но и психологическую поддержку. Стоимость процедуры вывода из запоя может значительно различаться в зависимости от множества факторов, включая метод лечения, тяжесть состояния пациента и место проведения лечения. Рассмотрим более подробно основные аспекты, влияющие на цену вывода из запоя.
Получить дополнительные сведения – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom sankt-peterburg
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой состояние, при котором организм человека испытывает серьезное воздействие этанола, что приводит к нарушению нормальной физиологической деятельности. Это состояние сопровождается сильными физическими и психологическими расстройствами, которые требуют профессионального вмешательства. Однако многие люди, страдающие алкогольной зависимостью, сталкиваются с трудностью признания своей проблемы, опасаясь утраты репутации и конфиденциальности. В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем анонимный вывод из запоя в Санкт-Петербурге, предоставляя высококачественное лечение с гарантией сохранения личной информации.
Выяснить больше – vyvod iz zapoya anonimno nedorogo
Как побороть лудоманию https://teletype.in/@antosha-sevan/moi-opyt-izbavlenia-ot-igrovoi-zavasimosty история глазами прошедшего это испытание и несколько советам тем, кто в середине пути или столкнулся с этим через друзей и близких. Описываю в статье как Вавада помогла мне избавиться от игровой зависимости
Получите свежие статьи https://advokatugra-86.ru и новости от адвоката, посвященные важным правовым вопросам. Профессиональные рекомендации и разборы актуальных событий в законодательстве помогут вам быть в курсе всех изменений.
Интоксикация организма, вызванная наркотиками, также является весомой причиной для вызова врача. Передозировка, смешение веществ или использование низкокачественных препаратов могут вызвать серьезные последствия для организма, включая потерю сознания, нарушения дыхания и сердечный приступ.
Разобраться лучше – нарколог на дом в москве
В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы понимаем, насколько важен своевременный и профессиональный подход к лечению зависимости. Наши специалисты готовы оказать квалифицированную помощь прямо у вас дома, обеспечивая полную безопасность и конфиденциальность на каждом этапе лечения.
Углубиться в тему – vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare v-sankt-peterburge
Круглосуточная медицинская помощь при алкогольном запое играет важнейшую роль в спасении жизни пациентов и их возвращении к нормальному состоянию. В данной статье рассмотрим ключевые аспекты вывода из запоя в домашних условиях, срочной помощи и работы нарколога.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom v-ekaterinburge
Как правило, для эффективного устранения токсинов из организма и восстановления нормального функционирования всех органов и систем, назначаются специальные препараты. К таким препаратам относятся растворы для восстановления водно-солевого баланса, витамины и медикаменты для поддержания нормальной работы печени, а также препараты, стабилизирующие психоэмоциональное состояние пациента.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – вызов нарколога на дом в екатеринбурге
Canadian Pharmacy Cialis Where to buy cialis online safely 164 Canada pharmacies online prescriptions online pharmacy Priligy online
Окунитесь в азарт с aviator slot ru Уникальная игра с захватывающим геймплеем и возможностью сорвать крупный выигрыш. Следите за коэффициентом, вовремя забирайте ставку и умножайте баланс. Испытайте удачу прямо сейчас!
Когда речь идет о лечении зависимостей, многие пациенты испытывают стресс от визита в медицинские учреждения, особенно если это касается такой деликатной темы, как алкоголизм. Лечение на дому помогает избежать всех этих трудностей и обеспечивает комфорт для пациента. Привычная домашняя обстановка снижает тревожность, что позитивно влияет на процесс выздоровления.
Детальнее – нарколог на дом стоимость в екатеринбурге
В первую очередь это вывод из запоя, который проводится с применением современных инфузионных растворов. Процедура включает внутривенное введение препаратов, устраняющих абстиненцию, восстанавливающих водно-солевой баланс и нормализующих работу внутренних органов. Это помогает снять тревожность, нормализовать сон и восстановить общее состояние.
Изучить вопрос глубже – нарколог в москве
Когда речь идет о лечении зависимостей, многие пациенты испытывают стресс от визита в медицинские учреждения, особенно если это касается такой деликатной темы, как алкоголизм. Лечение на дому помогает избежать всех этих трудностей и обеспечивает комфорт для пациента. Привычная домашняя обстановка снижает тревожность, что позитивно влияет на процесс выздоровления.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – нарколог на дом в екатеринбурге
Новости музыки Украины https://musicnews.com.ua популярные жанры, тренды и полезные советы для музыкантов. Узнавайте больше о мире музыки и развивайте свои навыки!
купить диплом в чебоксарах
Одной из самых частых причин является затяжной запой. Алкогольная интоксикация, сопровождающая это состояние, не только ухудшает общее самочувствие, но и создает угрозу для здоровья. Повышенное давление, нарушения сердечного ритма, головные боли и тошнота — это лишь некоторые симптомы, которые требуют вмешательства врача.
Выяснить больше – нарколог на дом в москве
Ставки на спорт https://betting-ru.ru ваш шанс превратить знания в выигрыш! Лучшие коэффициенты, огромный выбор событий и удобный интерфейс. Делайте прогнозы и побеждайте!
диплом колледжа купить
Процесс вызова специалиста на дом продуман до мелочей, чтобы максимально упростить задачу для пациента и его близких.
Разобраться лучше – narkolog na dom
Одной из самых частых причин является затяжной запой. Алкогольная интоксикация, сопровождающая это состояние, не только ухудшает общее самочувствие, но и создает угрозу для здоровья. Повышенное давление, нарушения сердечного ритма, головные боли и тошнота — это лишь некоторые симптомы, которые требуют вмешательства врача.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-moskva/
Алкогольный запой представляет собой серьезное состояние, которое требует немедленного медицинского вмешательства. Это состояние характеризуется длительным и бесконтрольным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к разрушению как физического, так и психоэмоционального здоровья человека. Для эффективного и безопасного вывода из запоя стационарное лечение является оптимальным решением, особенно при тяжелых случаях интоксикации. В стационаре клиники «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем комплексную программу вывода из запоя, которая включает детоксикацию, восстановление организма и психотерапевтическую помощь.
Подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom cena v-sankt-peterburge
Запой — это опасное состояние, которое развивается у людей с алкогольной зависимостью и характеризуется длительным непрерывным потреблением алкоголя. Это состояние приводит к серьезным нарушениям в организме, как физическим, так и психоэмоциональным. Длительный запой может вызвать множество осложнений, таких как поражение внутренних органов, нервной системы, а также проблемы в социальной и семейной жизни. Однако современная медицина предоставляет эффективные методы вывода из запоя, и одним из наиболее удобных и востребованных является вывод из запоя на дому.
Узнать больше – vyvod iz zapoya kapelnica na domu sankt-peterburg
Во-вторых, время вызова имеет значение. Ночные или праздничные визиты, как правило, стоят дороже, поскольку требуют мобилизации персонала в нестандартное время. Если пациенту нужна экстренная помощь, стоимость может быть увеличена из-за оперативного реагирования.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narcolog-na-dom-ektb55.ru/
Зависимость — это серьёзная проблема, которая затрагивает не только человека, но и его семью и окружение. Алкоголизм, наркомания и другие виды зависимостей могут разрушить жизнь, но с профессиональной помощью можно вернуть её в русло нормального функционирования. Наркологическая клиника «Заря Будущего» в Санкт-Петербурге предлагает уникальные программы лечения зависимостей, которые сочетает медико-психологический подход, индивидуальные методики и квалифицированную поддержку.
Подробнее – narkologiya vyvod iz zapoya na domu
Запой — это опасное состояние, которое развивается у людей с алкогольной зависимостью и характеризуется длительным непрерывным потреблением алкоголя. Это состояние приводит к серьезным нарушениям в организме, как физическим, так и психоэмоциональным. Длительный запой может вызвать множество осложнений, таких как поражение внутренних органов, нервной системы, а также проблемы в социальной и семейной жизни. Однако современная медицина предоставляет эффективные методы вывода из запоя, и одним из наиболее удобных и востребованных является вывод из запоя на дому.
Углубиться в тему – vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare anonimno
Запой — это опасное состояние, которое развивается у людей с алкогольной зависимостью и характеризуется длительным непрерывным потреблением алкоголя. Это состояние приводит к серьезным нарушениям в организме, как физическим, так и психоэмоциональным. Длительный запой может вызвать множество осложнений, таких как поражение внутренних органов, нервной системы, а также проблемы в социальной и семейной жизни. Однако современная медицина предоставляет эффективные методы вывода из запоя, и одним из наиболее удобных и востребованных является вывод из запоя на дому.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya na domu kruglosutochno sankt-peterburg
Запой — это опасное состояние, которое развивается у людей с алкогольной зависимостью и характеризуется длительным непрерывным потреблением алкоголя. Это состояние приводит к серьезным нарушениям в организме, как физическим, так и психоэмоциональным. Длительный запой может вызвать множество осложнений, таких как поражение внутренних органов, нервной системы, а также проблемы в социальной и семейной жизни. Однако современная медицина предоставляет эффективные методы вывода из запоя, и одним из наиболее удобных и востребованных является вывод из запоя на дому.
Получить дополнительную информацию – наркология вывод из запоя на дому санкт-петербург
Запойное пьянство характеризуется продолжительным и интенсивным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к серьезным физическим и психологическим последствиям. Часто пациенты сталкиваются с различными заболеваниями, такими как цирроз печени, панкреатит, алкогольный делирий и другие. Алкогольное опьянение не только ухудшает качество жизни, но также может угрожать жизни пациента. В условиях стационара лечение может быть более эффективным, однако многие люди предпочитают проходить данную процедуру на дому, чтобы избежать стигматизации и сохранить чувство приватности.
Подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya vyzov na dom v-ekaterinburge
купить диплом в старом осколе
Цены на услуги зависят от нескольких факторов. Один из ключевых – квалификация специалиста. Опытные врачи, обладающие высоким уровнем профессионализма, оценивают свою работу дороже, но их помощь часто оказывается более эффективной.
Углубиться в тему – платный нарколог на дом москва
купить диплом спб вуз prema-diploms.ru .
Современный ритм жизни в Москве, с его постоянным стрессом, высокой интенсивностью и зачастую перегрузками, становится одной из причин, провоцирующих развитие зависимостей. Проблемы с алкоголем и наркотиками не всегда решаются быстро, и чаще всего требуют немедленного вмешательства профессионалов. В таких случаях вызов нарколога на дом становится оптимальным решением, которое сочетает комфорт, безопасность и высокий уровень медицинской поддержки.
Узнать больше – https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-moskva/
При вызове нарколога можно рассчитывать на широкий спектр процедур, направленных на стабилизацию состояния пациента.
Углубиться в тему – врач нарколог на дом платный в москве
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой состояние, при котором организм человека испытывает серьёзное воздействие этанола. Это приводит к нарушениям нормальной физиологической деятельности и ухудшению состояния здоровья. Анонимный вывод из запоя — это медицинская помощь, направленная на устранение последствий чрезмерного употребления алкоголя с соблюдением строгой конфиденциальности.
Получить дополнительные сведения – vyvod iz zapoya
https://cleanliness-cleaning.ru/
Кроме того, анонимность является важной составляющей этой услуги. Лечение дома исключает возможность столкновения с посторонними людьми и помогает пациентам сохранить свою репутацию. Клиника «Гармония и Свет» обеспечивает полную конфиденциальность, предоставляя пациентам возможность получать помощь без лишних вопросов и обсуждений.
Выяснить больше – нарколог на дом цены в екатеринбурге
Алкогольный запой представляет собой серьезное состояние, которое требует немедленного медицинского вмешательства. Это состояние характеризуется длительным и бесконтрольным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к разрушению как физического, так и психоэмоционального здоровья человека. Для эффективного и безопасного вывода из запоя стационарное лечение является оптимальным решением, особенно при тяжелых случаях интоксикации. В стационаре клиники «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем комплексную программу вывода из запоя, которая включает детоксикацию, восстановление организма и психотерапевтическую помощь.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom cena
купить диплом инженера по охране труда 4russkiy365-diplomy.ru .
Как правило, для эффективного устранения токсинов из организма и восстановления нормального функционирования всех органов и систем, назначаются специальные препараты. К таким препаратам относятся растворы для восстановления водно-солевого баланса, витамины и медикаменты для поддержания нормальной работы печени, а также препараты, стабилизирующие психоэмоциональное состояние пациента.
Детальнее – http://narcolog-na-dom-ektb55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-ekaterinburg/
Когда пациент решает обратиться за помощью к наркологу на дом, ему предстоит пройти ряд этапов лечения, каждый из которых будет направлен на устранение последствий алкоголизма. Врач проведет первичный осмотр, выслушает жалобы пациента и на основе собранной информации начнёт индивидуальную программу лечения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – вызов нарколога цена в екатеринбурге
В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы понимаем, насколько важен своевременный и профессиональный подход к лечению зависимости. Наши специалисты готовы оказать квалифицированную помощь прямо у вас дома, обеспечивая полную безопасность и конфиденциальность на каждом этапе лечения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно санкт-петербург
Зависимость — это серьёзная проблема, которая затрагивает не только человека, но и его семью и окружение. Алкоголизм, наркомания и другие виды зависимостей могут разрушить жизнь, но с профессиональной помощью можно вернуть её в русло нормального функционирования. Наркологическая клиника «Заря Будущего» в Санкт-Петербурге предлагает уникальные программы лечения зависимостей, которые сочетает медико-психологический подход, индивидуальные методики и квалифицированную поддержку.
Ознакомиться с деталями – vyvod iz zapoya vyzov na dom
https://чистые-услуги.рф/
Запой — это состояние, при котором человек не может прекратить употребление алкоголя на протяжении длительного времени, что вызывает физическую и психологическую зависимость. Это крайне опасное состояние, требующее немедленного вмешательства специалистов. Наркологическая клиника «Преображение» в Екатеринбурге предоставляет профессиональную помощь в лечении запоя, используя самые эффективные и безопасные методы.
Детальнее – vyvod iz zapoya cena
Круглосуточная медицинская помощь при алкогольном запое играет важнейшую роль в спасении жизни пациентов и их возвращении к нормальному состоянию. В данной статье рассмотрим ключевые аспекты вывода из запоя в домашних условиях, срочной помощи и работы нарколога.
Узнать больше – вывод из запоя срочно круглосуточно
В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы понимаем, насколько важен своевременный и профессиональный подход к лечению зависимости. Наши специалисты готовы оказать квалифицированную помощь прямо у вас дома, обеспечивая полную безопасность и конфиденциальность на каждом этапе лечения.
Подробнее тут – vyvod iz zapoya na domu nedorogo sankt-peterburg
С увеличением темпа жизни и нарастающим стрессом, многие люди в Екатеринбурге сталкиваются с зависимостями, особенно с алкогольной. Алкогольная зависимость является одной из наиболее распространённых проблем, требующих немедленного вмешательства специалистов. Важно помнить, что в сложных ситуациях, связанных с зависимостью, помощь не должна откладываться. Вызов нарколога на дом в Екатеринбурге становится идеальным вариантом для тех, кто не может или не хочет покидать свой дом, но нуждается в медицинской помощи.
Получить дополнительные сведения – нарколог на дом екатеринбург
купить аттестат об окончании 11 классов
Узнайте стоимость диплома высшего и среднего образования и процесс получения
Одной из самых частых причин является затяжной запой. Алкогольная интоксикация, сопровождающая это состояние, не только ухудшает общее самочувствие, но и создает угрозу для здоровья. Повышенное давление, нарушения сердечного ритма, головные боли и тошнота — это лишь некоторые симптомы, которые требуют вмешательства врача.
Подробнее – платный нарколог на дом в москве
Запой — это опасное состояние, которое развивается у людей с алкогольной зависимостью и характеризуется длительным непрерывным потреблением алкоголя. Это состояние приводит к серьезным нарушениям в организме, как физическим, так и психоэмоциональным. Длительный запой может вызвать множество осложнений, таких как поражение внутренних органов, нервной системы, а также проблемы в социальной и семейной жизни. Однако современная медицина предоставляет эффективные методы вывода из запоя, и одним из наиболее удобных и востребованных является вывод из запоя на дому.
Изучить вопрос глубже – вывод из запоя капельница санкт-петербург
Pinco Casino is one of the best casinos presented online in the last five years. In addition to the welcome deposit and bonus based on the main type (sports betting or gaming slots), the Pinco casino website has a number of bonuses depending on the amount and order of the deposit, special promotions, cashback, etc. Visit now: http://www.pinko-casino-495.ru
Флебологическая клиникапроводит диагностику и лечение варикоза, флебита, трофических изменения ткани в амбулаторно в клинике и на дому Узин вен ног
Флебологическая клиникапроводит диагностику и лечение варикоза, флебита, трофических изменения ткани в амбулаторно в клинике и на дому консультация флеболог
Флебологическая клиникапроводит диагностику и лечение варикоза, флебита, трофических изменения ткани в амбулаторно в клинике и на дому Флеболог бесплатно
Как получить диплом стоматолога быстро и официально
купить диплом повара в ростове на дону
химчистка дивана недорого
Одним из самых привлекательных аспектов вызова нарколога на дом является гибкость. Вы можете согласовать время визита врача, подходящее именно для вас, включая вечернее или ночное время. Это позволяет совмещать лечение с работой и личными делами, не нарушая привычный ритм жизни.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/
купить медицинский диплом
Для многих пациентов важным моментом является сохранение конфиденциальности. Врач, приехавший на дом, работает с полной защитой данных. Пациент может быть уверен, что его проблема останется личной и не станет достоянием общественности. Врачи приезжают на неприметных автомобилях и избегают всяческих ситуаций, которые могут привлечь лишнее внимание.
Подробнее – вызов нарколога цена в москве
Будущая первая пара США запустила несколько мем-токенов в период перед инаугурации избранного президента Дональда Трампа, которые уже ценятся миллиарды USD на бумаге. Но время запуска цифрового актива Трампа, всего за несколько дней до принятия полномочий, встревожило этических аналитиков и даже часть игроков цифровой экономики.
Однако актив новоизбранного президента резко упала до $40 после того, как Мелания выпустила свою личный токен. С тех пор она восстановила часть этих снижений и продавалась около $60 утром в понедельник. $MELANIA котировалась чуть более $12 утром в понедельник, согласно криптоплатформе.
$TRUMP — первый токен, санкционированная новым президентом, который когда-то раскритиковал биткоин, назвав его «пустышкой».
Трамп получил мощную поддержку криптоиндустрии на этих избирательных кампаниях после того, как он одобрил токены и пообещал Америке «главный криптоцентр».
В июле 2024 года Трамп выступил на крупнейшем съезде криптовалют и с тех пор выбрал Говарда Лютника, который помогает цифровой проект Tether, директором ведомства по торговле. Лютник — один из многих активистов криптовалют, утверждённых в новое правительство Трампа.
Данную новость опубликовало агентство новостей Агентство новостей Агентство новостей Новостное агентство firsttake.ru
В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы понимаем, насколько важен своевременный и профессиональный подход к лечению зависимости. Наши специалисты готовы оказать квалифицированную помощь прямо у вас дома, обеспечивая полную безопасность и конфиденциальность на каждом этапе лечения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – анонимный вывод из запоя на дому в санкт-петербурге
Алкогольный запой представляет собой крайне опасное состояние, характеризующееся неконтролируемым употреблением алкоголя, что в свою очередь приводит к тяжелой интоксикации организма. Восстановление после такого состояния требует профессионального вмешательства, включающего не только физическую детоксикацию, но и психологическую поддержку. Стоимость процедуры вывода из запоя может значительно различаться в зависимости от множества факторов, включая метод лечения, тяжесть состояния пациента и место проведения лечения. Рассмотрим более подробно основные аспекты, влияющие на цену вывода из запоя.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – вывод из запоя анонимно санкт-петербург
Одним из самых привлекательных аспектов вызова нарколога на дом является гибкость. Вы можете согласовать время визита врача, подходящее именно для вас, включая вечернее или ночное время. Это позволяет совмещать лечение с работой и личными делами, не нарушая привычный ритм жизни.
Подробнее – вызов нарколога на дом москва
Быстрая покупка диплома старого образца: возможные риски
В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы понимаем, насколько важен своевременный и профессиональный подход к лечению зависимости. Наши специалисты готовы оказать квалифицированную помощь прямо у вас дома, обеспечивая полную безопасность и конфиденциальность на каждом этапе лечения.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-19.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-v-kruglosutochno-v-sankt-peterburge/]vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno [/url]
Ситуации, требующие вмешательства нарколога, могут быть различными. Наиболее распространенным поводом является состояние тяжелого алкогольного или наркотического опьянения, при котором пациент уже не может самостоятельно справляться с последствиями интоксикации. Это может быть вызвано передозировкой, длительным употреблением веществ или острой реакцией организма на токсичные соединения.
Углубиться в тему – http://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-moskva/
[url=https://holodilnikirk.ru/]ремонт холодильников на дому[/url] в городе Иркутск. Сделаем все с высочайшим качеством, починим сломавшийся холодильников в кратчайшие сроки https://holodilnikirk.ru/
Алкогольный запой представляет собой серьезное состояние, которое требует немедленного медицинского вмешательства. Это состояние характеризуется длительным и бесконтрольным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к разрушению как физического, так и психоэмоционального здоровья человека. Для эффективного и безопасного вывода из запоя стационарное лечение является оптимальным решением, особенно при тяжелых случаях интоксикации. В стационаре клиники «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем комплексную программу вывода из запоя, которая включает детоксикацию, восстановление организма и психотерапевтическую помощь.
Подробнее тут – наркология вывод из запоя анонимно санкт-петербург
eloncasino eloncasino .
В современном мире проблема зависимостей становится всё более острой. Давление повседневных стрессов, сложные жизненные обстоятельства и финансовые трудности нередко приводят людей к алкоголизму, наркомании и игровым расстройствам. Эти состояния не только разрушают здоровье, но и лишают человека социальной стабильности.
Изучить вопрос глубже – vyvod iz zapoya na domu kruglosutochno v-sankt-peterburge
Zeus vs Hades https://zeus-vs-hades-download.ru эпичная битва богов! Игровой автомат с грозными бонусами, фриспинами и множителями. Выберите сторону Зевса или Аида и сорвите большой выигрыш!
Мир смешанных единоборств https://ufc-ru.ru (MMA) в UFC! Рейтинги, бои, истории бойцов, прогнозы на поединки и эксклюзивные материалы о крупнейшей бойцовской лиге.
sky pharmacy online drugstore
Все о легкой атлетике https://athletics-ru.ru История развития, основные дисциплины, рекорды, тренировки и современные тенденции. Узнайте больше о королеве спорта!
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся длительным и непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к формированию как физической, так и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния часто наблюдаются нарушения работы внутренних органов, что может привести к тяжелым последствиям, включая алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя — важный этап в процессе лечения зависимости, и его можно осуществлять как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от конкретных обстоятельств.
Узнать больше – вывод из запоя с выездом санкт-петербург
Купить диплом Рязань
Запой — это опасное состояние, которое развивается у людей с алкогольной зависимостью и характеризуется длительным непрерывным потреблением алкоголя. Это состояние приводит к серьезным нарушениям в организме, как физическим, так и психоэмоциональным. Длительный запой может вызвать множество осложнений, таких как поражение внутренних органов, нервной системы, а также проблемы в социальной и семейной жизни. Однако современная медицина предоставляет эффективные методы вывода из запоя, и одним из наиболее удобных и востребованных является вывод из запоя на дому.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – наркологическая клиника в санкт-петербурге
В современном мире проблема зависимостей становится всё более острой. Давление повседневных стрессов, сложные жизненные обстоятельства и финансовые трудности нередко приводят людей к алкоголизму, наркомании и игровым расстройствам. Эти состояния не только разрушают здоровье, но и лишают человека социальной стабильности.
Выяснить больше – вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Casino is not just a game of luck; it’s a thrilling challenge that can be mastered with the right strategy. Imagine the excitement of hitting 21 and beating the dealer with confidence. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced player, learning best casino payouts can transform your gaming experience and lead to significant wins. Don’t miss out on the opportunity to improve your skills and enjoy the rewards. Start playing blackjack today and take the first step towards becoming a pro!
https://je-tall-sf-marketing-43.sgp1.digitaloceanspaces.com/research/je-tall-sf-marketing-(418).html
The entire look was the perfect match for the couple’s tradition-filled day.
Алкогольная зависимость становится всё более распространенной проблемой, требующей внимания как со стороны медицинского сообщества, так и общества в целом. Вывод из запоя — это сложный и ответственный процесс, необходимый для восстановления здоровья пациента и его интеграции в нормальную жизнь. Профессиональное вмешательство позволяет минимизировать последствия длительного употребления алкоголя и нормализовать состояние организма.
Детальнее – вывод из запоя с выездом
It’s really a fantastic website✅ thanks for sharing✅ There’s no doubt i would fully rate it after i read 티비위키 드라마
Услуги нарколога на дому включают весь спектр мероприятий, направленных на стабилизацию состояния пациента и помощь в борьбе с зависимостью. Среди наиболее востребованных процедур:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – выезд нарколога на дом цена в москве
Запой — это опасное состояние, которое развивается у людей с алкогольной зависимостью и характеризуется длительным непрерывным потреблением алкоголя. Это состояние приводит к серьезным нарушениям в организме, как физическим, так и психоэмоциональным. Длительный запой может вызвать множество осложнений, таких как поражение внутренних органов, нервной системы, а также проблемы в социальной и семейной жизни. Однако современная медицина предоставляет эффективные методы вывода из запоя, и одним из наиболее удобных и востребованных является вывод из запоя на дому.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – vyvod iz zapoya cena sankt-peterburg
Алкогольный запой представляет собой крайне опасное состояние, характеризующееся неконтролируемым употреблением алкоголя, что в свою очередь приводит к тяжелой интоксикации организма. Восстановление после такого состояния требует профессионального вмешательства, включающего не только физическую детоксикацию, но и психологическую поддержку. Стоимость процедуры вывода из запоя может значительно различаться в зависимости от множества факторов, включая метод лечения, тяжесть состояния пациента и место проведения лечения. Рассмотрим более подробно основные аспекты, влияющие на цену вывода из запоя.
Разобраться лучше – вывод из запоя цена в санкт-петербурге
Ищете взломанными приложениями на Android? Тогда вы зашли по адресу! Сегодня мы расскажем, как установить игры с модами интересных приложений.
Зачем скачивать модифицированные игры? Причина очевидна: они дают возможность использовать все уровни, разблокировать закрытые функции и многое другое. Такие модификации превращают геймплей приятнее.
Если вы хотите, чтобы скачать надежные взломанные приложения, предлагаем посетить этот сайт – droids-hack.ru. Там вы найдете огромный выбор взломанных игр.
Некоторые из самых востребованных игр для модификации: Clash of Clans, а также множество других. Любая из этих игр может быть скачана взломанной версии, что позволяет использовать неограниченными возможностями.
Если вы только начинаете, взломанные приложения могут показаться сложными, но на самом деле ничего сложного. Как правило, нужно скачать APK-файл и запускаете его на устройстве. Важно помнить: обязательно источник безопасен и проверен.
Однако, стоит учитывать, что использование взломанных игр может привести к правила лицензий, в связи с этим действуйте осторожно.
Если вас интересуют подобных приложениях, пишите нам. Будем рады помочь!
Cassino online Pin Up https://888casino-official-brazil.site ganhos sem limites! Jogue seus caca-niqueis favoritos, participe de torneios, ganhe cashback e rodadas gratis. Licenca, seguranca e pagamentos rapidos!
elon online casino elon online casino .
Алкогольный запой представляет собой крайне опасное состояние, характеризующееся неконтролируемым употреблением алкоголя, что в свою очередь приводит к тяжелой интоксикации организма. Восстановление после такого состояния требует профессионального вмешательства, включающего не только физическую детоксикацию, но и психологическую поддержку. Стоимость процедуры вывода из запоя может значительно различаться в зависимости от множества факторов, включая метод лечения, тяжесть состояния пациента и место проведения лечения. Рассмотрим более подробно основные аспекты, влияющие на цену вывода из запоя.
Выяснить больше – вывод из запоя капельница на дому санкт-петербург
casino elon http://www.eloncasinofun.com .
Стоимость услуги формируется на основе различных факторов, включая сложность состояния пациента, срочность вызова, квалификацию врача и расстояние до места вызова. Чтобы сделать правильный выбор, важно учитывать все аспекты, влияющие на цену, и понимать, как получить качественную помощь по справедливой стоимости.
Получить дополнительную информацию – нарколог на дом недорого в екатеринбурге
Алкогольный запой представляет собой серьезное состояние, которое требует немедленного медицинского вмешательства. Это состояние характеризуется длительным и бесконтрольным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к разрушению как физического, так и психоэмоционального здоровья человека. Для эффективного и безопасного вывода из запоя стационарное лечение является оптимальным решением, особенно при тяжелых случаях интоксикации. В стационаре клиники «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем комплексную программу вывода из запоя, которая включает детоксикацию, восстановление организма и психотерапевтическую помощь.
Получить дополнительные сведения – вывод из запоя цена наркология
Важно понимать, что алкоголизм — это хроническое заболевание, требующее комплексного лечения. Одной детоксикации недостаточно для полного избавления от зависимости. После выхода из запоя необходимо продолжить терапию, включающую психологическую поддержку, медикаментозное лечение и социальную адаптацию.
Детальнее – vyvod iz zapoya anonimno v-sankt-peterburge
Купить диплом специалиста в Астрахани
Специалисты клиники «Второй Шанс» предлагают профессиональную медицинскую помощь при запоях, обеспечивая безопасный и эффективный вывод из этого состояния. Для удобства пациентов мы оказываем услуги как в условиях стационара, так и на дому. Благодаря современным методам детоксикации и индивидуальному подходу наши врачи помогают минимизировать риски и ускорить процесс восстановления.
Подробнее тут – vyvod iz zapoya kapelnica sankt-peterburg
Еще одной причиной вызова нарколога может быть абстинентный синдром, возникающий после прекращения употребления алкоголя или наркотиков. Это состояние сопровождается физическими и психологическими проявлениями, такими как дрожь, тревога, бессонница, боли в мышцах.
Углубиться в тему – https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru
https://50style.ru/
Важно отметить, что некоторые клиники предоставляют скидки для новых клиентов или на отдельные процедуры. Однако стоит избегать слишком низких цен, так как это может свидетельствовать о недостаточном уровне профессионализма или отсутствии лицензии у специалиста.
Детальнее – http://narcolog-na-dom-ektb55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg-tseny/
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся длительным и непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к формированию как физической, так и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния часто наблюдаются нарушения работы внутренних органов, что может привести к тяжелым последствиям, включая алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя — важный этап в процессе лечения зависимости, и его можно осуществлять как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от конкретных обстоятельств.
Разобраться лучше – наркология вывод из запоя на дому в санкт-петербурге
Во-вторых, время вызова имеет значение. Ночные или праздничные визиты, как правило, стоят дороже, поскольку требуют мобилизации персонала в нестандартное время. Если пациенту нужна экстренная помощь, стоимость может быть увеличена из-за оперативного реагирования.
Подробнее тут – вызов нарколога ценаекатеринбург
Клиника «Преображение» предлагает услуги анонимного вывода из запоя в Екатеринбурге, обеспечивая высокое качество медицинской помощи и соблюдение всех этических норм.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya na domu cena ekaterinburg
Алкогольный запой представляет собой крайне опасное состояние, характеризующееся неконтролируемым употреблением алкоголя, что в свою очередь приводит к тяжелой интоксикации организма. Восстановление после такого состояния требует профессионального вмешательства, включающего не только физическую детоксикацию, но и психологическую поддержку. Стоимость процедуры вывода из запоя может значительно различаться в зависимости от множества факторов, включая метод лечения, тяжесть состояния пациента и место проведения лечения. Рассмотрим более подробно основные аспекты, влияющие на цену вывода из запоя.
Подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya anonimno sankt-peterburg
Запой — это состояние, при котором человек не может прекратить употребление алкоголя на протяжении длительного времени, что вызывает физическую и психологическую зависимость. Это крайне опасное состояние, требующее немедленного вмешательства специалистов. Наркологическая клиника «Преображение» в Екатеринбурге предоставляет профессиональную помощь в лечении запоя, используя самые эффективные и безопасные методы.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – вывод из запоя срочно круглосуточно
Revamp enhance your ride with our premium superior car tuning services. We specialize in unique modifications that elevate both efficiency and design. From engine tuning to exterior upgrades, we’ve got you covered. Experience the ultimate transformation at https://phoenix-autobodyshop.com/ and let our skilled team bring your vision to life. Visit us today and drive with superiority!
Запойное пьянство характеризуется продолжительным и интенсивным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к серьезным физическим и психологическим последствиям. Часто пациенты сталкиваются с различными заболеваниями, такими как цирроз печени, панкреатит, алкогольный делирий и другие. Алкогольное опьянение не только ухудшает качество жизни, но также может угрожать жизни пациента. В условиях стационара лечение может быть более эффективным, однако многие люди предпочитают проходить данную процедуру на дому, чтобы избежать стигматизации и сохранить чувство приватности.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya vyzov na dom
Во-вторых, время вызова имеет значение. Ночные или праздничные визиты, как правило, стоят дороже, поскольку требуют мобилизации персонала в нестандартное время. Если пациенту нужна экстренная помощь, стоимость может быть увеличена из-за оперативного реагирования.
Разобраться лучше – http://narcolog-na-dom-ektb55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-ekaterinburg
В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы понимаем, насколько важен своевременный и профессиональный подход к лечению зависимости. Наши специалисты готовы оказать квалифицированную помощь прямо у вас дома, обеспечивая полную безопасность и конфиденциальность на каждом этапе лечения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – narkolog vyvod iz zapoya cena sankt-peterburg
Алкогольный запой — одно из самых опасных проявлений зависимости, требующее немедленного вмешательства. Длительное употребление спиртного приводит к интоксикации организма, поражает внутренние органы, нарушает работу нервной системы и может привести к необратимым последствиям. Бесконтрольное пьянство сопровождается высокой физической и психологической зависимостью, и выйти из этого состояния самостоятельно практически невозможно.
Разобраться лучше – narkologicheskaya klinika
Когда речь идет о лечении зависимостей, многие пациенты испытывают стресс от визита в медицинские учреждения, особенно если это касается такой деликатной темы, как алкоголизм. Лечение на дому помогает избежать всех этих трудностей и обеспечивает комфорт для пациента. Привычная домашняя обстановка снижает тревожность, что позитивно влияет на процесс выздоровления.
Подробнее тут – нарколог екатеринбург
Легальная покупка диплома ПТУ с сокращенной программой обучения
В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы понимаем, насколько важен своевременный и профессиональный подход к лечению зависимости. Наши специалисты готовы оказать квалифицированную помощь прямо у вас дома, обеспечивая полную безопасность и конфиденциальность на каждом этапе лечения.
Узнать больше – narkolog vyvod iz zapoya cena v-sankt-peterburge
Круглосуточная медицинская помощь при алкогольном запое играет важнейшую роль в спасении жизни пациентов и их возвращении к нормальному состоянию. В данной статье рассмотрим ключевые аспекты вывода из запоя в домашних условиях, срочной помощи и работы нарколога.
Подробнее – наркология вывод из запоя на дому екатеринбург
https://cryptoanalyzer.ru/
https://clean-sharks.ru/
Свежие и актуальные новости https://sugar-news.com.ua Украины и мира! Будьте в курсе последних событий, аналитики и трендов. Читайте последние новости Украины онлайн!
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой состояние, при котором организм человека испытывает серьёзное воздействие этанола. Это приводит к нарушениям нормальной физиологической деятельности и ухудшению состояния здоровья. Анонимный вывод из запоя — это медицинская помощь, направленная на устранение последствий чрезмерного употребления алкоголя с соблюдением строгой конфиденциальности.
Разобраться лучше – вывод из запоя с выездом цена в екатеринбурге
Важно отметить, что некоторые клиники предоставляют скидки для новых клиентов или на отдельные процедуры. Однако стоит избегать слишком низких цен, так как это может свидетельствовать о недостаточном уровне профессионализма или отсутствии лицензии у специалиста.
Подробнее – нарколог на дом стоимость в екатеринбурге
Алкогольный запой представляет собой крайне опасное состояние, характеризующееся неконтролируемым употреблением алкоголя, что в свою очередь приводит к тяжелой интоксикации организма. Восстановление после такого состояния требует профессионального вмешательства, включающего не только физическую детоксикацию, но и психологическую поддержку. Стоимость процедуры вывода из запоя может значительно различаться в зависимости от множества факторов, включая метод лечения, тяжесть состояния пациента и место проведения лечения. Рассмотрим более подробно основные аспекты, влияющие на цену вывода из запоя.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – vyvod iz zapoya na domu nedorogo kapelnica v-sankt-peterburge
Одним из самых привлекательных аспектов вызова нарколога на дом является гибкость. Вы можете согласовать время визита врача, подходящее именно для вас, включая вечернее или ночное время. Это позволяет совмещать лечение с работой и личными делами, не нарушая привычный ритм жизни.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-moskva/
купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр в калуге
Еще одной причиной вызова нарколога может быть абстинентный синдром, возникающий после прекращения употребления алкоголя или наркотиков. Это состояние сопровождается физическими и психологическими проявлениями, такими как дрожь, тревога, бессонница, боли в мышцах.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом цена москва[/url]
Кроме того, врач, работающий на выезде, может уделить больше времени пациенту, что позволяет индивидуально подойти к решению проблемы.
Выяснить больше – вызов нарколога на дом цена в москве
Pharmacy On Line Brand viagra supremesuppliersindia.com
Prednisone online pharmacy
В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы понимаем, насколько важен своевременный и профессиональный подход к лечению зависимости. Наши специалисты готовы оказать квалифицированную помощь прямо у вас дома, обеспечивая полную безопасность и конфиденциальность на каждом этапе лечения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – vyvod iz zapoya na domu nedorogo sankt-peterburg
В современном мире проблема зависимостей становится всё более острой. Давление повседневных стрессов, сложные жизненные обстоятельства и финансовые трудности нередко приводят людей к алкоголизму, наркомании и игровым расстройствам. Эти состояния не только разрушают здоровье, но и лишают человека социальной стабильности.
Узнать больше – vyvod iz zapoya na domu v-sankt-peterburge
skypharmacy online
Для многих пациентов важным моментом является сохранение конфиденциальности. Врач, приехавший на дом, работает с полной защитой данных. Пациент может быть уверен, что его проблема останется личной и не станет достоянием общественности. Врачи приезжают на неприметных автомобилях и избегают всяческих ситуаций, которые могут привлечь лишнее внимание.
Узнать больше – http://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru
1.Сравните предложения. Обратитесь в несколько клиник и центров, чтобы узнать диапазон цен и выбрать наиболее подходящий вариант.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – врач нарколог на дом платный москва
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой состояние, при котором организм человека испытывает серьезное воздействие этанола, что приводит к нарушению нормальной физиологической деятельности. Это состояние сопровождается сильными физическими и психологическими расстройствами, которые требуют профессионального вмешательства. Однако многие люди, страдающие алкогольной зависимостью, сталкиваются с трудностью признания своей проблемы, опасаясь утраты репутации и конфиденциальности. В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем анонимный вывод из запоя в Санкт-Петербурге, предоставляя высококачественное лечение с гарантией сохранения личной информации.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – вывод из запоя капельница на дому в санкт-петербурге
https://vsprogress.ru/
В данном тексте вы узнаете, как организовать вызов нарколога в Москве, что влияет на стоимость услуги, а также почему этот формат помощи становится все более популярным.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru
https://clean-list.ru/
Пластиковые окна с системой микропроветривания – подробности здесь https://hedgedoc.eclair.ec-lyon.fr/s/NBiIqrFZW
В современном мире проблема зависимостей становится всё более острой. Давление повседневных стрессов, сложные жизненные обстоятельства и финансовые трудности нередко приводят людей к алкоголизму, наркомании и игровым расстройствам. Эти состояния не только разрушают здоровье, но и лишают человека социальной стабильности.
Получить дополнительную информацию – вывод из запоя срочно круглосуточно санкт-петербург
Лучшие эксперты в одном месте! b2b маркетплейс маркетплейс и агрегатор экспертных компаний помогает найти надежных специалистов по разным направлениям. Удобный выбор, проверенные отзывы и рейтинг!
Алкогольный запой представляет собой серьезное состояние, которое требует немедленного медицинского вмешательства. Это состояние характеризуется длительным и бесконтрольным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к разрушению как физического, так и психоэмоционального здоровья человека. Для эффективного и безопасного вывода из запоя стационарное лечение является оптимальным решением, особенно при тяжелых случаях интоксикации. В стационаре клиники «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем комплексную программу вывода из запоя, которая включает детоксикацию, восстановление организма и психотерапевтическую помощь.
Разобраться лучше – вывод из запоя врач на дом
Запойное пьянство характеризуется продолжительным и интенсивным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к серьезным физическим и психологическим последствиям. Часто пациенты сталкиваются с различными заболеваниями, такими как цирроз печени, панкреатит, алкогольный делирий и другие. Алкогольное опьянение не только ухудшает качество жизни, но также может угрожать жизни пациента. В условиях стационара лечение может быть более эффективным, однако многие люди предпочитают проходить данную процедуру на дому, чтобы избежать стигматизации и сохранить чувство приватности.
Изучить вопрос глубже – vyvod iz zapoya vrach na dom v-ekaterinburge
Основной задачей нарколога, выезжающего на дом, является помощь в любой ситуации, связанной с зависимостью. Все процедуры и методики подбираются индивидуально, в зависимости от состояния пациента.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru
shop augmentin
Современный ритм жизни в Москве, с его постоянным стрессом, высокой интенсивностью и зачастую перегрузками, становится одной из причин, провоцирующих развитие зависимостей. Проблемы с алкоголем и наркотиками не всегда решаются быстро, и чаще всего требуют немедленного вмешательства профессионалов. В таких случаях вызов нарколога на дом становится оптимальным решением, которое сочетает комфорт, безопасность и высокий уровень медицинской поддержки.
Ознакомиться с деталями – нарколог в москве
Жизнь в мегаполисе, таком как Москва, предъявляет к человеку множество требований и вызовов. В условиях постоянного стресса и давления вероятность столкнуться с проблемами, связанными с алкоголизмом или наркоманией, возрастает. В таких ситуациях вызов нарколога на дом в Москве становится не роскошью, а необходимостью. В этой статье рассмотрим, когда и как можно воспользоваться этой услугой, а также разберем стоимость и основные преимущества.
Подробнее – частный нарколог на дом москва
pharmaceuticals no prescription Canadian Online Pharmacy Cheap pills without a prescription
post accutane side effects process of accutane accutane medication vitamin a accutane do you need a prescription for accutane
Клиника «Преображение» предлагает услуги анонимного вывода из запоя в Екатеринбурге, обеспечивая высокое качество медицинской помощи и соблюдение всех этических норм.
Выяснить больше – narkologicheskaya klinika
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся длительным и непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к формированию как физической, так и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния часто наблюдаются нарушения работы внутренних органов, что может привести к тяжелым последствиям, включая алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя — важный этап в процессе лечения зависимости, и его можно осуществлять как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от конкретных обстоятельств.
Узнать больше – вывод из запоя на дому недорого в санкт-петербурге
Запой — это опасное состояние, которое развивается у людей с алкогольной зависимостью и характеризуется длительным непрерывным потреблением алкоголя. Это состояние приводит к серьезным нарушениям в организме, как физическим, так и психоэмоциональным. Длительный запой может вызвать множество осложнений, таких как поражение внутренних органов, нервной системы, а также проблемы в социальной и семейной жизни. Однако современная медицина предоставляет эффективные методы вывода из запоя, и одним из наиболее удобных и востребованных является вывод из запоя на дому.
Ознакомиться с деталями – вывод из запоя с выездом цена
Либет Казино – это новый уровень онлайн развлечений! Регистрируйтесь на нашем сайте уже сейчас и погружайтесь в мир азарта вместе с Либет Казино! либет казино сайт
Клиника «Второй Шанс» создана для комплексной помощи тем, кто столкнулся с зависимостью. Мы не просто снимаем симптомы, а работаем над коренными причинами проблемы, помогая пациентам восстановить физическое и психологическое состояние, адаптироваться к жизни без вредных привычек и избежать рецидивов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – нарколог на дом вывод из запоя санкт-петербург
Клиника «Второй Шанс» в Санкт-Петербурге работает круглосуточно, предоставляя помощь в любой момент. Мы гарантируем конфиденциальность, внимательное отношение и профессиональный подход на каждом этапе лечения. Наша цель — не просто вывести человека из состояния запоя, а помочь ему вернуться к полноценной жизни без зависимости.
Детальнее – быстрый вывод из запоя в стационаре в санкт-петербурге
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся длительным и непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к формированию как физической, так и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния часто наблюдаются нарушения работы внутренних органов, что может привести к тяжелым последствиям, включая алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя — важный этап в процессе лечения зависимости, и его можно осуществлять как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от конкретных обстоятельств.
Получить дополнительную информацию – вывод из запоя с выездом на дом в санкт-петербурге
Важно отметить, что некоторые клиники предоставляют скидки для новых клиентов или на отдельные процедуры. Однако стоит избегать слишком низких цен, так как это может свидетельствовать о недостаточном уровне профессионализма или отсутствии лицензии у специалиста.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narcolog-na-dom-ektb55.ru/
Usa Pharmacy No Script Cialis kaufen Dutasteride sky pharmacy online drugstore review L thyroxine
Одним из самых привлекательных аспектов вызова нарколога на дом является гибкость. Вы можете согласовать время визита врача, подходящее именно для вас, включая вечернее или ночное время. Это позволяет совмещать лечение с работой и личными делами, не нарушая привычный ритм жизни.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-moskva/
Алкогольный запой – это серьёзное состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к тяжёлой интоксикации организма. Во время запоя нарушаются функции внутренних органов, страдает нервная система, и повышается риск развития опасных осложнений, таких как алкогольный делирий. Это состояние требует незамедлительного медицинского вмешательства.
Выяснить больше – вывод из запоя с выездом на дом екатеринбург
https://digi238sa.netlify.app/research/digi238sa-(295)
A fit-and-flare silhouette will intensify your figure however nonetheless really feel gentle and airy.
Алкогольный запой представляет собой серьезное состояние, которое требует немедленного медицинского вмешательства. Это состояние характеризуется длительным и бесконтрольным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к разрушению как физического, так и психоэмоционального здоровья человека. Для эффективного и безопасного вывода из запоя стационарное лечение является оптимальным решением, особенно при тяжелых случаях интоксикации. В стационаре клиники «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем комплексную программу вывода из запоя, которая включает детоксикацию, восстановление организма и психотерапевтическую помощь.
Подробнее тут – bystry vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare
Алкогольный запой – это серьёзное состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к тяжёлой интоксикации организма. Во время запоя нарушаются функции внутренних органов, страдает нервная система, и повышается риск развития опасных осложнений, таких как алкогольный делирий. Это состояние требует незамедлительного медицинского вмешательства.
Получить больше информации – вывод из запоя цена
В клинике работает команда квалифицированных специалистов, которые осуществляют вывод из запоя, обеспечивая полный контроль над состоянием пациента и устраняя все последствия длительного употребления алкоголя.
Получить больше информации – вывод из запоя с выездом на дом екатеринбург
Важно отметить, что некоторые клиники предоставляют скидки для новых клиентов или на отдельные процедуры. Однако стоит избегать слишком низких цен, так как это может свидетельствовать о недостаточном уровне профессионализма или отсутствии лицензии у специалиста.
Узнать больше – вызов нарколога ценаекатеринбург
Алкогольный запой представляет собой серьезное состояние, которое требует немедленного медицинского вмешательства. Это состояние характеризуется длительным и бесконтрольным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к разрушению как физического, так и психоэмоционального здоровья человека. Для эффективного и безопасного вывода из запоя стационарное лечение является оптимальным решением, особенно при тяжелых случаях интоксикации. В стационаре клиники «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем комплексную программу вывода из запоя, которая включает детоксикацию, восстановление организма и психотерапевтическую помощь.
Получить дополнительные сведения – наркологическая клиника санкт-петербург
Клиника «Преображение» предлагает услуги анонимного вывода из запоя в Екатеринбурге, обеспечивая высокое качество медицинской помощи и соблюдение всех этических норм.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya anonimno v-ekaterinburge
Запой — это опасное состояние, которое развивается у людей с алкогольной зависимостью и характеризуется длительным непрерывным потреблением алкоголя. Это состояние приводит к серьезным нарушениям в организме, как физическим, так и психоэмоциональным. Длительный запой может вызвать множество осложнений, таких как поражение внутренних органов, нервной системы, а также проблемы в социальной и семейной жизни. Однако современная медицина предоставляет эффективные методы вывода из запоя, и одним из наиболее удобных и востребованных является вывод из запоя на дому.
Разобраться лучше – срочный вывод из запоя на дому санкт-петербург
Когда пациент решает обратиться за помощью к наркологу на дом, ему предстоит пройти ряд этапов лечения, каждый из которых будет направлен на устранение последствий алкоголизма. Врач проведет первичный осмотр, выслушает жалобы пациента и на основе собранной информации начнёт индивидуальную программу лечения.
Выяснить больше – нарколог на дом недорого екатеринбург
аттестат об окончании 9 классов купить аттестат об окончании 9 классов купить .
Проведение лечения в домашней обстановке значительно снижает уровень стресса и тревожности. Пациенту не нужно тратить силы на поездки в медицинские учреждения, что особенно важно при ограниченной мобильности. Домашняя атмосфера создает идеальные условия для открытого диалога с врачом, что существенно повышает эффективность терапии и шансы на успешное выздоровление.
Узнать больше – врач нарколог на дом платный в москве
Купить диплом техникума, колледжа в Белгороде
диплом менеджмент купить диплом менеджмент купить .
Если интересна тематика про “Интерьеров”, то рекомендуем посмотреть раздел – все про Интерьеров.- With regards, Trevon
Клиника «Гармония и Свет» предоставляет качественные услуги нарколога на дому, обеспечивая пациентам комфортное лечение в привычной обстановке. Это позволяет не только своевременно получить квалифицированную помощь, но и сделать процесс лечения максимально непринужденным и анонимным.
Получить больше информации – нарколог на дом стоимость в екатеринбурге
Клиника «Второй Шанс» в Санкт-Петербурге работает круглосуточно, предоставляя помощь в любой момент. Мы гарантируем конфиденциальность, внимательное отношение и профессиональный подход на каждом этапе лечения. Наша цель — не просто вывести человека из состояния запоя, а помочь ему вернуться к полноценной жизни без зависимости.
Изучить вопрос глубже – vyvod iz zapoya na domu kruglosutochno sankt-peterburg
Важно отметить, что некоторые клиники предоставляют скидки для новых клиентов или на отдельные процедуры. Однако стоит избегать слишком низких цен, так как это может свидетельствовать о недостаточном уровне профессионализма или отсутствии лицензии у специалиста.
Детальнее – нарколог на дом екатеринбург
Le meilleur code bonus 1xBet et obtenez plus de 100% de bonus de 100€. Les amateurs de sport seront ravis de decouvrir une vaste gamme de marches sportifs, englobant des choix tres apprecies tels que le cricket, le football, le tennis et bien d’autres.
Code Promo 1xBet
https://underatexassky.com/pages/2code_promo_163.html
Code promo de 1xBet – l’utilisation de ce code vous permettra d’obtenir un bonus de 30% supplementaire, allant jusqu’a 100$. Le bonus est accorde sous la forme de 130% du montant de votre premier depot. Cette offre est reservee aux nouveaux utilisateurs majeurs apres leur inscription. Profitez du code promo pour augmenter votre bonus de bienvenue de 100% a 130%. Les fonds seront credites sur votre solde de jeu, et le bonus devra etre mise sur des paris sportifs. Ce code promo est valable jusqu’au 31 decembre 2025. Utiliser le code promo 1xBet lors de l’inscription avec 1xBet 2025. Cela vous permettra d’obtenir leur excellent bonus de bienvenue allant sous forme de paris gratuits.
Приветствуем вас на нашем веб-сайте!
Здесь вы найдёте всё необходимое для успешного
управления своими финансами.
Мы предлагаем широкий спектр финансовых
продуктов, которые помогут вам достичь ваших целей и
обеспечить стабильность в будущем.
В нашем ассортименте представлены
различные виды банковских продуктов, инвестиции, страхование, кредиты и многое другое.
Мы постоянно обновляем нашу
базу данных, чтобы вы всегда были в
курсе последних тенденций
и инноваций на финансовом рынке.
Наши специалисты помогут вам
выбрать наиболее подходящий продукт, учитывая ваши индивидуальные потребности и предпочтения.
Мы предоставляем консультации и рекомендации, чтобы
вы могли принять обоснованное решение и
избежать возможных рисков.
Не упустите возможность воспользоваться нашими
услугами и откройте для себя мир финансовых
возможностей! Заходите на наш сайт, ознакомьтесь с каталогом продуктов и начните свой путь к финансовой стабильности прямо сейчас!
ипотека на квартиру
On this subject internet page, you’ll see my best information, be sure to look over this level of detail BJ야동
Обращение к специалисту требуется в ситуациях, когда самостоятельное справление с проблемой становится невозможным или небезопасным. Одной из наиболее распространенных причин вызова нарколога является алкогольная интоксикация, связанная с запоем. В таких случаях состояние пациента может быть опасным, а попытки справиться с ситуацией без профессионального вмешательства чреваты осложнениями.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – нарколог в москве
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой состояние, при котором организм человека испытывает серьёзное воздействие этанола. Это приводит к нарушениям нормальной физиологической деятельности и ухудшению состояния здоровья. Анонимный вывод из запоя — это медицинская помощь, направленная на устранение последствий чрезмерного употребления алкоголя с соблюдением строгой конфиденциальности.
Получить дополнительные сведения – анонимный вывод из запоя на дому в екатеринбурге
Хотите играть в Steam-игры shared-steam.org/ дешевле? Shared-Steam.org предлагает аренду аккаунтов с топовыми играми. Безопасность, доступность и удобство – ваш гейминг без границ!
Кроме того, врач, работающий на выезде, может уделить больше времени пациенту, что позволяет индивидуально подойти к решению проблемы.
Получить больше информации – нарколог на дом недорого москва
Важно понимать, что алкоголизм — это хроническое заболевание, требующее комплексного лечения. Одной детоксикации недостаточно для полного избавления от зависимости. После выхода из запоя необходимо продолжить терапию, включающую психологическую поддержку, медикаментозное лечение и социальную адаптацию.
Подробнее тут – вывод из запоя на дому в санкт-петербурге
В современном мире проблема зависимостей становится всё более острой. Давление повседневных стрессов, сложные жизненные обстоятельства и финансовые трудности нередко приводят людей к алкоголизму, наркомании и игровым расстройствам. Эти состояния не только разрушают здоровье, но и лишают человека социальной стабильности.
Детальнее – вывод из запоя на дому цена
порно с немкой порно с немкой .
Услуги нарколога на дому включают весь спектр мероприятий, направленных на стабилизацию состояния пациента и помощь в борьбе с зависимостью. Среди наиболее востребованных процедур:
Углубиться в тему – http://narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru
Запой — это опасное состояние, которое развивается у людей с алкогольной зависимостью и характеризуется длительным непрерывным потреблением алкоголя. Это состояние приводит к серьезным нарушениям в организме, как физическим, так и психоэмоциональным. Длительный запой может вызвать множество осложнений, таких как поражение внутренних органов, нервной системы, а также проблемы в социальной и семейной жизни. Однако современная медицина предоставляет эффективные методы вывода из запоя, и одним из наиболее удобных и востребованных является вывод из запоя на дому.
Получить дополнительную информацию – vyvod iz zapoya cena sankt-peterburg
Обширный ассортимент и приятные цены – у нас можно приобрести аккаунты на разный запрос. Желаете заказать профили? Наш магазин продает топовые предложения по разным ставкам.
Кроме того, анонимность является важной составляющей этой услуги. Лечение дома исключает возможность столкновения с посторонними людьми и помогает пациентам сохранить свою репутацию. Клиника «Гармония и Свет» обеспечивает полную конфиденциальность, предоставляя пациентам возможность получать помощь без лишних вопросов и обсуждений.
Подробнее – частный нарколог на дом екатеринбург
Клиника «Второй Шанс» в Санкт-Петербурге работает круглосуточно, предоставляя помощь в любой момент. Мы гарантируем конфиденциальность, внимательное отношение и профессиональный подход на каждом этапе лечения. Наша цель — не просто вывести человека из состояния запоя, а помочь ему вернуться к полноценной жизни без зависимости.
Получить дополнительную информацию – вывод из запоя капельница
где купить диплом врача
viagra noprescription
Важно отметить, что некоторые клиники предоставляют скидки для новых клиентов или на отдельные процедуры. Однако стоит избегать слишком низких цен, так как это может свидетельствовать о недостаточном уровне профессионализма или отсутствии лицензии у специалиста.
Получить дополнительную информацию – нарколог екатеринбург
Create images deep-nude easily with AI. Remove clothes from anyone in the image and enjoy their nakedness.
Важно понимать, что алкоголизм — это хроническое заболевание, требующее комплексного лечения. Одной детоксикации недостаточно для полного избавления от зависимости. После выхода из запоя необходимо продолжить терапию, включающую психологическую поддержку, медикаментозное лечение и социальную адаптацию.
Подробнее – нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в санкт-петербурге
Wow news for all us
Преимущества домашнего лечения также заключаются в индивидуальном подходе. Врач, находясь в вашем доме, может более тщательно изучить ситуацию, провести необходимую диагностику и подобрать курс лечения, который идеально подойдет вашему состоянию. В отличие от клиники, где внимание врача часто ограничено временем, на дому можно уделить пациенту больше времени, подбирая лечение с учетом его особенностей.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-moskva
Le meilleur code bonus 1xBet et obtenez plus de 100% de bonus de 100€. Les amateurs de sport seront ravis de decouvrir une vaste gamme de marches sportifs, englobant des choix tres apprecies tels que le cricket, le football, le tennis et bien d’autres.
1xbet meilleur code promo l’utilisation de ce code vous permettra d’obtenir un bonus de 30% supplementaire, allant jusqu’a 100$. Le bonus est accorde sous la forme de 130% du montant de votre premier depot. Cette offre est reservee aux nouveaux utilisateurs majeurs apres leur inscription. Profitez du code promo pour augmenter votre bonus de bienvenue de 100% a 130%. Les fonds seront credites sur votre solde de jeu, et le bonus devra etre mise sur des paris sportifs. Ce code promo est valable jusqu’au 31 decembre 2025. Utiliser le code promo 1xBet lors de l’inscription avec 1xBet 2025. Cela vous permettra d’obtenir leur excellent bonus de bienvenue allant sous forme de paris gratuits.
Le code promo 1xBet pour profiter de l’offre 100% VIP Bonus pour 2025 jusqu’a 130€ sur les paris sportifs ou de 1950€ + 150 tours gratuits. Ce code bonus special vous permettra de recevoir un bonus majore lors de votre inscription sur le site du bookmaker 1xBet.com ! Examinons les subtilites du programme de bonus du bookmaker 1xbet. Quels sont les codes promotionnels, quels types de bonus sont disponibles aujourd’hui pour les joueurs qui ont choisi la plateforme de jeu de ce bookmaker pour les paris sportifs.
Power Guard – это автобаферы, амортизирующие кольца, которые встраиваются в заднюю подвеску автомобиля и тем самым смягчают ее работу. Автобаферы Power Guard плмогают уменьшить нагрузку на подвеску при экстремальном вождении, неровных дорогах, ухабах, вибрациях и колебаниях. Уменьшение нагрузок для штатных пружин амортизаторов. По статистике автобаферы Power Guard продлевают жизнь подвески автомобиля на 20-70 тысяч километров кольцо амортизирующее
Модульная система: позволяет создавать индивидуальные комбинации для гостиной и спальни, с применением более 10 разных элементов https://mebel-24.blogspot.com/2025/01/2025.html
Power Guard – это автобаферы, амортизирующие кольца, которые встраиваются в заднюю подвеску автомобиля и тем самым смягчают ее работу. Автобаферы Power Guard плмогают уменьшить нагрузку на подвеску при экстремальном вождении, неровных дорогах, ухабах, вибрациях и колебаниях. Уменьшение нагрузок для штатных пружин амортизаторов. По статистике автобаферы Power Guard продлевают жизнь подвески автомобиля на 20-70 тысяч километров рейтинг авто амортизаторов
Модульная система: позволяет создавать индивидуальные комбинации для гостиной и спальни, с применением более 10 разных элементов https://mebel-24.blogspot.com/2025/01/2025.html
С увеличением темпа жизни и нарастающим стрессом, многие люди в Екатеринбурге сталкиваются с зависимостями, особенно с алкогольной. Алкогольная зависимость является одной из наиболее распространённых проблем, требующих немедленного вмешательства специалистов. Важно помнить, что в сложных ситуациях, связанных с зависимостью, помощь не должна откладываться. Вызов нарколога на дом в Екатеринбурге становится идеальным вариантом для тех, кто не может или не хочет покидать свой дом, но нуждается в медицинской помощи.
Углубиться в тему – вызов нарколога на дом в екатеринбурге
Алкогольная зависимость становится всё более распространенной проблемой, требующей внимания как со стороны медицинского сообщества, так и общества в целом. Вывод из запоя — это сложный и ответственный процесс, необходимый для восстановления здоровья пациента и его интеграции в нормальную жизнь. Профессиональное вмешательство позволяет минимизировать последствия длительного употребления алкоголя и нормализовать состояние организма.
Детальнее – vyvod iz zapoya cena narkologiya v-ekaterinburge
Одним из самых привлекательных аспектов вызова нарколога на дом является гибкость. Вы можете согласовать время визита врача, подходящее именно для вас, включая вечернее или ночное время. Это позволяет совмещать лечение с работой и личными делами, не нарушая привычный ритм жизни.
Узнать больше – выезд нарколога на дом цена москва
Power Guard – это автобаферы, амортизирующие кольца, которые встраиваются в заднюю подвеску автомобиля и тем самым смягчают ее работу. Автобаферы Power Guard плмогают уменьшить нагрузку на подвеску при экстремальном вождении, неровных дорогах, ухабах, вибрациях и колебаниях. Уменьшение нагрузок для штатных пружин амортизаторов. По статистике автобаферы Power Guard продлевают жизнь подвески автомобиля на 20-70 тысяч километров автобаферы нива
Модульная система: позволяет создавать индивидуальные комбинации для гостиной и спальни, с применением более 10 разных элементов https://mebel-24.blogspot.com/2025/01/2025.html
Unleash enhance your vehicle’s full potential with our premium exclusive tuning services. We offer tailored modifications to transform your car’s performance, aesthetics, and comfort. Our expert experienced technicians use state-of-the-art innovative technology to deliver flawless enhancements. https://americasbestcertifiedautobody.com/ Whether you seek remarkable speed, handling, or luxury, we provide high-quality solutions. Trust us to reinvent your driving experience. Contact us today and enjoy the ultimate in automotive customization!
В первую очередь это вывод из запоя, который проводится с применением современных инфузионных растворов. Процедура включает внутривенное введение препаратов, устраняющих абстиненцию, восстанавливающих водно-солевой баланс и нормализующих работу внутренних органов. Это помогает снять тревожность, нормализовать сон и восстановить общее состояние.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – выезд нарколога на дом цена москва
Преимущества домашнего лечения также заключаются в индивидуальном подходе. Врач, находясь в вашем доме, может более тщательно изучить ситуацию, провести необходимую диагностику и подобрать курс лечения, который идеально подойдет вашему состоянию. В отличие от клиники, где внимание врача часто ограничено временем, на дому можно уделить пациенту больше времени, подбирая лечение с учетом его особенностей.
Подробнее тут – вызов нарколога на дом москва
Как правило, для эффективного устранения токсинов из организма и восстановления нормального функционирования всех органов и систем, назначаются специальные препараты. К таким препаратам относятся растворы для восстановления водно-солевого баланса, витамины и медикаменты для поддержания нормальной работы печени, а также препараты, стабилизирующие психоэмоциональное состояние пациента.
Получить дополнительные сведения – частный нарколог на дом екатеринбург
Услуги нарколога на дому включают весь спектр мероприятий, направленных на стабилизацию состояния пациента и помощь в борьбе с зависимостью. Среди наиболее востребованных процедур:
Углубиться в тему – narcolog-na-dom-v-moskve55.ru/
Ситуации, требующие вмешательства нарколога, могут быть различными. Наиболее распространенным поводом является состояние тяжелого алкогольного или наркотического опьянения, при котором пациент уже не может самостоятельно справляться с последствиями интоксикации. Это может быть вызвано передозировкой, длительным употреблением веществ или острой реакцией организма на токсичные соединения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – нарколог на дом в москве
Запой — это опасное состояние, которое развивается у людей с алкогольной зависимостью и характеризуется длительным непрерывным потреблением алкоголя. Это состояние приводит к серьезным нарушениям в организме, как физическим, так и психоэмоциональным. Длительный запой может вызвать множество осложнений, таких как поражение внутренних органов, нервной системы, а также проблемы в социальной и семейной жизни. Однако современная медицина предоставляет эффективные методы вывода из запоя, и одним из наиболее удобных и востребованных является вывод из запоя на дому.
Выяснить больше – вывод из запоя на дому санкт-петербург
Важно понимать, что алкоголизм — это хроническое заболевание, требующее комплексного лечения. Одной детоксикации недостаточно для полного избавления от зависимости. После выхода из запоя необходимо продолжить терапию, включающую психологическую поддержку, медикаментозное лечение и социальную адаптацию.
Изучить вопрос глубже – вывод из запоя анонимно недорого в санкт-петербурге
Когда речь идет о лечении зависимостей, многие пациенты испытывают стресс от визита в медицинские учреждения, особенно если это касается такой деликатной темы, как алкоголизм. Лечение на дому помогает избежать всех этих трудностей и обеспечивает комфорт для пациента. Привычная домашняя обстановка снижает тревожность, что позитивно влияет на процесс выздоровления.
Получить дополнительную информацию – нарколог на дом цены в екатеринбурге
Одним из самых привлекательных аспектов вызова нарколога на дом является гибкость. Вы можете согласовать время визита врача, подходящее именно для вас, включая вечернее или ночное время. Это позволяет совмещать лечение с работой и личными делами, не нарушая привычный ритм жизни.
Получить больше информации – https://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-moskva
Turkiye’deki slot makineleri buyuk kazancl slotlar gercek parayla oynanabilen slotlar kapsaml bir baks! Nerede oynan?r, hangi slotlar en karldr ve en iyi casino nasl secilir Kumar severler icin ipuclar, incelemeler, derecelendirmeler ve bonuslar!
Важно понимать, что алкоголизм — это хроническое заболевание, требующее комплексного лечения. Одной детоксикации недостаточно для полного избавления от зависимости. После выхода из запоя необходимо продолжить терапию, включающую психологическую поддержку, медикаментозное лечение и социальную адаптацию.
Изучить вопрос глубже – быстрый вывод из запоя в стационаре санкт-петербург
Turkiye Slotlar Rehberi Demo slotlar En Iyi Slotlar ve Casinolar! Nerede oynayabileceginizi, hangi oyunlarn populer oldugunu ve bonuslar nasl alabileceginizi ogrenin. Oyun alanlar ve guncel eglencelere dair kapsaml bir genel baks!
купить диплом за 11 класс
Круглосуточная медицинская помощь при алкогольном запое играет важнейшую роль в спасении жизни пациентов и их возвращении к нормальному состоянию. В данной статье рассмотрим ключевые аспекты вывода из запоя в домашних условиях, срочной помощи и работы нарколога.
Получить дополнительную информацию – vyvod iz zapoya kapelnica ekaterinburg
С увеличением темпа жизни и нарастающим стрессом, многие люди в Екатеринбурге сталкиваются с зависимостями, особенно с алкогольной. Алкогольная зависимость является одной из наиболее распространённых проблем, требующих немедленного вмешательства специалистов. Важно помнить, что в сложных ситуациях, связанных с зависимостью, помощь не должна откладываться. Вызов нарколога на дом в Екатеринбурге становится идеальным вариантом для тех, кто не может или не хочет покидать свой дом, но нуждается в медицинской помощи.
Выяснить больше – http://narcolog-na-dom-ektb55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-ekaterinburg
Важно отметить, что некоторые клиники предоставляют скидки для новых клиентов или на отдельные процедуры. Однако стоит избегать слишком низких цен, так как это может свидетельствовать о недостаточном уровне профессионализма или отсутствии лицензии у специалиста.
Детальнее – нарколог в екатеринбурге
Клиника «Второй Шанс» в Санкт-Петербурге работает круглосуточно, предоставляя помощь в любой момент. Мы гарантируем конфиденциальность, внимательное отношение и профессиональный подход на каждом этапе лечения. Наша цель — не просто вывести человека из состояния запоя, а помочь ему вернуться к полноценной жизни без зависимости.
Изучить вопрос глубже – bystry vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare v-sankt-peterburge
В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы понимаем, насколько важен своевременный и профессиональный подход к лечению зависимости. Наши специалисты готовы оказать квалифицированную помощь прямо у вас дома, обеспечивая полную безопасность и конфиденциальность на каждом этапе лечения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – вывод из запоя с выездом санкт-петербург
Алкогольный запой – это серьёзное состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к тяжёлой интоксикации организма. Во время запоя нарушаются функции внутренних органов, страдает нервная система, и повышается риск развития опасных осложнений, таких как алкогольный делирий. Это состояние требует незамедлительного медицинского вмешательства.
Ознакомиться с деталями – вывод из запоя на дому в екатеринбурге
Узнайте, как приобрести диплом о высшем образовании без рисков
https://filedn.eu/lXvDNJGJo3S0aUrNKUTnNkb/marketing-310/research/je-tall-sf-marketing-(315).html
Discover our hand-picked assortment of mom of the bride dresses and you’re guaranteed to be best-dressed – apart from the bride, of course!
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся длительным и непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к формированию как физической, так и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния часто наблюдаются нарушения работы внутренних органов, что может привести к тяжелым последствиям, включая алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя — важный этап в процессе лечения зависимости, и его можно осуществлять как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от конкретных обстоятельств.
Подробнее тут – вывод из запоя на дому недорого капельница
Клиника «Гармония и Свет» предоставляет качественные услуги нарколога на дому, обеспечивая пациентам комфортное лечение в привычной обстановке. Это позволяет не только своевременно получить квалифицированную помощь, но и сделать процесс лечения максимально непринужденным и анонимным.
Изучить вопрос глубже – нарколог на дом цены в екатеринбурге
Проведение лечения в домашней обстановке значительно снижает уровень стресса и тревожности. Пациенту не нужно тратить силы на поездки в медицинские учреждения, что особенно важно при ограниченной мобильности. Домашняя атмосфера создает идеальные условия для открытого диалога с врачом, что существенно повышает эффективность терапии и шансы на успешное выздоровление.
Подробнее – нарколог на дом москва
Современный ритм жизни в Москве, с его постоянным стрессом, высокой интенсивностью и зачастую перегрузками, становится одной из причин, провоцирующих развитие зависимостей. Проблемы с алкоголем и наркотиками не всегда решаются быстро, и чаще всего требуют немедленного вмешательства профессионалов. В таких случаях вызов нарколога на дом становится оптимальным решением, которое сочетает комфорт, безопасность и высокий уровень медицинской поддержки.
Выяснить больше – вызов нарколога на дом цена москва
Важно понимать, что алкоголизм — это хроническое заболевание, требующее комплексного лечения. Одной детоксикации недостаточно для полного избавления от зависимости. После выхода из запоя необходимо продолжить терапию, включающую психологическую поддержку, медикаментозное лечение и социальную адаптацию.
Разобраться лучше – narkologiya vyvod iz zapoya na domu
Клиника «Второй Шанс» в Санкт-Петербурге работает круглосуточно, предоставляя помощь в любой момент. Мы гарантируем конфиденциальность, внимательное отношение и профессиональный подход на каждом этапе лечения. Наша цель — не просто вывести человека из состояния запоя, а помочь ему вернуться к полноценной жизни без зависимости.
Подробнее тут – vyvod iz zapoya kapelnica v-sankt-peterburge
Круглосуточная медицинская помощь при алкогольном запое играет важнейшую роль в спасении жизни пациентов и их возвращении к нормальному состоянию. В данной статье рассмотрим ключевые аспекты вывода из запоя в домашних условиях, срочной помощи и работы нарколога.
Изучить вопрос глубже – vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare anonimno
купить диплом о высшем образовании психолога
Алкогольный запой — одно из самых опасных проявлений зависимости, требующее немедленного вмешательства. Длительное употребление спиртного приводит к интоксикации организма, поражает внутренние органы, нарушает работу нервной системы и может привести к необратимым последствиям. Бесконтрольное пьянство сопровождается высокой физической и психологической зависимостью, и выйти из этого состояния самостоятельно практически невозможно.
Детальнее – vyvod iz zapoya vyzov na dom
клининг стоимость услуг
грузоперевозки в городе грузоперевозки минск
En tant que bookmaker en ligne et casino, 1xBet propose une large gamme de promotions et de recompenses a ses utilisateurs, et le code promo 1xbet en est juste l’un d’entre eux. Le code de promotion 1xbet offre aux joueurs la possibilite de participer a des promotions et de recevoir diverses recompenses, telles que des paris gratuits. Chaque code bonus est unique et est emis par le bureau du bookmaker dans le cadre d’une promotion specifique. Selon les termes de la promotion, l’utilisation d’un tel code offre aux joueurs certains avantages. Afin de beneficier du code de promotion 1xbet, les joueurs doivent respecter certaines conditions et l’utiliser dans un delai specifique. De plus, chaque code promo a son propre format et peut etre utilise de differentes manieres, que ce soit une seule fois ou plusieurs fois.
code promo gratuit Entrez le code bonus 1xBet dans le champ d’inscription en 2025 et accedez a toutes les sections disponibles sur le site. Vous pouvez choisir entre un bonus exclusif pour les paris sportifs allant jusqu’a 100% a 78 000 XOF, ou un bonus pour le casino allant jusqu’a €1950 + 150 tours gratuits. Tous les codes promo des bonus offerts par le bookmaker 1xBet en 2025 sont disponibles Codes bonus Aucun depot requis lors de l’inscription. Enregistrez-vous des a present avec notre bonus code 1xBet valable 2025 pour beneficier d’un bonus de 100% jusqu’a 130$. Utilisez le bonus promotionnel lors de l’ouverture de votre nouveau compte 1xbet afin de recevoir votre bonus de bienvenue.
Кроме того, анонимность является важной составляющей этой услуги. Лечение дома исключает возможность столкновения с посторонними людьми и помогает пациентам сохранить свою репутацию. Клиника «Гармония и Свет» обеспечивает полную конфиденциальность, предоставляя пациентам возможность получать помощь без лишних вопросов и обсуждений.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – narcolog-na-dom-ektb55.ru/
Кроме того, врач, работающий на выезде, может уделить больше времени пациенту, что позволяет индивидуально подойти к решению проблемы.
Узнать больше – вызов нарколога ценамосква
A nobleman is a member of the aristocratic class. Nobles had special benefits and position that distinguished them from other layers of the population. They were associated with aristocratic clans and had the right to land possession, inclusion in government of the state and military service. The nobility was also connected with special way of life, culture and enlightenment.
https://www.doktorlee.com/китайская-медицина/
Жизнь в мегаполисах, подобных Москве, нередко становится причиной развития различных зависимостей. В критических ситуациях может понадобиться экстренная наркологическая помощь. Это оптимальный вариант для тех, кто нуждается в квалифицированной медицинской поддержке, не выходя из собственного жилья. В данной статье мы детально разберем услуги круглосуточной наркологической помощи на дому в Москве, порядок вызова врача, а также рассмотрим цены и достоинства данного метода лечения.
Детальнее – https://narcolog-na-dom-msk55.ru/
Клиника «Гармония и Свет» предоставляет качественные услуги нарколога на дому, обеспечивая пациентам комфортное лечение в привычной обстановке. Это позволяет не только своевременно получить квалифицированную помощь, но и сделать процесс лечения максимально непринужденным и анонимным.
Получить дополнительную информацию – нарколог на дом стоимость екатеринбург
Знакомства в Уфе ufavip.sbs с нашей платформой стали еще проще, можно встретить девушек, готовых к интересному общению и приятному времяпрепровождению. Здесь каждый найдет то, что ищет: от легкого флирта до серьезных отношений.
квартирный переезд из минска в брест https://perevozimgruz.by/pereezd-v-druguyu-stranu/
Цены на услуги зависят от нескольких факторов. Один из ключевых – квалификация специалиста. Опытные врачи, обладающие высоким уровнем профессионализма, оценивают свою работу дороже, но их помощь часто оказывается более эффективной.
Подробнее – http://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru
Когда пациент решает обратиться за помощью к наркологу на дом, ему предстоит пройти ряд этапов лечения, каждый из которых будет направлен на устранение последствий алкоголизма. Врач проведет первичный осмотр, выслушает жалобы пациента и на основе собранной информации начнёт индивидуальную программу лечения.
Углубиться в тему – вызов нарколога ценаекатеринбург
https://uborka-kvartir-luberci.ru/
Клиника «Второй Шанс» создана для комплексной помощи тем, кто столкнулся с зависимостью. Мы не просто снимаем симптомы, а работаем над коренными причинами проблемы, помогая пациентам восстановить физическое и психологическое состояние, адаптироваться к жизни без вредных привычек и избежать рецидивов.
Узнать больше – vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare anonimno v-sankt-peterburge
купить диплом в екатеринбурге о среднем специальном образовании
Важно отметить, что некоторые клиники предоставляют скидки для новых клиентов или на отдельные процедуры. Однако стоит избегать слишком низких цен, так как это может свидетельствовать о недостаточном уровне профессионализма или отсутствии лицензии у специалиста.
Получить дополнительную информацию – нарколог на дом в екатеринбурге
В некоторых случаях помощь нарколога требуется для выведения пациента из запоя. Это состояние опасно не только ухудшением физического самочувствия, но и риском серьезных осложнений, таких как инсульт или инфаркт.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – narkolog na dom
Как правило, для эффективного устранения токсинов из организма и восстановления нормального функционирования всех органов и систем, назначаются специальные препараты. К таким препаратам относятся растворы для восстановления водно-солевого баланса, витамины и медикаменты для поддержания нормальной работы печени, а также препараты, стабилизирующие психоэмоциональное состояние пациента.
Выяснить больше – вызов нарколога ценаекатеринбург
Online Pharmacy Buying dog thyroxine healthy man viagra offer
Canadian health
В клинике работает команда квалифицированных специалистов, которые осуществляют вывод из запоя, обеспечивая полный контроль над состоянием пациента и устраняя все последствия длительного употребления алкоголя.
Подробнее тут – вывод из запоя анонимно
sky pharmacy canada mail order
ghostwriter elektrotechnik
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся длительным и непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к формированию как физической, так и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния часто наблюдаются нарушения работы внутренних органов, что может привести к тяжелым последствиям, включая алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя — важный этап в процессе лечения зависимости, и его можно осуществлять как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от конкретных обстоятельств.
Углубиться в тему – вывод из запоя в стационаре
Одной из самых частых причин является затяжной запой. Алкогольная интоксикация, сопровождающая это состояние, не только ухудшает общее самочувствие, но и создает угрозу для здоровья. Повышенное давление, нарушения сердечного ритма, головные боли и тошнота — это лишь некоторые симптомы, которые требуют вмешательства врача.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narcolog-na-dom-moskva55.ru
Алкоголизм — это хроническое прогрессирующее заболевание, связанное с физической и психической зависимостью от этанола. Запой, как его крайнее проявление, представляет собой длительное употребление алкоголя, сопровождающееся тяжелыми нарушениями работы организма, включая абстинентный синдром и потенциальные угрозы для жизни. Лечение запоя требует комплексного подхода, включающего медицинские процедуры, психотерапию и реабилитационные меры.
Получить больше информации – vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno narkologiya v-ekaterinburge
Специалисты клиники «Второй Шанс» предлагают профессиональную медицинскую помощь при запоях, обеспечивая безопасный и эффективный вывод из этого состояния. Для удобства пациентов мы оказываем услуги как в условиях стационара, так и на дому. Благодаря современным методам детоксикации и индивидуальному подходу наши врачи помогают минимизировать риски и ускорить процесс восстановления.
Разобраться лучше – вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно в санкт-петербурге
Хорошего времени суток, автолюбители!
Ищете надежный автосервис, который фокусируется на восстановлении выхлопной системы? В «Катализатор» в Ярославле мы предлагаем только высококлассные услуги:
Услуги, которые мы предоставляем:
Демонтаж катализатора
Проверка и замена глушителей
Ремонт и установка гофры, пламегасителей и резонаторов
Ремонт и установка фланцевых соединений
Компьютерная диагностика
Мы гарантируем профессиональный подход и качественное выполнение работ.
Ваш автомобиль заслуживает лучшего!
Не упустите возможность! Узнайте больше о наших услугах и запишитесь на прием на нашем сайте: https://katalizator-yaroslavl.ru/.
Ваши эксперты в ремонте автомобилей,
Команда «Катализатор».
Не ждите, пока проблема усугубится!
healthy male viagra Canadian Pharmacy Cialis Buy viagra uk tesco
Как не попасть впросак при покупке диплома колледжа или ПТУ в России
Canadian Pharmacy Femara Us online rx canada pharmacy 24h Cialis en vente libre
https://uborka-kvartir-balashiha.ru/
Welcome to HackersList!
Our platform connects you with top hackers specializing in secure data access, social media recovery, and system penetration testing. We offer fast, reliable services designed to solve your most complex digital challenges. Our experts ensure full anonymity with encrypted communication and secure payment handling. Trust our professionals to deliver discreet, effective solutions that protect your privacy at every step.
https://hackerslist.com/hacker-services/
Thank you for choosing HackersList!
Is it possible to win at Lucky Jet? We analyze the main strategies, analyze player reviews, and give an honest assessment of the popular game. Read to avoid mistakes and increase your chances of success!
квартирный переезд в минске https://perevozimgruz.by
**Добро пожаловать на наш сайт! Откройте лучшие финансовые
решения прямо сейчас!**
**Наши предложения**
Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент финансовых продуктов:
ипотеки, потребительские кредиты и дебетовые карты, чтобы помочь вам
достичь ваших целей и воплотить мечты в реальность.
**Ипотеки для вашего дома**
Планируете покупку жилья?
Наши ипотечные программы созданы
для вас. Оформите кредит на нашем сайте за несколько минут, выбрав
лучшие условия и сроки погашения.
**Преимущества наших дебетовых карт**
Наши карты обеспечивают
удобство безналичных платежей и множество бонусов:
– **Кэшбэк на повседневные покупки**
– **Специальные акции у партнеров**
Оформите карту онлайн и получите все преимущества уже сегодня!
**Быстрые займы для непредвиденных расходов**
Нужны деньги до зарплаты или на
неожиданные расходы? Наши займы – это
быстро и удобно. Мы предлагаем прозрачные
условия и мгновенное одобрение заявок.
**Наши преимущества:**
– **Простота и Удобство:** Оформите заявку онлайн за считанные минуты.
– **Надежность и Прозрачность:** Честные условия без скрытых комиссий.
– **Индивидуальный Подход:** Мы учитываем ваши личные обстоятельства.
Не упустите шанс улучшить свою финансовую ситуацию!
Оформите ипотеку, дебетовую карту или займ на нашем сайте уже сегодня и насладитесь всеми
преимуществами сотрудничества с надежным финансовым партнером.
Переходите на наш сайт и сделайте шаг к своим мечтам!
Zaymigo в Междуреченске
Automatically updated databases for Xrumer 23 and GSA Search Engine Ranker
We offer the best website databases for working with Xrumer 23 ai Strong and GSA Search Engine Ranker. The databases are suitable for a professional SEO company and creating hundreds of thousands of backlinks. Our databases are used by many SEO professionals from different countries of the world. The price for the databases is low, having bought them you receive updates for 12 months. You can read more and order a subscription to the databases here: https://dseo24.monster/vip-base-for-xrumer-and-gsa-ser/ On the site page you can choose any language of the pages.
купить диплом о высшем образовании в екатеринбурге
Нагреватель хомутовый из оцинкованной стали выполнятся по индивидуальных чертежам заказчика, при соблюдении всех нормативов и стандартов https://rusupakten.ru/product/eko-14-4/
Хомутовый нагреватель оцинкованный стандарт:Хомутовый нагреватель оцинкованный под заказ:
Алкогольная зависимость — это серьезная проблема, требующая немедленного вмешательства. Если вы или ваши близкие столкнулись с запоем, важно получить профессиональную помощь как можно скорее, чтобы избежать ухудшения здоровья. Наркологическая клиника «Шаг к Трезвости» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вывода из запоя на дому, что является удобным и эффективным решением для тех, кто не может или не хочет посещать стационар.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya kapelnica krasnodar
Современная жизнь, особенно в крупном городе, как Красноярск, часто становится причиной различных зависимостей. Работа в условиях постоянного стресса, высокий ритм жизни и эмоциональные перегрузки могут привести к проблемам, которые требуют неотложной медицинской помощи. Одним из наиболее удобных решений в такой ситуации является вызов нарколога на дом.
Подробнее – нарколог на дом в красноярске
продвижение сайтов частный оптимизатор https://seo-go.ru/
Приобретение диплома ПТУ с сокращенной программой обучения в Москве
1xbet apk code promo – utilisez-le pour vous inscrire et obtenir un bonus de 130% sur le montant de votre premier depot, pouvant aller jusqu’a 130$. Ces fonds doivent etre mises dans la section sportive, ou vous devez placer des paris avec une cote minimale de 1,4 et un wager x5.
Code Promo 1xBet
https://funtasylands.com/articles/futbolki_dlya_zanyatiy_fizkulyturoy.html
Code promo de 1xBet – l’utilisation de ce code vous permettra d’obtenir un bonus de 30% supplementaire, allant jusqu’a 100$. Le bonus est accorde sous la forme de 130% du montant de votre premier depot. Cette offre est reservee aux nouveaux utilisateurs majeurs apres leur inscription. Profitez du code promo pour augmenter votre bonus de bienvenue de 100% a 130%. Les fonds seront credites sur votre solde de jeu, et le bonus devra etre mise sur des paris sportifs. Ce code promo est valable jusqu’au 31 decembre 2025.
Приветствуем вас на нашем веб-сайте!
Здесь вы найдёте всё необходимое для успешного управления своими финансами.
Мы предлагаем широкий спектр финансовых продуктов, которые помогут вам достичь ваших целей и обеспечить
стабильность в будущем.
В нашем ассортименте представлены различные виды банковских продуктов, инвестиции, страхование, кредиты и многое
другое. Мы постоянно обновляем нашу базу данных, чтобы вы всегда
были в курсе последних тенденций и инноваций на финансовом рынке.
Наши специалисты помогут вам выбрать наиболее подходящий
продукт, учитывая ваши индивидуальные потребности
и предпочтения. Мы предоставляем консультации и рекомендации,
чтобы вы могли принять обоснованное решение и
избежать возможных рисков.
Не упустите возможность воспользоваться нашими услугами и откройте для себя
мир финансовых возможностей!
Заходите на наш сайт, ознакомьтесь с каталогом продуктов и начните
свой путь к финансовой стабильности прямо сейчас!
Кредит Под залог в Ульяновске
Покупка диплома о среднем полном образовании: как избежать мошенничества?
https://marketing13.sgp1.digitaloceanspaces.com/research/marketing-(246).html
Besides, is there something better than mother/daughter shopping?
blue mountain pharmacy canada
Алкогольный запой — это состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над своим потреблением алкоголя, что может вызвать серьезные физические и психологические проблемы. В таких ситуациях крайне важно получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь как можно скорее. Однако многие люди опасаются обращаться за помощью, переживая за свою репутацию и возможное раскрытие личной информации. В клинике «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже мы гарантируем анонимность на всех этапах лечения, сохраняя высокий уровень медицинской помощи и заботясь о каждом пациенте.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – вывод из запоя в стационаре в воронеже
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся длительным и непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к формированию как физической, так и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния часто наблюдаются нарушения работы внутренних органов, что может привести к тяжелым последствиям, включая алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя — важный этап в процессе лечения зависимости, и его можно осуществлять как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от конкретных обстоятельств.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom cena
Стоимость вывода из запоя зависит от ряда факторов, таких как состояние пациента, выбранная программа лечения и место проведения процедуры. Мы предлагаем прозрачное ценообразование, чтобы вы могли заранее ознакомиться с возможными затратами на лечение.
Получить дополнительные сведения – вывод из запоя в стационаре челябинск
mostbet com официальный сайт скачать https://www.gtrtt.com.kg .
1win кликер mabc.com.kg .
порно мультфильм порно мультфильм .
порно milf порно milf .
Алкогольная зависимость — это серьезная проблема, требующая немедленного вмешательства. Если вы или ваши близкие столкнулись с запоем, важно получить профессиональную помощь как можно скорее, чтобы избежать ухудшения здоровья. Наркологическая клиника «Шаг к Трезвости» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вывода из запоя на дому, что является удобным и эффективным решением для тех, кто не может или не хочет посещать стационар.
Подробнее тут – вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в краснодаре
порно гинеколог порно гинеколог .
В мегаполисах, таких как Красноярск, число людей, сталкивающихся с зависимостью от алкоголя или наркотиков, значительно возрастает. Для таких людей, а также для их близких, важным аспектом является своевременная и качественная помощь. В критические моменты, когда необходимо срочное вмешательство, вызов нарколога на дом становится наиболее удобным и эффективным решением. Это позволяет избежать стрессовых ситуаций, связанных с поездками в клинику, и получить необходимую медицинскую помощь прямо на дому.
Получить больше информации – вызов нарколога ценакрасноярск
Banda Casino — это лицензионное онлайн казино, которое предлагает пользователям уникальный опыт игры на деньги. С широким ассортиментом игровых автоматов Казино Banda зеркало на сегодня
Le meilleur code bonus 1xBet et obtenez plus de 100% de bonus de 100€. Les amateurs de sport seront ravis de decouvrir une vaste gamme de marches sportifs, englobant des choix tres apprecies tels que le cricket, le football, le tennis et bien d’autres.
Code Promo 1xBet
https://www.anak2u.com.my/pages/code_promo_132.html
Code promo de 1xBet – l’utilisation de ce code vous permettra d’obtenir un bonus de 30% supplementaire, allant jusqu’a 100$. Le bonus est accorde sous la forme de 130% du montant de votre premier depot. Cette offre est reservee aux nouveaux utilisateurs majeurs apres leur inscription. Profitez du code promo pour augmenter votre bonus de bienvenue de 100% a 130%. Les fonds seront credites sur votre solde de jeu, et le bonus devra etre mise sur des paris sportifs. Ce code promo est valable jusqu’au 31 decembre 2025. Utiliser le code promo 1xBet lors de l’inscription avec 1xBet 2025. Cela vous permettra d’obtenir leur excellent bonus de bienvenue allant sous forme de paris gratuits.
Banda Casino — это лицензионное онлайн казино, которое предлагает пользователям уникальный опыт игры на деньги. С широким ассортиментом игровых автоматов Банда Казино официальный сайт
Компания 1хБет предоставляет всем 100% бонус за первый депозит до 32500 рублей (или эквивалент в другой валюте по актуальному курсу). Кроме того, вас ожидает приветственный пакет в 1xBet казино до €1950 +150 фриспинов для игры в слоты и игровые автоматы. 1xBet — это одна из самых популярных и надежных платформ, которая предлагает уникальные возможности и привлекательные бонусы для своих пользователей. Независимо от того, являетесь ли вы новичком в мире ставок или опытным игроком, промокоды 1xBet — это отличный способ повысить свои шансы на выигрыш.
Промокод 1xBet
http://www.zdrave-hubnuti.org/stp/pgs/1xbet_poluchit_bonus_na_pervuy_depozit_6500_rubley.html
Промокод 1хБет на сегодня – предоставляет вам возможность получить 100%-й бонус до 32 500 ? и Приветственный пакет до 1500 евро + 150 фриспинов для игры в разделе азартных игр 1хБет. 1xBet — это известная онлайн-платформа для ставок, которая славится своими щедрыми бонусами и привлекательными предложениями. Если вы ищете уникальный игровой опыт и дополнительные шансы на успех, то бонусы 1xBet станут отличным выбором для вас.
Бонусы являются одной из главных особенностей, которые делают 1xBet привлекательной для множества игроков. Как новый, так и постоянный пользователь, вы сможете воспользоваться различными видами бонусов, которые помогут увеличить ваши шансы на выигрыш. От приветственных бонусов до регулярных акций, 1xBet предлагает множество вариантов, чтобы удовлетворить ваши потребности и предпочтения.
Один из самых популярных бонусов, предоставляемых 1xBet, – это приветственный бонус для новых игроков. Как только вы зарегистрируетесь на платформе, вам будет предложен щедрый приветственный пакет, который включает в себя бонус на первый депозит. Это означает, что вы получите дополнительные средства на свой игровой счет, чтобы увеличить свои возможности для ставок. Такой бонус является отличным стартом в вашем игровом путешествии и помогает вам исследовать различные игры и спортивные события.
Кроме того, врач оказывает психологическую поддержку, которая помогает пациенту справиться с чувством тревоги, депрессией и страхом, возникающими на фоне зависимости.
Ознакомиться с деталями – вызов нарколога цена в красноярске
Banda Casino — это лицензионное онлайн казино, которое предлагает пользователям уникальный опыт игры на деньги. С широким ассортиментом игровых автоматов Банда Казино регистрация
Алкогольный запой представляет собой крайне опасное состояние, характеризующееся неконтролируемым употреблением алкоголя, что в свою очередь приводит к тяжелой интоксикации организма. Восстановление после такого состояния требует профессионального вмешательства, включающего не только физическую детоксикацию, но и психологическую поддержку. Стоимость процедуры вывода из запоя может значительно различаться в зависимости от множества факторов, включая метод лечения, тяжесть состояния пациента и место проведения лечения. Рассмотрим более подробно основные аспекты, влияющие на цену вывода из запоя.
Подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya
купить диплом маси 2orik-diploms.ru .
аттестат купить в новосибирске
If you would like to take a good deal from this piece of writing then you have to apply such strategies to your won webpage.
viagra no prescription
Кружевной бюстгальтер https://www.wildberries.ru/catalog/117605496/detail.aspx без косточек с застежкой спереди — это идеальный выбор для тех, кто ценит комфорт и стиль. Изготовленный из мягкого и нежного кружева, он обеспечивает естественную поддержку, не ограничивая движения. Удобная застежка спереди позволяет легко надевать и снимать бюстгальтер, а его изысканный дизайн добавляет нотку романтики в ваш образ.
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой серьёзную медицинскую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запойное состояние характеризуется длительным и бесконтрольным потреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к возникновению как физической, так и психической зависимости. Данное явление может вызвать нарушения в работе внутренних органов, значительно увеличивая вероятность развития алкогольного делирия, который представляет собой острое состояние, требующее неотложной медицинской помощи. Вывод из запоя это ключевая часть лечения зависимости, которая может осуществляться как в стационаре, так и в амбулаторных условиях, в зависимости от конкретной ситуации и состояния пациента.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – narkologiya vyvod iz zapoya na domu krasnodar
Стоимость вывода из запоя зависит от ряда факторов, таких как состояние пациента, выбранная программа лечения и место проведения процедуры. Мы предлагаем прозрачное ценообразование, чтобы вы могли заранее ознакомиться с возможными затратами на лечение.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно в челябинске
Как приобрести аттестат о среднем образовании в Москве и других городах
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой серьёзную медицинскую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запойное состояние характеризуется длительным и бесконтрольным потреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к возникновению как физической, так и психической зависимости. Данное явление может вызвать нарушения в работе внутренних органов, значительно увеличивая вероятность развития алкогольного делирия, который представляет собой острое состояние, требующее неотложной медицинской помощи. Вывод из запоя это ключевая часть лечения зависимости, которая может осуществляться как в стационаре, так и в амбулаторных условиях, в зависимости от конкретной ситуации и состояния пациента.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-12.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница краснодар[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, необходимая для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Это состояние, часто характеризующееся физическими и психоэмоциональными нарушениями, требует профессионального вмешательства. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть разнообразными и варьироваться от легкой тревожности до серьезных нарушений в функционировании внутренних органов. Квалифицированная помощь в этот период позволяет минимизировать риски и значительно ускорить процесс выздоровления.
Получить дополнительные сведения – vyvod iz zapoya kapelnica na domu
?El paraiso del juego en Pin Up Casino https://ganar-apuestas-deportivas.com te espera! Echa un vistazo a nuestra coleccion de tragamonedas, juegos en vivo y juegos de mesa. Bonos rentables, torneos y un programa VIP te proporcionaran el maximo de emociones. ?Empieza a jugar ahora y gana!
Запой представляет собой состояние, характеризующееся длительным непрерывным употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к физической и психической зависимости. Этот процесс может длиться от нескольких дней до недель. Алкогольные напитки негативно влияют на функционирование внутренних органов, вызывая серьёзные нарушения, включая алкоголизм. При необходимости вывода из запоя важно обратиться за медицинской помощью, что можно осуществить на дому. В данной статье рассмотрим ключевые аспекты данной процедуры.
Узнать больше – narkologicheskij centr v-chelyabinske
Медицинский специалист с особой осторожностью и профессионализмом выполняет процедуру установки капельницы, внимательно контролируя состояние пациента. Первым этапом проводится тщательная дезинфекция кожного покрова специальным антисептическим средством для исключения риска инфицирования. После этого врач осуществляет аккуратную венепункцию, максимально снижая неприятные ощущения для пациента. Вся манипуляция проходит в спокойной обстановке, способствующей расслаблению пациента. Медработник постоянно следит за корректностью установки системы и скоростью поступления лечебного раствора.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-msk55.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-tsena-moskva/
Медикаментозное лечение — это еще один важный этап. Оно включает использование препаратов, которые помогают пациенту восстановиться как физически, так и психологически. Нарколог контролирует процесс лечения, чтобы исключить побочные эффекты и скорректировать терапию при необходимости.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narcolog-na-dom-v-krasnoyarske55.ru/narkolog-na-dom-krasnoyarsk-tseny
Стоимость вывода из запоя зависит от ряда факторов, таких как состояние пациента, выбранная программа лечения и место проведения процедуры. Мы предлагаем прозрачное ценообразование, чтобы вы могли заранее ознакомиться с возможными затратами на лечение.
Получить больше информации – vyvod iz zapoya na domu chelyabinsk
Медикаментозное лечение — это еще один важный этап. Оно включает использование препаратов, которые помогают пациенту восстановиться как физически, так и психологически. Нарколог контролирует процесс лечения, чтобы исключить побочные эффекты и скорректировать терапию при необходимости.
Детальнее – платный нарколог на дом красноярск
Запой — это опасное состояние, которое развивается у людей с алкогольной зависимостью и характеризуется длительным непрерывным потреблением алкоголя. Это состояние приводит к серьезным нарушениям в организме, как физическим, так и психоэмоциональным. Длительный запой может вызвать множество осложнений, таких как поражение внутренних органов, нервной системы, а также проблемы в социальной и семейной жизни. Однако современная медицина предоставляет эффективные методы вывода из запоя, и одним из наиболее удобных и востребованных является вывод из запоя на дому.
Получить дополнительные сведения – вывод из запоя на дому цена в санкт-петербурге
Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся утратой контроля над употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к тяжелой интоксикации организма. Вывод из запоя — это комплексный процесс, направленный на устранение последствий интоксикации и восстановление нормального функционирования организма. Цена данной процедуры может значительно различаться в зависимости от нескольких факторов, и в этой статье мы подробно рассмотрим, что влияет на стоимость вывода из запоя в Краснодаре, в том числе в клинике «Шаг к Трезвости».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – быстрый вывод из запоя в стационаре краснодар
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся длительным и непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к формированию как физической, так и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния часто наблюдаются нарушения работы внутренних органов, что может привести к тяжелым последствиям, включая алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя — важный этап в процессе лечения зависимости, и его можно осуществлять как в стационаре, так и на дому, в зависимости от конкретных обстоятельств.
Углубиться в тему – вывод из запоя капельница на дому в санкт-петербурге
После того как вы получили виртуальный номер, откройте приложение Telegram и начните процесс регистрации. Введите ваш новый номер телефона, и вам придёт SMS с кодом подтверждения https://sarny.net.ua/kak-virtualnyj-nomer-telefona-pomogaet-v-biznese.html
После того как вы получили виртуальный номер, откройте приложение Telegram и начните процесс регистрации. Введите ваш новый номер телефона, и вам придёт SMS с кодом подтверждения http://zvonkov.net.ua/arenda-virtualnogo-nomera-telefona-ot-hottelecom/
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой актуальную медицинскую проблему, требующую тщательного подхода. Запой характеризуется длительным, непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что ведёт к физической и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния могут возникнуть тяжёлые нарушения функций органов, увеличивается риск развития таких состояний, как алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя становится ключевым этапом в лечении зависимостей, который может осуществляться как в стационарных условиях, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента. В клинике «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске мы предлагаем круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить максимально эффективное и безопасное лечение при любом варианте вывода из запоя.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – narkologicheskaya klinika chelyabinsk
https://adamex-online.ru
После того как вы получили виртуальный номер, откройте приложение Telegram и начните процесс регистрации. Введите ваш новый номер телефона, и вам придёт SMS с кодом подтверждения https://dikb.ru/virtualnye-nomera-telefona-kak-i-zachem-ih-arendovat.html
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, необходимая для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Это состояние, часто характеризующееся физическими и психоэмоциональными нарушениями, требует профессионального вмешательства. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть разнообразными и варьироваться от легкой тревожности до серьезных нарушений в функционировании внутренних органов. Квалифицированная помощь в этот период позволяет минимизировать риски и значительно ускорить процесс выздоровления.
Подробнее – вывод из запоя анонимно недорого в челябинске
Запой представляет собой состояние, характеризующееся длительным непрерывным употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к физической и психической зависимости. Этот процесс может длиться от нескольких дней до недель. Алкогольные напитки негативно влияют на функционирование внутренних органов, вызывая серьёзные нарушения, включая алкоголизм. При необходимости вывода из запоя важно обратиться за медицинской помощью, что можно осуществить на дому. В данной статье рассмотрим ключевые аспекты данной процедуры.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – vyvod iz zapoya na domu kruglosutochno
перевозка мебели грузчики в минске
купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр .
Стоимость вывода из запоя зависит от ряда факторов, таких как состояние пациента, выбранная программа лечения и место проведения процедуры. Мы предлагаем прозрачное ценообразование, чтобы вы могли заранее ознакомиться с возможными затратами на лечение.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно челябинск
Медикаментозное лечение — это еще один важный этап. Оно включает использование препаратов, которые помогают пациенту восстановиться как физически, так и психологически. Нарколог контролирует процесс лечения, чтобы исключить побочные эффекты и скорректировать терапию при необходимости.
Подробнее тут – частный нарколог на дом в красноярске
Каталог финансовых организаций https://srochno-zaym-online.ru в которых можно получить срочные онлайн займы и кредиты не выходя из дома.
hdrezka фильмы мелодрамы с субтитрами бесплатно популярные фильмы 2025
В клинике «Заря Будущего» мы понимаем, насколько важен своевременный и профессиональный подход к лечению зависимости. Наши специалисты готовы оказать квалифицированную помощь прямо у вас дома, обеспечивая полную безопасность и конфиденциальность на каждом этапе лечения.
Подробнее – вывод из запоя врач на дом в санкт-петербурге
купить цветы томск
Наркологическая клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже специализируется на лечении алкогольной зависимости и предлагает профессиональные услуги по выводу из запоя. Мы стремимся создать атмосферу доверия, где каждый пациент сможет получить необходимую поддержку.
Изучить вопрос глубже – vyvod iz zapoya vyzov na dom voronezh
Алкогольный запой – это серьёзное состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к тяжёлой интоксикации организма. Во время запоя нарушаются функции внутренних органов, страдает нервная система, и повышается риск развития опасных осложнений, таких как алкогольный делирий. Это состояние требует незамедлительного медицинского вмешательства.
Разобраться лучше – vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno ekaterinburg
Наркологическая клиника «Союз Здоровья» в Воронеже специализируется на лечении алкогольной зависимости и предлагает профессиональные услуги по выводу из запоя. Мы стремимся создать атмосферу доверия, где каждый пациент сможет получить необходимую поддержку.
Ознакомиться с деталями – bystry vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare voronezh
Медицинский специалист с особой осторожностью и профессионализмом выполняет процедуру установки капельницы, внимательно контролируя состояние пациента. Первым этапом проводится тщательная дезинфекция кожного покрова специальным антисептическим средством для исключения риска инфицирования. После этого врач осуществляет аккуратную венепункцию, максимально снижая неприятные ощущения для пациента. Вся манипуляция проходит в спокойной обстановке, способствующей расслаблению пациента. Медработник постоянно следит за корректностью установки системы и скоростью поступления лечебного раствора.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – капельница от запоя на дому в москве
Yo, fellow adventurer! This is gonna be the start of something awesome.
Exploring this website evokes the magical experience of standing under the Northern Lights in Iceland, where every click reveals a breathtaking display of color and wonder. The creators are like skilled artisans of light, crafting an experience that is mesmerizing and ethereal. I can almost feel the chill in the air as I witness their awe-inspiring work unfold before me.
Your website is like a gorgeous red velvet cake, rich and beautiful! Let’s combine our flavors for a spectacular online treat Copper chromate recycling
Stay epic
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, необходимая для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Это состояние, часто характеризующееся физическими и психоэмоциональными нарушениями, требует профессионального вмешательства. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть разнообразными и варьироваться от лёгкой тревожности до серьёзных нарушений в функционировании внутренних органов. Квалифицированная помощь в этот период позволяет минимизировать риски и значительно ускорить процесс выздоровления.
Разобраться лучше – bystry vyvod iz zapoya v stacionare voronezh
При сильной интоксикации требуется полное очищение организма от токсинов. Детоксикация помогает нормализовать работу внутренних органов, улучшить общее состояние пациента и восстановить баланс жидкостей в организме. Специалист использует современные препараты, включая электролиты, глюкозу и антиоксиданты, для безопасного и эффективного очищения организма.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – частный нарколог на дом в красноярске
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой серьезную медицинскую проблему, которая влечет за собой не только физические, но и психологические проблемы. Периоды запоя, характеризующиеся бесконтрольным употреблением алкоголя, могут привести к тяжелым последствиям. Симптомы абстиненции требуют незамедлительного вмешательства. Анонимность в процессе реабилитации становится важным аспектом, помогающим пациентам избежать стыда и социального осуждения.
Углубиться в тему – вывод из запоя анонимно недорого
Услуга вызова нарколога на дом в Красноярске — это удобный и современный способ получения медицинской помощи. Она идеально подходит для тех, кто нуждается в профессиональной поддержке, но по каким-либо причинам не может или не хочет посещать клинику.
Подробнее тут – вызов нарколога на дом красноярск
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, необходимая для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Это состояние, часто характеризующееся физическими и психоэмоциональными нарушениями, требует профессионального вмешательства. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть разнообразными и варьироваться от легкой тревожности до серьезных нарушений в функционировании внутренних органов. Квалифицированная помощь в этот период позволяет минимизировать риски и значительно ускорить процесс выздоровления.
Изучить вопрос глубже – наркология вывод из запоя на дому в челябинске
грузоперевозки минск гродно https://perevozimgruz.by/kvartirnyj-pereezd-iz-minska-v-grodno/
Детоксикация организма является не менее важной услугой, особенно в случаях, когда зависимость сопровождается тяжелыми интоксикациями. В процессе детоксикации нарколог проводит внутривенные инфузии с препаратами, направленными на очищение организма от токсинов. Врач тщательно контролирует состояние пациента, следя за работой сердца, давления и других жизненно важных показателей.
Разобраться лучше – выезд нарколога на дом цена в красноярске
Гарантированная анонимность при выводе из запоя в Челябинске. В клинике «Перекресток Надежды» мы строго соблюдаем политику конфиденциальности. Информация о пациенте и его состоянии здоровья остаётся закрытой. Это особенно важно для тех, кто ценит свою репутацию и не хочет разглашения. Мы обеспечиваем анонимность как в стационаре, так и при оказании услуг на дому, сохраняя высокий уровень медицинской помощи.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya gorod chelyabinsk
Помощь? почему с мягким знаком https://e-pochemuchka.ru/pomoshh-pochemu-s-myagkim-znakom/
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, необходимая для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Это состояние, часто характеризующееся физическими и психоэмоциональными нарушениями, требует профессионального вмешательства. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть разнообразными и варьироваться от легкой тревожности до серьезных нарушений в функционировании внутренних органов. Квалифицированная помощь в этот период позволяет минимизировать риски и значительно ускорить процесс выздоровления.
Подробнее – быстрый вывод из запоя в стационаре
В клинике работает команда квалифицированных специалистов, которые осуществляют вывод из запоя, обеспечивая полный контроль над состоянием пациента и устраняя все последствия длительного употребления алкоголя.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – narkolog vyvod iz zapoya cena ekaterinburg
Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся утратой контроля над употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к тяжелой интоксикации организма. Вывод из запоя — это комплексный процесс, направленный на устранение последствий интоксикации и восстановление нормального функционирования организма. Цена данной процедуры может значительно различаться в зависимости от нескольких факторов, и в этой статье мы подробно рассмотрим, что влияет на стоимость вывода из запоя в Краснодаре, в том числе в клинике «Шаг к Трезвости».
Получить дополнительную информацию – vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno v-krasnodare
Стоимость вывода из запоя зависит от ряда факторов, таких как состояние пациента, выбранная программа лечения и место проведения процедуры. Мы предлагаем прозрачное ценообразование, чтобы вы могли заранее ознакомиться с возможными затратами на лечение.
Углубиться в тему – нарколог вывод из запоя цена
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой актуальную медицинскую проблему, требующую тщательного подхода. Запой характеризуется длительным, непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что ведёт к физической и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния могут возникнуть тяжёлые нарушения функций органов, увеличивается риск развития таких состояний, как алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя становится ключевым этапом в лечении зависимостей, который может осуществляться как в стационарных условиях, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента. В клинике «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске мы предлагаем круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить максимально эффективное и безопасное лечение при любом варианте вывода из запоя.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – vyvod iz zapoya anonimno
Алкоголизм — это хроническое прогрессирующее заболевание, связанное с физической и психической зависимостью от этанола. Запой, как его крайнее проявление, представляет собой длительное употребление алкоголя, сопровождающееся тяжелыми нарушениями работы организма, включая абстинентный синдром и потенциальные угрозы для жизни. Лечение запоя требует комплексного подхода, включающего медицинские процедуры, психотерапию и реабилитационные меры.
Узнать больше – vyvod-iz-zapoya-20.ru
В таких ситуациях вывод из запоя на дому становится оптимальным решением, особенно если пациент не может или не хочет посещать стационар. Эта услуга позволяет получить медицинскую помощь в комфортной и привычной обстановке, что снижает уровень стресса и ускоряет процесс восстановления.
Получить больше информации – vyvod iz zapoya na domu voronezh
Гарантированная анонимность при выводе из запоя в Челябинске. В клинике «Перекресток Надежды» мы строго соблюдаем политику конфиденциальности. Информация о пациенте и его состоянии здоровья остаётся закрытой. Это особенно важно для тех, кто ценит свою репутацию и не хочет разглашения. Мы обеспечиваем анонимность как в стационаре, так и при оказании услуг на дому, сохраняя высокий уровень медицинской помощи.
Углубиться в тему – вывод из запоя с выездом в челябинске
Кроме того, врач оказывает психологическую поддержку, которая помогает пациенту справиться с чувством тревоги, депрессией и страхом, возникающими на фоне зависимости.
Углубиться в тему – http://narcolog-na-dom-v-krasnoyarske55.ru/
Запой — это опасное состояние, которое развивается у людей с алкогольной зависимостью и характеризуется длительным непрерывным потреблением алкоголя. Это состояние приводит к серьезным нарушениям в организме, как физическим, так и психоэмоциональным. Длительный запой может вызвать множество осложнений, таких как поражение внутренних органов, нервной системы, а также проблемы в социальной и семейной жизни. Однако современная медицина предоставляет эффективные методы вывода из запоя, и одним из наиболее удобных и востребованных является вывод из запоя на дому.
Выяснить больше – вывод из запоя на дому в санкт-петербурге
Рекомендую эту компанию для строительства загородных домов, подробнее тут https://www.indiegogo.com/individuals/38101402
Услуга вызова нарколога на дом в Красноярске — это удобный и современный способ получения медицинской помощи. Она идеально подходит для тех, кто нуждается в профессиональной поддержке, но по каким-либо причинам не может или не хочет посещать клинику.
Подробнее – вызов нарколога на дом красноярск
Запой — это состояние, характеризующееся утратой контроля над употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к тяжелой интоксикации организма. Вывод из запоя — это комплексный процесс, направленный на устранение последствий интоксикации и восстановление нормального функционирования организма. Цена данной процедуры может значительно различаться в зависимости от нескольких факторов, и в этой статье мы подробно рассмотрим, что влияет на стоимость вывода из запоя в Краснодаре, в том числе в клинике «Шаг к Трезвости».
Углубиться в тему – narkolog vyvod iz zapoya cena
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой серьезную медицинскую проблему, которая влечет за собой не только физические, но и психологические проблемы. Периоды запоя, характеризующиеся бесконтрольным употреблением алкоголя, могут привести к тяжелым последствиям. Симптомы абстиненции требуют незамедлительного вмешательства. Анонимность в процессе реабилитации становится важным аспектом, помогающим пациентам избежать стыда и социального осуждения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – вывод из запоя капельница краснодар
диплом техникума спб купить диплом техникума спб купить .
https://akril-servis.ru/
купить диплом в грозном
Алкогольный запой представляет собой серьезное состояние, которое требует немедленного медицинского вмешательства. Это состояние характеризуется длительным и бесконтрольным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к разрушению как физического, так и психоэмоционального здоровья человека. Для эффективного и безопасного вывода из запоя стационарное лечение является оптимальным решением, особенно при тяжелых случаях интоксикации. В стационаре клиники «Заря Будущего» мы предлагаем комплексную программу вывода из запоя, которая включает детоксикацию, восстановление организма и психотерапевтическую помощь.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-19.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-sankt-peterburge/]вывод из запоя цена в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Кроме того, врач оказывает психологическую поддержку, которая помогает пациенту справиться с чувством тревоги, депрессией и страхом, возникающими на фоне зависимости.
Подробнее тут – нарколог на дом стоимость красноярск
Запой — это тяжелое состояние, возникающее вследствие длительного и непрерывного употребления алкоголя, которое сопровождается физической и психической зависимостью. Это опасное явление требует незамедлительного вмешательства специалистов. Вывод из запоя — это комплексный процесс медицинской детоксикации, который включает в себя очищение организма от токсинов, нормализацию функций внутренних органов и поддержку психоэмоционального состояния пациента. В случае тяжелого запоя стационарное лечение становится оптимальным решением для безопасного и эффективного вывода из этого состояния. В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как проходит вывод из запоя в стационаре клиники «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске, а также особенности анонимности, скорости лечения и участия нарколога.
Ознакомиться с деталями – vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno
Алкоголизм — это хроническое прогрессирующее заболевание, связанное с физической и психической зависимостью от этанола. Запой, как его крайнее проявление, представляет собой длительное употребление алкоголя, сопровождающееся тяжелыми нарушениями работы организма, включая абстинентный синдром и потенциальные угрозы для жизни. Лечение запоя требует комплексного подхода, включающего медицинские процедуры, психотерапию и реабилитационные меры.
Разобраться лучше – срочный вывод из запоя на дому
A nobleman is a member of the aristocratic estate. Nobles had exclusive benefits and status that distinguished them from other layers of the population. They were associated with noble clans and had the right to land possession, inclusion in government of the state and military service. The nobility was also associated with a certain way of life, culture and education.
https://culterperu.blogspot.com/2025/01/blog-post.html
Pharmacy Rx One Viagra Metformin healthy man viagra Thyroxine online no prescription
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой актуальную медицинскую проблему, требующую тщательного подхода. Запой характеризуется длительным, непрерывным употреблением спиртных напитков, что ведёт к физической и психической зависимости. На фоне запойного состояния могут возникнуть тяжёлые нарушения функций органов, увеличивается риск развития таких состояний, как алкогольный делирий. Вывод из запоя становится ключевым этапом в лечении зависимостей, который может осуществляться как в стационарных условиях, так и на дому, в зависимости от состояния пациента. В клинике «Перекресток Надежды» в Челябинске мы предлагаем круглосуточную помощь, чтобы обеспечить максимально эффективное и безопасное лечение при любом варианте вывода из запоя.
Детальнее – narkologiya vyvod iz zapoya anonimno
Canadian Pharmacy No Prescription Rio rico pharmacy canada pharmacy 24 hour drug store
Buy levothyroxine 100mcg online generic
купить диплом училище
northwestern canada drugs
elon bet casino elon bet casino .
elon bet casino elon bet casino .
1вин сайт официальный http://www.bbcc.com.kg .
Каталог финансовых организаций srochno-zaym-online.ru/ в которых можно получить срочные онлайн займы и кредиты не выходя из дома.
hdrezka подборки резка смотреть криминал full hd онлайн
healthy man complaints Canada Pharmacy 24 Hour Drug Store Accessrx prescription drugs
https://je-tall-marketing-254.sgp1.digitaloceanspaces.com/research/je-tall-sf-marketing-(244).html
However, to determine whether or not or not you also wants to coordinate with each mothers, verify in with the bride.
Клиника «Шаг к Трезвости» в Краснодаре предлагает анонимный вывод из запоя, обеспечивая полную конфиденциальность и безопасность на каждом этапе лечения. Мы понимаем, что для многих людей важно сохранить свою личную информацию в тайне, и гарантируем, что все данные о пациенте и его состоянии здоровья останутся закрытыми. Независимо от того, выбрал ли пациент стационарное лечение или вывод из запоя на дому, мы обеспечиваем высококачественную медицинскую помощь с полным соблюдением принципов конфиденциальности.
Подробнее – anonimny vyvod iz zapoya na domu krasnodar
https://arenda-t.ru
Процесс лечения алкогольной зависимости состоит из последовательных этапов, каждый из которых критически важен для успешного выздоровления.
Получить больше информации – срочный вывод из запоя красноярск
Online Pharmacy India Viagra coupon Ed drugs online northwest pharmacy canada Canadapharmacy
Капельница от запоя представляет собой внутривенное введение специального раствора, который помогает организму справиться с последствиями алкогольной интоксикации. Этот метод используется для того, чтобы уменьшить проявления похмелья, таких как головная боль, тошнота, бессонница и раздражительность. Кроме того, капельница способствует нормализации работы внутренних органов и систем, ускоряя восстановление после длительного алкоголизма.
Углубиться в тему – капельницы от запоя в екатеринбурге
аттестат 9 класс купить
Процесс получения диплома стоматолога: реально ли это сделать быстро?
аттестат купить в новосибирске
Клиника «Освобождение» в Рязани предоставляет услугу круглосуточного вывода из запоя на дому, что позволяет пациенту получить медицинскую помощь в привычной обстановке, избегая лишнего стресса, связанного с госпитализацией.
Выяснить больше – нарколог на дом вывод из запоя
무리한 소비는 자원 소모와 배경 파괴를 초래할 수 있으며, 롯데모바일상품권 소비주의적인 가치관은 소수의 소비에만 초점을 맞추어 금전적 불평등을 증가시킬 수 있다. 그래서, 쇼핑을 할 경우는 지속 가능한 소비를 실천하고, 고유의 필요에 따라 적당히 선택하는 것이 중요해요.
신세계백화점상품권 매입
Запойное состояние представляет собой серьёзную угрозу для здоровья, поскольку сопровождается тяжёлой интоксикацией организма и нарушением психоэмоционального состояния. Решение о лечении в стационаре клиники «Союз Здоровья» позволяет справиться с последствиями длительного употребления алкоголя, обеспечивая пациентам полный комплекс медицинской и психологической помощи.
Получить дополнительные сведения – вывод из запоя цена наркология воронеж
Форум для кулинаров https://food-recipe.ru и рестораторов! Лучшие рецепты, тренды гастрономии, обсуждения ресторанного бизнеса. Общайтесь, делитесь опытом и вдохновляйтесь новыми идеями. Присоединяйтесь к нашему кулинарному сообществу!
Алкогольная зависимость становится всё более распространенной проблемой, требующей внимания как со стороны медицинского сообщества, так и общества в целом. Вывод из запоя — это сложный и ответственный процесс, необходимый для восстановления здоровья пациента и его интеграции в нормальную жизнь. Профессиональное вмешательство позволяет минимизировать последствия длительного употребления алкоголя и нормализовать состояние организма.
Углубиться в тему – вывод из запоя капельница
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой серьезную медицинскую проблему, которая влечет за собой не только физические, но и психологические проблемы. Периоды запоя, характеризующиеся бесконтрольным употреблением алкоголя, могут привести к тяжелым последствиям. Симптомы абстиненции требуют незамедлительного вмешательства. Анонимность в процессе реабилитации становится важным аспектом, помогающим пациентам избежать стыда и социального осуждения.
Подробнее – вывод из запоя анонимно недорого
Быстрое обучение и получение диплома магистра – возможно ли это?
Для многих пользователей получение доступа к WhatsApp стало необходимостью, но не у всех есть возможность использовать свой номер телефона. На счастье, существует несколько способов, как можно зарегистрироваться в WhatsApp без номера http://zvonkov.net.ua/arenda-virtualnogo-nomera-telefona-ot-hottelecom/
Для многих пользователей получение доступа к WhatsApp стало необходимостью, но не у всех есть возможность использовать свой номер телефона. На счастье, существует несколько способов, как можно зарегистрироваться в WhatsApp без номера https://lifepeople.info/novosti/virtualnyj-nomer-dlya-telegram-svoboda-obshheniya-i-zashhita-konfidencialnosti/
Для многих пользователей получение доступа к WhatsApp стало необходимостью, но не у всех есть возможность использовать свой номер телефона. На счастье, существует несколько способов, как можно зарегистрироваться в WhatsApp без номера https://sarny.net.ua/kak-virtualnyj-nomer-telefona-pomogaet-v-biznese.html
Купить диплом о среднем полном образовании, в чем подвох и как избежать обмана?
Ремонтируем холодильники в Иркутске и области. Быстрый Ремонтируем холодильников за адекватную стоимость https://holodilnikirk.ru/
Алкогольная интоксикация, или запой, представляет собой состояние, при котором организм человека испытывает серьёзное воздействие этанола. Это приводит к нарушениям нормальной физиологической деятельности и ухудшению состояния здоровья. Анонимный вывод из запоя — это медицинская помощь, направленная на устранение последствий чрезмерного употребления алкоголя с соблюдением строгой конфиденциальности.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – быстрый вывод из запоя в стационаре екатеринбург
купить диплом расценки 2orik-diploms.ru .
Красивые поздравления https://photofile.ru/otkrytki-so-svechami-vechnaya-i-svetlaya-pamyat-110-kartinok в одном месте! Огромный выбор картинок и открыток для любого повода. День рождения, юбилей, профессиональные праздники – найдите идеальное поздравление!
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой серьезную медицинскую проблему, которая влечет за собой не только физические, но и психологические проблемы. Периоды запоя, характеризующиеся бесконтрольным употреблением алкоголя, могут привести к тяжелым последствиям. Симптомы абстиненции требуют незамедлительного вмешательства. Анонимность в процессе реабилитации становится важным аспектом, помогающим пациентам избежать стыда и социального осуждения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – вывод из запоя в краснодаре
Запой представляет собой сложное состояние, связанное с длительным употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к формированию зависимости. Это явление не только нарушает нормальную жизнедеятельность, но также вызывает серьезные физические и психологические расстройства. Стационарное лечение становится необходимым для восстановления здоровья и профилактики осложнений. В стационаре клиники «Шаг к Трезвости» в Краснодаре мы предлагаем комплексный подход, включающий медикаментозное лечение, психотерапию и постоянный контроль со стороны квалифицированных специалистов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – narkologicheskij centr krasnodar
Алкогольная зависимость — это длительное и прогрессирующее заболевание, при котором развивается как физическая, так и психическая зависимость от алкоголя. Одним из самых тяжелых проявлений болезни является запой — длительное употребление алкоголя, которое может сопровождаться нарушениями работы организма и абстинентным синдромом, представляющим серьезную угрозу для здоровья. Эффективное лечение запоя требует комплексного подхода, включающего медикаментозную терапию, психотерапию и реабилитационные мероприятия.
Изучить вопрос глубже – вывод из запоя с выездом в твери
Наша компания предлагает нержавеющие сетки ТУ 14-4-507-99 производства Северсталь метиз ОСПАЗ со склада
г.Орел. В наличии огромный ассортиментнержавеющие сетки ГОСТ 6613-86.
Вы можете купить нержавеющие сетки ТУ 14-4-167-91 светлую и оцинкованную.
У нас всегда в наличии огромный выбор нержавеющие сетки ТУ14-4-432-94, цены от производителя.
Продажа нержавеющие сетки ТУ 14-4-697-2001 оптом и в розницу со склада г.Орел.
“Looking for exciting online casino games? Masal Bet is the place to find new slot hits from leading brands.
At https://masalbet.casino/tr/, you’ll find newbie gifts and a user-friendly interface.
Join now and get exclusive offers.
Play fresh new game releases with MasalBet!
“
Кроме того, врач приедет в любое удобное для пациента время, даже ночью, обеспечив круглосуточный доступ к медицинской помощи. Специалист подбирает индивидуальный состав капельницы, что позволяет оптимально поддержать организм в зависимости от состояния пациента.
Ознакомиться с деталями – капельница от запоя в екатеринбурге
“Looking for exciting slots to play? AbeBet Casino offers endless variety online slots for all players!
At AbeBet https://abe.bet/tr/games/demo/fire_joker, you’ll find slot hits from leading providers.
Sign up now to get newbie gifts.
Dive into a world of winnings with Abe Bet! “
В клинике «Рассвет» в Твери мы предлагаем круглосуточную помощь при алкогольных запоях, обеспечивая быстрый вывод токсинов из организма с помощью капельниц и других эффективных методик.
Выяснить больше – вывод из запоя врач на дом
“Looking for exciting slots to play? Abe Bet Casino offers endless variety online slots for all players!
At Abe Bet abe.bet/tr/games/demo/jetx, you’ll find popular slots from top developers.
Register now to get newbie gifts.
Dive into a world of winnings with AbeBet! “
Длительное злоупотребление алкоголем приводит к состоянию запоя, которое сопровождается физической и психологической зависимостью. Это тяжёлое состояние наносит серьёзный вред организму и требует профессиональной медицинской помощи. Для восстановления здоровья и предотвращения осложнений важным шагом становится вывод из запоя, который помогает пациенту стабилизировать состояние.
Ознакомиться с деталями – вывод из запоя на дому недорого в рязани
Алкогольная зависимость становится всё более распространенной проблемой, требующей внимания как со стороны медицинского сообщества, так и общества в целом. Вывод из запоя — это сложный и ответственный процесс, необходимый для восстановления здоровья пациента и его интеграции в нормальную жизнь. Профессиональное вмешательство позволяет минимизировать последствия длительного употребления алкоголя и нормализовать состояние организма.
Выяснить больше – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom cena v-ekaterinburge
“Официальный веб-сайт казино Рояль предлагает располагающую обстановку для любителей казино. С его изысканным дизайном и высококачественным выбором игр, Рояль является оптимальным местом для тех, кто ценит качественное азартное развлечение. Исследуйте разнообразный выбор игровых автоматов и настольных игр на авторизованном веб-сайте https://royalcasino-slots.com/ru/.
Казино Рояль предоставляет первоклассное обслуживание клиентов и поддержку. Внимательная команда поддержки доступна круглосуточно, настроена реагировать на различные вопросы и исправить проблемы, гарантируя непрерывную игру и удовлетворение.”
В клинике работает команда квалифицированных специалистов, которые осуществляют вывод из запоя, обеспечивая полный контроль над состоянием пациента и устраняя все последствия длительного употребления алкоголя.
Углубиться в тему – вывод из запоя срочно круглосуточно в екатеринбурге
Новый уникальный маркетплейс NOVA, есть все! Москва, Питер, всегда свежие клады!Акция для новых магазинов – продай на 1 млн, получи 100к!Приглашаем к сотрудничеству рекламодателей!
Клиника «Шаг к Трезвости» в Краснодаре предлагает анонимный вывод из запоя, обеспечивая полную конфиденциальность и безопасность на каждом этапе лечения. Мы понимаем, что для многих людей важно сохранить свою личную информацию в тайне, и гарантируем, что все данные о пациенте и его состоянии здоровья останутся закрытыми. Независимо от того, выбрал ли пациент стационарное лечение или вывод из запоя на дому, мы обеспечиваем высококачественную медицинскую помощь с полным соблюдением принципов конфиденциальности.
Получить больше информации – наркологический центр в краснодаре
Need some more money? Robot will earn them really fast.] https://topinnews.info/
Такой метод лечения помогает быстро устранить последствия алкоголизма и минимизировать риски для здоровья пациента.
Получить дополнительные сведения – стоимость капельницы от запоя в екатеринбурге
https://www.quora.com/Is-Del-Mar-Energy-Inc-a-legitimate-company
Программы лечения разрабатываются индивидуально и могут включать как визит врача на дом, так и стационарное пребывание. Стоимость услуг формируется в зависимости от необходимых процедур и остается прозрачной, позволяя пациентам сосредоточиться на главном – восстановлении здоровья и возвращении к полноценной жизни.
Получить дополнительную информацию – вывод из запоя санкт-петербург
“Твой решение для гемблинга – казино Слотозал!
Слотозал предоставляет разнообразный набор слот-машин, выгодные предложения и надежный уровень безопасности. Интерфейс сайта понятен, навигация легка, что способствует оперативно найти избранные игры. Служба поддержки непрерывно настроена помочь с любыми вопросами. Запишитесь на законном сайте casinoslotozal.net/ru/ и начните завоевывать призы уже!”
https://bal-ufa.ru/
Алкогольная зависимость требует быстрого и квалифицированного вмешательства, поскольку она может привести к тяжелым последствиям для здоровья. Капельница от запоя — один из наиболее эффективных методов, помогающих вывести организм из состояния алкогольной интоксикации и восстановить нормальное самочувствие. В Екатеринбурге эта процедура доступна как в медицинских учреждениях, так и на дому, что позволяет пациентам выбрать наиболее удобный и комфортный способ лечения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – капельница от запоя в екатеринбурге
Многим людям удобнее проходить эту процедуру в домашних условиях, где профессиональная помощь оказывается в комфортной и привычной обстановке. Такой подход позволяет минимизировать стресс, связанный с госпитализацией. Однако в более сложных случаях стационарное лечение остаётся необходимым, так как только оно обеспечивает круглосуточное наблюдение и комплексную поддержку специалистов.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – vyvod iz zapoya vyzov na dom
Запойное пьянство характеризуется продолжительным и интенсивным потреблением алкоголя, что приводит к серьезным физическим и психологическим последствиям. Часто пациенты сталкиваются с различными заболеваниями, такими как цирроз печени, панкреатит, алкогольный делирий и другие. Алкогольное опьянение не только ухудшает качество жизни, но также может угрожать жизни пациента. В условиях стационара лечение может быть более эффективным, однако многие люди предпочитают проходить данную процедуру на дому, чтобы избежать стигматизации и сохранить чувство приватности.
Изучить вопрос глубже – vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno narkologiya
Алкоголизм — это хроническое заболевание, которое характеризуется патологической зависимостью от этанола. Периоды запоя, когда человек неконтролируемо потребляет алкоголь, могут привести к разнообразным медицинским осложнениям, как физическим, так и психологическим. Запой становится не только причиной ухудшения здоровья, но и причиной множества социальных и личных проблем. На этом фоне возникает необходимость вывода из запоя, процесс, который должен учитывать индивидуальные особенности пациента. Важно, что анонимность в реабилитации играет ключевую роль, помогая избежать стигматизации и увеличивая шансы на успешное восстановление.
Детальнее – vyvod iz zapoya anonimno nedorogo
Полезные советы по безопасной покупке диплома о высшем образовании
Клиника «Освобождение» в Рязани предоставляет услугу круглосуточного вывода из запоя на дому, что позволяет пациенту получить медицинскую помощь в привычной обстановке, избегая лишнего стресса, связанного с госпитализацией.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – вывод из запоя срочно круглосуточно в рязани
on line pharmacy
Процедура капельницы особенно показана в случаях, когда симптомы похмелья выражены настолько сильно, что пациент не в состоянии справиться с ними самостоятельно. Головная боль, тошнота, рвота, усталость и раздражительность — все это признаки того, что организму необходимо восстановление. Капельница помогает не только ускорить процесс очищения, но и минимизировать риск осложнений, таких как нарушение работы сердца и печени.
Разобраться лучше – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-ektb55.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-v-stacionare-ekaterinburg/
Запой – это состояние, возникающее из-за длительного употребления алкоголя и характеризующееся физической и психологической зависимостью. Оно требует комплексного медицинского вмешательства для устранения последствий и предотвращения дальнейшего ухудшения здоровья. Стационарное лечение в клинике «Освобождение» в Рязани – это эффективный способ вернуть пациента к нормальной жизни, предоставляя ему комфортные условия и круглосуточную помощь специалистов.
Узнать больше – vyvod iz zapoya na domu kruglosutochno ryazan
аттестат о среднем специальном образовании купить аттестат о среднем специальном образовании купить .
Запойное состояние представляет собой серьёзную угрозу для здоровья, поскольку сопровождается тяжёлой интоксикацией организма и нарушением психоэмоционального состояния. Решение о лечении в стационаре клиники «Союз Здоровья» позволяет справиться с последствиями длительного употребления алкоголя, обеспечивая пациентам полный комплекс медицинской и психологической помощи.
Углубиться в тему – vyvod iz zapoya anonimno
Вывод из запоя — это медицинская процедура, необходимая для восстановления организма после длительного употребления алкоголя. Это состояние, часто характеризующееся физическими и психоэмоциональными нарушениями, требует профессионального вмешательства. Симптомы абстиненции могут быть разнообразными и варьироваться от лёгкой тревожности до серьёзных нарушений в функционировании внутренних органов. Квалифицированная помощь в этот период позволяет минимизировать риски и значительно ускорить процесс выздоровления.
Разобраться лучше – вывод из запоя врач на дом в воронеже
купить диплом сварщика
buy cialis
작년 국내외 온/오프라인쇼핑 시장 규모 165조원을 넘어서는 수준이다. 미국에서는 이달 28일 블랙프라이데이와 사이버먼데이로 이어지는 연말 타다주브 쇼핑 시즌이 기다리고 있습니다. 허나 이번년도는 글로벌 물류대란이 변수로 떠증가했다. 전 세계 제공망 차질로 주요 소매유통기업들이 상품 재고 확보에 하기 곤란함을 겪고 있기 때문입니다. 어도비는 연말 계절 미국 소매기업의 할인율이 전년보다 1%포인트(P)가량 줄어들 것으로 전망했었다.
두사트
фриспины без депозита с выводом бездеп
Запойное состояние представляет собой серьёзную угрозу для здоровья, поскольку сопровождается тяжёлой интоксикацией организма и нарушением психоэмоционального состояния. Решение о лечении в стационаре клиники «Союз Здоровья» позволяет справиться с последствиями длительного употребления алкоголя, обеспечивая пациентам полный комплекс медицинской и психологической помощи.
Разобраться лучше – срочный вывод из запоя на дому
лучшие фильмы онлайн фильмы популярные фильмы 2025 бесплатно
Маркетплейс нового поколения https://x-nova.live уникальный сервис для удобных покупок и продаж. Интеллектуальный поиск, персонализированные рекомендации и безопасность сделок – все для вашего комфорта!
Experimenting with Different Layouts
With a satisfying L-shaped layout as my baseтАЪ I delved into the finer detailsтАЪ transforming my digital sketch into a truly personalized design. I meticulously selected cabinet styles from the extensive library offered by the softwareтАЪ opting for sleekтАЪ modern shaker-style cabinets in a warmтАЪ honey-toned oak finish. The program allowed me to visualize these choices in real-timeтАЪ rotating the cabinets to ensure they complemented the overall aesthetic. NextтАЪ I chose countertops. I initially considered graniteтАЪ but the virtual rendering showed it clashing slightly with the cabinet color. I then experimented with quartzтАЪ settling on a beautifulтАЪ light-grey option that beautifully contrasted with the oak. The software’s realistic rendering capabilities were invaluable here. I spent a considerable amount of time tweaking the backsplashтАЪ finally settling on a subway tile pattern in a soft whiteтАЪ which provided a clean and classic look. Adding lighting was another key step. I strategically placed recessed lighting above the countertops and pendant lights above the islandтАЪ creating a warm and inviting ambiance. I even experimented with different flooring optionsтАЪ virtually laying down various types of tile and hardwood to see how they interacted with the rest of the design. I was particularly pleased with a light-colored oak wood floor that tied in seamlessly with the cabinetry. Beyond the major elementsтАЪ I focused on the smaller details. I carefully selected hardwareтАЪ opting for brushed nickel pulls and knobs that added a touch of sophistication. I also integrated various appliancesтАЪ choosing models based on their size and aestheticsтАЪ ensuring they fit harmoniously within the design. The software allowed me to fine-tune every aspectтАЪ from the placement of outlets to the positioning of spice racksтАЪ ensuring a highly functional and visually appealing kitchen. It was a truly rewarding processтАЪ seeing my initial concept evolve into a cohesive and detailed designтАЪ ready to be shared and potentially implemented in the real world. The level of customization was impressiveтАЪ allowing me to create a space that was uniquely mine.
avtovestie.ru
B5XvZR9ny
Before I even thought about buying shelves or hanging rodsтАЪ I knew I needed a proper planтАд Armed with a measuring tape and a notebookтАЪ I meticulously documented every inch of my tiny closetтАд I measured the widthтАЪ the depthтАЪ and the heightтАЪ noting any obstructions like pipes or electrical outletsтАд This detailed assessment was crucialтАд I also carefully inventoried my belongingsтАд I pulled everything out тАУ every shirtтАЪ every pair of pantsтАЪ every scarf and shoe тАУ and sorted it into categoriesтБЪ topsтАЪ bottomsтАЪ dressesтАЪ shoesтАЪ accessoriesтАЪ etcтАд This helped me visualize the amount of space I needed for each categoryтАд Then came the fun partтБЪ sketching! I drew several different layouts in my notebookтАЪ experimenting with different shelving configurations and hanging rod placementsтАд I considered the placement of my longer dresses and coatsтАЪ and how to best utilize the vertical spaceтАд I also thought about the flow of the closet тАУ how easily I could access different itemsтАд I even considered the type of storage solutions I might need тАУ baskets for smaller itemsтАЪ drawers for folded clothesтАЪ etcтАд InitiallyтАЪ I considered custom built-insтАЪ but the cost was prohibitiveтАд ThereforeтАЪ I opted for a more budget-friendly approachтАЪ focusing on maximizing the space with readily available shelving and storage solutionsтАд My planning phase took a few eveningsтАЪ but it was worth itтАд Having a clear plan before I started shopping prevented impulsive purchases and ensured I bought the right amount of storage to perfectly fit my spaceтАд It was surprisingly satisfying to see my ideas take shape on paperтАЪ and I felt a sense of accomplishment even before IтАЩd started the actual transformationтАд
For instance‚ you could use a deep charcoal gray grout with white subway tiles for a sophisticated look‚ or opt for glossy black fixtures against crisp white walls for a sleek‚ contemporary feel. If you prefer a vintage aesthetic‚ consider pairing black and white patterned tiles with white cabinetry and black accents. Don’t be afraid to experiment with different shades of white – from bright‚ clean whites to warmer‚ creamier tones – to find the perfect complement to your chosen black. Remember‚ the key is to create a cohesive and balanced look that reflects your personal style and complements the overall design of your bathroom. Explore online resources for inspiration; many websites and magazines showcase stunning black and white bathroom palettes. Pay attention to how different shades of black and white interact with each other and the other elements in the bathroom design.
В клинике «Рассвет» в Твери мы предлагаем круглосуточную помощь при алкогольных запоях, обеспечивая быстрый вывод токсинов из организма с помощью капельниц и других эффективных методик.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – вывод из запоя на дому цена
Своевременное начало лечения играет решающую роль, так как промедление может усугубить как физическое, так и психическое состояние. Квалифицированные специалисты готовы оказать помощь в любое время, гарантируя анонимность и индивидуальный подход.
Углубиться в тему – вывод из запоя с выездом на дом
과학기술정보통신부는 1일 이번년도 3D 프린팅 설계 제작 업체 개발(R&D) 예산 크기와 사용 내용을 담은 ‘2027년도 연구개발산업 종합시작계획’을 선언하며 양자기술을 19대 중점 투자방향 중 처음으로 거론했다. 양자기술 분야 R&D 예산은 2029년 321억 원에서 올해 692억 원으로 증액됐다.
3D 프린팅 설계 제작
Алкогольная зависимость — это серьезная проблема, требующая незамедлительного вмешательства, чтобы избежать тяжелых последствий для здоровья. Запойное пьянство может привести к различным заболеваниям, таким как цирроз печени, панкреатит и другие опасные состояния. К счастью, современная медицина предлагает эффективные методы решения этой проблемы. Для тех, кто не хочет или не может посетить стационар, есть возможность пройти процедуру капельницы от запоя на дому в Твери.
Разобраться лучше – narkolog vyvod iz zapoya cena
Запой – это состояние, возникающее из-за длительного употребления алкоголя и характеризующееся физической и психологической зависимостью. Оно требует комплексного медицинского вмешательства для устранения последствий и предотвращения дальнейшего ухудшения здоровья. Стационарное лечение в клинике «Освобождение» в Рязани – это эффективный способ вернуть пациента к нормальной жизни, предоставляя ему комфортные условия и круглосуточную помощь специалистов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno v-ryazani
В этой статье мы расскажем о возможностях клиники для лечения алкогольной интоксикации круглосуточно, включая вывод из запоя в стационаре и на дому, а также о роли профессионалов, таких как нарколог, в процессе лечения.
Разобраться лучше – наркология вывод из запоя на дому в краснодаре
Длительное злоупотребление алкоголем приводит к состоянию запоя, которое сопровождается физической и психологической зависимостью. Это тяжёлое состояние наносит серьёзный вред организму и требует профессиональной медицинской помощи. Для восстановления здоровья и предотвращения осложнений важным шагом становится вывод из запоя, который помогает пациенту стабилизировать состояние.
Получить больше информации – наркологическая клиника в рязани
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой серьёзную медицинскую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запойное состояние характеризуется длительным и бесконтрольным потреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к возникновению как физической, так и психической зависимости. Данное явление может вызвать нарушения в работе внутренних органов, значительно увеличивая вероятность развития алкогольного делирия, который представляет собой острое состояние, требующее неотложной медицинской помощи. Вывод из запоя это ключевая часть лечения зависимости, которая может осуществляться как в стационаре, так и в амбулаторных условиях, в зависимости от конкретной ситуации и состояния пациента.
Узнать больше – vyvod iz zapoya s vyezdom krasnodar
Алкогольный запой – это серьёзное состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над употреблением алкоголя, что приводит к тяжёлой интоксикации организма. Во время запоя нарушаются функции внутренних органов, страдает нервная система, и повышается риск развития опасных осложнений, таких как алкогольный делирий. Это состояние требует незамедлительного медицинского вмешательства.
Разобраться лучше – вывод из запоя екатеринбург
Запойное состояние представляет собой серьёзную угрозу для здоровья, поскольку сопровождается тяжёлой интоксикацией организма и нарушением психоэмоционального состояния. Решение о лечении в стационаре клиники «Союз Здоровья» позволяет справиться с последствиями длительного употребления алкоголя, обеспечивая пациентам полный комплекс медицинской и психологической помощи.
Углубиться в тему – вывод из запоя цена наркология
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой сложное и хроническое заболевание, которое влияет не только на физическое, но и на психологическое состояние пациента. Периоды запоя, влекущие за собой неконтролируемое употребление алкоголя, могут привести к опасным последствиям для здоровья и жизни. Абстинентные симптомы, такие как тремор, тошнота, головная боль и другие проявления, требуют немедленного медицинского вмешательства. В таких ситуациях важно не только быстро устранить физическое воздействие алкоголя, но и предоставить пациенту психологическую поддержку.
Узнать больше – vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой серьезную медицинскую проблему, которая влечет за собой не только физические, но и психологические проблемы. Периоды запоя, характеризующиеся бесконтрольным употреблением алкоголя, могут привести к тяжелым последствиям. Симптомы абстиненции требуют незамедлительного вмешательства. Анонимность в процессе реабилитации становится важным аспектом, помогающим пациентам избежать стыда и социального осуждения.
Выяснить больше – нарколог вывод из запоя цена
Кроме того, врач приедет в любое удобное для пациента время, даже ночью, обеспечив круглосуточный доступ к медицинской помощи. Специалист подбирает индивидуальный состав капельницы, что позволяет оптимально поддержать организм в зависимости от состояния пациента.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-ektb55.ru/kapelnicza-na-domu-ekaterinburg-ot-zapoya
canadian pharcharmy online
Алкогольный запой — это состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над употреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к токсической нагрузке на организм. Это опасное состояние требует не только быстрого медицинского вмешательства, но и внимательного подхода к восстановлению здоровья пациента. Процесс вывода из запоя включает в себя комплекс процедур, направленных на устранение последствий интоксикации и восстановление нормального функционирования организма. Важно учитывать, что стоимость этой процедуры может значительно варьироваться в зависимости от нескольких факторов.
Детальнее – вывод из запоя на дому в краснодаре
Запой — это состояние, при котором человек не может прекратить употребление алкоголя на протяжении длительного времени, что вызывает физическую и психологическую зависимость. Это крайне опасное состояние, требующее немедленного вмешательства специалистов. Наркологическая клиника «Преображение» в Екатеринбурге предоставляет профессиональную помощь в лечении запоя, используя самые эффективные и безопасные методы.
Узнать больше – narkolog na dom vyvod iz zapoya v-ekaterinburge
Такой метод лечения помогает быстро устранить последствия алкоголизма и минимизировать риски для здоровья пациента.
Разобраться лучше – после капельницы от запоя на дому екатеринбург
Своевременное начало лечения играет решающую роль, так как промедление может усугубить как физическое, так и психическое состояние. Квалифицированные специалисты готовы оказать помощь в любое время, гарантируя анонимность и индивидуальный подход.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – narkolog vyvod iz zapoya cena
Для достижения эффективных результатов в лечении запоя необходима квалифицированная помощь специалистов. Наркологическая клиника «Излечение» в Краснодаре предоставляет профессиональные услуги по выводу из запоя, гарантируя безопасность, комфорт и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Изучить вопрос глубже – вывод из запоя анонимно недорого в краснодаре
В центре доступны различные варианты лечения – от амбулаторного наблюдения до интенсивных стационарных программ. Ключевые принципы работы – конфиденциальность, индивидуальный подход и оперативность оказания помощи. Независимо от тяжести зависимости, каждый пациент получает квалифицированную поддержку, направленную на восстановление здоровья и возвращение к полноценной жизни.
Узнать больше – анонимный вывод из запоя на дому
Алкогольная зависимость — это серьезная проблема, требующая немедленного вмешательства. Если вы или ваши близкие столкнулись с запоем, важно получить профессиональную помощь как можно скорее, чтобы избежать ухудшения здоровья. Наркологическая клиника «Шаг к Трезвости» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу вывода из запоя на дому, что является удобным и эффективным решением для тех, кто не может или не хочет посещать стационар.
Изучить вопрос глубже – vyvod iz zapoya kruglosutochno v-krasnodare
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой серьёзную медицинскую проблему, требующую специализированного подхода. Запойное состояние характеризуется длительным и бесконтрольным потреблением спиртных напитков, что приводит к возникновению как физической, так и психической зависимости. Данное явление может вызвать нарушения в работе внутренних органов, значительно увеличивая вероятность развития алкогольного делирия, который представляет собой острое состояние, требующее неотложной медицинской помощи. Вывод из запоя это ключевая часть лечения зависимости, которая может осуществляться как в стационаре, так и в амбулаторных условиях, в зависимости от конкретной ситуации и состояния пациента.
Разобраться лучше – vyvod iz zapoya gorod krasnodar
Алкоголизм — это хроническое прогрессирующее заболевание, связанное с физической и психической зависимостью от этанола. Запой, как его крайнее проявление, представляет собой длительное употребление алкоголя, сопровождающееся тяжелыми нарушениями работы организма, включая абстинентный синдром и потенциальные угрозы для жизни. Лечение запоя требует комплексного подхода, включающего медицинские процедуры, психотерапию и реабилитационные меры.
Углубиться в тему – вывод из запоя цена в екатеринбурге
Алкоголизм — это хроническое прогрессирующее заболевание, связанное с физической и психической зависимостью от этанола. Запой, как его крайнее проявление, представляет собой длительное употребление алкоголя, сопровождающееся тяжелыми нарушениями работы организма, включая абстинентный синдром и потенциальные угрозы для жизни. Лечение запоя требует комплексного подхода, включающего медицинские процедуры, психотерапию и реабилитационные меры.
Получить дополнительную информацию – вывод из запоя цена екатеринбург
Алкогольный запой — это тяжелое состояние, при котором человек теряет контроль над количеством потребляемого алкоголя. Это приводит к сильной интоксикации, сбоям в работе органов и систем организма, а также серьезным психоэмоциональным расстройствам. Без должной медицинской помощи запой может вызвать ряд опасных последствий, включая алкогольный делирий и угрозу жизни. Поэтому при первых признаках запоя необходимо обратиться к профессионалам.
Получить дополнительные сведения – narkologiya vyvod iz zapoya na domu v-tveri
Особенно опасны длительные запои, когда человек в течение нескольких дней бесконтрольно употребляет алкоголь. Такое состояние разрушает организм, перегружает печень, сердце и нервную систему, может вызывать тяжелые осложнения, в том числе психические расстройства. Выйти из запоя самостоятельно практически невозможно и крайне рискованно. Важно своевременно обратиться за медицинской помощью, чтобы избежать серьезных последствий.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – vyvod iz zapoya anonimno
Для тех, кто не может приехать в клинику, специалисты проводят детоксикацию на дому. С помощью современных препаратов организм мягко очищается от токсинов, уменьшается нагрузка на внутренние органы, снимаются неприятные симптомы абстиненции. Однако при тяжелом состоянии или наличии осложнений может потребоваться круглосуточное наблюдение в стационаре, где пациенту обеспечивается полная медицинская поддержка.
Выяснить больше – наркология вывод из запоя на дому санкт-петербург
Запойное состояние представляет собой серьёзную угрозу для здоровья, поскольку сопровождается тяжёлой интоксикацией организма и нарушением психоэмоционального состояния. Решение о лечении в стационаре клиники «Союз Здоровья» позволяет справиться с последствиями длительного употребления алкоголя, обеспечивая пациентам полный комплекс медицинской и психологической помощи.
Изучить вопрос глубже – вывод из запоя врач на дом в воронеже
Canadian Pharmacy No Prescription Viagra pills for sale cheap supreme suppliers mumbai
Azithromycin for sale online
Множество игроков предпочитают франк казино за удобную систему ставок и выгодные бонусы. Слоты действительно интересные, а поддержка работает в любое время. Рекомендую внести депозит, потому что результатом я удовлетворен.
Множество игроков предпочитают легзо зеркало за простую систему ставок и выгодные бонусы. Слоты действительно разнообразные, а поддержка работает круглосуточно. Рекомендую зарегистрироваться, потому что результатом я впечатлен.
Множество игроков предпочитают казино за удобную систему ставок и щедрые бонусы. Слоты действительно интересные, а поддержка работает в любое время. Рекомендую попробовать, потому что результатом я удовлетворен.
Множество игроков предпочитают maxbet за простую систему ставок и регулярные бонусы. Слоты действительно интересные, а поддержка работает круглосуточно. Рекомендую внести депозит, потому что результатом я доволен.
sky pharmacy Canada Pharmacy 24 Hour Drug Store Sky pharmacy online
Onlinepharmacy Best india viagra and price Viagra online sales skypharmacy Cheap viagra overnight
online pharmacy
canadian pharmacy no prescription
cialis without a doctor’s prescription
Immerse yourself in the world of cutting-edge technology with the global version of the POCO M6 Pro, which combines advanced features, stylish design, and an affordable price. This smartphone is designed for those who value speed, quality, and reliability.
Why is the POCO M6 Pro your ideal choice?
– Powerful Processor: The octa-core Helio G99-Ultra delivers lightning-fast performance. Gaming, streaming, multitasking—everything runs smoothly and without lag.
– Stunning Display: The 6.67-inch AMOLED screen with FHD+ resolution (2400×1080) and a 120Hz refresh rate offers incredibly sharp and vibrant visuals. With a touch sampling rate of 2160 Hz, every touch is ultra-responsive.
– More Memory, More Possibilities: Choose between the 8/256 GB or 12/512 GB configurations to store all your files, photos, videos, and apps without compromise.
– Professional Camera: The 64 MP main camera with optical image stabilization (OIS), along with additional 8 MP and 2 MP modules, allows you to capture stunning photos in any conditions. The 16 MP front camera is perfect for selfies and video calls.
– Long Battery Life, Fast Charging: The 5000 mAh battery ensures all-day usage, while the powerful 67W turbo charging brings your device back to life in just a few minutes.
– Global Version: Support for multiple languages, Google Play, and all necessary network standards (4G/3G/2G) makes this smartphone universal for use anywhere in the world.
– Convenience and Security: The built-in fingerprint sensor and AI-powered face unlock provide quick and reliable access to your device.
– Additional Features: NFC, IR blaster, dual speakers, and IP54 splash resistance—everything you need for a comfortable experience.
The POCO M6 Pro is not just a smartphone; it’s your reliable companion in the world of technology.
Hurry and grab it at a special price of just 15,000 rubles! Treat yourself to a device that impresses with its power, style, and functionality.
Take a step into the future today—purchase it on AliExpress!
northwest pharmacy canada
Сопровождение мужчин — это особая услуга, которая может включать в себя как деловые, так и личные аспекты.
В современном мире многие мужчины ищут профессионалов, которые могут помочь им в различных сферах жизни:
от бизнес-мероприятий до социальных встреч – эскорт москвы
Canada Pharmacy 24 Hour Drug Store Free viagra blackcialis.net
Viagra buy in canada
cheap viagra samples
Выход из запоя — это важнейший этап на пути к избавлению от алкогольной зависимости. Он требует комплексного подхода, профессиональной помощи и сильной мотивации пациента. В условиях, когда анонимность и комфорт становятся ключевыми факторами для многих людей, вывод из запоя на дому приобретает все большее значение. Это решение позволяет человеку получить необходимую помощь, не покидая дома, и избежать стресса, связанного с госпитализацией.
Получить больше информации – vyvod-iz-zapoya-16.ru/vivod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-krasnodare/
lasik online pharmacy no script Canadian Pharmacy Cialis Viagra online india
Cryptocurrency tax news
viagra without a prescription
cialis online
click here aionlinepharmacy.com
Canada Pharmacy 24 Hour Drug Store Cialis generic canadian pharmacy no prescription
Tadalafil cialis from india
canada pharmacy 24h
sky pharmacy
canadian pharcharmy online
generic cialis online Canadian Pharmacy Cialis Lasix
Pharmacy Online Fast shipping viagra Viagra 40 pills for $99 healthy man viagra offer Generic viagra best prices
onlinepharmacy
Onlinepharmacy Buy amoxicillin 500mg no prescription healthy male viagra
Buy viagra online reviews
sky pharmacy
A nobleman is a representative of the aristocratic estate. Nobles had exclusive privileges and position that distinguished them from other layers of the population. They were associated with noble clans and could to land ownership property, inclusion in management of the state and army service. The nobility was also associated with special way of life, art and education.
https://mostdeliciousstew.blogspot.com/2025/02/most-delicious-stew.html
mexican pharmacy no prescription needed Generic Cialis Online Pharmacy Reviews Generic viagra online canadian pharmacy
Onlinepharmacy Cialis online Real cialis no generic canadian online pharmacies Cheap sildenafil 100mg
ordering cialis without a prescription
canadian pharmacy cialis 20mg
Canada Pharmacy 24 Hour Drug Store Lisinopril 10 mg no prescription healthy man
Viagra express mail
canadian pharmacy no prescription
skypharmacy online
canadian pharmacy no prescription Canadian Pharmacy Cialis Online drugstore no prescription
Pharmacy Rx One Review Pharmacy online Buy generic cialis online uk canadian pharmacies Viagra pills
on line pharmacy
pharmacy online without prescription
A nobleman is a member of the noble class. Nobles had exclusive benefits and position that distinguished them from other groups of the population. They were connected with aristocratic clans and had the right to land possession, participation in management of the state and military service. The nobility was also associated with a certain way of life, art and enlightenment.
https://nilerivertourist.blogspot.com/2025/02/nile-river.html
Hello and welcome!
Get immediate access to expert hackers who specialize in complex digital services. Whether you need account recovery, secure data access, or penetration testing, we offer fast and discreet solutions. Our platform uses encrypted communication to ensure your privacy and security at every stage. Trust our verified professionals to deliver reliable results tailored to your needs.
https://hackerslist.com/
Thank you for choosing HackersList!
A nobleman is a member of the aristocratic estate. Nobles had special benefits and status that distinguished them from other groups of the population. They were connected with noble clans and had the right to land ownership property, participation in government of the state and military service. The nobility was also connected with a certain way of life, art and education.
https://swimmingforallpeople.blogspot.com/2025/02/swimming.html
pharmacy without dr prescriptions
Online Pharmacy Comprar viagra healthy man pills
Canada pacription drugs
Игровая платформа 7k — это новейшая платформа для онлайн-азартных игр с огромным выбором активностей. Здесь можно найти популярные слот-машины, настольные игры и игры с живыми дилерами с профессиональными дилерами. Оформление сайта пространный и комфортный, что делает игру удобной и неповторимой. На https://neva-spb.com/ru/ предусмотрены классные призы для игроков. В целом, платформа предоставляет великолепный опыт для каждого игрока.
“Ваш решение для гемблинга – казино Слотозал!
Слотозал показывает широкий выбор слот-машин, выгодные предложения и значительный уровень безопасности. Интерфейс веб-сайта понятен, навигация удобна, что дает возможность оперативно найти предпочтенные игры. Команда поддержки непрерывно готова содействовать с различными вопросами. Пройдите регистрацию на официальном сайте на сайте и начните выигрывать сегодня!”
“Официальный веб-сайт казино Рояль предлагает располагающую обстановку для азартных игроков. С его стильным дизайном и элитным выбором игр, Рояль является великолепным местом для тех, кто полагается качественное азартное развлечение. Исследуйте многочисленные игровых автоматов и настольных игр на официальном веб-сайте https://royalcasino-slots.com/.
Казино Рояль обеспечивает высокое качество клиентов и поддержку. Внимательная команда поддержки в наличии круглосуточно, настроена откликнуться на любые вопросы и урегулировать проблемы, обеспечивая безпрерывную игру и удовлетворение.”
“Официальный веб-сайт казино Рояль предлагает стильную обстановку для поклонников азартных игр. С его стильным дизайном и высококачественным выбором игр, Рояль является великолепным местом для тех, кто высоко ценит качественное азартное развлечение. Исследуйте разнообразный выбор игровых автоматов и настольных игр на главном веб-сайте royalcasino-slots.com.
Казино Рояль предоставляет первоклассное обслуживание клиентов и поддержку. Отзывчивая команда поддержки доступна круглосуточно, оборудована отреагировать на любые возникающие вопросы и разрешить проблемы, предоставляя непрерывную игру и удовлетворение.”
“Looking for high-quality slots to play? AbeBet Casino offers endless variety online slots for all players!
At Abe Bet https://abe.bet/tr/games/demo/pragmatic_play_mustang_gold, you’ll find slot hits from leading providers.
Join now to get newbie gifts.
Dive into an atmosphere of thrill with Abe Bet! “
cialis without a doctor’s prescription
canadian pharmacy no prescription
healthy man
Canadian Pharmacy No Prescription Viagra prices usa canadian health
Cialis in canada
american pharmacy online no script Buy cialis without prescription
Strattera http://canadapharmacyonlinedrugstore.com/ Dapoxetine
skypharmacy Canadian Pharmacy Cialis Canadian pharmacy cialis 5 mg
Welcome, one and all.
I can’t believe my eyes!
best streaming guides on popcorntime
Later, alligator!
canadian pharmacy
cialis online
canadian pharmacy without prescription
buy amoxicillin 500mg no prescription
Canadian Pharmacy Online No Script For sale zithromax z pak oral healthy man generic viagra
Vigra
buy amoxicillin without prescription uk
cialis online without prescription
canadian pharmacy cialis 5mg
canadian pharcharmy online
Siberian Wellness — это натуральное средство, которое, по словам производителя, помогает укрепить защитные силы организма, улучшить общее самочувствие и повысить уровень энергии. Отзывы о нем разнообразны.
» https://multi-level-marketing.ru/
» https://t.me/s/siberian_wellnass_rf
Разные стратегии – разная занятость – разный доход. Но вы точно получите 10–25% от суммы заказов Клиентов, которые пришли по вашей рекомендации. По статистике, в первый месяц это 5–10 тысяч рублей. Дальше – зависит от вашей активности. Через месяц, два, три, полгода доход у многих составляет более 50 000 рублей ежемесячно!
Наш бизнес необычный, непривычный для многих,
но при грамотном подходе надежный, стабильный и интересный.
Основной движущей силой вашего бизнеса должны стать лидерские качества
и умение мотивировать…
В чем я вам помогу
Продвижение — один из самых простых и действенных способов продвинуть товары наверх поисковой выдачи и не терять потенциальных покупателей
Как запустить рекламу, чтобы получить больше клиентов, привлечение клиентов, продвижение в Telegram и соцсеть. Увеличение конверсии. Экономия бюджета. Стратегии. Быстрый запуск · 14+
glucophage no perscriptionpharmacy
buy cheap cialis discount online Predisone
online pharmacies Generic Cialis Online Pharmacy Reviews Generic levitra professional 20 mg
canadian pharmacy online cialis
Tadapox review http://northwestpharmacydrugstore.com/ Vigra
order cipro online supreme suppliers
https://www.clspharmacy.com
brand viagra 100mg
Canada Pharmacy 24 Hour Drug Store Levitra online healthy man viagra offer
Viagra for sale in usa
supreme suppliers
canadian pharmacy cialis
Professional databases for Xumer 23 and GSA Search Engine Ranker
We offer the best website databases for working with Xrumer 23 ai Strong and GSA Search Engine Ranker. The databases are suitable for a professional SEO company and creating hundreds of thousands of backlinks. Our databases are used by many SEO professionals from different countries of the world. The price for the databases is low, having bought them you receive updates for 12 months. You can read more and order a subscription to the databases here: https://dseo24.monster/vip-base-for-xrumer-and-gsa-ser/ On the site page you can choose any language of the pages.
cialis generico prezzo piu basso
healthy male viagra
healthy man cialis
Здравствуйте, автолюбители!
Ищете проверенный автосервис, который фокусируется на модернизации выхлопной системы? В «Катализатор» в Ярославле мы предлагаем только проверенные услуги:
Услуги, которые мы предоставляем:
Демонтаж катализатора
Замена и ремонт глушителей
Установка и замена гофры, пламегасителей и резонаторов
Ремонт и установка фланцевых соединений
Компьютерный анализ
Мы гарантируем индивидуальный подход и качественное выполнение работ.
Ваш автомобиль заслуживает лучшего!
Не упустите возможность! Узнайте больше о наших услугах и запишитесь на прием на нашем сайте: https://katalizator-yaroslavl.ru/.
С наилучшими пожеланиями,
Команда «Катализатор».
Не ждите, пока проблема усугубится!
canadian non prescription pharmacy
canadian pharmacy
canada pharmacy no prescription
Welcome to HackersList!
Connect with professional hackers for secure and effective digital solutions. From recovering locked accounts to testing system vulnerabilities, we provide fast and discreet services. Our platform prioritizes privacy with encrypted communication and secure payments, ensuring your needs are handled with confidentiality and care.
https://hackerslist.com/
Thank you for choosing HackersList!
canada pharmacy online
Greatest news for all us
Круглозвенные цепи — это не просто элемент механики, а настоящая находка для бизнеса! Они широко используются в различных отраслях: от сельского хозяйства до строительства, обеспечивая надежную передачу усилия и долговечность – роликовый подшипник.
Хотите создать идеальное покрытие для вашего участка или дорожного покрытия? Тогдаотсев идеально подойдет для вас!
Наш высококачественный отсева щебня обеспечит прочность, долговечность и надежность вашего покрытия. Благодаря правильной фракции отсева,
он обладает отличной укладываемостью и прекрасно дренирует воду, что делает его идеальным выбором для любых работ – щебень оптом от производителя.
Сертификат ТР ТС – документ, подтверждающий безопасность продукции и соответствие требованиям
конкретного технического регламента Таможенного Союза. Быстро оформим получить декларацию соответствия.
cost effective ed drugs
The strongest databases for Xrumer 23 and GSA Search Engine Ranker
We offer the best website databases for working with Xrumer 23 ai Strong and GSA Search Engine Ranker. The databases are suitable for a professional SEO company and creating hundreds of thousands of backlinks. Our databases are used by many SEO professionals from different countries of the world. The price for the databases is low, having bought them you receive updates for 12 months. You can read more and order a subscription to the databases here: https://dseo24.monster/vip-base-for-xrumer-and-gsa-ser/ On the site page you can choose any language of the pages.
pharmacy express canada
Когда речь идет о ремонте, выбор правильной краски — это один из самых важных этапов. Строительные краски не только придают вашему интерьеру стильный вид, но и защищают поверхности от внешних воздействий. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент высококачественных строительных красок, которые удовлетворят потребности как профессиональных строителей, так и домашних мастеров – краска для внутренних и наружных работ.
Сертификат ТР ТС – документ, подтверждающий безопасность продукции и соответствие требованиям
конкретного технического регламента Таможенного Союза. Быстро оформим сертификат соответствия тс.
canadian health and care mall
Круглозвенные цепи — это не просто элемент механики, а настоящая находка для бизнеса! Они широко используются в различных отраслях: от сельского хозяйства до строительства, обеспечивая надежную передачу усилия и долговечность – подшипник роликовый.
viagra vs cialis
Светодиодные лампы становятся все более популярными благодаря своей энергоэффективности, долговечности и экологичности. Мы предлагаем вам уникальную возможность — приобретать светодиодные лампы напрямую от завода. – завод светильников.
ghostwriter politikwissenschaften
“Ваш выбор для гемблинга – казино Слотозал!
Слотозал предлагает широкий ассортимент слотов, привлекательные предложения и значительный уровень безопасности. Интерфейс сайта интуитивно понятен, навигация удобна, что позволяет быстро отыскать предпочтенные игры. Поддержка всегда готова ассистировать с различными вопросами. Зарегистрируйтесь на основном портале на сайте и начните побеждать немедленно!”
Предлагаем вам высококачественный тротуарный бордюр – идеальное решение для обрамления дорожек, газонов, цветников и других элементов ландшафтного дизайна.
Наш тротуарный бордюр отличается прочностью, долговечностью и устойчивостью к воздействию внешних факторов, что делает его идеальным выбором для любых условий эксплуатации – [url=https://jdis.co/sovremenne-tehnologii-i-trend-v-ukladke-trotuarnoy-plitki-praktitchnosty-stetika-i-dolgovetchnosty.html]тротуарная плитка купить в краснодаре[/url]
“Официальный веб-сайт казино Рояль предлагает стильную обстановку для гемблеров. С его стильным дизайном и расширенным выбором игр, Рояль является идеальным местом для тех, кто полагается качественное азартное развлечение. Исследуйте широкий спектр игровых автоматов и настольных игр на авторизованном веб-сайте https://royalcasino-slots.com/ru/.
Казино Рояль защищает первоклассное обслуживание клиентов и поддержку. Отзывчивая команда поддержки доступна круглосуточно, готова ответить на любые возникающие вопросы и решить проблемы, обеспечивая безпрерывную игру и удовлетворение.”
“Looking for top-notch slots to play? Abe Bet Casino offers the best online slots for all players!
At AbeBet abe-casino.com/tr/games/demo/pragmatic_play_starlight_princess_1000, you’ll find popular slots from renowned brands.
Sign up now to get newbie gifts.
Dive into real gameplay with AbeBet! “
“Looking for top-quality online casino games? MasalBet is the place to find favorite games from top developers.
At https://denizliotoekspertiz.com, you’ll find exclusive promotions and simple gameplay.
Sign up now and get amazing bonuses.
Play fresh new game releases with Masal Bet!
“
Это казино предпочитают Вулкан Рояль Казахстан за гибкую систему ставок и щедрые бонусы. Слоты действительно разнообразные, а поддержка работает в любое время. Рекомендую зарегистрироваться, потому что результатом я доволен.
canadas rx no prescription paypal
buy levothyroxine without prescription
Good news for all us
canadian pharmacy without prescription
Приветственные бонусы и промоакции 1xBet 2025
1хбет промокоды на слоты дает эксклюзивный бонус до 32500 рублей для ставок на спорт. Нужно будет взять этот код из нашего источника и ввести его при регистрации. Платформа дает 4 способа авторизации на выбор, и пополнить счет на сумму от 100 RUB, после чего на игровой баланс поступит 130% от суммы первого депозита, их нужно будет отыграть в разделе ставок на спорт с вейджером х5, цепочка событий должна состоять не менее чем из 3-х с коэффициентом от 1,4. На отыгрыш Вам дается 30 дней, от дня активации кода. Почему этот бонус нужно использовать без раздумий?
При его вводе, Вам деньги начисляет именно букмекер 1xBet, тоесть играете Вы за его счет, и заработать кругленькую сумму можно без вложения своих средств.
online drugstore
Greetings!
Connect with professional hackers for secure and effective digital solutions. From recovering locked accounts to testing system vulnerabilities, we provide fast and discreet services. Our platform prioritizes privacy with encrypted communication and secure payments, ensuring your needs are handled with confidentiality and care.
https://hackerslist.com/
Thank you for choosing HackersList!
Качественный асфальт выдерживает любые погодные условия и нагрузки, что делает его идеальным для парковок, дорожек и дворов – стоимость строительства грунтовых дорог
healthy male viagra
Официальный веб-сайт казино Рояль предлагает искусно оформленную обстановку для любителей казино. С его изящным дизайном и высококачественным выбором игр, Рояль является великолепным местом для тех, кто ценит качественное азартное развлечение. Исследуйте многочисленные игровых автоматов и настольных игр на авторизованном веб-сайте https://royalcasino-slots.com/.
Казино Рояль защищает высокое качество клиентов и поддержку. Поддерживающая команда поддержки доступна круглосуточно, оборудована ответить на все вопросы и разрешить проблемы, предоставляя безпрерывную игру и удовлетворение.
Официальный веб-сайт казино Рояль предлагает изысканную обстановку для любителей казино. С его стильным дизайном и расширенным выбором игр, Рояль является идеальным местом для тех, кто ценит качественное азартное развлечение. Исследуйте широкий спектр игровых автоматов и настольных игр на официальном веб-сайте royalcasino-slots.com.
Казино Рояль предоставляет первоклассное обслуживание клиентов и поддержку. Поддерживающая команда поддержки доступна круглосуточно, оборудована отреагировать на любые возникающие вопросы и решить проблемы, предоставляя беспрерывную игру и удовлетворение.
universal drugstore canada
Когда речь идет о ремонте, выбор правильной краски — это один из самых важных этапов. Строительные краски не только придают вашему интерьеру стильный вид, но и защищают поверхности от внешних воздействий. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент высококачественных строительных красок, которые удовлетворят потребности как профессиональных строителей, так и домашних мастеров – краски оптом.
ez online pharmacy buy viagra usa
Здравствуйте! Сервис «Катализатор» на связи!
«Пахнет выхлопом в салоне?» — мы знаем, как это исправить!
Промедление — враг вашего кошелька:
Ржавый резонатор прорвёт — ремонт двигателя обойдётся в 3 раза дороже.
Ищете, где недорого отремонтировать выхлопную систему в Ярославле?
Что делаем:
Замена гофры глушителя — материалы + работа от 3000?!
Почему 9 из 10 клиентов возвращаются?
Свой склад запчастей — не ждём поставок 2 недели.
«Дорого!» — А вы считали, во что обойдётся игнор?
Ремонт сейчас: 5000-15000?
Как с нами связаться?:
Запишитесь онлайн за 1 минуту
С уважением, команда «Катализатор».
P.P.S. Приведите друга — получите скидку 20% на следующий ремонт!
canadian pharmacy cialis 5 mg
online pharmacies no prescription
pharmaceuticals no prescription
sky pharmacy online drugstore review
Immerse yourself in the world of cutting-edge technology with the global version of the POCO M6 Pro, which combines advanced features, stylish design, and an affordable price. This smartphone is designed for those who value speed, quality, and reliability.
Why is the POCO M6 Pro your ideal choice?
– Powerful Processor: The octa-core Helio G99-Ultra delivers lightning-fast performance. Gaming, streaming, multitasking—everything runs smoothly and without lag.
– Stunning Display: The 6.67-inch AMOLED screen with FHD+ resolution (2400×1080) and a 120Hz refresh rate offers incredibly sharp and vibrant visuals. With a touch sampling rate of 2160 Hz, every touch is ultra-responsive.
– More Memory, More Possibilities: Choose between the 8/256 GB or 12/512 GB configurations to store all your files, photos, videos, and apps without compromise.
– Professional Camera: The 64 MP main camera with optical image stabilization (OIS), along with additional 8 MP and 2 MP modules, allows you to capture stunning photos in any conditions. The 16 MP front camera is perfect for selfies and video calls.
– Long Battery Life, Fast Charging: The 5000 mAh battery ensures all-day usage, while the powerful 67W turbo charging brings your device back to life in just a few minutes.
– Global Version: Support for multiple languages, Google Play, and all necessary network standards (4G/3G/2G) makes this smartphone universal for use anywhere in the world.
– Convenience and Security: The built-in fingerprint sensor and AI-powered face unlock provide quick and reliable access to your device.
– Additional Features: NFC, IR blaster, dual speakers, and IP54 splash resistance—everything you need for a comfortable experience.
The POCO M6 Pro is not just a smartphone; it’s your reliable companion in the world of technology.
Hurry and grab it at a special price of just 15,000 rubles! Treat yourself to a device that impresses with its power, style, and functionality.
Take a step into the future today—purchase it on AliExpress!
pharmacy no prescription
Качественный асфальт выдерживает любые погодные условия и нагрузки, что делает его идеальным для парковок, дорожек и дворов – укладка асфальта
buy metronidazole 500mg no prescription
Сертификат ТР ТС – документ, подтверждающий безопасность продукции и соответствие требованиям
конкретного технического регламента Таможенного Союза. Быстро оформим сертификат соответствия тр тс получить.
Сопровождение мужчин — это особая услуга, которая может включать в себя как деловые, так и личные аспекты.
В современном мире многие мужчины ищут профессионалов, которые могут помочь им в различных сферах жизни:
от бизнес-мероприятий до социальных встреч – снять элитную проститутку на ночь
Hello and welcome!
Confidential and reliable, our hacker-for-hire platform connects you with experts for various tasks. From account recovery to advanced penetration testing, we offer services with full discretion. Our encryption protocols ensure your communication and payments remain private. Choose verified professionals for effective and secure results.
https://hackerslist.com/hacker-services/
Thank you for choosing HackersList!
Круглозвенные цепи — это не просто элемент механики, а настоящая находка для бизнеса! Они широко используются в различных отраслях: от сельского хозяйства до строительства, обеспечивая надежную передачу усилия и долговечность – купить роликовый подшипник.
Сопровождение мужчин — это особая услуга, которая может включать в себя как деловые, так и личные аспекты.
В современном мире многие мужчины ищут профессионалов, которые могут помочь им в различных сферах жизни:
от бизнес-мероприятий до социальных встреч – проститутка девушка москва
buying cialis online
Сертификат ТР ТС – документ, подтверждающий безопасность продукции и соответствие требованиям
конкретного технического регламента Таможенного Союза. Быстро оформим соформить сертификат тр тс.
Crypto news and analysis
canadian pharmacy
Качественный асфальт выдерживает любые погодные условия и нагрузки, что делает его идеальным для парковок, дорожек и дворов – укладка асфальта
suhagra supreme suppliers
Принимать финансовые решения может быть сложно. Но с нашим каталогом финансовых продуктов это стало проще, чем когда-либо!
дебетовая карта с бесплатными платежами
Мы собрали все лучшие финансовые продукты в одном месте, чтобы вы могли легко сравнить их и найти те, которые подходят именно вам. Наши экспертные обзоры и рейтинги помогут вам принять обоснованное решение, соответствующее вашим уникальным потребностям.
Независимо от того, ищете ли вы кредит наличными, дебетовую карту или инвестиционный счет, наш каталог финансовых продуктов поможет вам сделать правильный выбор.
canadian pharmacy clonidine
onlinepharmacy
usa pharmacy no script
canadian pharmacy no prescription
pharmacia online usa
online pharmacy canada
healthy man viagra
Качественный асфальт выдерживает любые погодные условия и нагрузки, что делает его идеальным для парковок, дорожек и дворов – укладка асфальта
Качественный асфальт выдерживает любые погодные условия и нагрузки, что делает его идеальным для парковок, дорожек и дворов – укладка асфальта
[url=https://bit.ly/3EGKSVc][img]https://tripacostarica.com/1/tp/sr/1.png[/img][/url]
[b][u]See[/u][/b] yourself waiting on the deck of a catamaran, a cool breeze touching with your hair, and around you appearing an enormous horizon, where the water mixes with the air. There is no chaos of cities, no noise of cars, just you and nature in its wild beauty. Chartering a yacht is not just a journey, it is an privilege to perceive absolute independence of action and a intense harmony with the surrounding world, which is difficult to achieve in normal life. Why not make this step instantly?
Liberty is what is so lacking in the contemporary person, confined in timetables, duties and enduring notifications. When you hire a vessel, you become the helmsman of your destiny. Want to journey to a private beach where no one interrupts your seclusion? Please! Want to uncover mysterious bays and islands that only local fishermen know about? Easy! No pre-set routes, no restrictions — just you and your longings. You can arise at dawn to see the sun coloring the water in yellow hues, or use the day exploring among coral reefs bursting with life. Hiring a vessel grants you freedom, allowing you to experience as unbound as the wind that inflates the sails.
[url=https://bit.ly/3EGKSVc][img]https://tripacostarica.com/1/tp/sr/2.png[/img][/url]
[b][u]But[/u][/b] freedom is only one side of the coin. The other is a profound bond with the world that cannot be felt while sitting in an office or wandering on asphalt. The sea is a active organism that calls, whispers and sometimes confronts. Attending to the sound of the tides, feeling the salty air and admiring the movement of the dolphins, you begin to grasp how trivial our everyday bustle is compared to the majesty of nature. Ship becomes your gateway into this world: you can throw anchor in the middle of the water, to gaze at the stars that seem more proximate than ever, or organize a picnic on the deck, enveloped only by the melodies of nature.
Renting a boat suits not only solo travelers craving internal peace, but also for those who cherish engagement. Envision this: you with family or kin sailing on a voyage, discussing stories under the heavens, playing social games on the deck, or simply enjoying the silence together. Cruiser becomes your exclusive sanctuary, where there is no room for dull routines or outside distractions. You can set up a romantic dinner at sunset, admiring as the sky becomes a collection of amber and deep shades, or host a lively party with melodies and moves under the open sky. Every moment on the yacht is a possibility to create recollections that will inspire you for extended years.
[u][b]Of course[/b][/u], hiring a motorboat is also an privilege to appreciate convenience. Modern vessels are outfitted with all the necessary: from ample cabins and cooking areas to baths and amusement systems. You can feel like you’re at a elite resort, but with the benefit of absolute mobility. Want to stop in a place where there isn’t a single resort? No problem! A yacht will bring you where no bus or craft can reach. This sense of rarity and self-sufficiency makes booking a vessel a singular experience that cannot be matched with anything else.
[url=https://bit.ly/3EGKSVc][img]https://tripacostarica.com/1/tp/sr/3.png[/img][/url]
But the [b][u]most vital[/u][/b] thing is that renting a boat is attainable to anyone who aspires of self-determination and ventures. You don’t have to be an trained sailor — expert crews and easy-to-handle vessels will make your journey stable and delightful. You can choose a motorboat of any dimension and category: from little models for duos to grand vessels for large parties. The system of renting is uncomplicated: just set your desires, identify a route, and rely on the professionals. In just a few days, you will be able to be on the deck, perceiving your heart beat in rhythm with the currents.
Don’t delay your aspirations for the future. Full freedom of action and intense unity with wildlife are waiting for you. Hire a yacht now and experience a world where there are no limits except those you set yourself. Depths calls — acknowledge its cry, and you will grasp what actual freedom is. It’s not just a trip, it’s a approach that drives, refreshes, and enriches with significance. Begin the first step — and let the wind lead you to where wishes become truth!
Complete freedom of action and deep unity with nature!
[url=https://bit.ly/3EGKSVc][b]Try it right now )[/b][/url]
my canadian pharmacy no script
Сообщите возможность поставки хомутового нагревателя со следующими параметрами: Диам 95 мм, ширина 35 мм, тангенцальный вывод в металлической изоляции 625 Вт, 5 шт, с ТП и без
canadian pharmacy without prescritption
Databases for Xrumer 23 ai Strong and GSA Search Engine Ranker with 12-month updates
We offer the best website databases for working with Xrumer 23 ai Strong and GSA Search Engine Ranker. The databases are suitable for a professional SEO company and creating hundreds of thousands of backlinks. Our databases are used by many SEO professionals from different countries of the world. The price for the databases is low, having bought them you receive updates for 12 months. You can read more and order a subscription to the databases here: https://dseo24.monster/vip-base-for-xrumer-and-gsa-ser/ On the site page you can choose any language of the pages.
online no script pharmacy
Качественный асфальт выдерживает любые погодные условия и нагрузки, что делает его идеальным для парковок, дорожек и дворов – укладка асфальта
erectile dysfunction drugs canada
canada online pharmacy
Hello and welcome!
Need to recover lost access to critical data or accounts? Our professional hacking services provide tailored support to handle such tasks securely and anonymously. Our platform emphasizes encrypted communication and confidentiality. From database access to social media recovery, our experts deliver fast results. We ensure that each project is completed with discretion and guaranteed satisfaction.
https://hackerslist.com/
Thank you for choosing HackersList!
sky pharmacy online
supreme suppliersmumbaiindia
sky pharmacy online drugstore
Повысьте эффективность своего производства с помощью наших приводных устройств! Наши инновационные устройства позволят вам значительно снизить расходы на электроэнергию,
увеличить производительность оборудования и снизить износ механизмов. Благодаря нашиему оборудованию вы сможете значительно увеличить производственные мощности и улучшить качество выпускаемой продукции – преобразователь частоты.
usa pills viagra
order canadian pharmacy no script
cialis overnight shipping from usa
Immerse yourself in the world of cutting-edge technology with the global version of the POCO M6 Pro, which combines advanced features, stylish design, and an affordable price. This smartphone is designed for those who value speed, quality, and reliability.
Why is the POCO M6 Pro your ideal choice?
– Powerful Processor: The octa-core Helio G99-Ultra delivers lightning-fast performance. Gaming, streaming, multitasking—everything runs smoothly and without lag.
– Stunning Display: The 6.67-inch AMOLED screen with FHD+ resolution (2400×1080) and a 120Hz refresh rate offers incredibly sharp and vibrant visuals. With a touch sampling rate of 2160 Hz, every touch is ultra-responsive.
– More Memory, More Possibilities: Choose between the 8/256 GB or 12/512 GB configurations to store all your files, photos, videos, and apps without compromise.
– Professional Camera: The 64 MP main camera with optical image stabilization (OIS), along with additional 8 MP and 2 MP modules, allows you to capture stunning photos in any conditions. The 16 MP front camera is perfect for selfies and video calls.
– Long Battery Life, Fast Charging: The 5000 mAh battery ensures all-day usage, while the powerful 67W turbo charging brings your device back to life in just a few minutes.
– Global Version: Support for multiple languages, Google Play, and all necessary network standards (4G/3G/2G) makes this smartphone universal for use anywhere in the world.
– Convenience and Security: The built-in fingerprint sensor and AI-powered face unlock provide quick and reliable access to your device.
– Additional Features: NFC, IR blaster, dual speakers, and IP54 splash resistance—everything you need for a comfortable experience.
The POCO M6 Pro is not just a smartphone; it’s your reliable companion in the world of technology.
Hurry and grab it at a special price of just 15,000 rubles! Treat yourself to a device that impresses with its power, style, and functionality.
Take a step into the future today—purchase it on AliExpress!
Цены в нашем прейскуранте не завышены и они значительно ниже, чем вы сможете найти в Москве и Московской области, к тому же, диагностика и выезд на дом при заказе ремонта не оплачиваются https://zapchasti-remont.ru/shop/noji/
canadian pharcharmy online
generic drugs online from india
http://bazydlyaxrumerkupitt.ru/ – Купить базы для Xrumer с гарантией результата
http://www.bazyydlyaxrumerkupitt.ru – Базы для Хрумера с высокой эффективностью
canadian pharmacy cialis
skypharmacy online
online pharmacy no dr prescriptions
http://bazydlyaxrumerkupitt.ru – Проверенные базы для Хрумера с гарантией
http://bazyydlyaxrumerkupitt.ru/ – Купить базы для Xrumer с гарантией доставки
xrumer базы – Готовые Xrumer базы для массового размещения ссылок
canadian pharmacy without prescritption
bazydlyaxrumerkupitt.ru – Лучшие базы для Xrumer и GSA
supreme supplies in india
https://www.bazyydlyaxrumerkupitt.ru/ – Официальный ресурс с базами для Xrumer
http://www.bazyydlyaxrumerkupitt.ru – Проверенные базы для Хрумера и других программ
https://bazyydlyaxrumerkupitt.ru – Свежие базы для Хрумера с обновлением
https://www.bazyydlyaxrumerkupitt.ru/ – Официальный магазин баз для Xrumer
http://www.bazyydlyaxrumerkupitt.ru – Проверенные базы для Хрумера и других программ
база xrumer – Актуальная база Xrumer для эффективного продвижения
http://bazyydlyaxrumerkupitt.ru/ – Купить базы для Xrumer с гарантией результата
база для хрумера – Проверенные базы для Хрумера с высокой эффективностью
Crave to revive swiftly – take a attractive chick, guy or tranny!
There is a vast range of luscious figures for you – fresh, pretty, seductive!
Shag their right now!
Crave to energize promptly – select a hot chick, dude or trans!
There is a large choice of appealing physiques for you – teen, stunning, hot!
Hump their at once!
Welcome to HackersList!
Hire expert hackers to access protected accounts, recover data, or secure your systems. We provide discreet and anonymous services using encrypted communication channels. Our platform is designed to deliver fast, reliable results while ensuring privacy and security. Experience professional digital solutions that meet your requirements effectively.
https://hackerslist.com/
Thank you for choosing HackersList!
Crave to boost quickly – grab a hot chick, fellow or trans!
There is a big selection of enticing figures for you – new, stunning, hot!
Hump their right now!
Desire to energize quickly – grab a hot chick, man or tranny!
There is a large assortment of enticing bodies for you – young, stunning, sexy!
Shag their instantly!
Need to revive instantly – pick a sexy girl, dude or tranny!
There is a vast variety of appealing shapes for you – teen, lovely, hot!
Fuck their now!
Your total command with powerful functional device – you become a racer, an aviator and a discoverer!
Personalize and improve device to suit you – study, investigate, navigate the world in your own way!
Get memorable satisfaction and unique sensations – through your achievements along with outcomes!
Click here to purchase cool device which your pal is missing right now!
Все специалисты ремонтной службы имеют сертификацию и огромный опыт работы с разными марками и моделями стиральных машин практически всех производителей https://zapchasti-remont.ru/shop/baki2/
Your complete authority above robust versatile equipment – you are a driver, an aviator along with a discoverer!
Personalize and boost system for yourself – study, research, explore the world however you like!
Feel remarkable joy and unique feelings – due to your successes along with outcomes!
Click here to buy neat model which your buddy hasn’t got right now!
Crave to boost promptly – pick a stunning babe, gent or transgender!
There is a huge choice of appealing figures for you – youthful, gorgeous, hot!
Shag their right now!
Universal stability is a shared dream, yet it remains challenging. Disputes, political turmoil, and poverty threaten progress. Dialogue among communities, equitable actions, and understanding can build a harmonious tomorrow.
https://fightinthestreet4health.blogspot.com/2025/04/fight-in-street.html
Planetary stability is a shared vision, yet it remains elusive. Wars, political disruption, and division threaten prosperity. Collaboration among countries, responsible plans, and trust can strengthen a resilient world.
https://swimmingforallpeople.blogspot.com/2025/02/swimming.html
Your full authority over strong practical device – you are a racer, an aviator plus a discoverer!
Tweak and boost model to your liking – learn, explore, navigate the world as you want!
Experience lasting satisfaction and unique emotions – thanks to your accomplishments as well as efforts!
Click here to order neat model which your friend lacks right now!
International stability is a shared dream, yet it remains challenging. Disputes, economic disruption, and injustice threaten security. Collaboration among peoples, equitable efforts, and empathy can foster a stable society.
https://thebesthandballplayersintheworld.blogspot.com/2025/04/the-best-handball-players-in-world.html
Planetary peace is a shared vision, yet it remains complex. Wars, financial chaos, and injustice threaten unity. Collaboration among countries, fair strategies, and compassion can create a harmonious society.
https://edasmak.blogspot.com/2025/04/qualities-of-chef.html
Комментарий Искал двигатель на пылесос LG,после короткой переписки оплатил заказ и он был отправлен в тот же день в г https://zapchasti-remont.ru/shop/elektrika_knopki_regulyatoryi_dlya_briggs_stratton/
Новосибирск и получил именно то,что заказывал! Всем советую данную компанию,даже если вы из другого города!
Your full command with dynamic practical machine – you transform into a driver, a navigator as well as an explorer!
Tweak and improve device to your liking – learn, research, navigate new horizons however you like!
Get remarkable pleasure and indescribable feelings – from your victories as well as performances!
Click here to order neat model what your buddy lacks right now!
Greetings!
Hire hackers for secure data access, account recovery, and system testing. Our platform offers encrypted communication, guaranteeing privacy and safe service handling. Trust our experts to deliver fast, effective solutions tailored to your needs with full confidentiality at every step. Experience advanced digital services today.
https://hackerslist.com/
Thank you for choosing HackersList!
Your total command with powerful functional gadget – you are a speedster, a pilot and an adventurer!
Tweak and improve model to your liking – study, explore, venture into your surroundings as you want!
Feel lasting delight and unique sensations – thanks to your victories along with performances!
Click here to order awesome gadget that your mate doesn’t have right now!
Casino is not just a game of luck; it’s a thrilling challenge that can be mastered with the right strategy. Imagine the excitement of hitting 21 and beating the dealer with confidence. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced player, learning slots online can transform your gaming experience and lead to significant wins. Don’t miss out on the opportunity to improve your skills and enjoy the rewards. Start playing blackjack today and take the first step towards becoming a pro!
Your absolute mastery of strong practical device – you become a racer, a pilot and an explorer!
Personalize and improve system to your liking – learn, research, discover the environment as you please!
Experience remarkable delight and incredible thrills – thanks to your accomplishments and efforts!
Click here to purchase awesome model what your friend lacks right now!
Casino is not just a game of luck; it’s a thrilling challenge that can be mastered with the right strategy. Imagine the excitement of hitting 21 and beating the dealer with confidence. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced player, learning free slots can transform your gaming experience and lead to significant wins. Don’t miss out on the opportunity to improve your skills and enjoy the rewards. Start playing blackjack today and take the first step towards becoming a pro!
Электронагревательный элемент входит в систему отопления пассажирских вагонов с напряжением питания 3000 Вольт, он взаимозаменяем с электронагревателем HH S 2-05 https://rusupakten.ru/product-tag/ten-dlya-galvaniki/